1) Which of the following is NOT a major function of the blood?
- a) Transportation of nutrients
- b) Regulation of blood pH
- c) Protection against infectious disease
- d) Transportation of heat
- e) Production of oxygen
e
2) Which of the following is NOT a true statement regarding blood?
- a) The normal average temperature of blood is around 100.4o
- b) The normal pH range for blood is 7.35-7.45.
- c) Hemocytoblasts are a common component of circulating blood.
- d) The primary circulating blood cell is the RBC.
- e) Blood is a liquid connective tissue consisting of cells and a liquid extracellular matrix.
c
3) The hematocrit is a measure of the percentage of whole blood occupied by
- a) WBCs.
- b) platelets.
- c) RBCs.
- d) plasma.
- e) plasma proteins.
c
4) What percentage of blood plasma is water?
- a) 95.1%
- b) 91.5%
- c) 88.5%
- d) 4.9%
- e) 8.5%
b
5) Which of the following plasma proteins plays a role in disease resistance?
- a) Albumin
- b) Globulins
- c) Fibrinogen
- d) Myoglobin
- e) Hemoglobin
b
6) Which of the following plasma proteins plays a role in blood clotting?
- a) Albumin
- b) Globulins
- c) Fibrinogen
- d) Prostaglandins
c
9) The process by which the formed elements of the blood develop is called
- a) hematospermia.
- b) hemopoiesis.
- c) thrombocytosis.
- d) hemostasis.
- e) polycythemia.
b
10) A megakaryoblast will develop into
- a) a red blood cell.
- b) a white blood cell.
- c) a platelet.
- d) either a white blood cell or a platelet.
- e) none of these choices.
c
11) During hemopoiesis, some of the myeloid stem cells will eventually develop into
- a) proerythroblasts.
- b) T lymphoblasts.
- c) B lymphoblasts.
- d) NK lymphoblasts.
- e) all of these choices.
a
12) Progressive liver failure may lead to serious bleeding problems due to
- a) reduced production of thrombopoietin
- b) a reduction in the production of platelets
- c) a reduction in the cholesterol production
- d) a reduction in the number of pluripotent stem cells
a,b
13) Which of the following hormones stimulates proliferation of red blood cells in red bone marrow?
- a) erythropoietin (EPO)
- b) thrombopoietin (TPO)
- c) human growth hormone (hGH)
- d) calcitonin (CT)
- e) follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
a
15) Ferritin is a protein used to
- a) break down iron
- b) store iron in the liver, muscle and spleen.
- c) oxidize iron in the peroxisomes.
- d) synthesize iron.
- e) absorb iron across intestinal cells.
b
14) Approximately, how many hemoglobin molecules are found in each RBC?
- a) 50 million
- b) 100 million
- c) 280 million
- d) 320 million
- e) 430 million
c
16) The major function of red blood cells is
- a) nutrient transport.
- b) cytokine stimulation.
- c) blood cell proliferation.
- d) gas transport.
- e) disease resistance.
d
17) Jaundice, a yellowing of the skin, is a condition caused by the deposition of bilirubin in the skin. It may be associated with
- a) excessive breakdown of red blood cells
- b) cancer of the bowel or pancreas
- c) blockage of bile drainage by gallstones
- d) increased atmospheric oxygen
a,b,c
18) Towards the end of erythropoiesis in the bone marrow, a red blood cell loses its nucleus and becomes a
- a) proerythroblast.
- b) megakaryocyte.
- c) progenitor cell.
- d) mature erythrocyte.
- e) reticulocyte.
e
19) Erythropoiesis may be stimulated by
- a) pulmonary disease that decreases available oxygen
- b) excessive bleeding
- c) traveling to high altitudes
- d) diving in deep water
a,b,c
20) Which of the following blood cells is a phagocyte?
- a) Neutrophil
- b) Platelet
- c) Lymphocyte
- d) Basophil
- e) Erythrocyte
a
21) Which of the following blood components is involved in reducing blood loss from a damaged blood vessel?
- a) Erythrocyte
- b) Platelet
- c) Lymphocyte
- d) Basophil
- e) Neutrophil
b
22) Which of the following blood cells releases granules that intensify the inflammatory response and promote hypersensitivity (allergic) reactions?
- a) Eosinophil
- b) Monocyte
- c) Lymphocyte
- d) Basophil
- e) Neutrophil
d
23) Which of the following blood cells phagocytizes antigen-antibody complexes and is effective against parasitic worms?
- a) Eosinophil
- b) Monocyte
- c) Lymphocyte
- d) Basophil
- e) Neutrophil
a
24) Which of the following blood cells are the main soldiers in the immune system defense of the body against microbial invaders?
- a) Eosinophil
- b) Macrophage
- c) Lymphocyte
- d) Basophil
- e) Platelet
c
25) Which of the following cells is NOT an agranular leukocyte?
- a) Monocytes
- b) Macrophage
- c) Lymphocyte
- d) Basophil
- e) All of these choices
d
The number of circulating white blood cells may be affected by several factors. A pregnant woman will often exhibit a reduction in the number of
- basophils
- lymphocytes
- monocytes
- neutrophils
a
individual exposed to radiation will exhibit a reduction in the number of
- basophils
- eosinophils
- monocytes
- neutrophils
d
28) The process of a white blood cell squeezing between endothelial cells to exit a blood vessel is called
- a) emigration.
- b) diaphysis.
- c) adhesion.
- d) opsonization.
- e) phagocytosis.
a
29) Which of the following chemical substances is NOT commonly released by mast cells?
- a) Heparin
- b) Histamine
- c) Nitric oxide
- d) Proteases
- e) All of these choices
c
30) Which of the following hormones stimulates the development of megakaryoblasts?
- a) Erythropoietin
- b) Thrombopoietin
- c) Nitric oxide
- d) Human growth hormone
- e) Heparin
b
31) Which of following correctly lists the sequence of steps that occur during hemostasis in response to a damaged blood vessel?
- a) vascular spasm, clotting, polycythemia
- b) hemolysis, vascular spasm, platelet plug formation
- c) emigration, clotting, hemolysis
- d) vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, clotting
- e) anemia, hemogenesis, platelet plug formation
d
32) The intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of blood clotting are identical after formation of
- a) thromboplastin.
- b) prothrombinase.
- c) clotting factor XII.
- d) fibrin.
- e) tissue factor.
b
33) Which of the following clotting factors is involved in strengthening and stabilizing a blood clot?
- a) Factor V
- b) Factor VII
- c) Factor XI
- d) Factor XIII
- e) Factor XIV
d
34) Which of the following situations could result in maternal antibodies attacking fetal blood cells during a second pregnancy?
- a) Mom is Rh negative and fetus is Rh negative
- b) Mom is Rh negative and fetus is Rh positive
- c) Mom is Rh positive and fetus is Rh negative
- d) Mom is Rh positive and fetus is Rh positive.
b
36) Which of the following opposes the action of thromboxane A2 by inhibiting platelet adhesion and release?
- a) Heparin
- b) Fibrinogen
- c) Plasmin
- d) Antithrombin
- e) Prostacyclin
e
37) Which of the following substances is an anticoagulant produced by mast cells and basophils?
- a) Heparin
- b) Fibrinogen
- c) Thromboxane A2
- d) Prostacyclin
e) Plasmin
a

8) Which of the cells in the diagram will eventually develop into macrophages?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) C
- d) D
- e) E
e

39) Which of the cells in the diagram will increase the number of nuclear lobes as they age?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) C
- d) D
- e) E
a

40) Which of the cells in the diagram can be subdivided into categories of small and large versions of this cell type?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) C
- d) D
- e) E
d
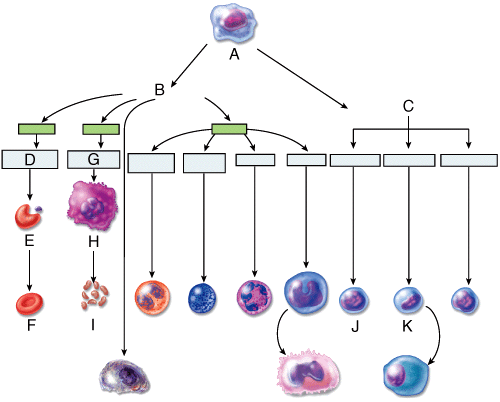
42) Which labeled cell in the diagram is a pluripotent stem cell?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) C
- d) D
- e) G
a

43) Which letter in the diagram indicates the correct position of a myeloid stem cell?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) C
- d) D
- e) G
b

44) Which labeled cell in the diagram will develop into platelets?
- a) H
- b) J
- c) K
- d) L
- e) E
a
47) Which of the following antibodies would you find in the plasma of a person with type O blood?
- a) anti-A
- b) anti-B
- c) anti-A and anti-B
- d) No antibodies to ABO blood group antigens
- e) Not enough information to answer
c
48) What blood type is a person if their plasma contains ONLY anti-A agglutinin?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) O
- d) AB
- e) Not enough information is provided to answer question.
b
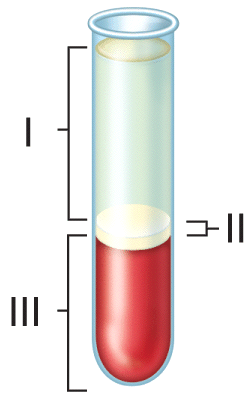
When blood from a normal adult is centrifuged, as shown in the figure, which of the following components occupies the greatest volume?
- a) plasma
- b) red blood cells
- c) platelets
- d) buffy coat
- e) white blood cells
a

54) What is the normal concentration range of the formed element that comprises the blood component labeled III in the figure?
- a) 400,000–1 million cells/μL
- b) 150–200 cells/μL
- c) 4.8–4 million cells/μL
- d) 150,000–400,000 cells/μL
- e) 5,000–10,000 cells/μL
c

55) Which of the following blood cell types normally comprises the highest percentage of the blood component labeled II in the figure?
- a) eosinophils
- b) monocytes
- c) lymphocytes
- d) neutrophils
- e) basophils
d

56) Which of the following blood cell types normally comprises the smallest percentage of the blood component labeled II in the figure?
- a) eosinophils
- b) monocytes
- c) lymphocytes
- d) neutrophils
- e) basophils
e

57) Which of the following types of proteins is present at the highest percentage in the blood component labeled I in the figure?
- a) globulin
- b) albumin
- c) fibrinogen
- d) thrombin
- e) keratin
b

58) Which of the following types of proteins is present at the lowest percentage of the blood component labeled I in the figure?
- a) globulin
- b) albumin
- c) fibrinogen
- d) all of the proteins listed are found in equal percentages
- e) none of proteins listed are found in component I
c
59) Which of the following precursor cells eventually gives rise to neutrophils?
- a) Megakaryoblast
- b) Proerythroblast
- c) T lymphoblast
- d) Monoblast
- e) Myeloblast
e
60) Which of the following precursor cells eventually gives rise to the platelets?
- a) Megakaryoblast
- b) Proerythroblast
- c) T lymphoblast
- d) Monoblast
- e) Myeloblast
a
62) Which of the following formed elements found in the blood are derived from reticulocytes?
- a) Platelets
- b) Erythrocytes
- c) T lymphocytes
- d) Monocytes
- e) Basophils
b
63) Umbilical cord stem cells
- a) are easier to collect than bone marrow stem cells
- b) are more likely to cause a graft-versus-host reaction
- c) are more abundant than bone marrow stem cells
- d) are less likely to transmit infections
a,c,d
64) Which of the following precursor cells gives rise to agranular leukocytes?
- a) Proerythroblast
- b) Megakaryoblast
- c) Lymphoblast
- d) Myeloblast
- e) None of the selections are correct.
c
65) Which of the following precursor cells gives rise to granular leukocytes?
- a) Proerythroblast
- b) Megakaryoblast
- c) Lymphoblast
- d) Myeloblast
- e) None of the selections are correct.
d

66) A high count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate bacterial infection, stress, or inflammation?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) C
- d) D
- e) E
a

67) A high count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate viral infections?
- a) A & B
- b) B & C
- c) C & D
- d) D & E
- e) E & C
d

68) A high count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate parasitic infection or autoimmune disease?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) C
- d) D
- e) E
b

69) A high count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate cancer or hypothyroidism?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) C
- d) D
- e) E
c

70) A high count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate fungal infection?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) C
- d) D
- e) E
e

71) A low count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate pregnancy, ovulation, or hyperthyroidism?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) C
- d) D
- e) E
c

72) A low count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate radiation exposure, or systemic lupus erythematosus?
- a) A
- b) B
- c) C
- d) D
- e) E
a

73) Low counts of which two cell types shown in the figure may result from treatment with cortisol?
- a) A & B
- b) B & C
- c) C & D
- d) D & E
- e) E & C
d
74) Serum is
- a) the same as plasma.
- b) plasma without the clotting factors.
- c) the same as lymph.
- d) formed during the first step in blood clotting.
- e) pulmonary interstitial fluid.
b
75) Reduced vitamin B12 absorption from the small intestine due to reduced intrinsic factor production in the stomach results in condition called
- a) hemorrhagic anemia.
- b) aplastic anemia.
- c) megaloblastic anemia.
- d) pernicious anemia.
- e) iron deficiency anemia.
d
76) Destruction of red bone marrow due to radiation results in
- a) hemorrhagic anemia.
- b) aplastic anemia.
- c) megaloblastic anemia.
- d) pernicious anemia.
b
77) A condition in which inadequate intake of vitamin B12 or folic acid causes production of large abnormal red blood cells is called
- a) hemorrhagic anemia.
- b) aplastic anemia.
- c) megaloblastic anemia.
- d) pernicious anemia.
- e) iron deficiency anemia.
c
78) Anemia is defined as
- a) a condition where blood does not clot properly.
- b) a condition where blood cells are lysed by the immune response.
- c) a condition where there is excessive bleeding.
- d) a condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood is reduced.
- e) none of these choices.
d
80) The average life span of an erythrocyte in the circulation is
- a) 4 to 5 years.
- b) 4 to 5 hours.
- c) 5 to 9 days.
- d) 120 days.
- e) 120 weeks.
d
81) Which of the following are characteristics of BOTH erythrocytes and platelets?
- a) no nucleus
- b) large segmented nucleus
- c) cytoplasmic granules
- d) lifespan of 5 to 9 days
- e) develop from myeloblasts
a
82) Which of the following formed elements in blood is removed by fixed macrophages in the spleen and liver after only 5 to 9 days in the circulation?
- a) erythrocytes
- b) platelets
- c) monocytes
- d) basophils
- e) eosinophils
b
83) A cord-blood transplant involves obtaining the stem cells to transplant into the diseased patient from
- a) the spermatic cord of a donor’s testes.
- b) the spinal cord of the patient.
- c) the umbilical cord of a donor shortly after birth.
- d) the irradiated bone marrow of the patient.
- e) the spinal cord of an aborted fetus.
c
84) If type A blood is infused into a patient with type O blood, which of the following adverse reactions would you expect to observe in the patient?
- a) Agglutination (clumping) of the transfused blood cells.
- b) Complement-induced hemolysis of the transfused blood cells.
- c) Released hemoglobin clogging the filtration membrane of the kidneys.
- d) There would be no adverse reactions as these blood types are compatible.
a,b,c
85) Which of the following blood types is a person whose blood cells were agglutinated by both anti-A serum and anti-B serum, but not by anti-Rh serum?
- a) AB negative
- b) AB positive
- c) O negative
- d) O positive
- e) None of the selections are correct
a