Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
blood
front 1 1) Which of the following is NOT a major function of the blood?
| back 1 e |
front 2 2) Which of the following is NOT a true statement regarding blood?
| back 2 c |
front 3 3) The hematocrit is a measure of the percentage of whole blood occupied by
| back 3 c |
front 4 4) What percentage of blood plasma is water?
| back 4 b |
front 5 5) Which of the following plasma proteins plays a role in disease resistance?
| back 5 b |
front 6 6) Which of the following plasma proteins plays a role in blood clotting?
| back 6 c |
front 7 9) The process by which the formed elements of the blood develop is called
| back 7 b |
front 8 10) A megakaryoblast will develop into
| back 8 c |
front 9 11) During hemopoiesis, some of the myeloid stem cells will eventually develop into
| back 9 a |
front 10 12) Progressive liver failure may lead to serious bleeding problems due to
| back 10 a,b |
front 11 13) Which of the following hormones stimulates proliferation of red blood cells in red bone marrow?
| back 11 a |
front 12 15) Ferritin is a protein used to
| back 12 b |
front 13 14) Approximately, how many hemoglobin molecules are found in each RBC?
| back 13 c |
front 14 16) The major function of red blood cells is
| back 14 d |
front 15 17) Jaundice, a yellowing of the skin, is a condition caused by the deposition of bilirubin in the skin. It may be associated with
| back 15 a,b,c |
front 16 18) Towards the end of erythropoiesis in the bone marrow, a red blood cell loses its nucleus and becomes a
| back 16 e |
front 17 19) Erythropoiesis may be stimulated by
| back 17 a,b,c |
front 18 20) Which of the following blood cells is a phagocyte?
| back 18 a |
front 19 21) Which of the following blood components is involved in reducing blood loss from a damaged blood vessel?
| back 19 b |
front 20 22) Which of the following blood cells releases granules that intensify the inflammatory response and promote hypersensitivity (allergic) reactions?
| back 20 d |
front 21 23) Which of the following blood cells phagocytizes antigen-antibody complexes and is effective against parasitic worms?
| back 21 a |
front 22 24) Which of the following blood cells are the main soldiers in the immune system defense of the body against microbial invaders?
| back 22 c |
front 23 25) Which of the following cells is NOT an agranular leukocyte?
| back 23 d |
front 24 The number of circulating white blood cells may be affected by several factors. A pregnant woman will often exhibit a reduction in the number of
| back 24 a |
front 25 individual exposed to radiation will exhibit a reduction in the number of
| back 25 d |
front 26 28) The process of a white blood cell squeezing between endothelial cells to exit a blood vessel is called
| back 26 a |
front 27 29) Which of the following chemical substances is NOT commonly released by mast cells?
| back 27 c |
front 28 30) Which of the following hormones stimulates the development of megakaryoblasts?
| back 28 b |
front 29 31) Which of following correctly lists the sequence of steps that occur during hemostasis in response to a damaged blood vessel?
| back 29 d |
front 30 32) The intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of blood clotting are identical after formation of
| back 30 b |
front 31 33) Which of the following clotting factors is involved in strengthening and stabilizing a blood clot?
| back 31 d |
front 32 34) Which of the following situations could result in maternal antibodies attacking fetal blood cells during a second pregnancy?
| back 32 b |
front 33 36) Which of the following opposes the action of thromboxane A2 by inhibiting platelet adhesion and release?
| back 33 e |
front 34 37) Which of the following substances is an anticoagulant produced by mast cells and basophils?
e) Plasmin | back 34 a |
front 35  8) Which of the cells in the diagram will eventually develop into macrophages?
| back 35 e |
front 36  39) Which of the cells in the diagram will increase the number of nuclear lobes as they age?
| back 36 a |
front 37  40) Which of the cells in the diagram can be subdivided into categories of small and large versions of this cell type?
| back 37 d |
front 38 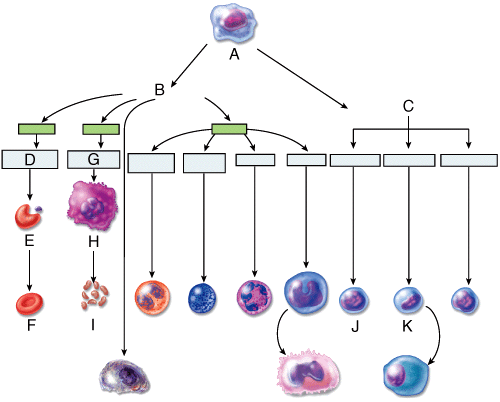 42) Which labeled cell in the diagram is a pluripotent stem cell?
| back 38 a |
front 39  43) Which letter in the diagram indicates the correct position of a myeloid stem cell?
| back 39 b |
front 40  44) Which labeled cell in the diagram will develop into platelets?
| back 40 a |
front 41 47) Which of the following antibodies would you find in the plasma of a person with type O blood?
| back 41 c |
front 42 48) What blood type is a person if their plasma contains ONLY anti-A agglutinin?
| back 42 b |
front 43 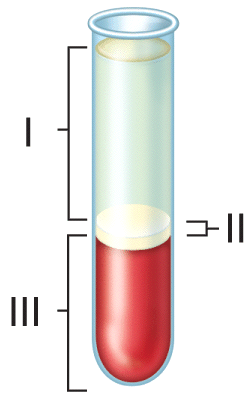 When blood from a normal adult is centrifuged, as shown in the figure, which of the following components occupies the greatest volume?
| back 43 a |
front 44  54) What is the normal concentration range of the formed element that comprises the blood component labeled III in the figure?
| back 44 c |
front 45  55) Which of the following blood cell types normally comprises the highest percentage of the blood component labeled II in the figure?
| back 45 d |
front 46  56) Which of the following blood cell types normally comprises the smallest percentage of the blood component labeled II in the figure?
| back 46 e |
front 47  57) Which of the following types of proteins is present at the highest percentage in the blood component labeled I in the figure?
| back 47 b |
front 48  58) Which of the following types of proteins is present at the lowest percentage of the blood component labeled I in the figure?
| back 48 c |
front 49 59) Which of the following precursor cells eventually gives rise to neutrophils?
| back 49 e |
front 50 60) Which of the following precursor cells eventually gives rise to the platelets?
| back 50 a |
front 51 62) Which of the following formed elements found in the blood are derived from reticulocytes?
| back 51 b |
front 52 63) Umbilical cord stem cells
| back 52 a,c,d |
front 53 64) Which of the following precursor cells gives rise to agranular leukocytes?
| back 53 c |
front 54 65) Which of the following precursor cells gives rise to granular leukocytes?
| back 54 d |
front 55  66) A high count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate bacterial infection, stress, or inflammation?
| back 55 a |
front 56  67) A high count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate viral infections?
| back 56 d |
front 57  68) A high count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate parasitic infection or autoimmune disease?
| back 57 b |
front 58  69) A high count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate cancer or hypothyroidism?
| back 58 c |
front 59  70) A high count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate fungal infection?
| back 59 e |
front 60  71) A low count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate pregnancy, ovulation, or hyperthyroidism?
| back 60 c |
front 61  72) A low count of which of the white blood cells shown in the figure may indicate radiation exposure, or systemic lupus erythematosus?
| back 61 a |
front 62  73) Low counts of which two cell types shown in the figure may result from treatment with cortisol?
| back 62 d |
front 63 74) Serum is
| back 63 b |
front 64 75) Reduced vitamin B12 absorption from the small intestine due to reduced intrinsic factor production in the stomach results in condition called
| back 64 d |
front 65 76) Destruction of red bone marrow due to radiation results in
| back 65 b |
front 66 77) A condition in which inadequate intake of vitamin B12 or folic acid causes production of large abnormal red blood cells is called
| back 66 c |
front 67 78) Anemia is defined as
| back 67 d |
front 68 80) The average life span of an erythrocyte in the circulation is
| back 68 d |
front 69 81) Which of the following are characteristics of BOTH erythrocytes and platelets?
| back 69 a |
front 70 82) Which of the following formed elements in blood is removed by fixed macrophages in the spleen and liver after only 5 to 9 days in the circulation?
| back 70 b |
front 71 83) A cord-blood transplant involves obtaining the stem cells to transplant into the diseased patient from
| back 71 c |
front 72 84) If type A blood is infused into a patient with type O blood, which of the following adverse reactions would you expect to observe in the patient?
| back 72 a,b,c |
front 73 85) Which of the following blood types is a person whose blood cells were agglutinated by both anti-A serum and anti-B serum, but not by anti-Rh serum?
| back 73 a |