How does the blastula relate to clevage?
The blastula stage signals the end of the period in embryogenesis known as cleavage.
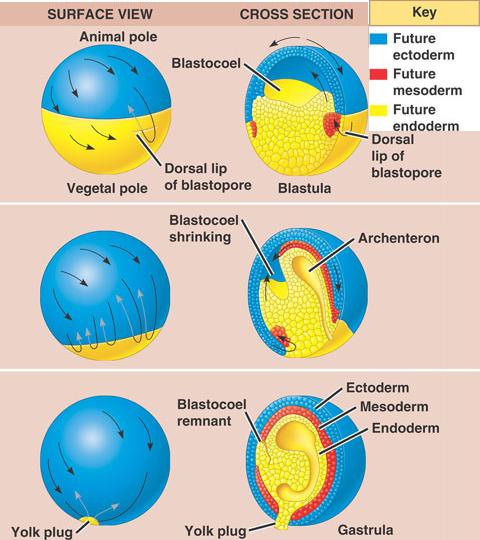
Blastula anotomical description
The blastula can be defined in anatomical terms as a hollow stage in the embryo’s development, with a cavity (the blastocoele), surrounded by an epithelial cellular layer called the blastoderm.
***The teleosts (bony Fishes) have a blastoderm that does not surround the “Blastocoele”
Blastula Formation

Blastula (single layer cell) Gastrula (Three cell layers- endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm)

Gastrula
- Rearrangement of cells of the embryo via morphogenetic movements
- Slower mitotic rate
- No significant growth
- metabolic change (increased oxidation)
- Embryonic nuclei become active
- Qualitative change in protein population
Gastrula 6 Primairy changes
- Rearrangement of cells of the embryo via morphogenetic movements
- Slower mitotic rate
- No significant growth
- metabolic change (increased oxidation)
- Embryonic nuclei become active
- Qualitative change in protein population
Real
New
Mice
Eat
Qualil
Frog Fate Map layers
Frog fate map external
Bony Fish fate map

Primary Organizers
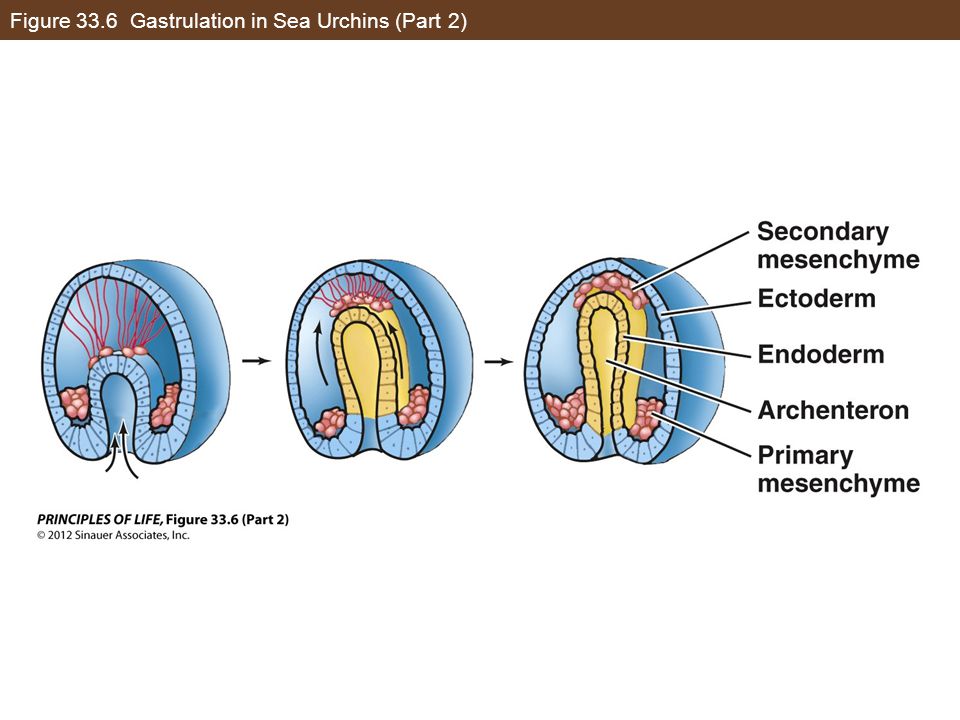
- Micromeres- sea urchin
- Gray crescent- frog
- Dorsal Lip of Blastopore- Amphibian, Frog*
- Primitive Streak- chick, human
Micromeres- sea urchin

Primary Organizers
Note: clevage is equal at 2 cell stage
16 cell stage early clevage not complete
no green no orange but later these sections will become
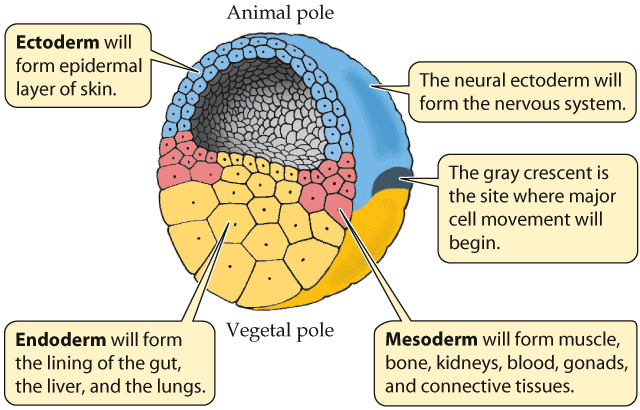
Gray crescent- frog
Primary Organizers
Dorsal Lip of Blastopore- Amphibian, Frog*

Primary Organizers
Primitive Streak- chick, human

Primary Organizers
Primairy mesenchyme vs Secondary mesenchyme
Teleosts/Bony fish
Blastoderm/Blastocoele
Blastoderm does not surround the blastocoel, instead has cell death tube . Removed during excavation.
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Mesoderm
Ectoderm Blue/Green
Endoderm Yellow
Mesoderm Red/Orange
Ectoderm
Endoderm
Mesoderm
become...

Prospective Significance
Prospective Fate of a cell or group of cells due to their anatomical position in the embryo
Prospective Potency
Developmental Potential of a cell or group of cells under varying conditions, wherein new influences (inductive influences) are encountered.
Induction
When one cell or group of cells influences the fate of another cell or group of cells without necessarily affecting itself
Inductor
The cell or group of cells responsible for the influence mentioned above.
Embryonic Competency
The ability of cells to respond to the influence of an inductor
Period of competency is a fixed period of time.
Determination
Fixing the fate of cells during development(narrowing of the prospective potency so that it more closely equals the prospecting significance) when the prospective potency and prospective significance are the same we say that cells are fully determined (happens during the s-period of the cell cycle)
Differentiation
Physical (Anatomical) and Genetic/Biochemical (Physiological) expression of the fixed fate of cells.
Spacial Differentiation
Spatially different parts of the embryo take on different anatomical structure. Morphogenesis/ Organogenesis
Temporal Differentiation
Over a period of time different cells in an organ differentiates into different, specific cell types. Cytodifferentiation Histogenesis
Morphogenesis/ Organogenesis
Spacial Differentiation
Cytodifferentiation Histogenesis
Temporal Differentiation
Morphogenetic (Formative) Movements
Invagination- pushing in of an epithelium
Epiboly- Spreading of an epithelial layer so that it covers over epithelia
Ingression (immigration)- breaking-up of an epithelium followed by inward migration of individual cells
Involution- inward migration of an epithelium
Separation of epithelial layers
Local thickening followed by evacation
Invagination , Ingression, involution

Epiboly

Additional Morphogenetic Formative movements
- Separation of epithelial layers
- Local thickening followed by evacation
Draw Early Gastrulation
TOP
Red- Non-notochordal mesoderm
Orange- Chrdomesoderm
Yellow- Endoderm
Green- Neural Ectoderm
Blue- Epidermal Ectoderm
Draw Mid Gastrulation
BOTTOM
Red- Non-notochordal mesoderm
Orange- Chrdomesoderm
Yellow- Endoderm
Green- Neural Ectoderm
Blue- Epidermal Ectoderm
Villus Arrangement
Diffuse
Cotyledons
Zonary
Discoidal
Bidiscoidal
ICM=Inner Cell mass
TB- Trophoblast
HB- Hypoblast
EB- Epiblast
MES- mesoderm
YS- Yolk Sac
CH- Chorion
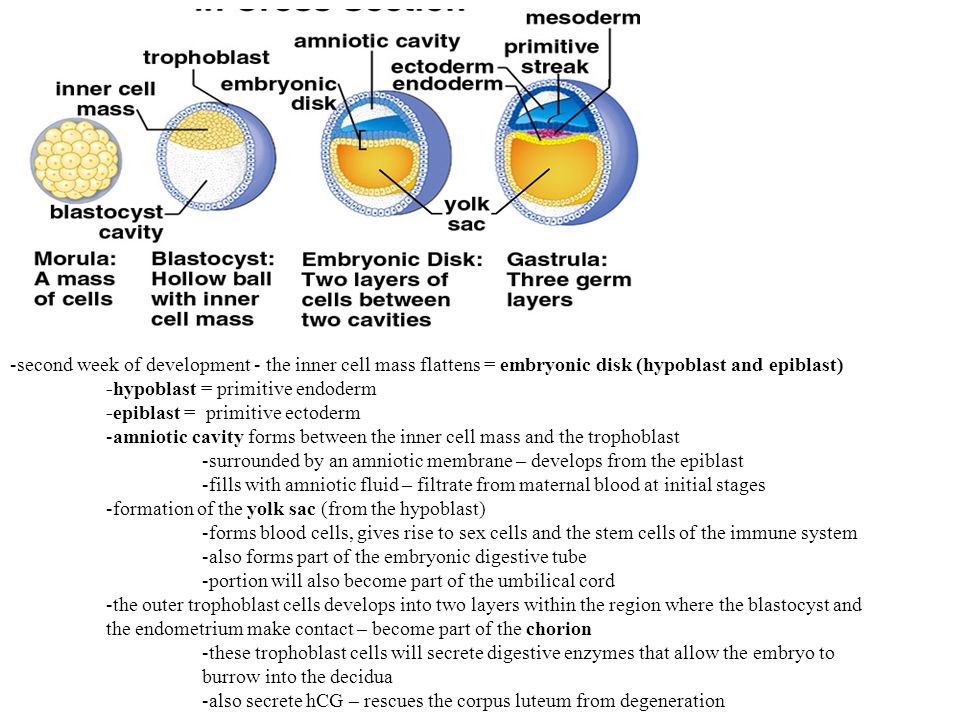
Chorion

Diffuse
Cotyledons
Zonary
Discoidal
Bidiscodal
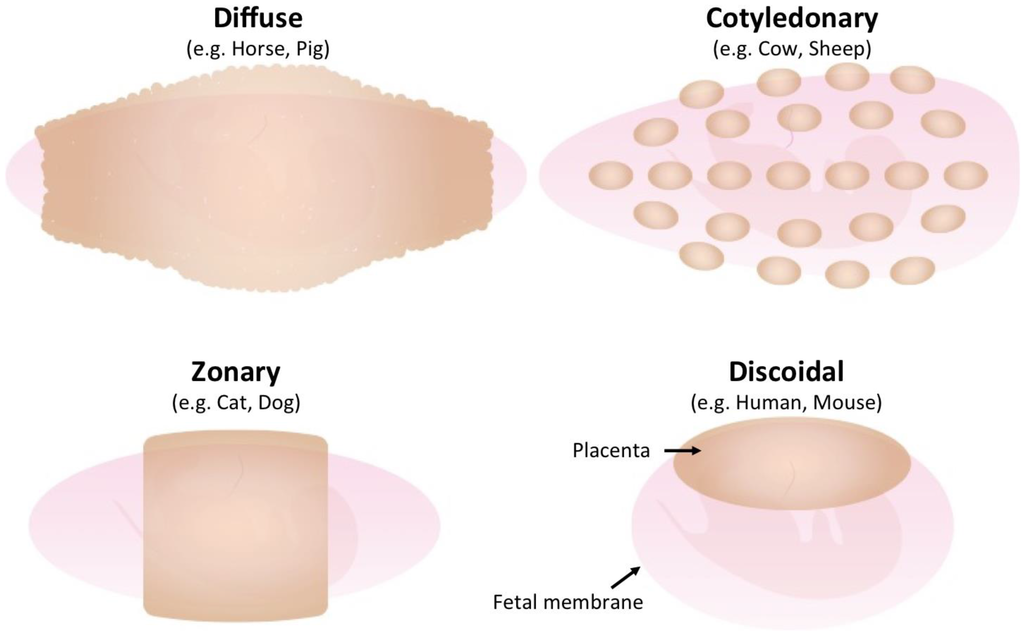
Bidiscodial-same as discoidal but with 2 disks
Area Opeca Vasculosa
Area Pellucida

COLOR
mid gastrulation
When orange meets orange gastrulation stops.

blastula
early gastrula
late gastrula

Amnion
Allantois
Yolk Sac
Chorion
Yolk Stalk
Heart rudiment
Yolk plug

Gastrulation in the Chick
- Invagination of primitive pit (streak)
- Ingression of mesoderm
Primary Organ Rudiment Formation in the Chick
NO
SUCH
STUPID
LUCK
I
BROUGHT
APPLES
ANYWAY
- Neural tube formation with epilepsy
- Separation of the chordomersoderm from segimental mesoderm
- Somites forom from dorsal portion of segmental mesoderm
- Lateral plate mesoderm splits to form splanchnic mesoderm, somatic mesoderm, coelom
- Intermediate mesoderm forms nephrostone
- Body folds close forming gut
- Exocoele forms amniotic folds
- Amniotic folds form amnion and chorion (serosa)
- Amniotic folds form yolk sacs
Primary Organ Rudiment Formation in the Chick
- #formation with epilepsy
- Separation of the # from # mesoderm
- Somites forom from # portion of segmental mesoderm
- ## mesoderm splits to form splanchnic mesoderm, somatic mesoderm, coelom
- Intermediate mesoderm forms #
- Body folds # forming gut
- # forms amniotic folds
- Amniotic folds form # and # (serosa)
- Amniotic # form yolk sacs
Primary Organ Rudiment Formation in the Chick
- Neural tube formation with epilepsy
- Separation of the chordomersoderm from segimental mesoderm
- Somites forom from dorsal portion of segmental mesoderm
- Lateral plate mesoderm splits to form splanchnic mesoderm, somatic mesoderm, coelom
- Intermediate mesoderm forms nephrostone
- Body folds close forming gut
- Exocoele forms amniotic folds
- Amniotic folds form amnion and chorion (serosa)
- Amniotic folds form yolk sacs
Hilde mangold
- Primary Organ Rudiment Formation in the Frog
- Discovery of Primary Embryonic Organizer by Hilde mangold
- demonstrated this effect with the frog’s dorsal lip (chordomesoderm)
Mangold ROL rude old lip
A.S.G. Curtiss crescent
demonstrated this effect with the frog’s gray crescent (presumptive chordomesoderm)
Determination
Determination vs Competency
?what a cell becomes vs its ability to become something ?
Types of Grafts
Always
Hang
Heavy
Xrays
- Autoplastic Transplant (autograft)- donor and host same individual
- Homolpastic transplant (homograft)- donor and host are different individuals of the same genus and species
- Heteroplastic transplant (hetrograft)- donor and host of same genus but different species
- Xenoplastic transplant (xenograft) donor and host more distant than genus
Autoplastic Transplant (autograft)
donor and host same individual
Homolpastic transplant (homograft)
donor and host are different individuals of the same genus and species
Heteroplastic transplant (hetrograft)
donor and host of same genus but different species
Xenoplastic transplant (xenograft)
donor and host more distant than genus