A controlled experiment
Control group
A localized group of organisms that belong to the same species is called a
A population
You find yourself standing next to a plant. List the things you and the plant have in common?
use oxygen and carbon to survive, are linear,
A friend of yours calls to say that his car would not start this morning. He asks for your help. You say that you think the battery must be dead. If so, then jump-starting the car from a good battery will solve the problem. In doing so, you are doing what part of the scientific process?
hypothesis
In the process of science, what do you test?
collected data
What four elements make up approximately 96 percent of living matter?
hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen
Trace elements are those required by an organism in only minute quantities. Which trace element that is required by humans and other vertebrates for normal thyroid function.
Iodine
A covalent chemical bond is one in which
outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill the outer electron shells of both atoms.
What results from an unequal sharing of electrons between atoms?
a polar covalent bond
 Explain the difference between covalent bonds and ionic bonds?
one of the atoms sharing electrons is more electronegative than the other atom.
Water molecules are attracted to one another by
Hydrogen Bond
How many electrons are involved in a single covalent bond?
a single covalent bond has 2 atoms which hold 1 electron each atom
2
An carbon atom has four electrons in its valence shell. What types of covalent bonds is it capable of forming?
single, double, or triple
When the atoms involved in a covalent bond have the same electronegativity, what type of bond results?
a nonpolar covalent bond
In a single molecule of water, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by
a polar covalent bond
The partial negative charge at one end of a water molecule is attracted to the partial positive charge of another water molecule. What is this attraction called?
a hydrogen bond
Explain why does water display a partial negative charge?
electrons shared between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms spend more time around the oxygen atom nucleus than around the hydrogen atom nucleus.
To act as an effective coolant in a car's radiator, a substance has to have the capacity to absorb a great deal of heat. You have a reference book with tables listing the physical properties of many liquids. In choosing a coolant for your car, which table would you check first?
specific heat
Which of the following effects can occur because of the high surface tension of water?
A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond.
Hydrophobic substances such as vegetable oil are
nonpolar substances that repel water molecules
Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize into a gas?
hydrogen bonds

Label the below diagram: water, oxygen, hydrogen, partial negative charge, partial positive charge, solute
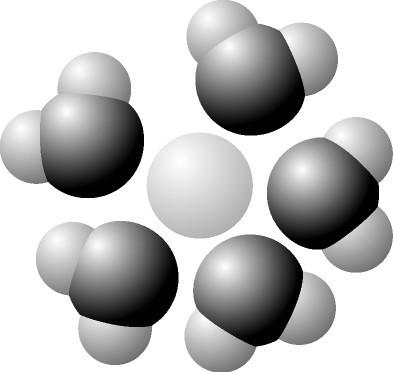
hydrogen oxygen na- the rest is positively charged
How would you bring an acidic solution to neutral?
you have a weak acid or a weak base half ionized in water
Why are molecules considered organic?
Organic molecules exist in all living things
What types of covalent bonds can carbon form?
carbon-carbon and carbon hydrogen bonds
Why is carbon so important in biology?
It can form a variety of carbon skeletons and host functional groups
The complexity and variety of organic molecules is due to
the chemical versatility of carbon atoms
A carbon atom is most likely to form what kind of bond(s) with other atoms?
covalent
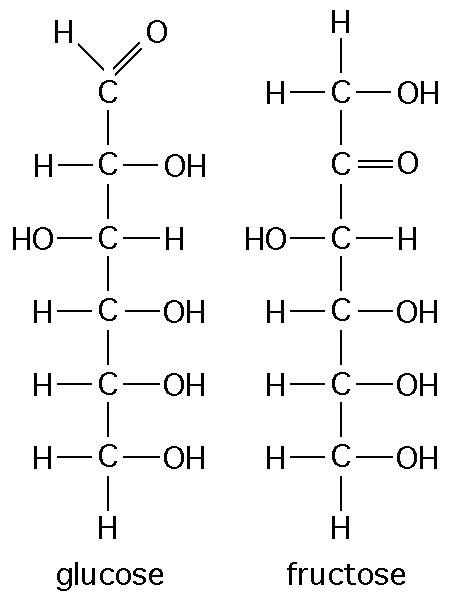
The figure above shows the structures of glucose and fructose. They both have the molecular formula C6H12O6, but how do they differ.
structural isomers
Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids? Draw these functional groups.
carboxyl and amino
Which class of organic molecules does NOT include polymers?
Lipids
List all polymers discussed in class and the group in which they belong.
1.carbohydrates,
2.lipids,
3.proteins, and
4.nucleic acids.
Monomers are the smaller part of the macromolecules
(polymers=many chained together).
•Monomers are linked together
to form polymers through dehydration reactions, which remove
water.
•Polymers are broken apart by hydrolysis, the addition
of water.
•These reactions are mediated by enzymes, specialized
macromolecules that speed up chemical reactions in cells.
Contrast dehydration reactions and hydrolysis?
Dehydration means to take water out.
Hydrolysis is the separation of two macromolecules by adding water.
Which polysaccharide is an important component in the structure of many animals and fungi?
Chitin
A molecule with the chemical formula C6H12O6Â would be considered a what?
glucose
carbohydrate and monosaccharide only
List all things lactose can be considered.
as a disaccharide
 In what types of organisms are starch and cellulose found? What is their function?
They are both polymers of glucose
List the types of covalent bonds discussed in class and the organic group in which they belong.
...
Phospholipids and triglycerides both
lipids
Describe how the structure of phospholipids interacts with water molecules.
...
Explain why chemically vegetable oil is a liquid at room temperature while animal fats are solid.
...
Contrast saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
...
List terms that describe how lipids behave in water.
...
What are the monomers of proteins?
Nucleotides
List the components of an amino acid.
Components: amino, carboxyl, H, R (variable) group
Side chain
classes: nonpolar, polar, acidic, basic
What component of amino acid structure varies among different amino acids?
...
Describe how protein structure and function are correlated? How can the structure of a protein be altered?
...
List the examples of proteins and lipids discussed in class.
...
Discuss the levels of protein structure folding.
primary structurelinear aequence of amino acids
secondary structurealpha helix and beta pleated sheet formed by hudrogen bonds between atoms of the polypeptide backbone
tertiary structure3d shape formed by interactions between r groups
quaternary structureassociation of multiple polypeptides
What are the monomers of nucleic acids?
nucleotides
ribonucleotide
Deoxyribonucleotide
List the purine nucleotides.
nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA; either adenine or guanine
List the pyrimidine nucleotides.
nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA; thymine, cytosine, or uracil
List the components of a nucleotide?
A sugar (called deoxyribose)
A Phosphate (1 phosphorus atom joined to 4 oxygen atoms)
One of 4 bases (Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine)
What is the primary functions of RNA?
1. Messanger RNA (mRNA)
2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
3. Transfer
RNA (tRNA)
When nucleotides polymerize to form a nucleic acid what bonds are formed
a covalent bond forms between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of a second
Contrast DNA and RNA.
While the sugar present in a RNA molecule is ribose, the sugar present in a molecule of DNA is deoxyribose
If one strand of a DNA molecule has the sequence of bases, ATTGCA, the other complementary strand would have the sequence
TAACGT
A major type of lipid found in cell membranes is
Phospholipids
You now know that the old cliché "oil and water don't mix" is true. Why?
Water exhibits polarity and oil does not.
If you eat a hamburger, you are mainly eating ground-up beef muscle tissue. What levels of organization are represented in this ground-up muscle?
Organelle, cell, and tissue
If you change the number of neutrons in an atom, you create
an isotope
Bonds between two atoms that are equally electronegative are
nonpolar covalent bonds
A covalent bond is likely to be polar when
one of the atoms sharing electrons is much more electronegative than the other atom.
Water molecules can form hydrogen bonds with
compounds that have polar covalent bonds.
What can be attributed to water's high specific heat?
A lake heats up more slowly than the air around it.
Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize?
hydrogen bonds
A strong acid like HCl dissociates
ionizes completely in an aqueous solution.
How many electron pairs does carbon share to complete its valence shell?
4
How many molecules of water are used to completely hydrolyze a polymer that is 11 monomers long?
10
Steroids are considered to be lipids because they
A family of lipids distinguished by a bulky four-ring structure
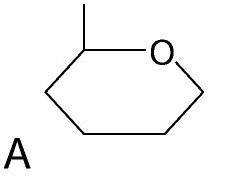
Monosaccharide Carbohydrate

Protein
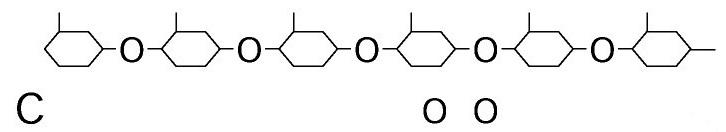
Polysaccharides
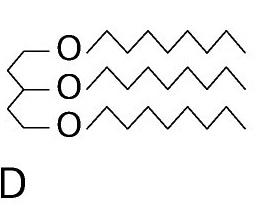
triglyceride
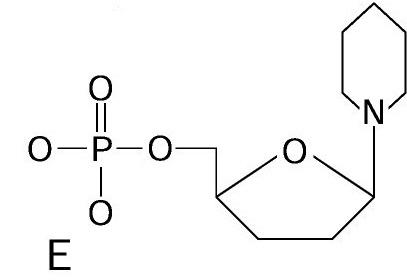
Nucleotide

Lipid and Fatty acid
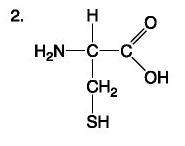
Amino Acid
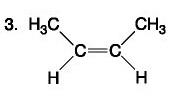
Carbohydrate
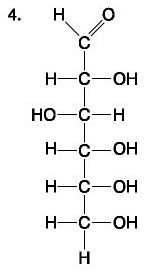
Lipid and Fatty acid
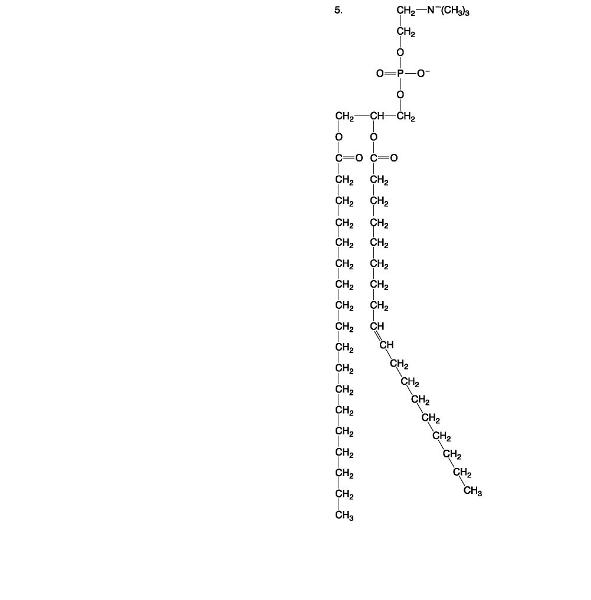
Phospholipid
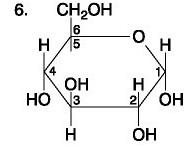
Carbohydrate
...
Amino acid
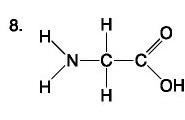
Amino Acid
...
lipid and fatty acid

...
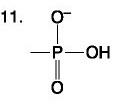
Nucleotide
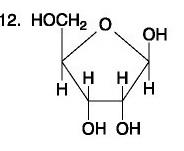
...
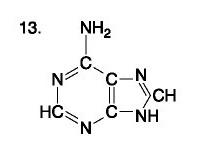
...
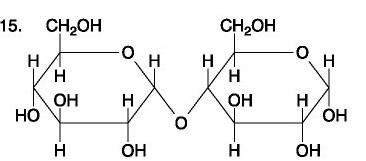
...