Female reproductive system is a more complex system than __________. Not only must she produce _________, but her body must prepare to nurture a ___________ _______ for approximately _________ months.
- male
- gametes
- developing fetus
- 9 months
- the _________ are the female gonads, as __________ are for male
- These are a ______ of gametes, ______ -shaped glands containing approximately __________ primordial follicles.
- ovaries
- testis
- 400,000 primordial follicles
- Ovaries are __________
- and __________ Sex Organs
- Ovaries are suspended by several ___________ called ____________ ligaments.
- gonads
- Primary
- ligaments
- Broad Ligaments
The suspensory ligaments and mesovarium are part of the _______ _____________, a _________ fold that "tents" over the uterus and support :
3 organs __________, ____________ and ___________.
- Broad ligaments
- peritoneal fold
- the uterine tubes,
- uterus and
- vagina

- Ovaries produce haploid ________ by ___________
- Ova is the female _____________
- Ova is the one to be _________ by male gamete _______
- Ova
- Oogenesis
- gamete
- fertilized
- spermatozoid
- Both ovaries are lined by ___________ _________, which consists
of:
- Simple __________ epithelium that covers the ovary.
- Bellow we find the _______ __________ which is a capsule of collagenous CT.
- Germinal Epithelium
- cuboidal
- tunica albuginea
- ___________ is the outer cortex, and the inner medulla
- The outer cortex region contain the _____ _____
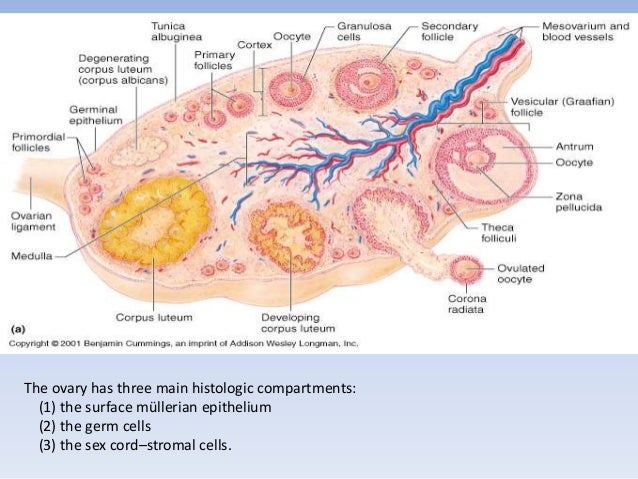
- Stroma
- Ovarian follicles
Grafian follicles, now called _________ __________ is a mature ________ and its surrounding tissue secrete ______________
- Vesicular Follicle
- Ovum
- Estrogen
Corpus __________ produces __________ and estrogen
- Corpus Luteum
- progesterone
Ova stages start with :
- Oocyte = ________, is a
- Secondary __________ is the last section of maturation of the oocyte.

- Oocyte (egg) is an immature egg encased by one or more layers
of very different cells called Follicle cells
- Oocyte are the product from meiosis of dormant cells.
- oocyte
3.- Secondary oocyte extend from the deepest part of the ovarian cortex and bulges from the surface of the ovary, and its oocyte sits proudly on a stalk of granulosa cells at one side of the antrum to be ovulated, This is called ________
- Ovulation
After ovulation, the ruptured follicle is transformed into a very different looking glandular structure called __________ ____________ (yellow body), which eventually degenerates. During all this process, it is going to release ____________ _________
- Corpus Luteum
- progesteron
- estrogen
The Uterine Tubes, also called _________ tubes or __________ form the initial part of the female duct system where mature ______ travel to the Uterus.
- Fallopian tubes
- oviducts
- ovum
1- The mature ova once released is caught by a structure called ___________ which is a ______ -shaped structure that sweep over the surface of the ___________ in search of the ovulated mature ______.
- fimbriae
- finger
- ovaries
- ovum
2-_____________ is the opening into the fallopian tube
Infundibulum
The Fallopian Tube is :
- approx. _____ long.
- Homologous to the________ ______ of the male.
- Fallopian tubes conveys the _______, to the __________
- 4"
- Ductus Deferens
- Ovum
- Uterus
- Fallopian tube is lined with:
- _________ cells which beat and carry the ovum toward the uterus.
- It takes about _____ days.
- Ciliated
- 3
Uterus, also called the ________, _____ -shaped, is the site of _________________ and ______________ of a fetus.
- the womb
- Implantation
- development
There are 3 basic layers of the uterus:

- Perimetrium
- Myometrium
- Endometrium
1- Perimetrium
- a serous membrane (visceral peritoneum)
- IT BECOMES the Broad Ligament
2- Myometrium
- 3 layers of smooth muscle
- 75% of the thickness of the uterus
3- Endometrium

- The nutritive inner lining which is divided in
- Stratum Functionalis
- Stratum Basales
Stratus Functionalis
is the one that shed during menstruation
Stratus Basales
is permanent and forms the site of menstruation, implantation of a zygote, and development of the fetus during pregnancy.
_____________ is the top dome shaped portion of the uterus
Fundus
____________ is the major and main portion at the center of the uterus
The Body
______________ is the lower neck portion of the uterus , and projects to the vagina (inferiorly)
The cervix
__________ os is between the uterine cavity and the cervical cavity

Internal Os
__________ os is where the cervix opens into the vagina
External Os
____________ is the female copulatory organ, which is:
- shape _________
- Tissue _________
- serves as a ______________ for menstrual flow, copulation and ???
Vagina
- Tubular
- fibromuscular organ
- passageway
Vagina is lined with :
- ___________
Vagina produces and _________ mucus to
- kill ________ and to act as a _____________
- Stratified squamous epithelium
- acidic mucus
- bacteria
- lubricant
Vagina is
- about _____ long.
- contain _________ which are a series of transverse folds.
- 4"
- Rugae
- The vagina orifice is __________ opening to the vagina
- the ______________ is a membrane sheet of tissue which may form a border around the orifice.
- exterior
- Hymen
_____________ is the external genetalia of the female; it includes:
Vullva
- Labium Majora
- Labium Minora
- The clitoris
- Anus
______________ is an elevation of adipose tissue which cushions the pubic _________ during sexual intercourse.
- Mons Pubis
- pubic symphysis
_________ _________ are two large longitudinal folds of skin; they are homologous to the ____________ in the male.
Labium _________ contain _________, ______ and ___
- The Labium Majora
- scrotum
- Majora
- adipose
- sweat glands
- oil glands
________ _________ are two smaller folds of skin medial to the labia __________.
They contain many _____ glands for ___________ during sexual intercourse.
- Labia minora
- majora
- oil
- lubrication
______________ is a small cylindrical mass of erectile tissue. It is covered by a prepuce and is homologous to the _____________ of the male.
- The clitoris
- penis
_____________ _____ are modified sweat glands that produce milk.
- Mammary Glands
Mammary Glands contain about ___ to ___ lobes or compartments, each of which is divided into several smaller compartments called __________.

- 15 to 20
- Lobules
The lobules contain milk-secretion glands called ______
alvioli
The alveoli drain milk into a series of ducts which open onto the surface of the ________ which is the pigmented projection located in the middle of a circular pigmented area called the _____________.
- niple
- areola
Ovarian Cycle is the ___________ events associated with the maturation of an _________.
- monthly
- ovum
GnRF means
Gonadotropin Releasing Factor
Gonadotropin Releasing Factor (GnRF) originates from __
Gonadotropin RF regulates ________________
Gonadotropin RF stimulates _________________
- Hypothalamus
- both cycles (menstrual and ovarian)
- the release of FSH and LH from the adenohypophysis
FSH stands for
Follicule Stimulated Hormone
LH stands for
Leutenizing Hormone
FSH is a hormone that __________ the development of ovarian follicular cells and stimulating them the ________ of estrogen
- Stimulates
- Secretion
LH is a hormone that
- stimulates maturation of the __________,
- brings about __________,
- stimulates production of ________ and _________
- stimulate production of _____ (pubis symphysis cartilage)
- follicles
- ovulation
- estrogen and progesteron
- relaxin
Estrogen is responsible for the development and maintenance of :
___________________________________
- Female reproductive structures
- secondary sex characteristics
- the breast
- endometrial lining of the uterus (stimulates Endometrial built up).
- control fluid and electrolyte balance
- increases protein anabolism (building)
Estrogen is ___________ to testosterone
analogous
The major source of Estrogen are:
- ovaries
- developing follicle
- corpus luteum
The stimulus for release of estrogen comes from
FSH (and LH)
___________- is a placental hormon that relaxes pubis symphysis and aids in the dilatation of the cervix
Relaxin
- The menstrual cycle start between the day____________ with an average of ____ days in its process.
- Menstruation discharges monthly about ____ to ___ ml of ________, _______, ______ and ________
- 24 to 35
- 28
- Fluid tissue
- blood
- mucus
- Epithelial cells from endothelium
- Menstruation is cause by a sudden drop in __________ and __________ levels.
- Last for about _____ days
- Estrogen
- progesteron
- 5
Stratus ________ degenerates, the uterine gland discharge their contests and ___________.
- Functionalis
- collapse
The flow of menstruation is from the _______, ______, ______ and __________ found in the stratum _________.
- Uterine cavity
- cervix to the
- vagina and
- exterior
- functionalis
Menstruation last about ____ days until ONLY the stratum __________ is left.
- 5
- basale
Ovulation cycle start on day ____ of ____, when __________ cycle is Starting. This process stimulates the Hypothalamus to produce _________________________, which stimulates ___________ pituitary to release hormones ________ and _________.
- 1 of 28 approx.
- menstruation
- GnRF (gonadotropin Releasing factor)
- Anterior
- FSH and LH
- Before day 1, primordial follicles became __________ follicles which were chosen from a set to start developing
- _____ hormone is released by anterior pituitary to stimulate the growth of the follicle to be ovulated.
- Primary Follicle
- FSH
After day __-___ (during the menstrual cycle) the follicles have developed into __________ follicle, which contain ___________ cells and fluid called ______________ fluid.
- 4-5
- Secondary follicle
- Follicular Cells
- Follicular Fluid
Follicular fluid forces the ovum to move to ____________ of the ____________
- the side
- follicle
Levels of ___________ and ___________ are raised during secondary follicular phase.
Only _____ follicle will mature, the rest will degenerate and undergo _________________.
- estrogen and FSH
- one
- apoptosis
Pre- ovulatory phase happen between the end of menstruation and __________; and last from day ____ to day ____
- ovulation
- 6
- 13
____ and ____ hormones from the pituitary work together to stimulate the follicles cells to produce __________.
This causes the ___________ lining from Uterus to built up, where glands develop and blood supply increases
This phase is also called _____________ in the uterus, due to the growth of the stratum ______________
- FSH and LH
- estrogen
- Endometrial
- Proliferative
- Functionalis
Also between days 6 to 13 (pre-ovulatory) is called _____________ phase, due to follicles cells producing more ___________, which becomes the ________ hormone.
- Follicular phase
- estrogen
- dominant hormone
Only ____ follicle will develop from about 20 follicles. It is going to be called _________ or _________ follicle.
During follicle developing levels of estrogen ___________.
- 1
- Grafian, or
- Vesicular follicle
- increases
FSH was the domain hormone during early pre-ovulatory phase, but now ____ is the dominant hormone close the time of _________ and is secreted in _________ concentrations
- LH
- ovulation
- High
Ovulation occurs with the rupture of the _______ follicle, and the __________ of the ovum on day ________.
- Grafian
- release
- 14
More increase of estrogen inhibits _________, therefore _________ is inhibited also.
- GnRF
- FSH
After ovulation, the Grafian follicle ___________, and becomes the Corpus ______________. where its cells enlarge and form the Corpus _____________.
- collapses
- hemorrhagicum
- Luteal
- Post-ovulatory phase is the time between _________ and ___________, and last from day ___ to _____ (in a ___ day cycle)
- Ovulation
- Mensus
- 15
- 28
- 28
LH stimulates the development of Corpus _________, which secretes _____________ and ______________.
- Luteal
- estrogen
- progesteron
- Progesteron prepares the endometrium for _____________ of a __________ ovum.
- It takes about ___ week for endometrium to be ready.
- implantation
- fertilized
- 1
FSH secretion and LH secretion ________, and now it is time for the _______ _______ to produce estrogen and ____________
- decrease
- Corpus Luteal
- Progesteron
If fertilization and implantation DO NOT occur, then the rising levels of estrogen and progesteron from the corpus luteum ________ GnRF and LH.
Corpus Luteum degenerates to become the corpus ________ and estrogen and progesteron levels ________
- Inhibit
- albicans
- decrease
What HCG stands for.
HCG is a hormone developed by the __________
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
- Placenta
If fertilization and implantation DO NOT occur, then the Corpus Luteal is __________ for ___-____ weeks (for ______ and ________ hormones production).
HCG will be the one producing _________ and ________ hormones in greater amounts than Corpus Luteal.
- maintain
- 8 to 10 weeks
- estrogen
- progesterone
- estrogen
- progesterone
Pregnancy is supported by __________ hormone.
Progesterone also supports __________ and _______ development after pregnancy.
- estrogen
- pregnancy
- breast
The first menstruation is called _________
Menarch
The last menstruation is called _________
Menopause
When menstrual cycles become less frequent is called
Climacteric
- Climacteric occurs when women are around ____ to ____ years old.
- It happens because ______ fail to respond to GnRF hormones, causing secondary effects physiological like : ______, _____, _________ _______, etc.
- 40 to 50
- ovaries
- Hotflashes
- sweating
- emotional instability
________ __________ is a method used to prevent the union of a sperm with a mature ovum
Birth Control