Choose the molecule or compound that exhibits dipole-dipole forces as its strongest intermolecular force.
SO2
H2
CF4
BCl3
NH3
SO2
Choose the pair of substances that are most likely to form a homogeneous solution.
LiF and C6H14
C3H8 and C2H5OH
Br2 and PF3
NH3 and CH3OH
NaCl and Hg
NH3 and CH3OH
Choose the substance with the highest boiling point.
CS2
HF
I2
KI
CH4
KI
Choose the substance with the lowest surface tension.
CH3CH2CH2CH3
H2O
C6H6
(CH3)2CO
CH3SH
CH3CH2CH2CH3
Choose the substance with the lowest vapor pressure at a given temperature.
He
BF3
BeCl2
CO2
PF5
BeCl2
Choose the substance with the lowest viscosity.
Cl2CHCH2Cl
Cl3CCCl3
Cl3CCHCl2
ClCH2CH2Cl
Cl2CHCHCl2
ClCH2CH2Cl
Give the change in condition to go from a liquid to a gas.
Cool or reduce pressure
Increase heat or reduce pressure
Cool or increase pressure
Increase heat or increase pressure
None of the above
Increase heat or reduce pressure
Give the characteristic of a first order reaction having only one reactant.
The rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactant.
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the natural logarithm of the concentration of the reactant.
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the square root of the concentration of the reactant.
The rate of the reaction is not proportional to the concentration of the reactant.
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the square of the concentration of the reactant.
The rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactant.
Give the term for the temperature at which the gas and liquid phases form a supercritical fluid.
Definite temperature.
Absolute temperature.
Critical temperature.
Fluid temperature.
Solid temperature
Critical temperature.
Given the following balanced equation, determine the rate of reaction
with respect to [NOCl]. If the rate of Cl2 loss is 4.84 ×
10-2 M/s, what is the rate of formation of NOCl?
2
NO(g) + Cl2(g) → 2 NOCl(g)
Answers:
4.84 × 10-2 M/s
1.61 × 10-2 M/s
1.45 × 10-1 M/s
9.68 × 10-2 M/s
2.42 × 10-2 M/s
9.68 × 10-2 M/s
Given the following rate law, how does the rate of reaction change if
the concentration of X is halved and the concentration of Y is
doubled?
Rate = k [X][Y]2
Answers:
The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 5.
The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 2.
The rate of reaction will decrease by a factor of 2.
The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 4.
The rate of reaction will remain unchanged.
The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 2.
How many half-lives are required for the concentration of reactant to decrease to 12.5% of its original value?
2
1.75
3
2.75
1
3
How much energy is required to vaporize 48.7 g of dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) at its boiling point, if its ΔHvap is 31.6 kJ/mol?
18.1 kJ
55.1 kJ
31.2 kJ
15.4 kJ
6.49 kJ
18.1 kJ
Place the following compounds in order of
decreasing
strength of intermolecular forces.
HF O2 CO2
Answers:
HF > O2 > CO2
O2 > CO2 > HF
CO2 > HF > O2
HF > CO2 > O2
CO2 > O2 > HF
HF > CO2 > O2
Place the following compounds in order of
increasing
strength of intermolecular forces.
CO2 F2 NH2CH3
Answers:
NH2CH3 < F2 < CO2
NH2CH3 < CO2 < F2
F2 < CO2 < NH2CH3
CO2 < NH2CH3 < F2
F2 < NH2CH3 < CO2
F2 < CO2 < NH2CH3
What are the units of k in a first order reaction?
1/s
What are the units of k in the following rate law?
Rate = k[X][Y]
M-1s-1
What data should be plotted to show that experimental concentration data fits a second-order reaction?
1/[reactant] vs. time
ln[reactant] vs. time
ln(k) vs. Ea
ln(k) vs. 1/T
[reactant] vs. time
1/[reactant] vs. time
What is the overall order of the following reaction, given the rate
law?
2 X + 3 Y → 2 Z Rate = k[X]1[Y]2
Answers:
1st order
0th order
2nd order
5th order
3rd order
3rd order
What is the overall order of the following reaction, given the rate
law?
2NO(g) + H2(g) → N2(g) +
2H2O(g) Rate = k[NO]2[H2]
Answers:
0th order
3rd order
4th order
2nd order
1st order
3rd order
What is the strongest type of intermolecular force present in CHF3?
hydrogen bonding
ion-dipole
dipole-dipole
dispersion
None of the above
dipole-dipole
What is the strongest type of intermolecular force present in H2?
dispersion
hydrogen bonding
ion-dipole
dipole-dipole
None of the above
dispersion
What is the strongest type of intermolecular force present in NH2CH3?
dipole-dipole
ion-dipole
dispersion
hydrogen bonding
None of the above
hydrogen bonding
represents the equation for a first-order half-life?
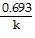
t 1/2 =
represents the integrated rate law for a first-order reaction?
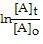
= -kt
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
Until a certain point, the potential energy of molecules decrease as they get closer to one another.
Intermolecular forces are generally stronger than bonding forces.
Increasing the pressure on a solid usually causes it to become a liquid.
Energy is given off when the attraction between two molecules is broken.
None of the above are true.
Until a certain point, the potential energy of molecules decrease as they get closer to one another.
Which substance below has the strongest intermolecular forces?
C3X2, ΔHvap= 36.4 kJ/mol
DX2, ΔHvap= 23.3 kJ/mol
BY2, ΔHvap= 26.7 kJ/mol
A2X, ΔHvap= 39.6 kJ/mol
EY3, ΔHvap= 21.5 kJ/mol
A2X, ΔHvap= 39.6 kJ/mol