
Chapter 17-Deuterostomes
What is this species Phylum and SubPhylum? What is this species called?
Phylum Chordata
SubPhylum Cephalochordata
Lancelet

Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
Find:
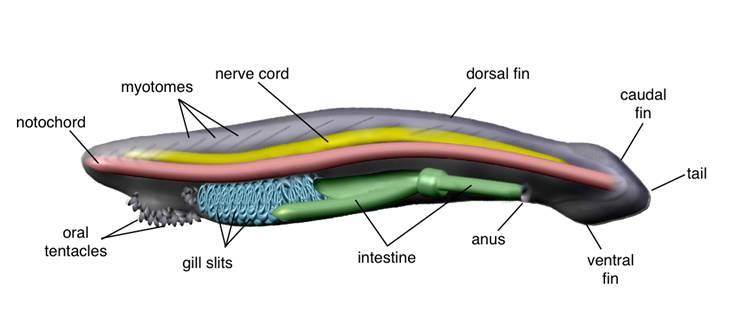
The mouth
The tentacles
The Notochord
The Dorsal Fin
The Pharynx Gills
The Nerve Cord
The Myomeres
The Intestine
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
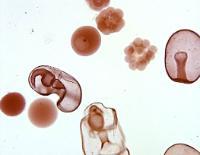
Find these stages in Starfish Development:
Unfertilized Egg
Fertilized Envelope
Four Cell Staged Embryo
Blastula
Gastrula
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
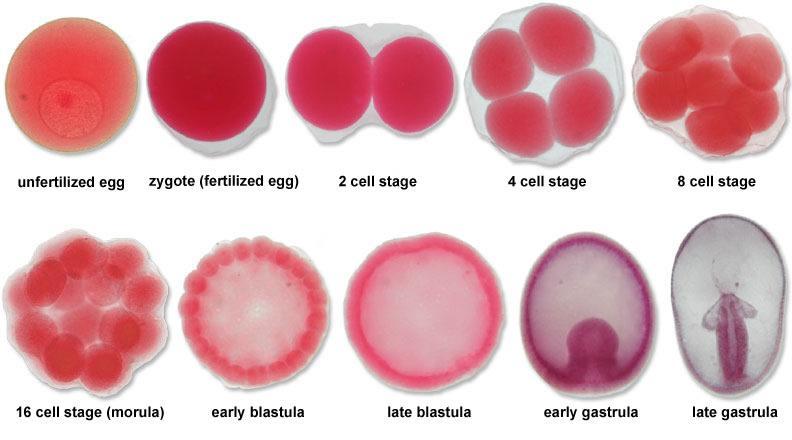
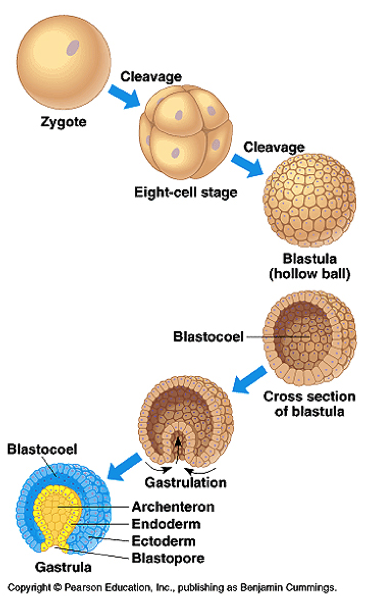
Identify Blastomere and Blastocoel
Know the stages to Gastrulation
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
What is the difference between early and late blastulas?
Early blastulas are bundles of cells, later blastulas are divided and have smaller more abundant cells.
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
Bipinnaria Larva (Starfish) display what type of Symmetry?
Bilateral
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
What are the benefits of the holes in the urchin shell?
Tube feet are within allowing for movement and stabilization.
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
How are tube feet effective?
There are multiple amounts of them that work together to form a strong suction.
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
What organisms are Echinodermata?
Asteroidea (Starfish)
Ophiuroidea (Brittle Stars)
Crinoidea (Feather Stars, Sea Lilies)
Echinoidea (Sea Urchins and Sand Dollars)
Holothuroid (Sea Cucumbers)
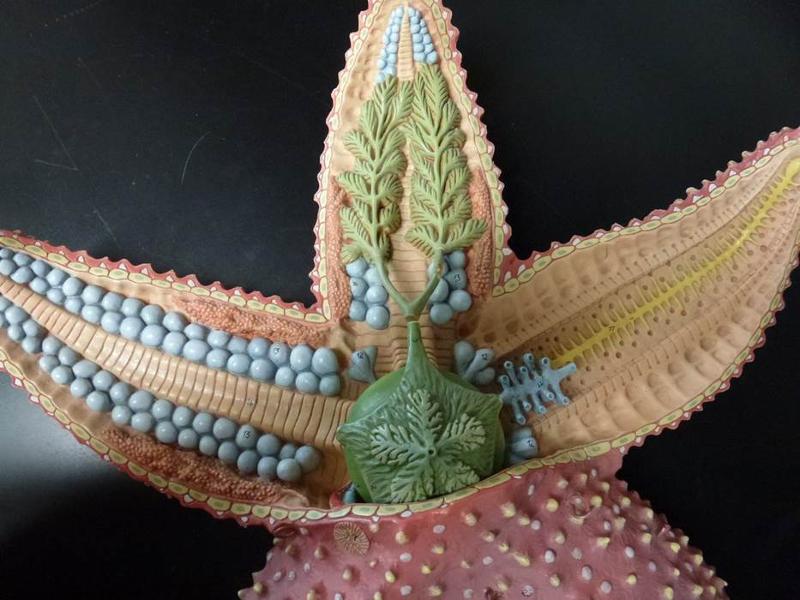

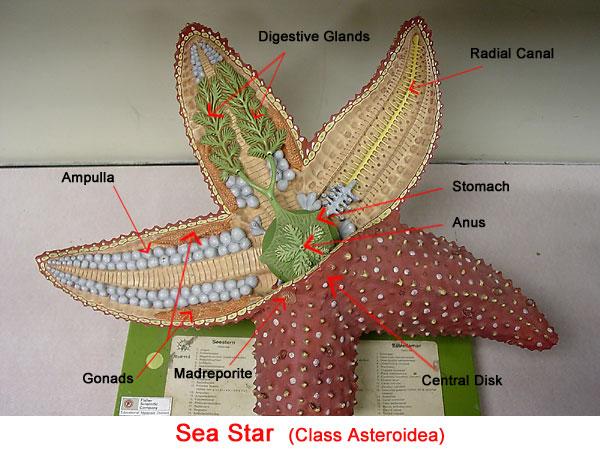
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
Identify the Mouth, Tube feet, Ampulla, Madreporite, Radial Nerve, and Neural Ring
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
What is this an image of?
Tunicate Larva
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
What is the pathway for a Tunicate to filter water?
Incurrent Siphon
Atrium
Stomach
Intestine
Excurrent Siphon
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
What appendages of a perch is similar to other organisms?
Pectoral Fins
Pelvic Fins
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
What are the three subphyla of Chordata?
Urochordata (Tunicates)
Cephalochordata (Lancelets)
Vertebrata (Frogs, Perch, Seahorse, other Fish)
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
All Chordates have?
a notochord
pharyngeal gill slits
a dorsal hollow nerve cord
a post-anal tail
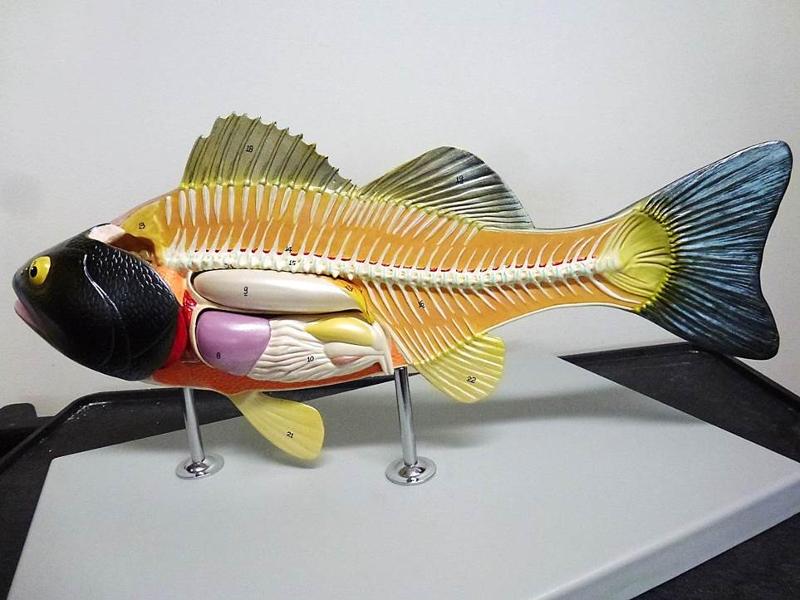

Identify Kidney, Gill Filaments, Heat, Liver, Stomach, Intestine, Swim Bladder, Gonad, Vent
Identify Anterior Fin, Posterior Dorsal Fin, Anal Fin, Pectoral Fin, Pelvic Fin
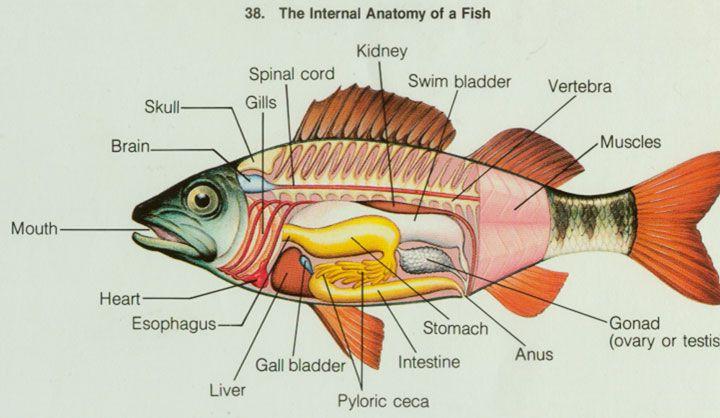
Chapter 17- Deuterostomes
A perch brain is made up of what?
Olfactory Bulb
Olfactory Lobe
Cerebrum
Optic Lobe
Cerebellum
Medulla
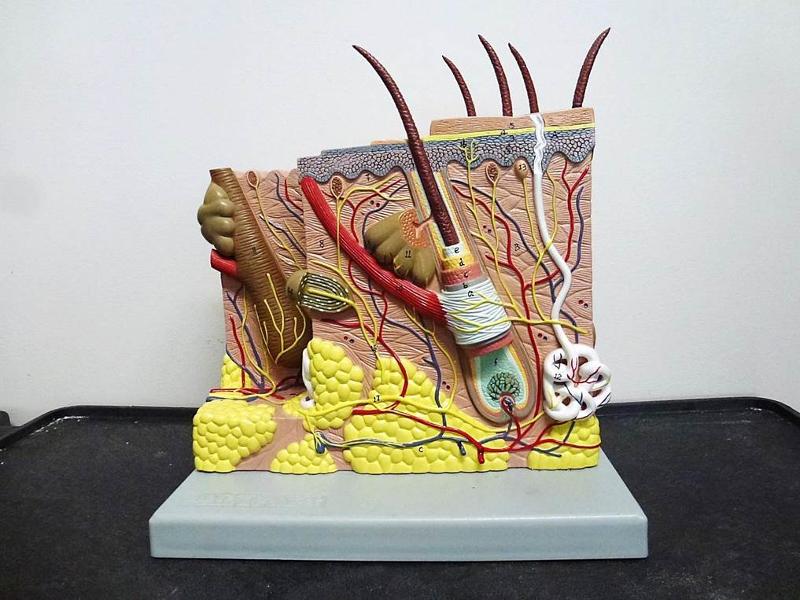

Chapter 18- Histology
Identify Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis, Hair Follicles, Sebaceous Glands, sweat glands, sweat glands, and adipose tissue
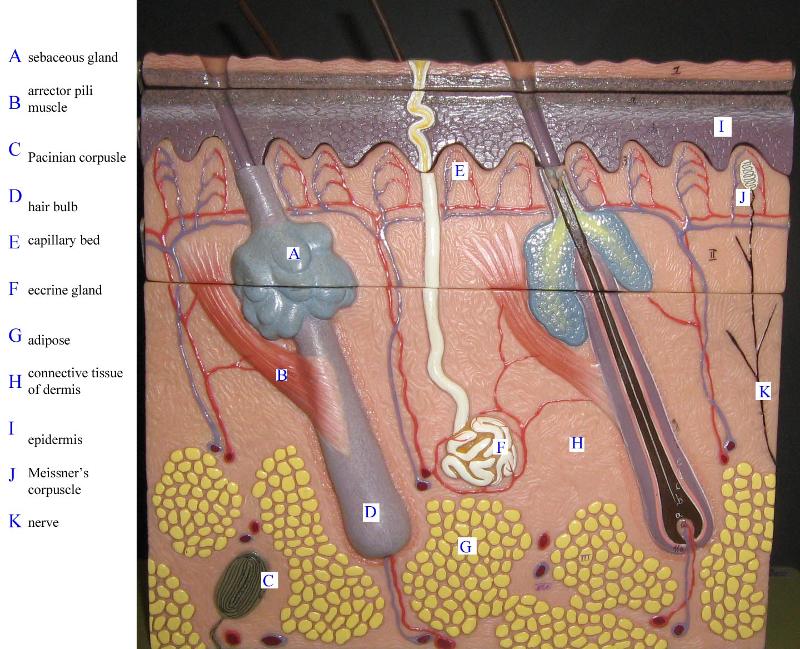
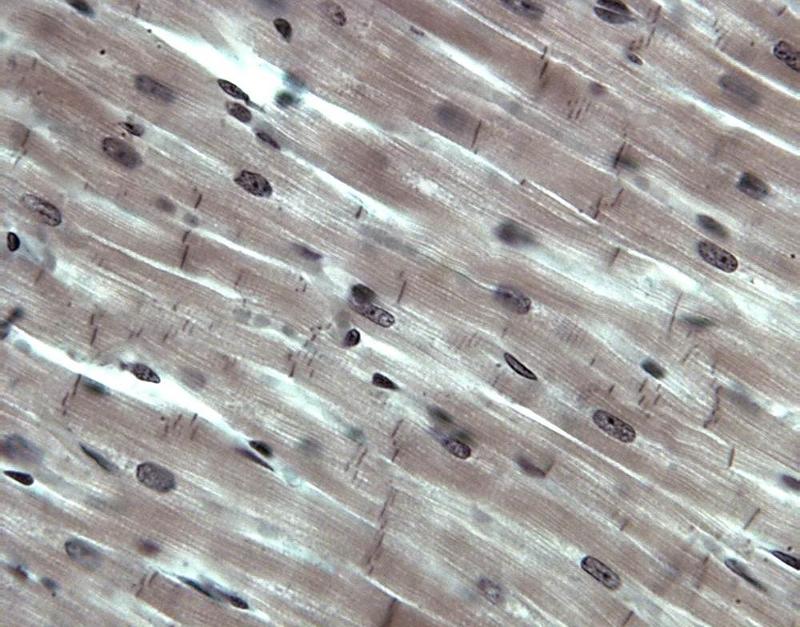
Chapter 18- Histology
What is this cell?
Cardiac Muscle
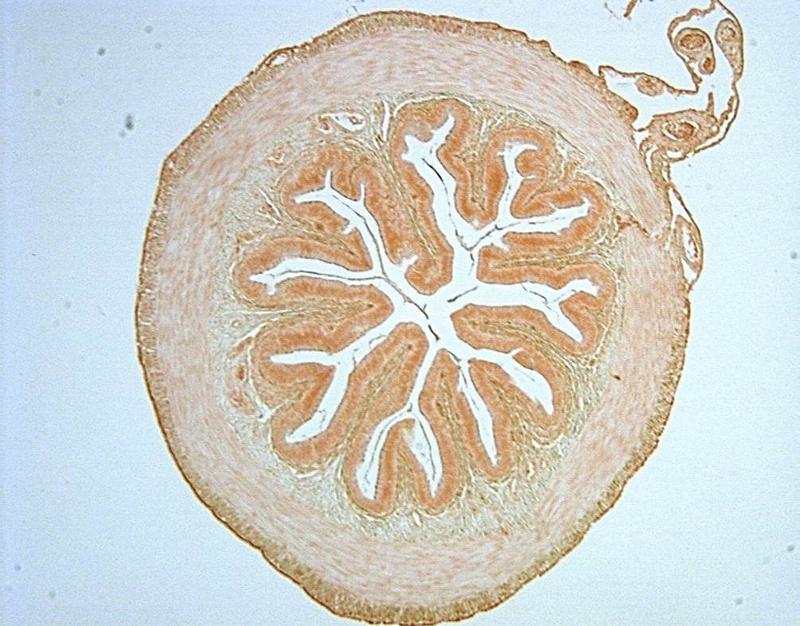
Chapter 18- Histology
This is an image of? What layer of muscle covers it?
Frog Intestine
Smooth Muscle
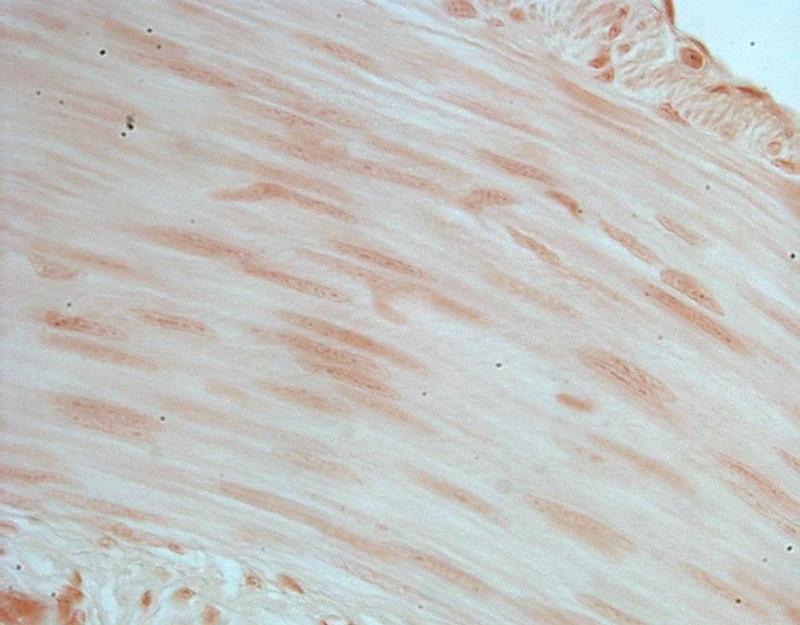
Chapter 18- Histology
What is this cell?
Smooth Muscle
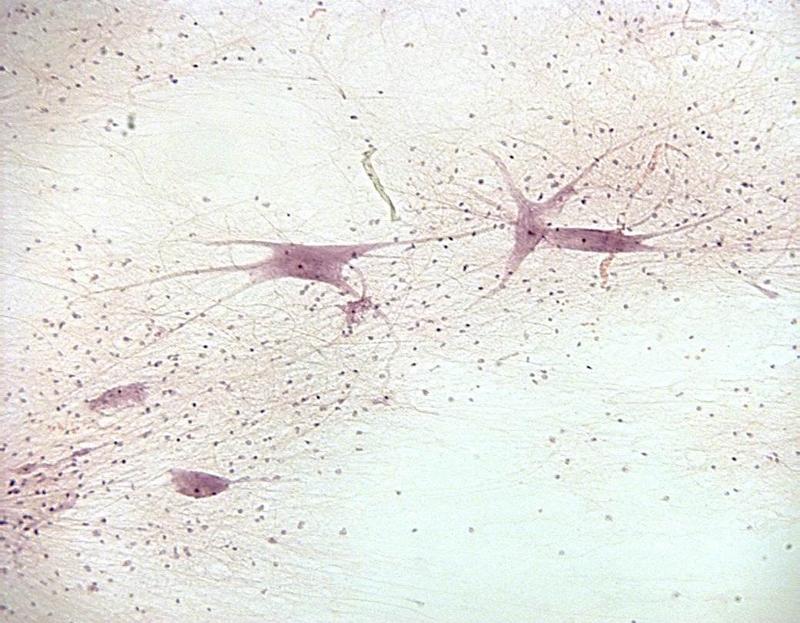
Chapter 18- Histology
What is this cell? What makes up these cells?
Nervous Tissue
Neurons (nucleus, cell body, axons, dendrites) & Gila
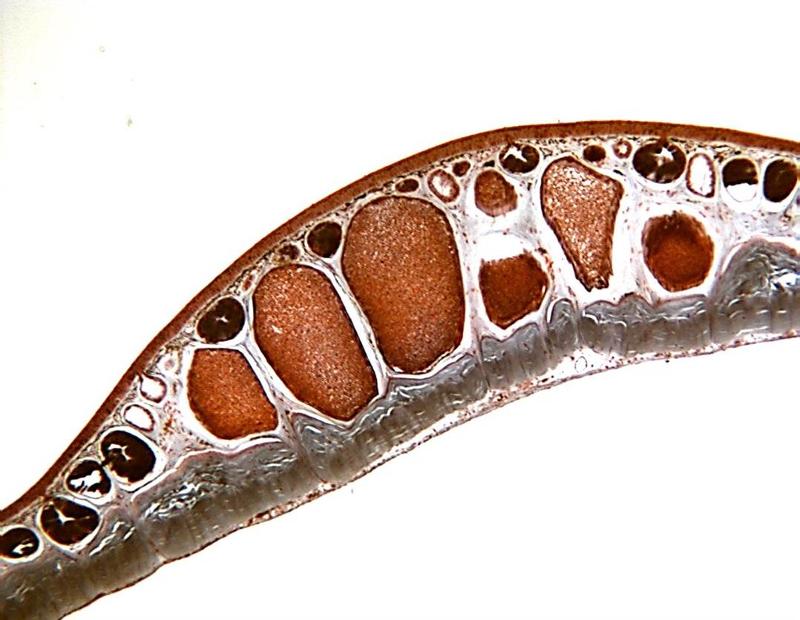
Chapter 18- Histology
Identify these parts of frog skin: Epidermis (Stratified Squamous Epithelium), Dermis, Chromatophores, Mucous Glands, poisons glands
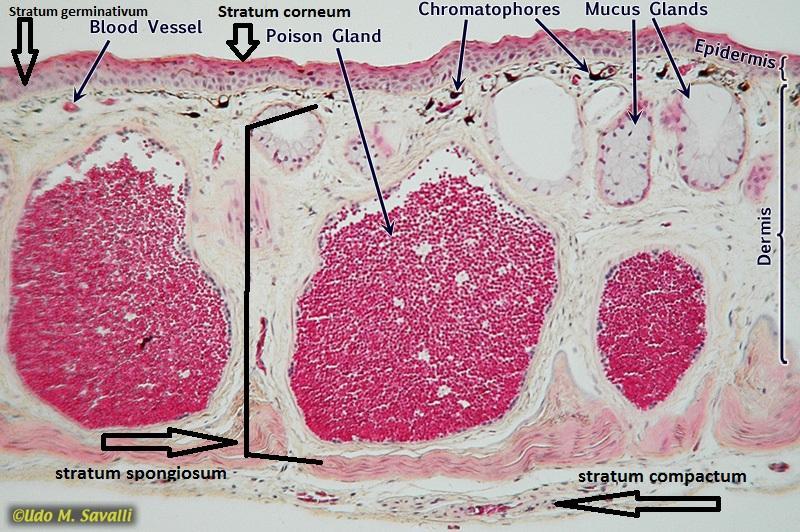
Chapter 18- Histology
What cell is this?
Human Skin
Chapter 18- Histology
What cell is this?
Skeletal Muscle
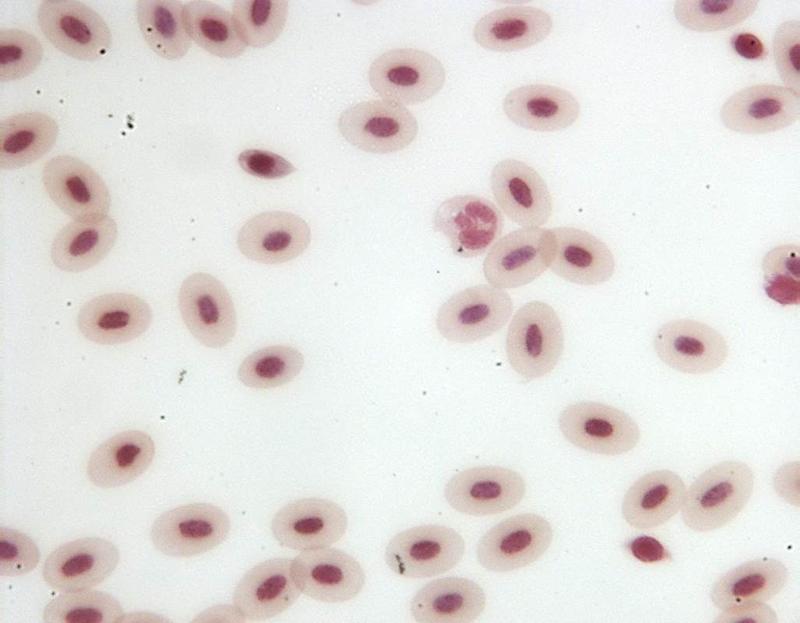
Chapter 18- Histology
What is this cell?
Frog Leukocytes

Chapter 18- Histology
What cells are these?
Human Blood Cells
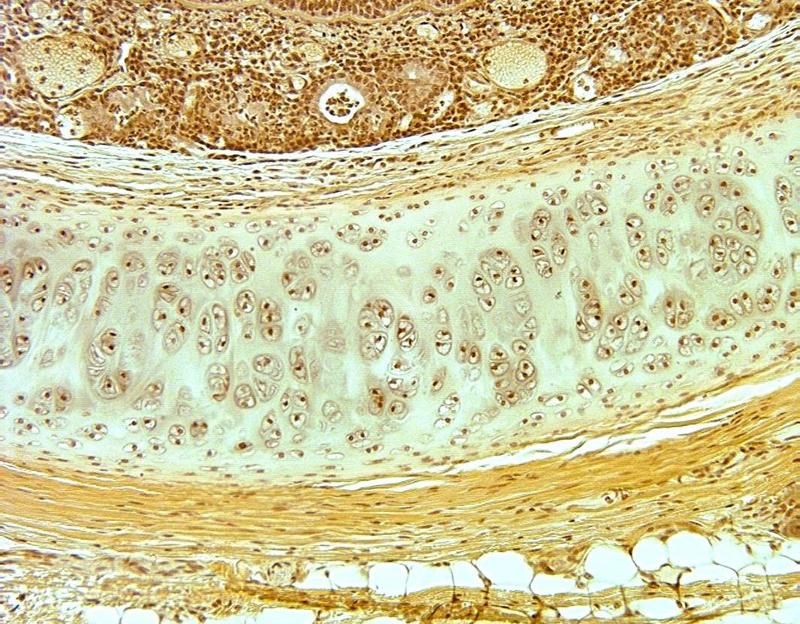
Chapter 18- Histology
What is this an image of?
Cartilage
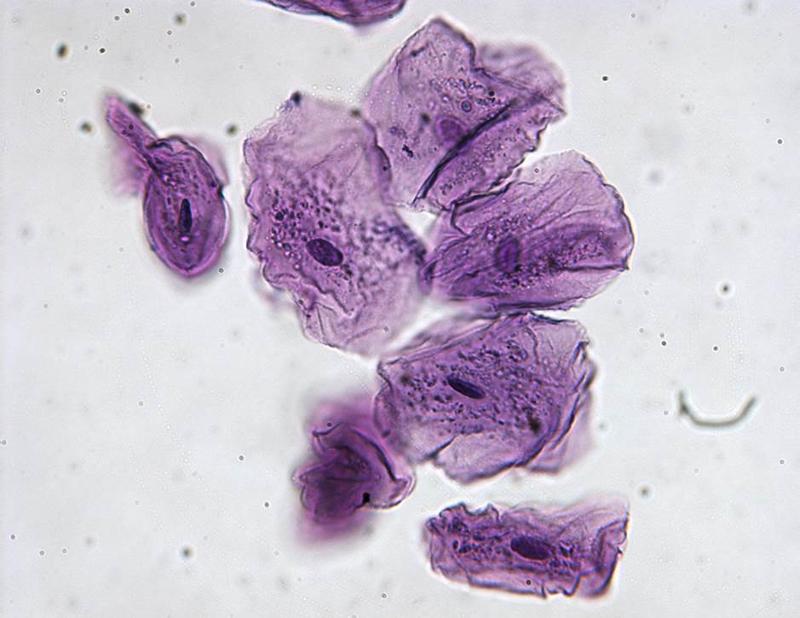
Chapter 18- Histology
What are these cells?
Human Cheek Cells
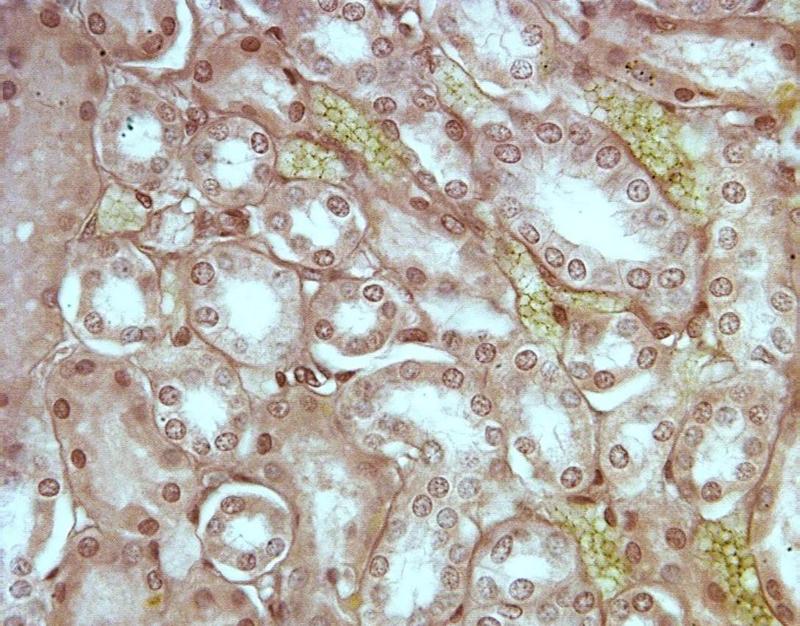
Chapter 18- Histology
What is this an image of? Identify Lumen, Columnar Epithelial tissue, nucleus.
Frog Kidney
Center= Lumen
Outer tissue= Columnar Epithelial
Dots= Nucleus
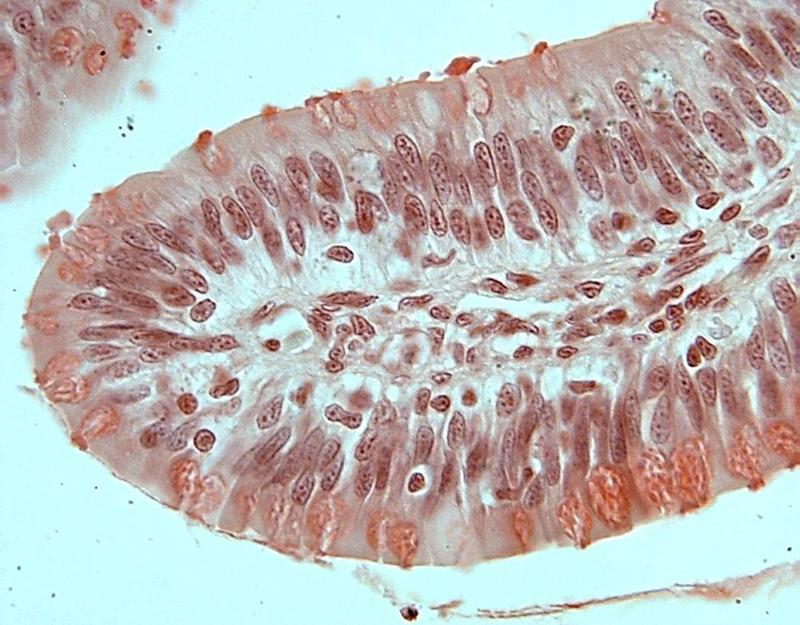
Chapter 18- Histology
What is this an image of?
Frog Intestine
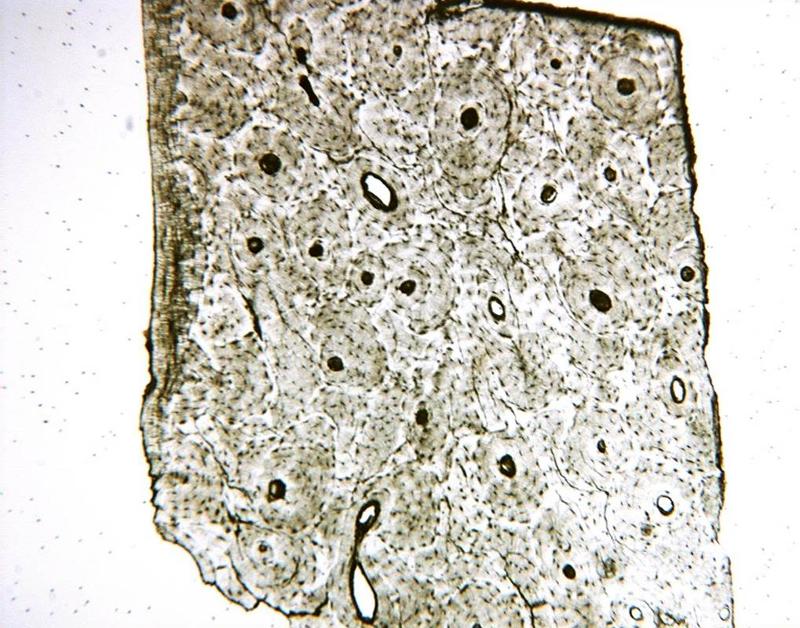
Chapter 18- Histology
What cell is this? Identify the Haversian Canal, lacunae, matrix, canaliculi
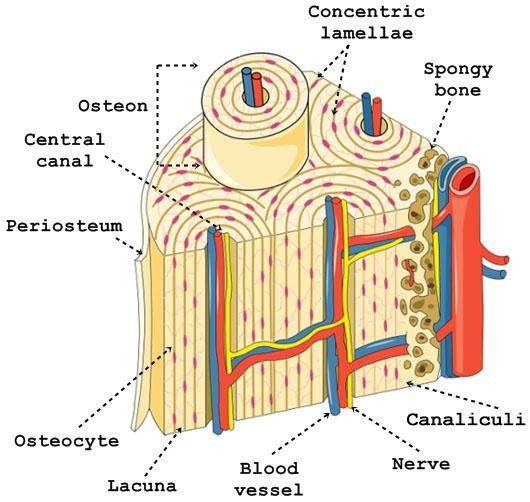
Bone
Chapter 18- Histology
Checks Cells are?
Stratified Squamous
Chapter 18- Histology
Types of Cells?
Simple Squamous
Simple Cuboidal
Simple Columnar
Stratified Squamous (Keratinized or not)
Chapter 18- Histology
What are red blood cells called?
What are bone cells called?
Erythrocytes
Chondrocytes
Chapter 18- Histology
What determines a frogs green color?
Chromatophores
Chapter 19- Anatomy of a Frog
Be able to Identify: Cloacal Aperture, External nares, Tympanic membrane
Cloacal Aperture- Butt Hole
External nares- nose
Tympanic membrane- side of head
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
What is special about frog skin?
It is used as a respiratory surface
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
What hole is located directly behind the tongue of a frog?
Glottis
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
What muscles are used?
Flexion of leg at knee?
Extension of leg at knee?
Flexion of foot at ankle?
Extension of foot at ankle?
Legs coming together?
Semimembranosus, Gracilis minor
Triceps Femoris
Peroneus
Gastrocnemius
Sartorius, Adductors, Gracilis Major
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
Describe how Frogs breathe?
Through skin
Start through nostrils, Buccal Cavity Expands, Nostrils close, Buccal Cavity (Contracts), Glottis opens, lungs expand, Glottis closes, oxygen distributed
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
What is the endoskeleton divided into?
Axial skeleton, and appendicular skeleton
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
Flexors:
Extensors:
Adductors:
Abductors:
Bend
Straighten
Toward Midline
Away from Midline
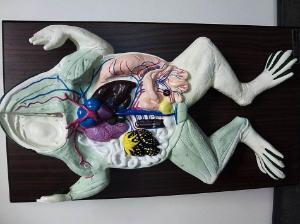
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
Be able to identify: Fat Bodies, Eggs or Testis, Intestine, Oviduct& Uterus if (Female), Cloaca, Kidney, Bladder, Lungs, Liver, Heart, Stomach, Small intestine, Spleen, Pancreas, Esophahus
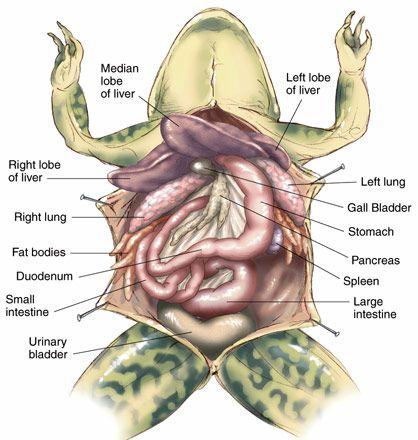
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
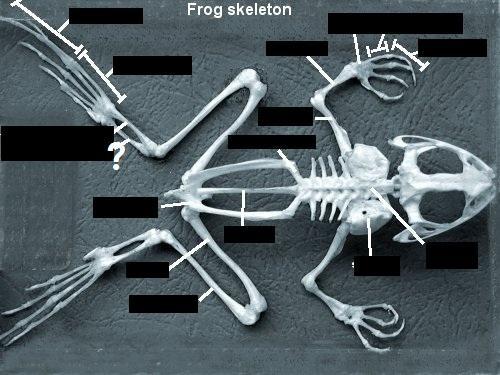
Identify the Bones
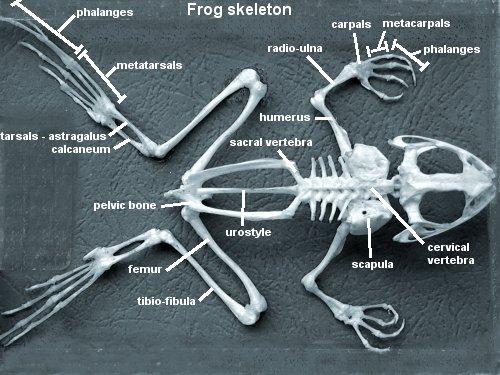
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
Study This and know it.
...
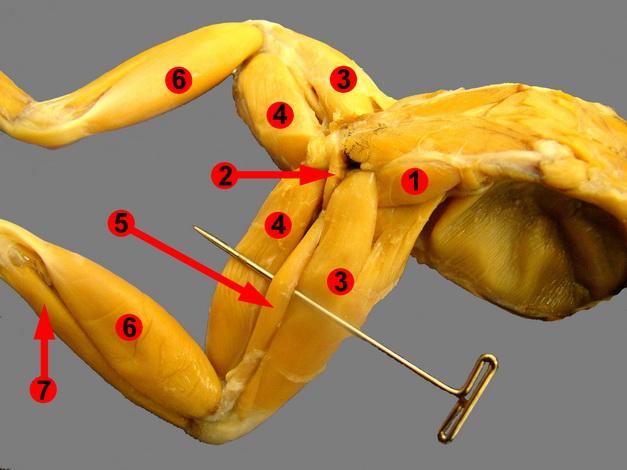
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
Know these muscles (NOT 1,2,5)
3.Tricep Femoris
4. Semimembranosus
6.Gastrocnemius
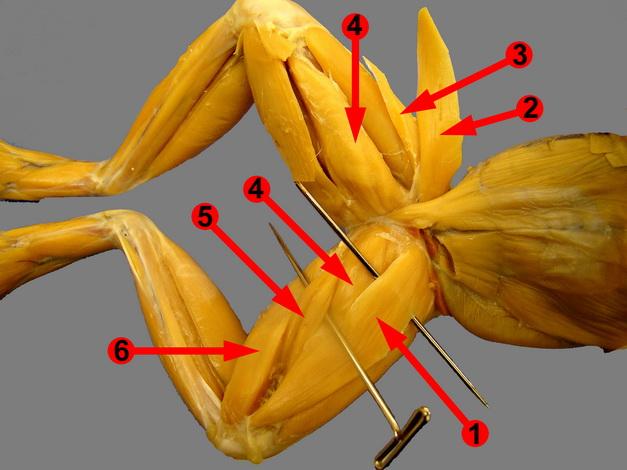
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
Know these muscles (NOT 2,3)
1. Sartorius
4. Adductors
5. Gracilis Major
6. Gracilis Minor
Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
Circulatory System is divided into what?
Pulmonary Circuit (Out of Heart)
Systemic Circuit (In the Heart)

Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog
Know parts of Frog Heart
...
Chapter 20- Ecology
Levels of Consumers?
Quaternary (Humans)
Tertiary (Carnivores)
Secondary (Carnivores)
Primary (Herbivores)
Decomposers (Bacterias, and Fungi) (Omnivores)
Producers (Photosynthetic Plants, Algae, Bacteria)
Chapter 20- Ecology
Abiotic Factors
Biotic Factors
Light, Temperature, Oxygen Level, Precipitation, Soil
Producers, Consumers, Decomposers
Chapter 20- Ecology
Define these:
Benthic zone
Pelagic Zone
Littoral Zone
Limnetic Zone
Profundal Zone
Bottom of a lake
Open Water
Shallow region along a shore(Photic)
Layer of water where light penetrates (Photic)
Water where light doesn't Penetrate (Aphotic)
Chapter 20- Ecology
Species Diversity
Species Richness
Relative Abundence
Species in that community
Number of species in the community
Number of individuals of a specific species
Chapter 20 -Ecology
Simpsons Dominance index
Add up all proportions and square each
Chapter 20- Ecology
Simpsons Diversity Index
1- Simpson dominance index