Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biol 112 Lab Exam 3 (17,18,19,20)
front 1  Chapter 17-Deuterostomes What is this species Phylum and SubPhylum? What is this species called? | back 1 Phylum Chordata SubPhylum Cephalochordata Lancelet |
front 2  Chapter 17- Deuterostomes Find: The mouth The tentacles The Notochord The Dorsal Fin The Pharynx Gills The Nerve Cord The Myomeres The Intestine | back 2 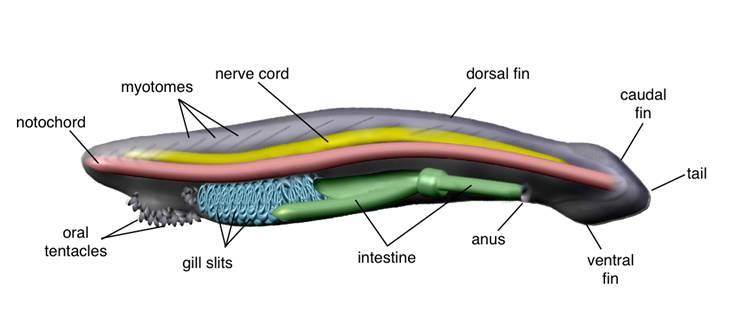 |
front 3 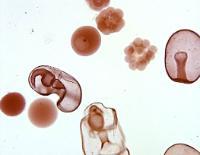 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes Find these stages in Starfish Development: Unfertilized Egg Fertilized Envelope Four Cell Staged Embryo Blastula Gastrula | back 3 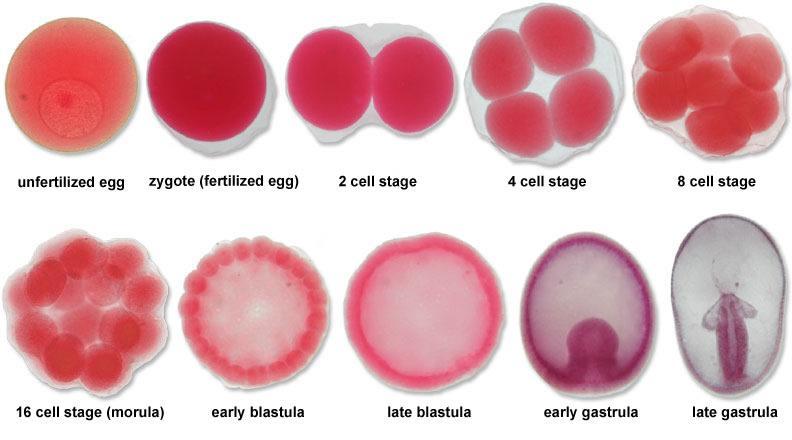 |
front 4 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes Identify Blastomere and Blastocoel Know the stages to Gastrulation | back 4 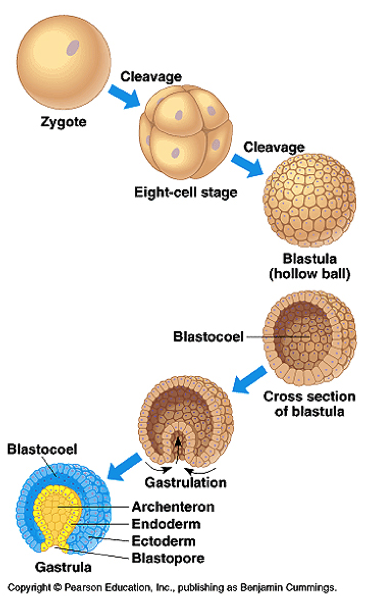 |
front 5 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes What is the difference between early and late blastulas? | back 5 Early blastulas are bundles of cells, later blastulas are divided and have smaller more abundant cells. |
front 6 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes Bipinnaria Larva (Starfish) display what type of Symmetry? | back 6 Bilateral |
front 7 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes What are the benefits of the holes in the urchin shell? | back 7 Tube feet are within allowing for movement and stabilization. |
front 8 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes How are tube feet effective? | back 8 There are multiple amounts of them that work together to form a strong suction. |
front 9 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes What organisms are Echinodermata? | back 9 Asteroidea (Starfish) Ophiuroidea (Brittle Stars) Crinoidea (Feather Stars, Sea Lilies) Echinoidea (Sea Urchins and Sand Dollars) Holothuroid (Sea Cucumbers) |
front 10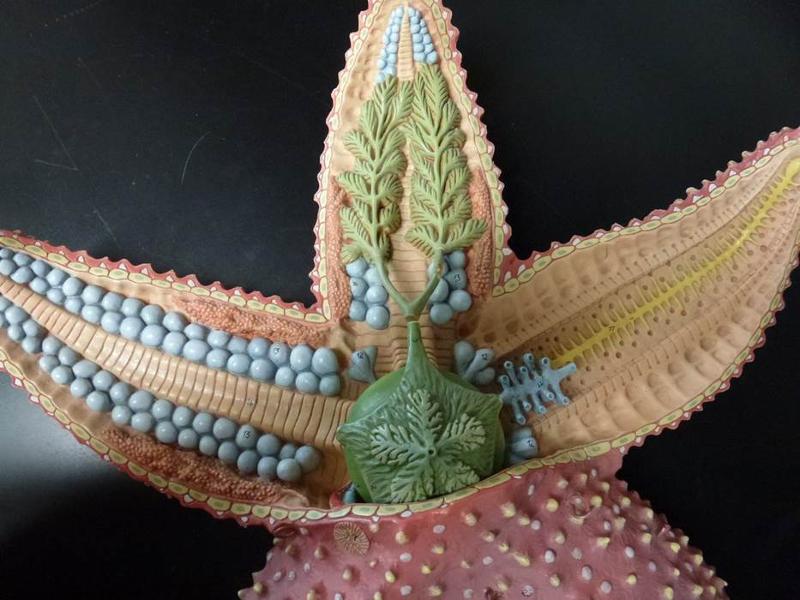  Chapter 17- Deuterostomes Identify the Mouth, Tube feet, Ampulla, Madreporite, Radial Nerve, and Neural Ring | back 10 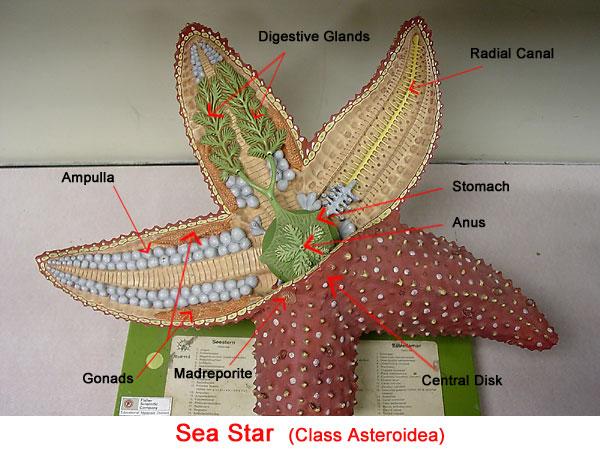 |
front 11 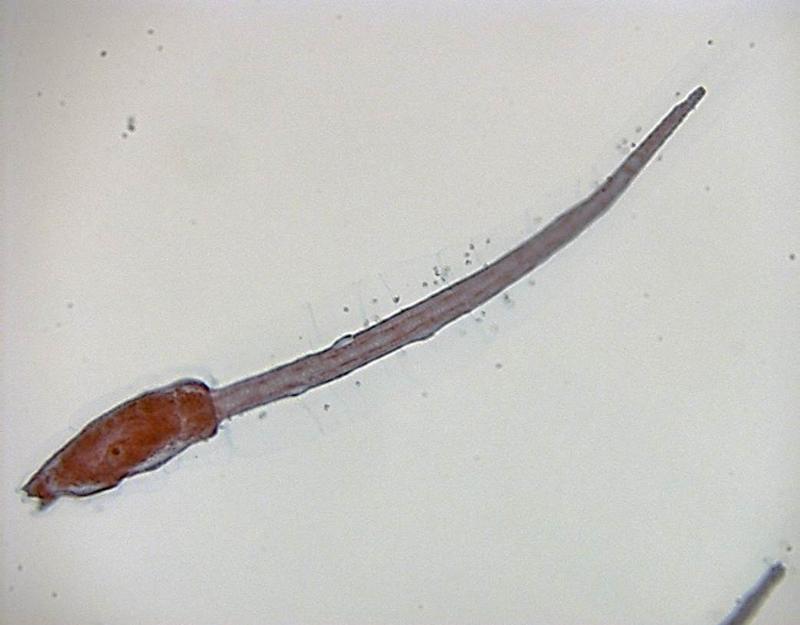 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes What is this an image of? | back 11 Tunicate Larva |
front 12 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes What is the pathway for a Tunicate to filter water? | back 12 Incurrent Siphon Atrium Stomach Intestine Excurrent Siphon |
front 13 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes What appendages of a perch is similar to other organisms? | back 13 Pectoral Fins Pelvic Fins |
front 14 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes What are the three subphyla of Chordata? | back 14 Urochordata (Tunicates) Cephalochordata (Lancelets) Vertebrata (Frogs, Perch, Seahorse, other Fish) |
front 15 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes All Chordates have? | back 15 a notochord pharyngeal gill slits a dorsal hollow nerve cord a post-anal tail |
front 16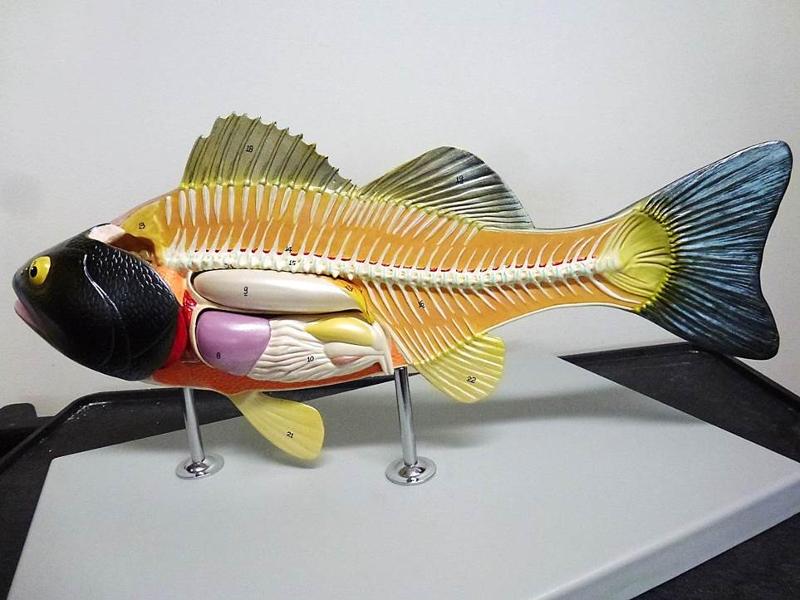  Identify Kidney, Gill Filaments, Heat, Liver, Stomach, Intestine, Swim Bladder, Gonad, Vent Identify Anterior Fin, Posterior Dorsal Fin, Anal Fin, Pectoral Fin, Pelvic Fin | back 16 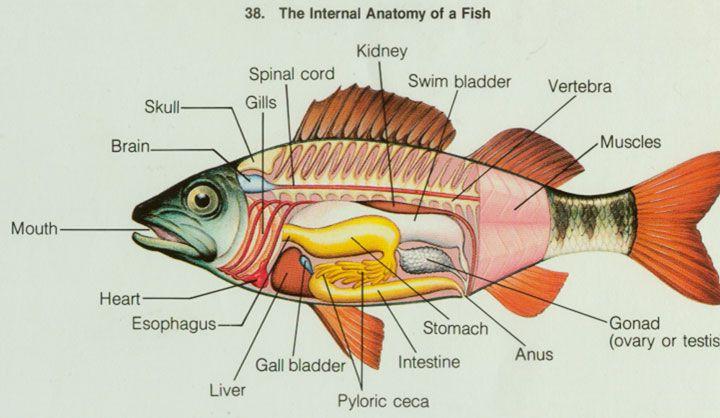 |
front 17 Chapter 17- Deuterostomes A perch brain is made up of what? | back 17 Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Lobe Cerebrum Optic Lobe Cerebellum Medulla |
front 18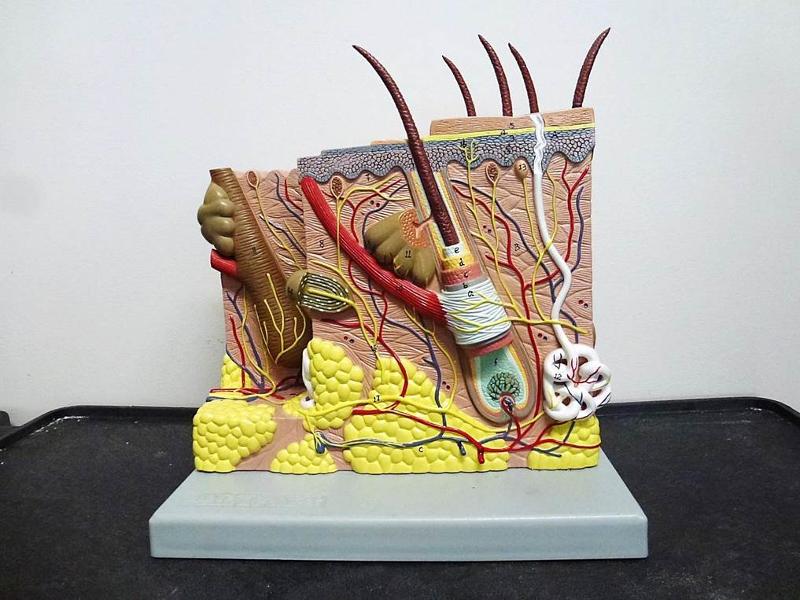  Chapter 18- Histology Identify Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis, Hair Follicles, Sebaceous Glands, sweat glands, sweat glands, and adipose tissue | back 18 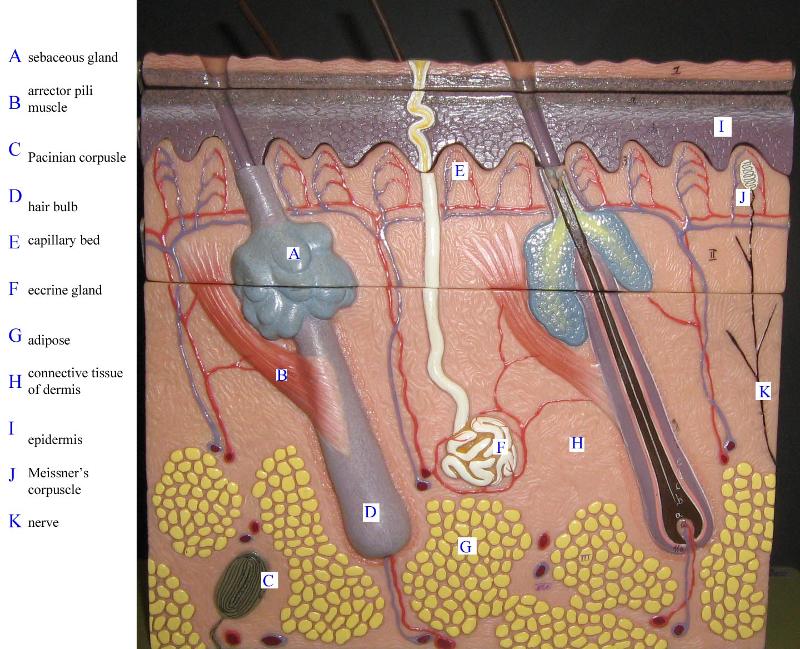 |
front 19 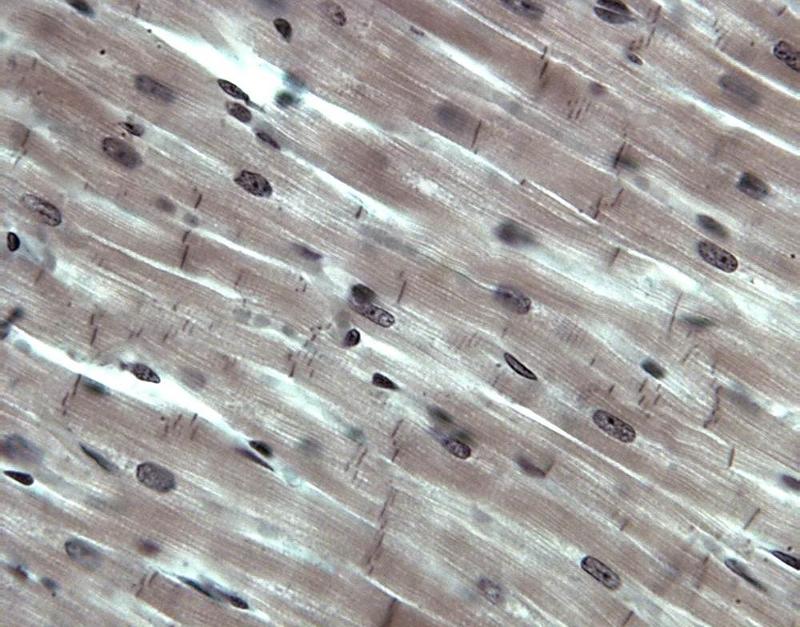 Chapter 18- Histology What is this cell? | back 19 Cardiac Muscle |
front 20 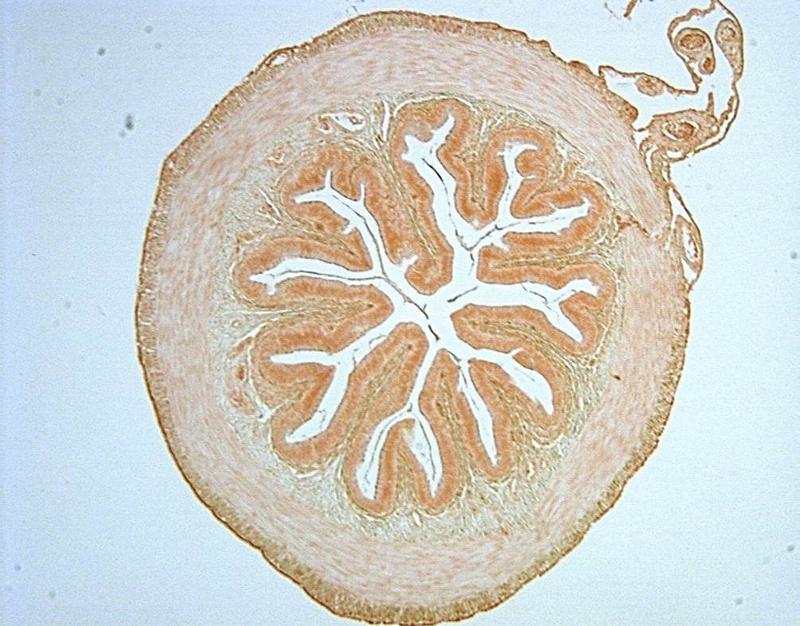 Chapter 18- Histology This is an image of? What layer of muscle covers it? | back 20 Frog Intestine Smooth Muscle |
front 21 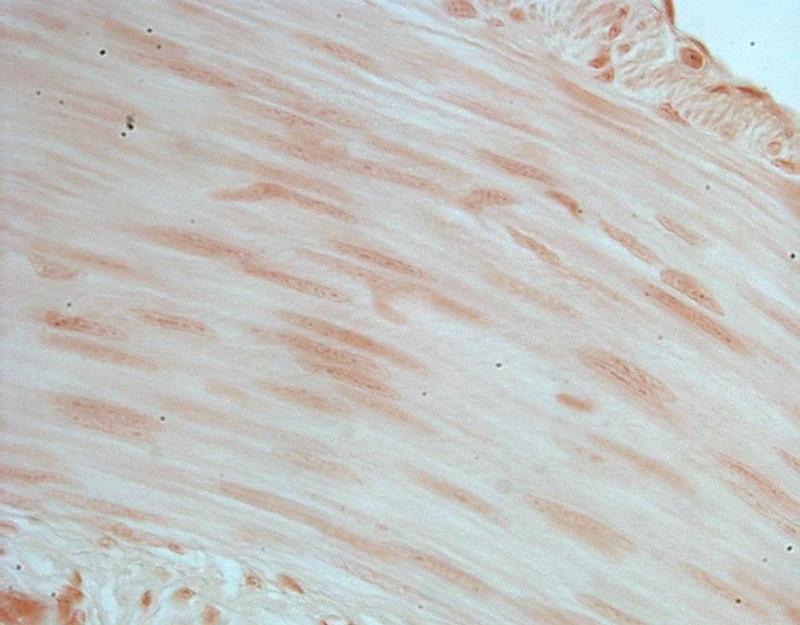 Chapter 18- Histology What is this cell? | back 21 Smooth Muscle |
front 22 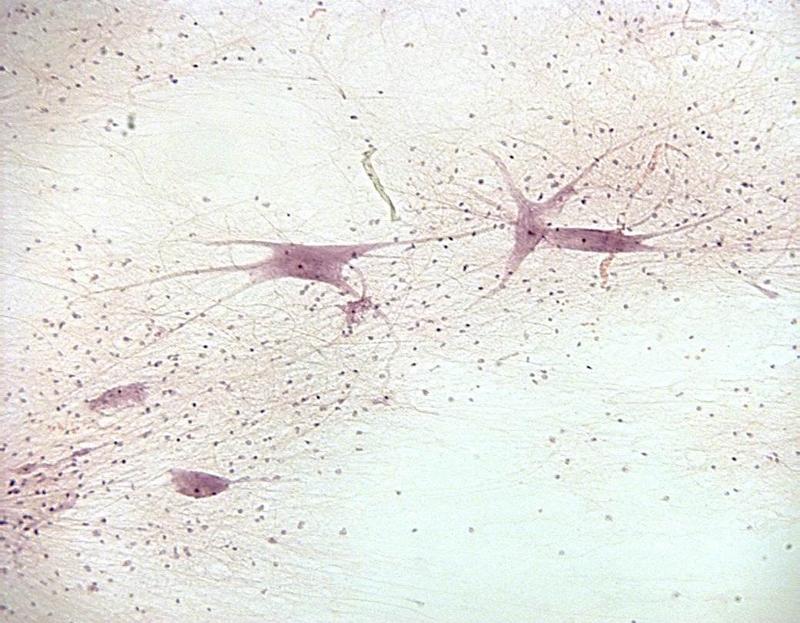 Chapter 18- Histology What is this cell? What makes up these cells? | back 22 Nervous Tissue Neurons (nucleus, cell body, axons, dendrites) & Gila |
front 23 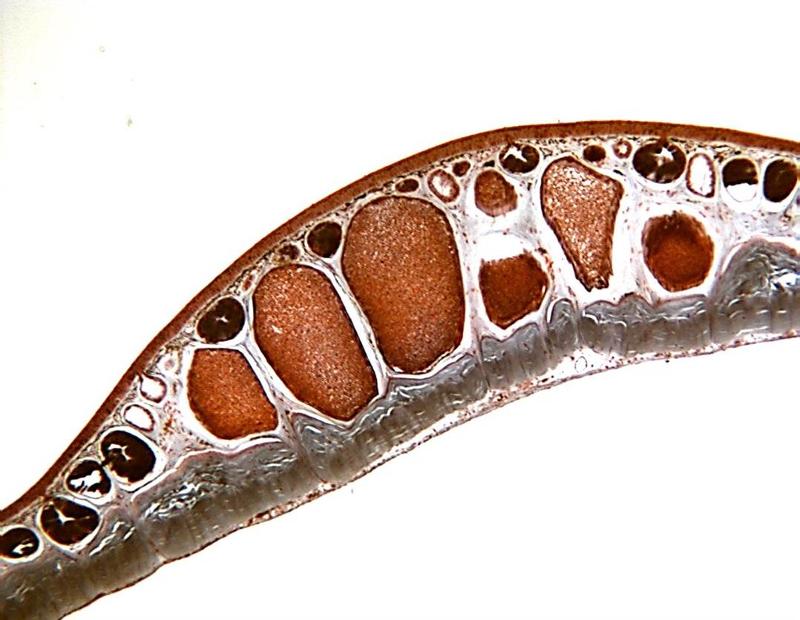 Chapter 18- Histology Identify these parts of frog skin: Epidermis (Stratified Squamous Epithelium), Dermis, Chromatophores, Mucous Glands, poisons glands | back 23 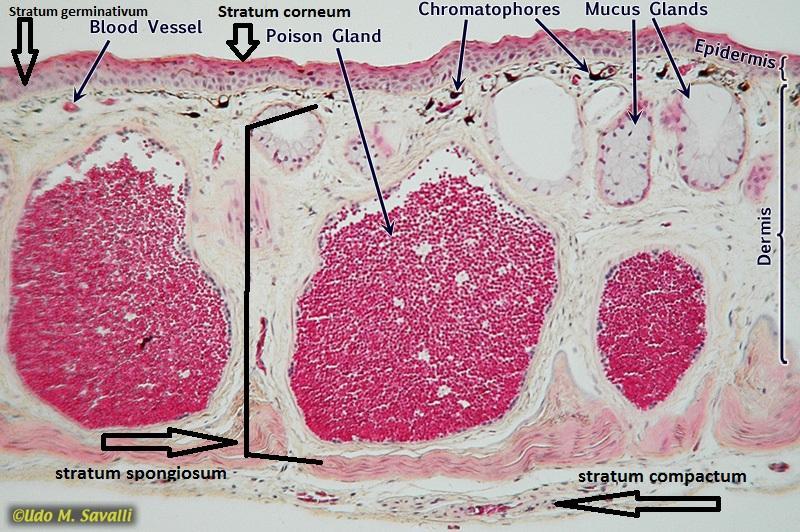 |
front 24 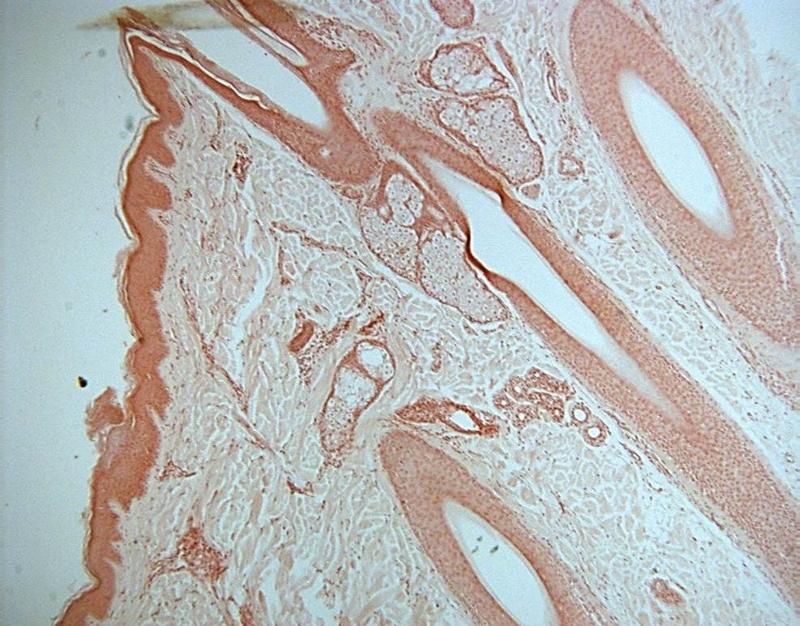 Chapter 18- Histology What cell is this? | back 24 Human Skin |
front 25 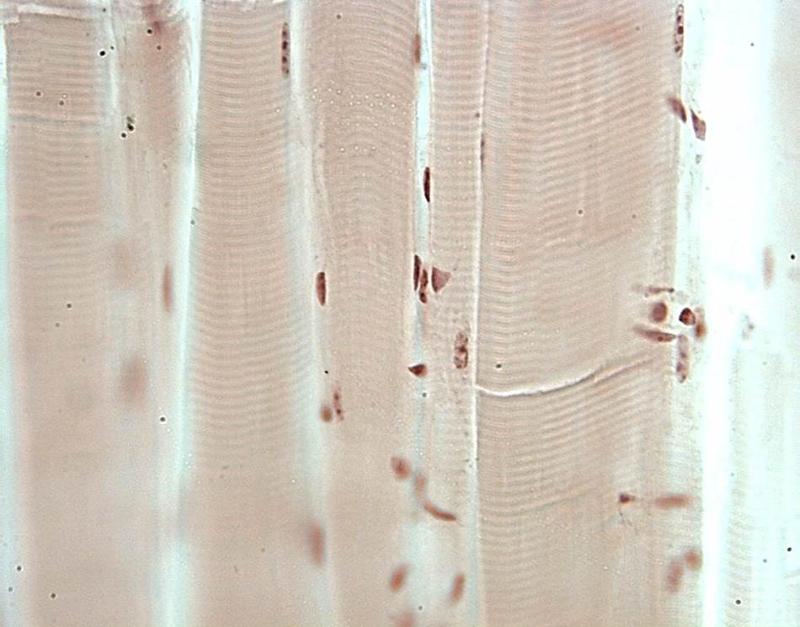 Chapter 18- Histology What cell is this? | back 25 Skeletal Muscle |
front 26 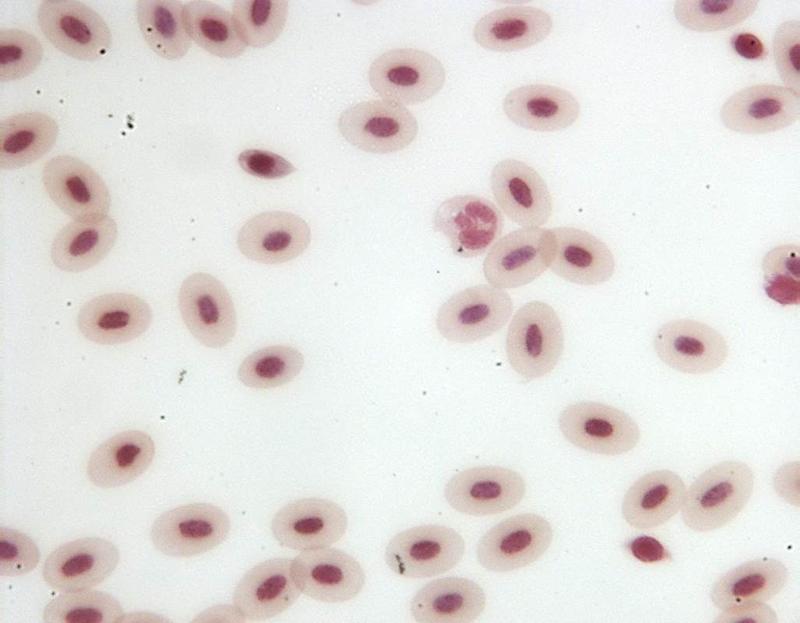 Chapter 18- Histology What is this cell? | back 26 Frog Leukocytes |
front 27  Chapter 18- Histology What cells are these? | back 27 Human Blood Cells |
front 28 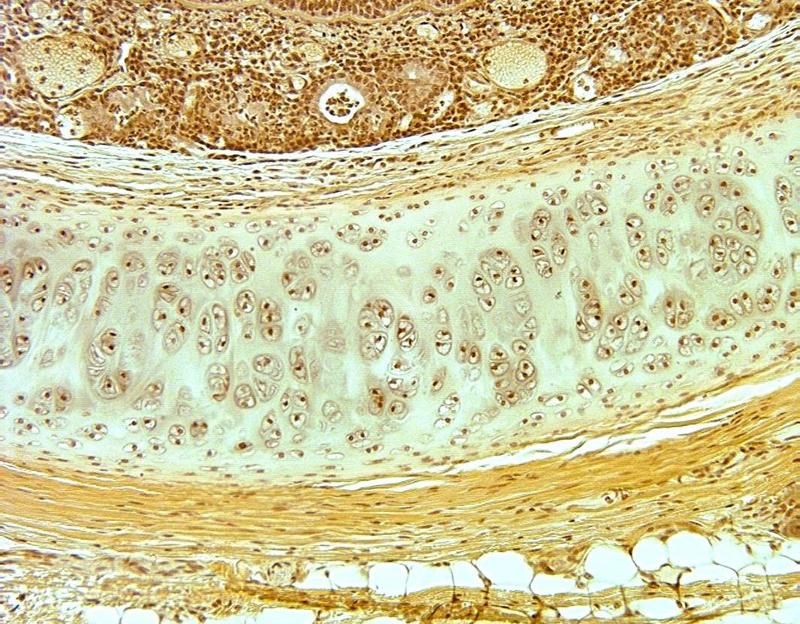 Chapter 18- Histology What is this an image of? | back 28 Cartilage |
front 29 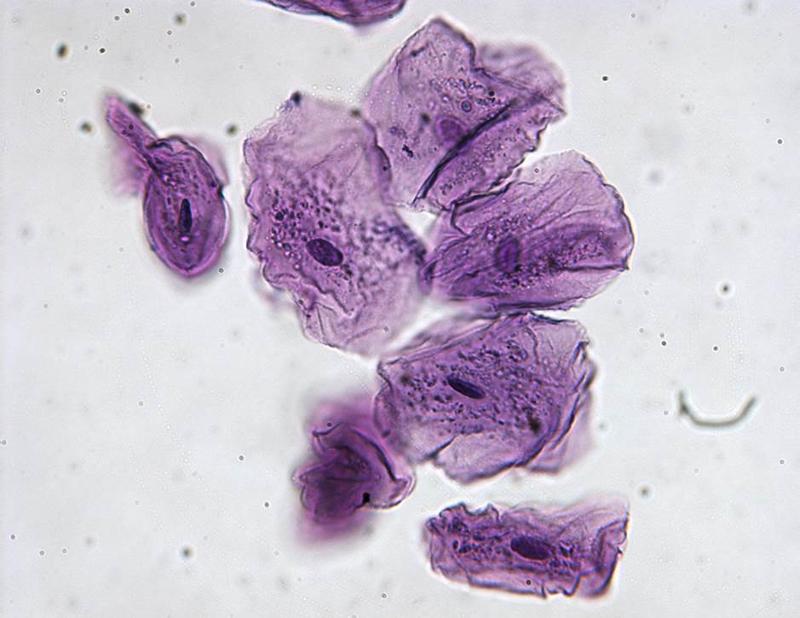 Chapter 18- Histology What are these cells? | back 29 Human Cheek Cells |
front 30 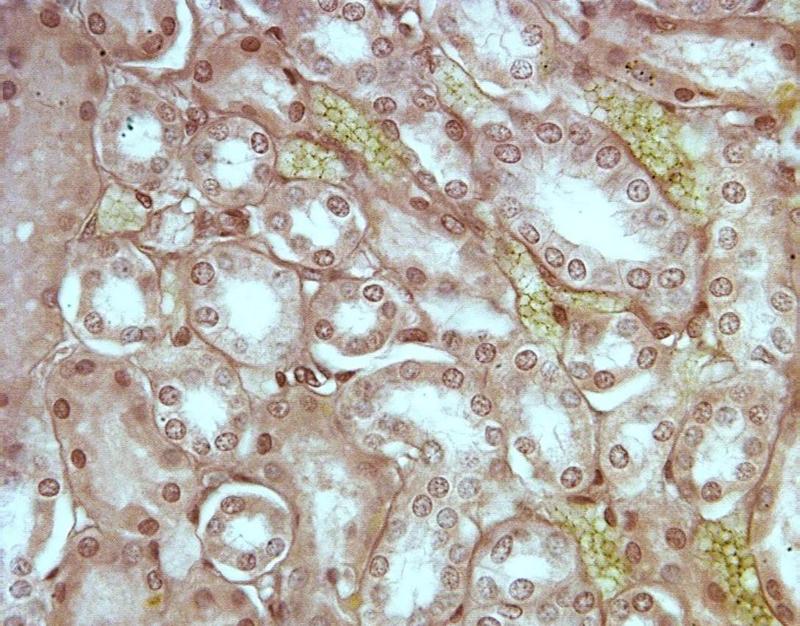 Chapter 18- Histology What is this an image of? Identify Lumen, Columnar Epithelial tissue, nucleus. | back 30 Frog Kidney Center= Lumen Outer tissue= Columnar Epithelial Dots= Nucleus |
front 31 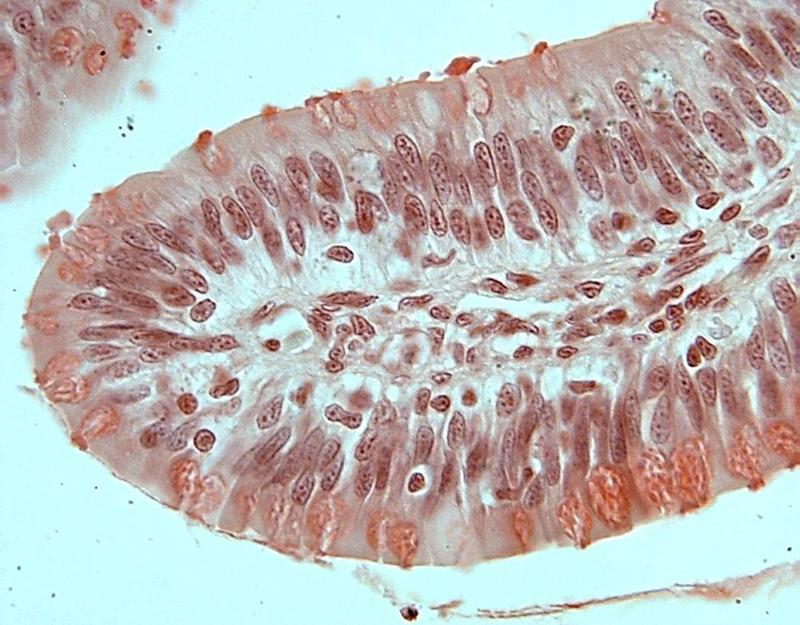 Chapter 18- Histology What is this an image of? | back 31 Frog Intestine |
front 32 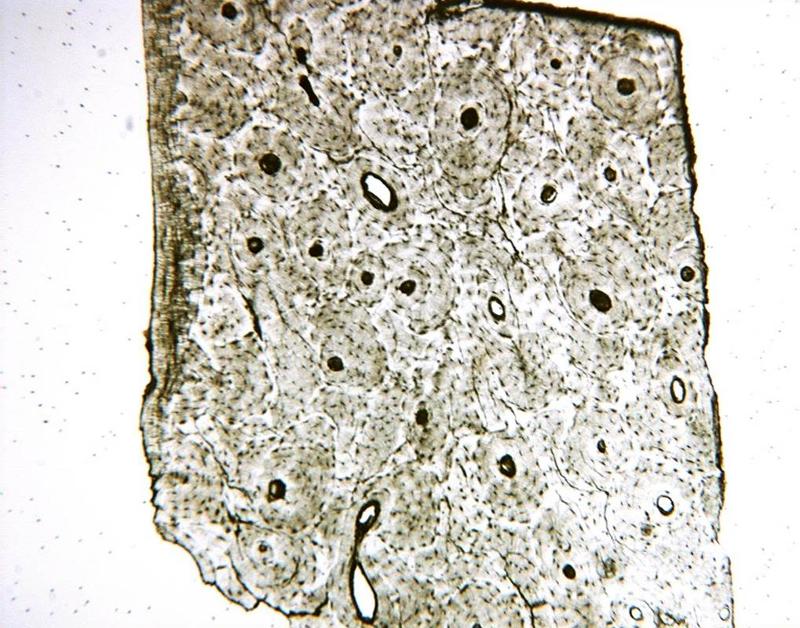 Chapter 18- Histology What cell is this? Identify the Haversian Canal, lacunae, matrix, canaliculi | back 32 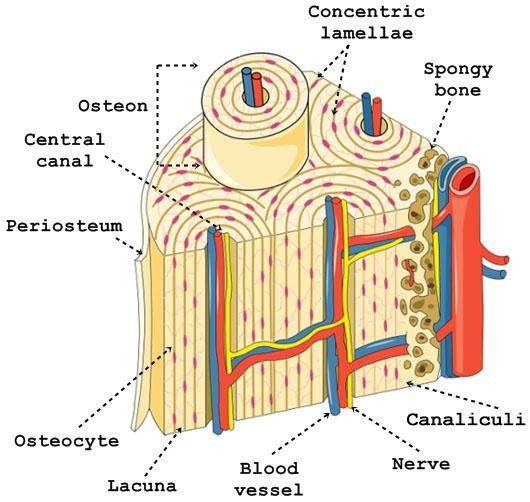 Bone |
front 33 Chapter 18- Histology Checks Cells are? | back 33 Stratified Squamous |
front 34 Chapter 18- Histology Types of Cells? | back 34 Simple Squamous Simple Cuboidal Simple Columnar Stratified Squamous (Keratinized or not) |
front 35 Chapter 18- Histology What are red blood cells called? What are bone cells called? | back 35 Erythrocytes Chondrocytes |
front 36 Chapter 18- Histology What determines a frogs green color? | back 36 Chromatophores |
front 37 Chapter 19- Anatomy of a Frog Be able to Identify: Cloacal Aperture, External nares, Tympanic membrane | back 37 Cloacal Aperture- Butt Hole External nares- nose Tympanic membrane- side of head |
front 38 Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog What is special about frog skin? | back 38 It is used as a respiratory surface |
front 39 Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog What hole is located directly behind the tongue of a frog? | back 39 Glottis |
front 40 Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog What muscles are used? Flexion of leg at knee? Extension of leg at knee? Flexion of foot at ankle? Extension of foot at ankle? Legs coming together? | back 40 Semimembranosus, Gracilis minor Triceps Femoris Peroneus Gastrocnemius Sartorius, Adductors, Gracilis Major |
front 41 Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog Describe how Frogs breathe? | back 41 Through skin Start through nostrils, Buccal Cavity Expands, Nostrils close, Buccal Cavity (Contracts), Glottis opens, lungs expand, Glottis closes, oxygen distributed |
front 42 Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog What is the endoskeleton divided into? | back 42 Axial skeleton, and appendicular skeleton |
front 43 Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog Flexors: Extensors: Adductors: Abductors: | back 43 Bend Straighten Toward Midline Away from Midline |
front 44 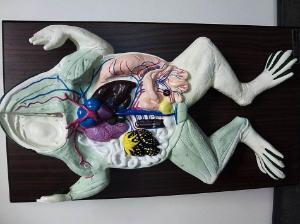 Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog Be able to identify: Fat Bodies, Eggs or Testis, Intestine, Oviduct& Uterus if (Female), Cloaca, Kidney, Bladder, Lungs, Liver, Heart, Stomach, Small intestine, Spleen, Pancreas, Esophahus | back 44 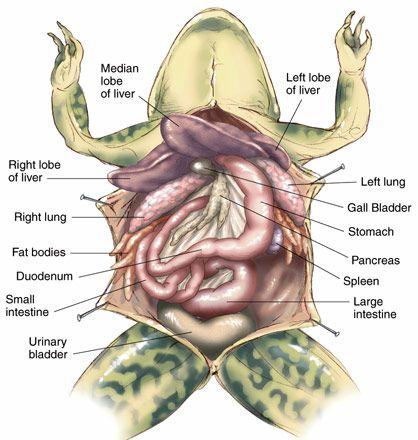 |
front 45  Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog Identify the Bones | back 45 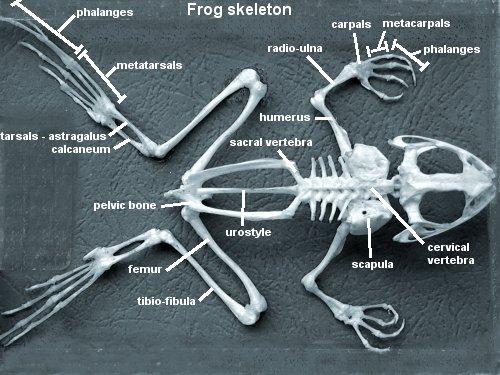 |
front 46  Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog Study This and know it. | back 46 no data |
front 47 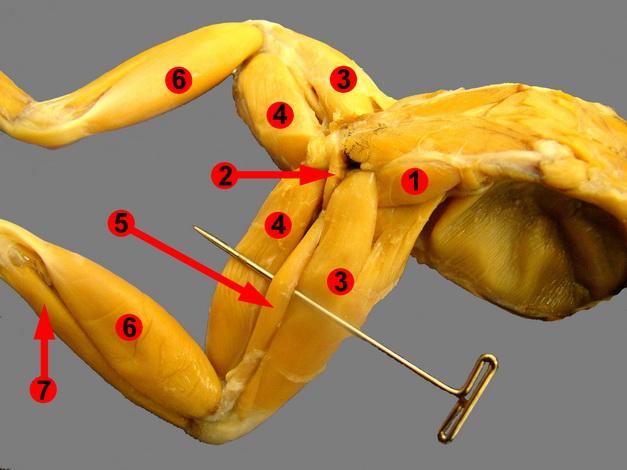 Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog Know these muscles (NOT 1,2,5) | back 47 3.Tricep Femoris 4. Semimembranosus 6.Gastrocnemius |
front 48 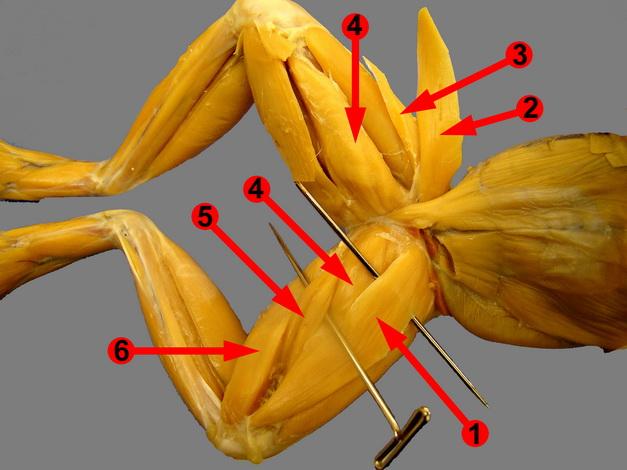 Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog Know these muscles (NOT 2,3) | back 48 1. Sartorius 4. Adductors 5. Gracilis Major 6. Gracilis Minor |
front 49 Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog Circulatory System is divided into what? | back 49 Pulmonary Circuit (Out of Heart) Systemic Circuit (In the Heart) |
front 50  Chapter 18- Anatomy of a Frog Know parts of Frog Heart | back 50 no data |
front 51 Chapter 20- Ecology Levels of Consumers? | back 51 Quaternary (Humans) Tertiary (Carnivores) Secondary (Carnivores) Primary (Herbivores) Decomposers (Bacterias, and Fungi) (Omnivores) Producers (Photosynthetic Plants, Algae, Bacteria) |
front 52 Chapter 20- Ecology Abiotic Factors Biotic Factors | back 52 Light, Temperature, Oxygen Level, Precipitation, Soil Producers, Consumers, Decomposers |
front 53 Chapter 20- Ecology Define these: Benthic zone Pelagic Zone Littoral Zone Limnetic Zone Profundal Zone | back 53 Bottom of a lake Open Water Shallow region along a shore(Photic) Layer of water where light penetrates (Photic) Water where light doesn't Penetrate (Aphotic) |
front 54 Chapter 20- Ecology Species Diversity Species Richness Relative Abundence | back 54 Species in that community Number of species in the community Number of individuals of a specific species |
front 55 Chapter 20 -Ecology Simpsons Dominance index | back 55 Add up all proportions and square each |
front 56 Chapter 20- Ecology Simpsons Diversity Index | back 56 1- Simpson dominance index |