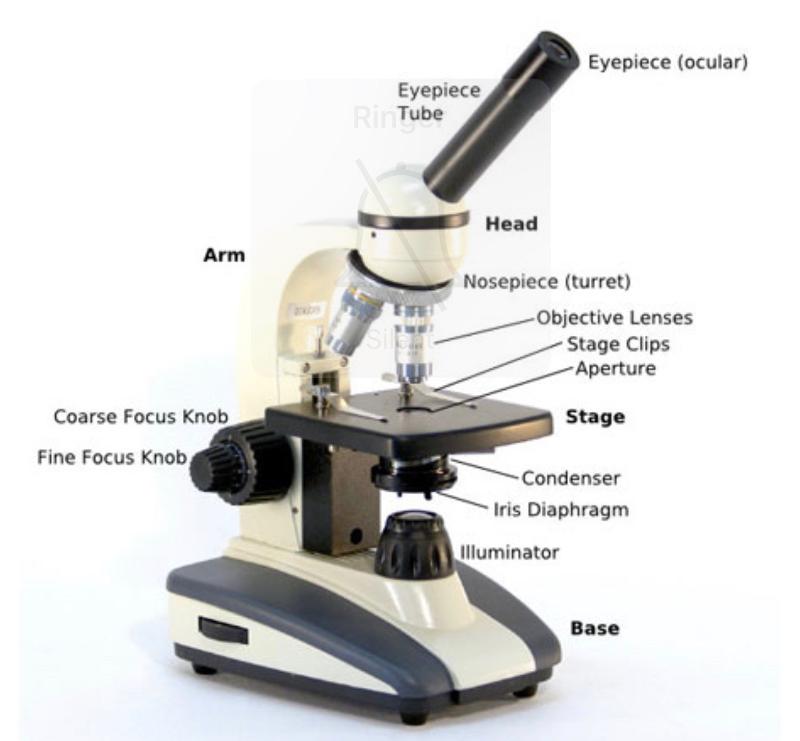
Condenser
Focuses light through specimen
Iris Diaphragm
Delivers concentrated beam of light to specimen
Coarse Adjustment Knob
For focusing on scanning. When the knob is turned, the stage moves up or down in order to coarse adjust the focus.
Fine Adjustment Knob
For precise focusing once initial focusing has been done.
Illuminator
Light Source
Stage
Holds microscope slide in position
Ocular Lens
Remagnifies image framed by objective lens.
Objective Lens
4 objective lenses on a microscope, consisting of 4X, 10x, 40x, nd 100x magnification powers. In order to obtain total magnification of an image, multiply eyepiece lens power by objective lens power.
Labeled Microscope

If you're looking at something under the microscope and want to move the slide backwards, what would you do?
Move it forward,
How to prepare an organism for staining
- Smear
- Air dry
- Heat fix
What's a negative stain?
When you stain the background and the organism is clear.
When do you do a negative stain?
When you can't heat fix an organism.
What color is a gram positive organism?
Purple
What color s a gram negative organism?
Red
A simple stain is...
Just coloring it.
Gram Stain Steps
- Crystal Violet
- Iodine
- Alcohol
- Safranin
If an acid fast stain is positive it is positive for...
Mycobacterium
If you do an endospore stain and find endospores, it is positive for what 2 genuses?
Bacillus and Clostridum.
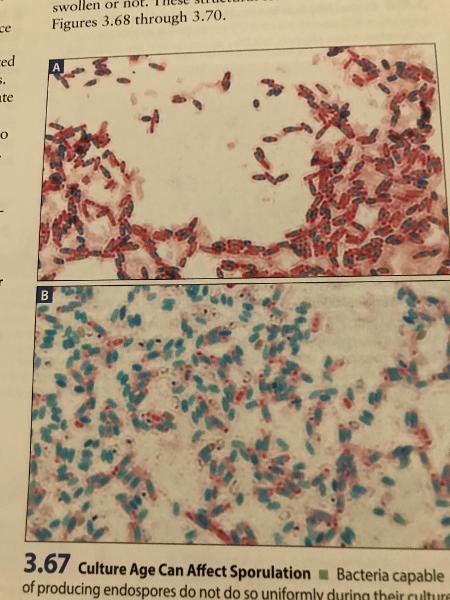
Endospore Stain Procedure
- Malachite Green
- Wash with water
- Safranin
(red rods, green cocci)
Acid Fast Stain
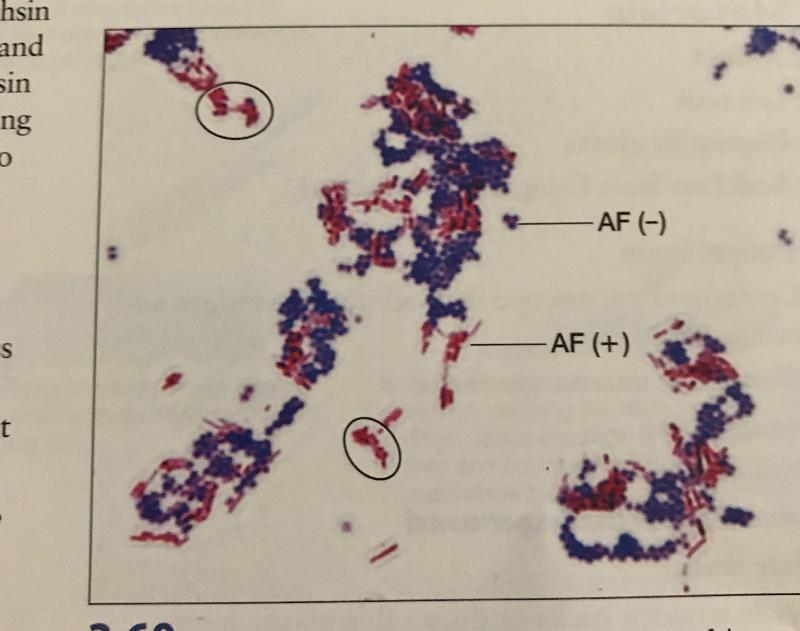
Acid fast Pos/Neg

Capsule Stain
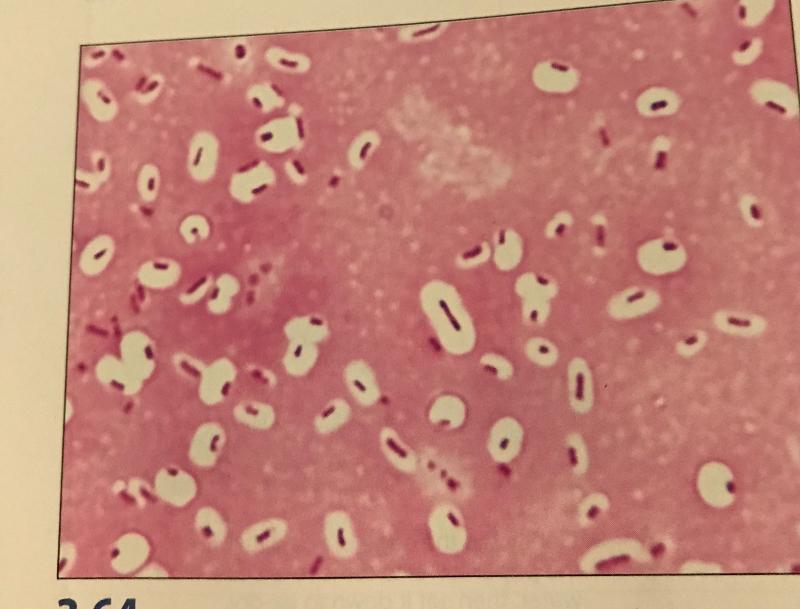
Endospore Stain
Blood Agar is selective for...
Streptococcus
Blood Agar is differential for...
An organism's ability to hemolyze red blood cells
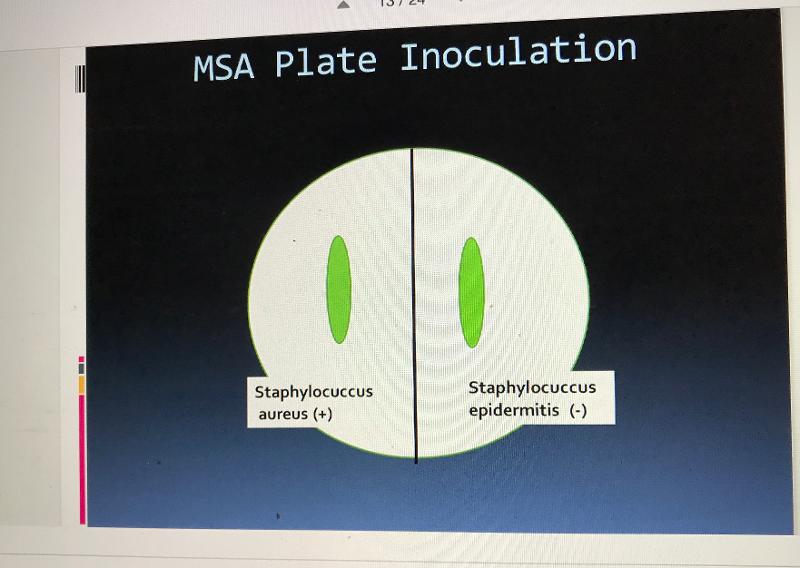
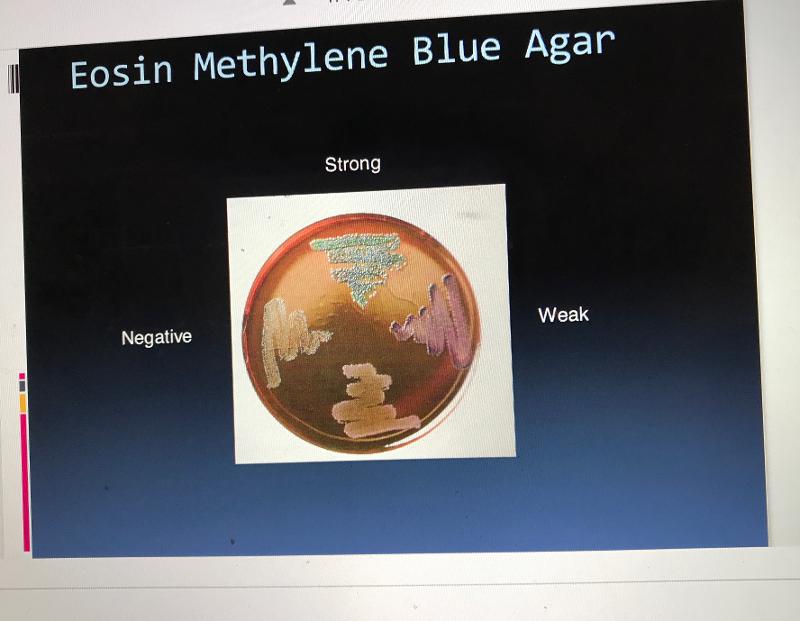
Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) Agar is selective for...
Members of enteric bacteria (Gram negative rods)
Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) Agar is differential for...
An organism's ability to ferment lactose.
Color of nonpathogen on EMB Agar?
Green
Color of weak pathogen on EMB Agar?
Pink
Color of strong pathogen on EMB Agar?
White
MacConkeys Agar is selective for....
Enteric gut bacteria
MacConkeys Agar is differential for...
An organism's ability to ferment lactose
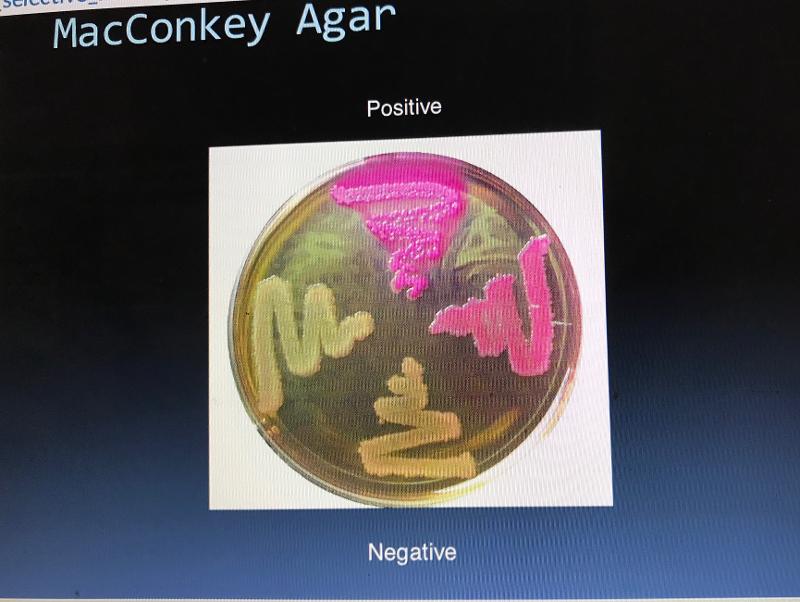
Color of nonpathogen on MAC Agar?
Pink
Color of pathogen on MAC Agar?
White
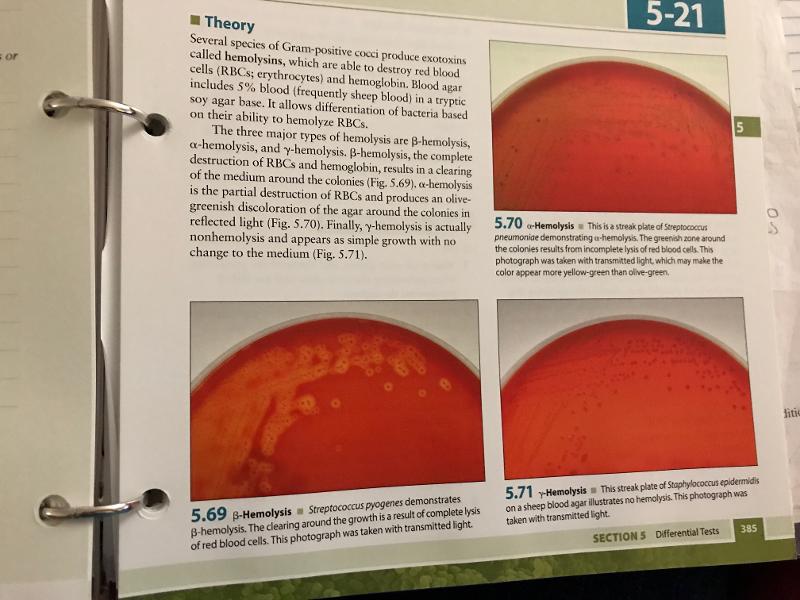
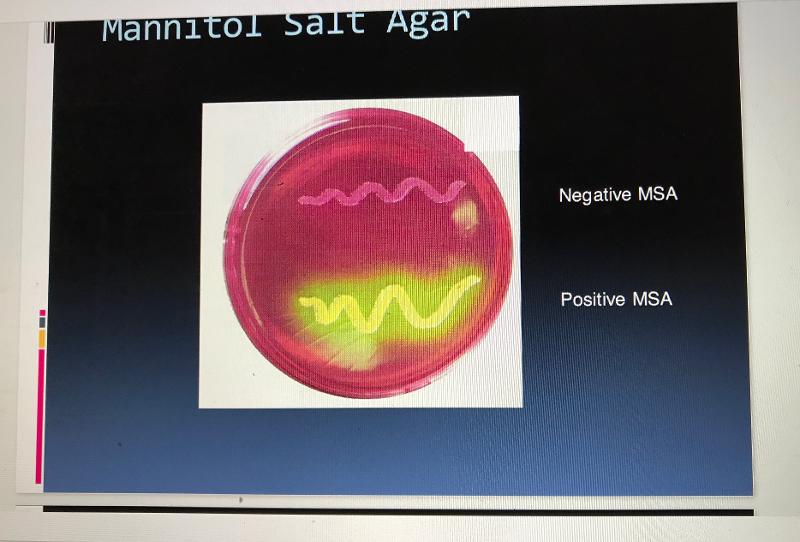
Mannitol Salt Agar is selective for...
Staphylococcus aureus
Mannitol Salt Agar is differential for...
An organism's ability to ferment the carbohydrate mannitol
Color of a pathogen on Mannitol Salt Agar plate?
Yellow
Color of nonpathogen on Mannitol Salt Agar plate?
Red
Blood Agar Plate Hemolysis
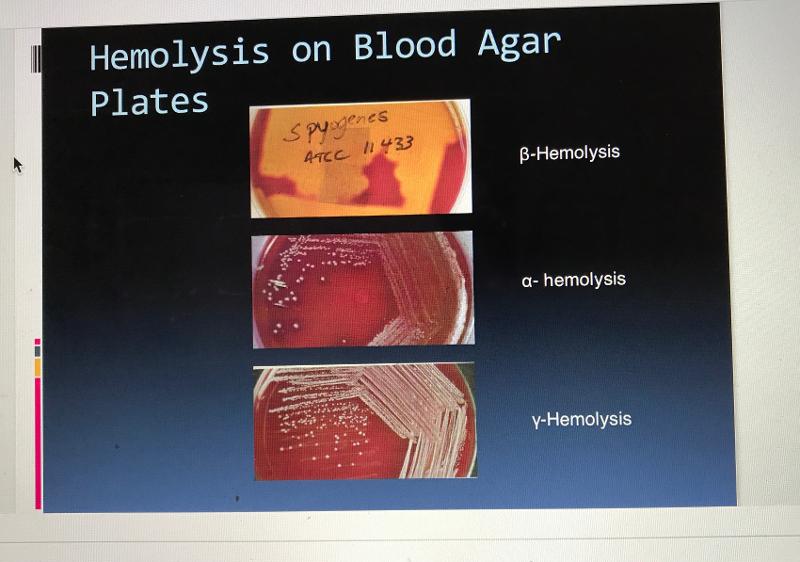
Blood Agar Plate Hemolysis 2
MSA Pos/Neg Colors
MSA organisms that are pos/neg
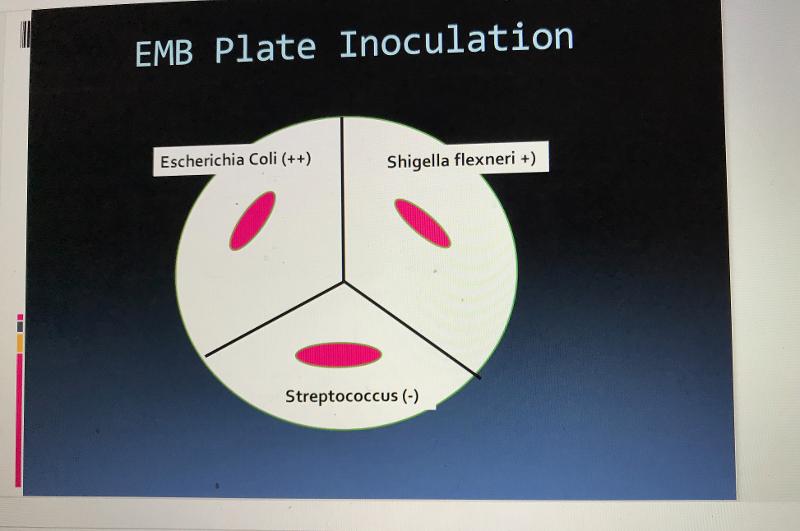
EMB pos/neg
EMB organisms that are pos/neg
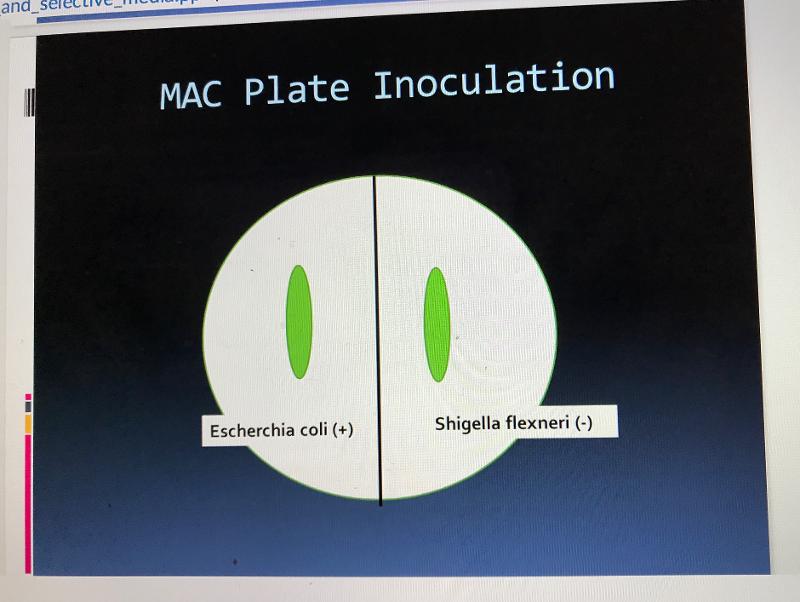
MAC pos/neg
MAC organisms that are pos/neg
What does a positive Oxidase test look like?
Dark blue/purple
What does a negative Oxidase test look like?
No color change
What is the color indicator in a fermentation test/MSA plate?
Phenol Red
What does a positive Catalase test look like?
Bubbles
What does a negative Catalase test look like?
No bubbles
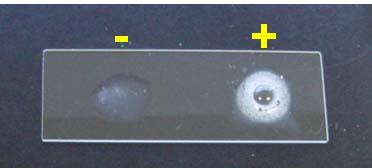
What does a positive Nitrate Reduction test look like?
Gas (non fermenter), Red color (after addition of reagents A and B), No color change (after addition of Zinc dust.)
What does a negative Nitrate Reduction test look like?
No gas, Red color (after addition of Zinc dust.)
What gas is produced from a fermentation test?
Carbon Dioxide
What does a positive Phenol Red test look like?
Yellow
What does a negative Phenol red test look like?
Red
What does a positive Methyl Red test look like?
Red
What does a negative Methyl Red test look like?
No color change; yellow
What does a positive Voges-Proskauer test look like?
Red ring; red
What does a negative Voges-Proskauer test look like?
No color change; yellow
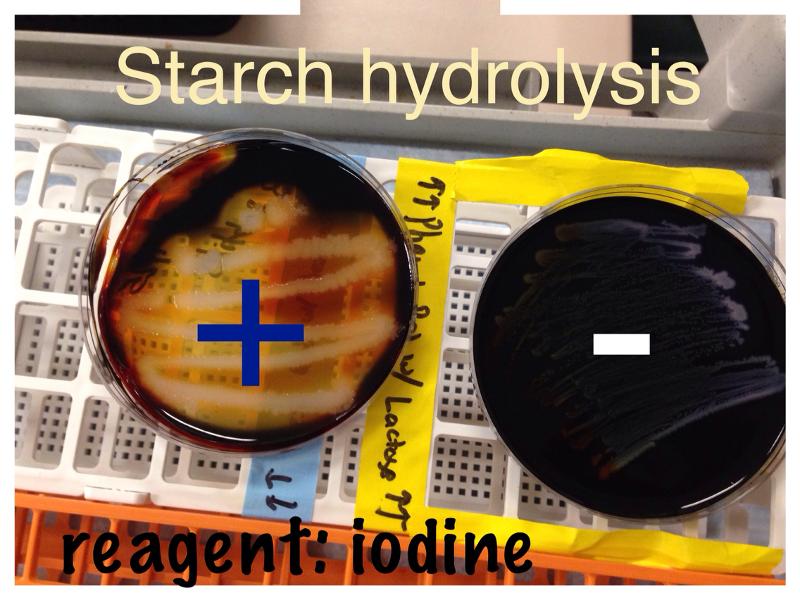
What does a positive Starch Hydrolysis test look like?
Halo
What does a negative Starch Hydrolysis test look like?
No halo
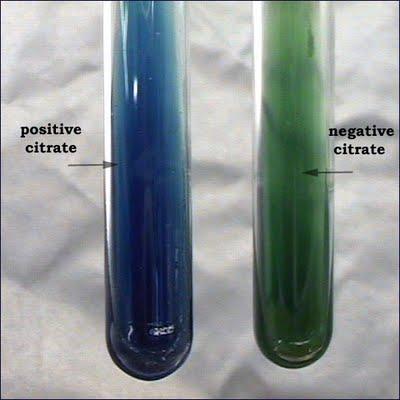
What does a positive Citrate test look like?
Blue, or there is no color change but growth is present
What does a negative Citrate test look like?
Green, no growth
What does a positive Sulfur Reduction test look like?
Black
What does a negative Sulfur Reduction test look like?
No black in medium; yellow
What does a positive Indole test look like?
Red ring
What does a negative Indole test look like?
No color change; yellow
What does a positive Motility test look like?
Growth radiating outwards from stab line
What does a negative Motility test look like?
No radiating growth
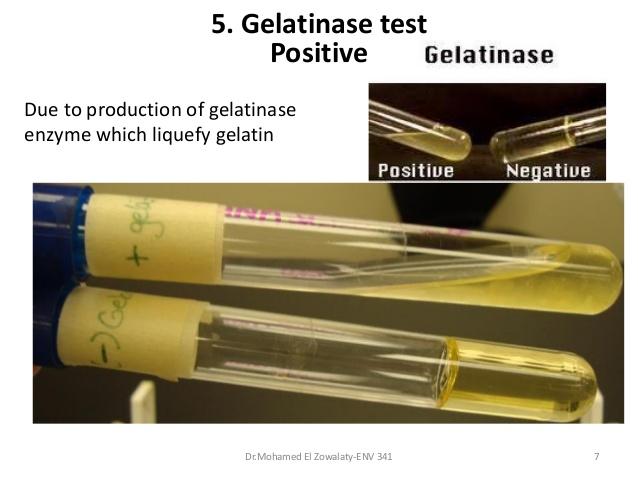
What does a positive Gelatinase test look like?
Liquid
What does a negative Gelatinase test look like?
Solid
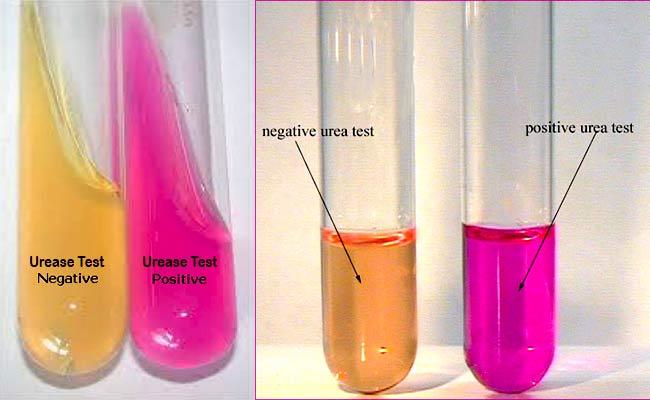
What does a positive Urease test look like?
Fuchsia (pink)
What does a negative Urease test look like?
Yellow
Oxidase test

Catalase test
Nitrate Reduction test

Methyl Red test

Voges-Proskauer test

Phenol Red Fermentation test

Starch Hydrolysis test
Citrate test

Sulfur test

Indole test

Motility test

Geltinase test
Urease test

- Fungi
- Yeast
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Fungi
- Sporagiospore
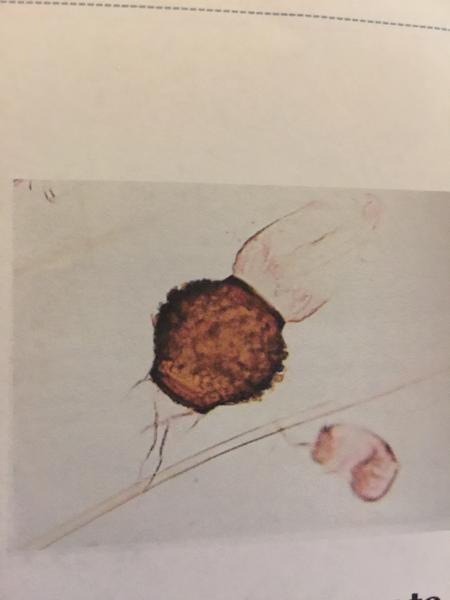
- Fungi
- Zygospore
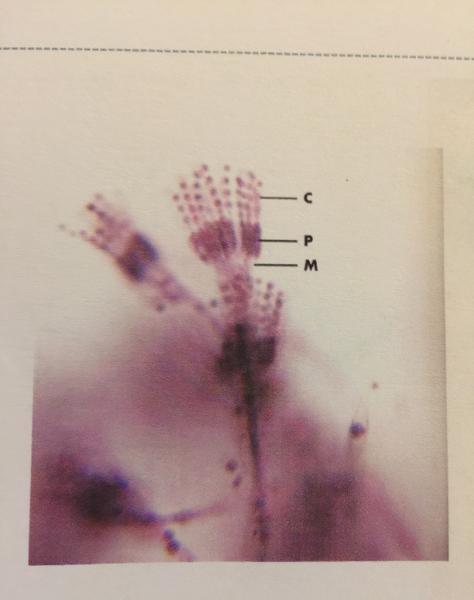
- Fungi
- Conidiospore
- Penicillum
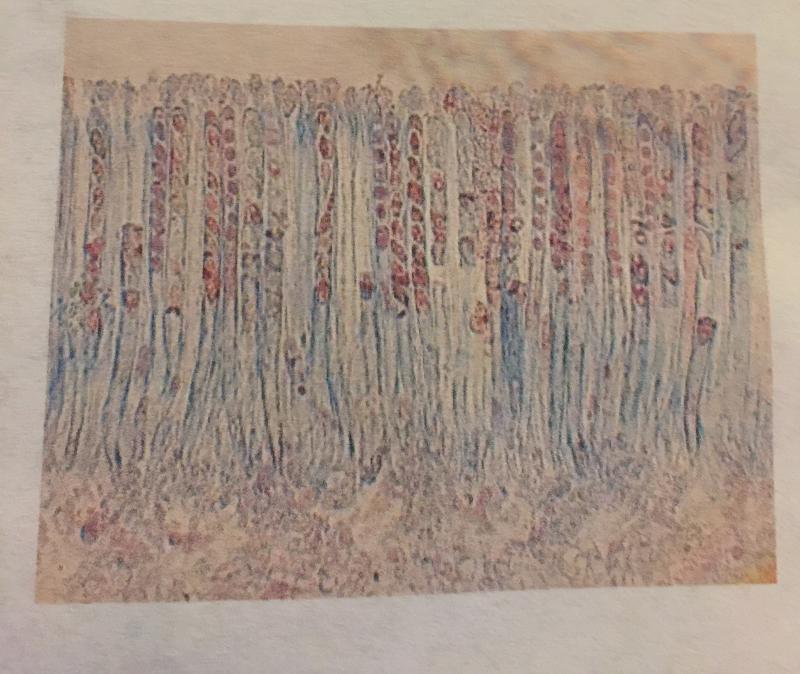
- Fungi
- Apothecium
- Pezzia cup
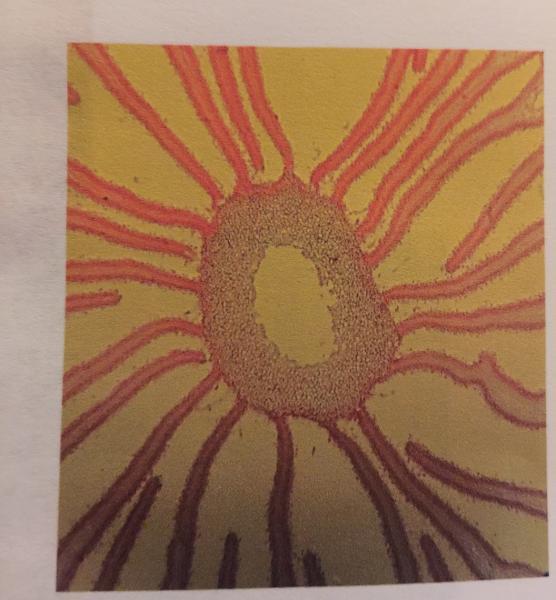
- Fungi
- Corpinus sp.
- Mushroom

- Lichen
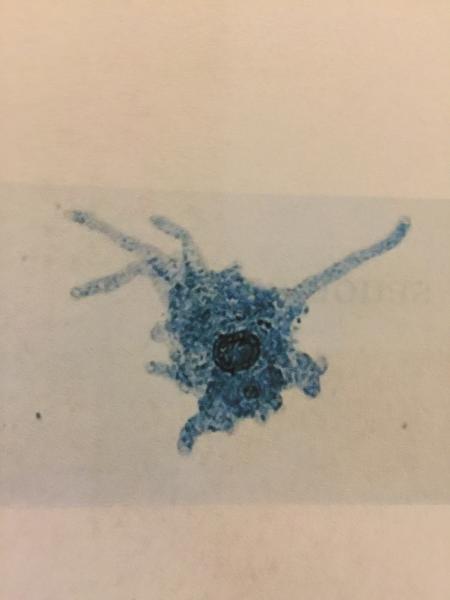
- Protozoa
- Amoeba
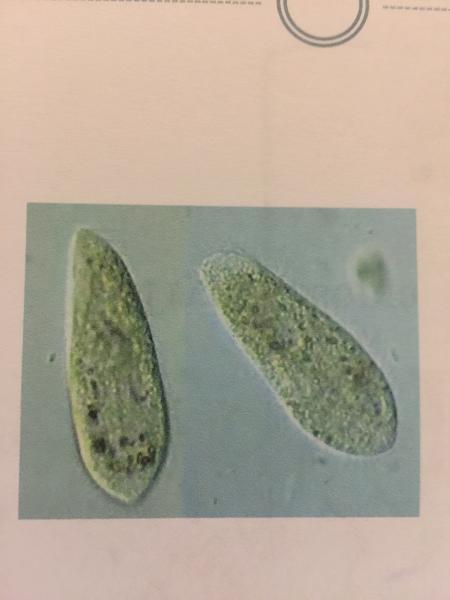
- Protozoa
- Paramecium
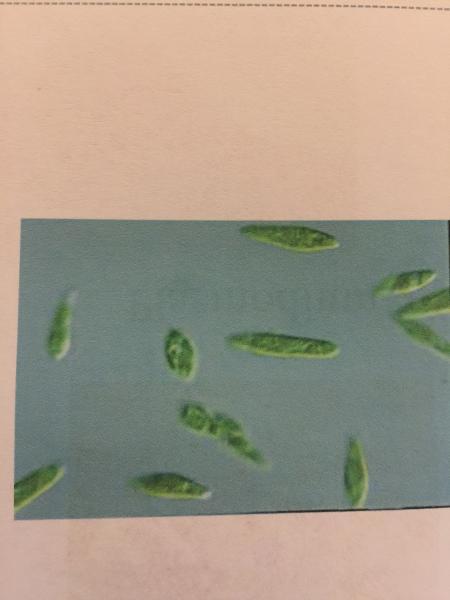
- Protzoa
- Euglena
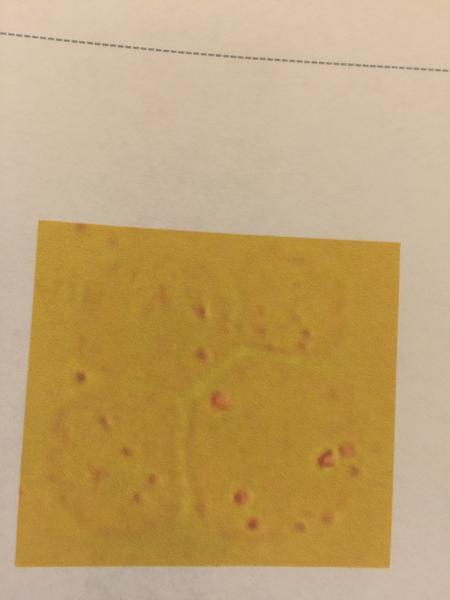
- Protozoa
- Trichomas
- Protozoa
- Trypanosoma
- Protozoa
- Plasmodium

- Trematodes
- Asian Liver Fluke
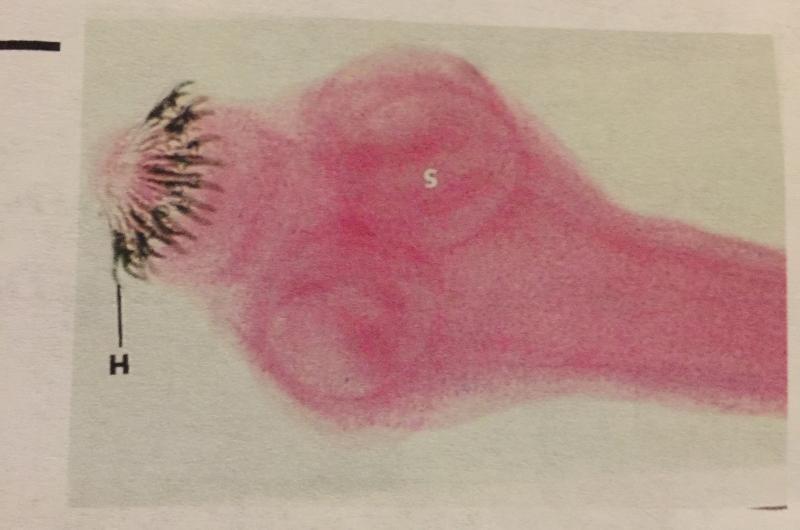
- Cestodes tapeworm
- Scolex
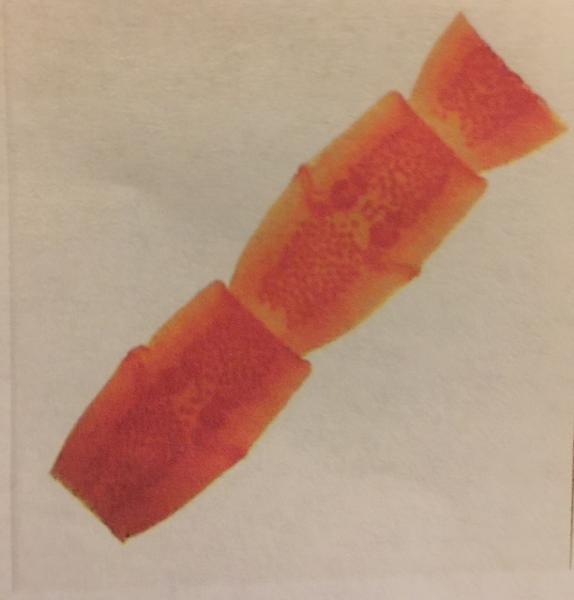
- Cestodes tapeworm
- Proglottids

- Nematodes
- Enterobius vermicularis Adult

- Nematodes
- Necator Americanus larvae
UV light works by Inducting genetic mutations called...
Thymine Dimmers
What kind of Agar does the Kirby-Bauer test use?
Mueller-Hinton
What do you measure in a Kirby-Bauer test?
Zone of inhibition
What do we measure the Zone of Inhibition in?
Millimeters
What does the Membrane Filter Technique use?
Eosin Methylene Blue agar (EMB) in combination with a membrane filter
When is water considered potable in the Membrane Filter Technique?
If the count is less than 1 coliform per 100 mLs.
What color is Methylene blue when it is oxidized?
Blue
What color is Methylene blue when it is reduced?
Colorless
What is an indicator of good quality milk in a Methylene Blue Reductase test?
It takes more than 6 hours to turn from blue to white.
What is the pH indicator in the Snyder test?
Bromcresol blue
What does a positive Snyder test look like?
Yellow
What does a negative Snyder test look like?
Green
The Snyder test is a test to detect...
The prescience of Lactobacillus in saliva as an indicator of dental care susceptbility.
Methylene Blue test

Snyder test

Positive is yellow
What does color change in less than 24 hours mean on a Snyder test?
High susceptibility
What does color change in less than 48 hours mean on a Snyder test?
Moderate susceptibility
What does no color change 72 hours mean on a Snyder Test?
Negative result or low susceptibility.
The Oxidase test differential for
Enterobacteriales and Pseudomonas
Phenol red differentiates between ______________ and _____________
E.Coli and Proteus vulgaris
MR/VP differential for
E.Coli and Enterobacter aerogenes
Catalase test differential for
Staphylococcus areus and Streptococcus
Nitrate Reduction differentiates for
Pseudomonas, Bacillus subtitles, e. coli
Citrate test differential for
E.Coli and Enterobacter aerogenes
Starch Hydrolysis differential for
Bacillus subtitles, pseudomonas arguenosa, e.coli
Urease differential for
Proteus and Enterobacter
Gelatinase differential for
E.Coli and Proteus
Sulfur differential for
E.Coli, Salmonella, Shigella
Indole differential for
E.Coli, Salmonella, Shigella
Motility differential for
E.Coli, Salmonella, Shigella