Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Microbiology Lab Practical
front 1 Condenser | back 1 Focuses light through specimen |
front 2 Iris Diaphragm | back 2 Delivers concentrated beam of light to specimen |
front 3 Coarse Adjustment Knob | back 3 For focusing on scanning. When the knob is turned, the stage moves up or down in order to coarse adjust the focus. |
front 4 Fine Adjustment Knob | back 4 For precise focusing once initial focusing has been done. |
front 5 Illuminator | back 5 Light Source |
front 6 Stage | back 6 Holds microscope slide in position |
front 7 Ocular Lens | back 7 Remagnifies image framed by objective lens. |
front 8 Objective Lens | back 8 4 objective lenses on a microscope, consisting of 4X, 10x, 40x, nd 100x magnification powers. In order to obtain total magnification of an image, multiply eyepiece lens power by objective lens power. |
front 9 Labeled Microscope | back 9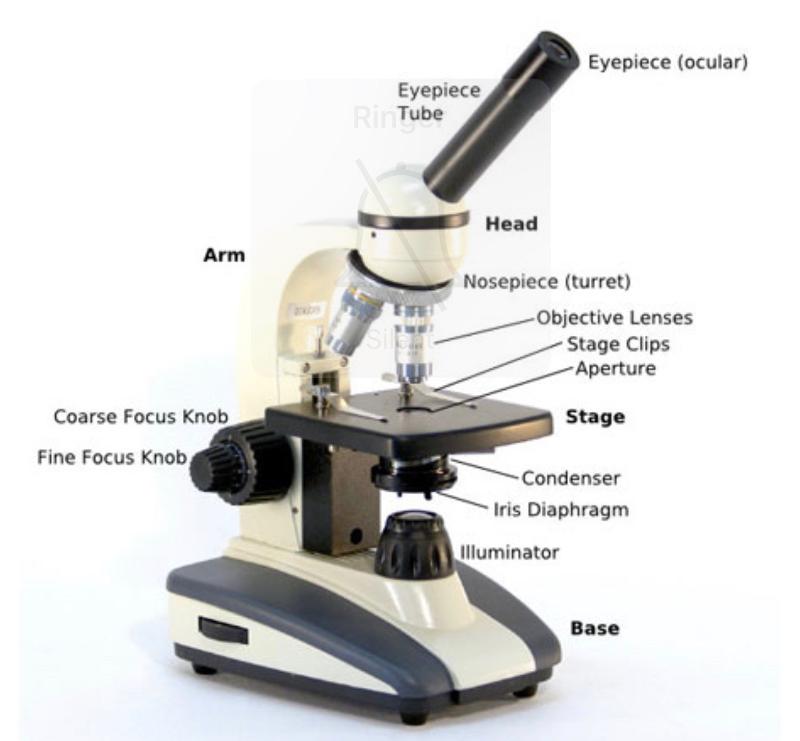  |
front 10 If you're looking at something under the microscope and want to move the slide backwards, what would you do? | back 10 Move it forward, |
front 11 How to prepare an organism for staining | back 11
|
front 12 What's a negative stain? | back 12 When you stain the background and the organism is clear. |
front 13 When do you do a negative stain? | back 13 When you can't heat fix an organism. |
front 14 What color is a gram positive organism? | back 14 Purple |
front 15 What color s a gram negative organism? | back 15 Red |
front 16 A simple stain is... | back 16 Just coloring it. |
front 17 Gram Stain Steps | back 17
|
front 18 If an acid fast stain is positive it is positive for... | back 18 Mycobacterium |
front 19 If you do an endospore stain and find endospores, it is positive for what 2 genuses? | back 19 Bacillus and Clostridum. |
front 20 Endospore Stain Procedure | back 20
(red rods, green cocci) |
front 21 Acid Fast Stain | back 21 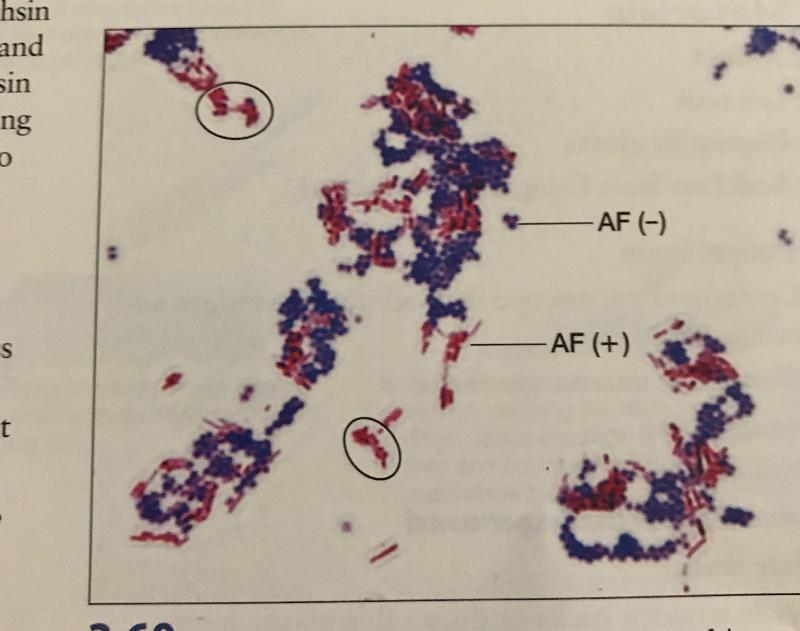 |
front 22 Acid fast Pos/Neg | back 22  |
front 23 Capsule Stain | back 23 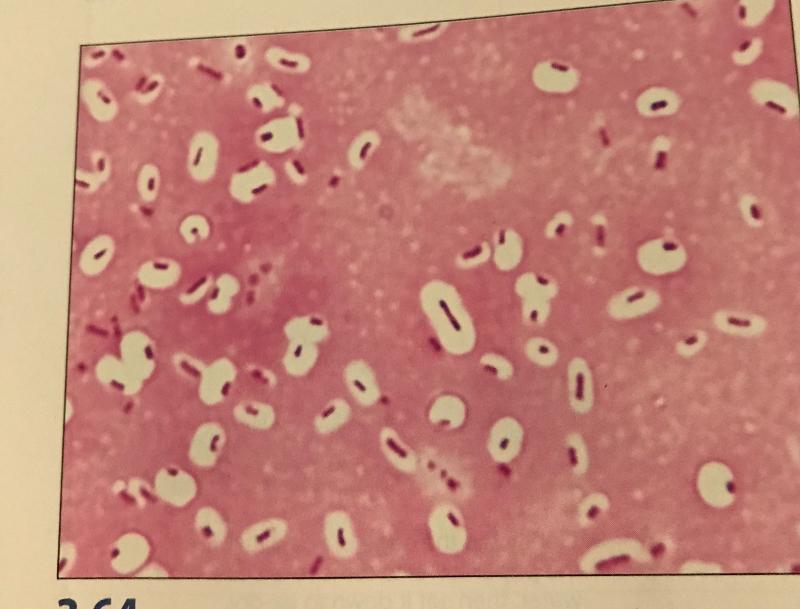 |
front 24 Endospore Stain | back 24 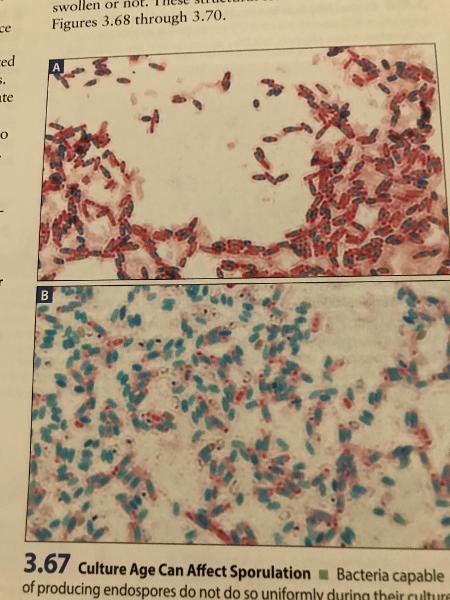 |
front 25 Blood Agar is selective for... | back 25 Streptococcus |
front 26 Blood Agar is differential for... | back 26 An organism's ability to hemolyze red blood cells |
front 27 Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) Agar is selective for... | back 27 Members of enteric bacteria (Gram negative rods) |
front 28 Eosin Methylene Blue (EMB) Agar is differential for... | back 28 An organism's ability to ferment lactose. |
front 29 Color of nonpathogen on EMB Agar? | back 29 Green |
front 30 Color of weak pathogen on EMB Agar? | back 30 Pink |
front 31 Color of strong pathogen on EMB Agar? | back 31 White |
front 32 MacConkeys Agar is selective for.... | back 32 Enteric gut bacteria |
front 33 MacConkeys Agar is differential for... | back 33 An organism's ability to ferment lactose |
front 34 Color of nonpathogen on MAC Agar? | back 34 Pink |
front 35 Color of pathogen on MAC Agar? | back 35 White |
front 36 Mannitol Salt Agar is selective for... | back 36 Staphylococcus aureus |
front 37 Mannitol Salt Agar is differential for... | back 37 An organism's ability to ferment the carbohydrate mannitol |
front 38 Color of a pathogen on Mannitol Salt Agar plate? | back 38 Yellow |
front 39 Color of nonpathogen on Mannitol Salt Agar plate? | back 39 Red |
front 40 Blood Agar Plate Hemolysis | back 40 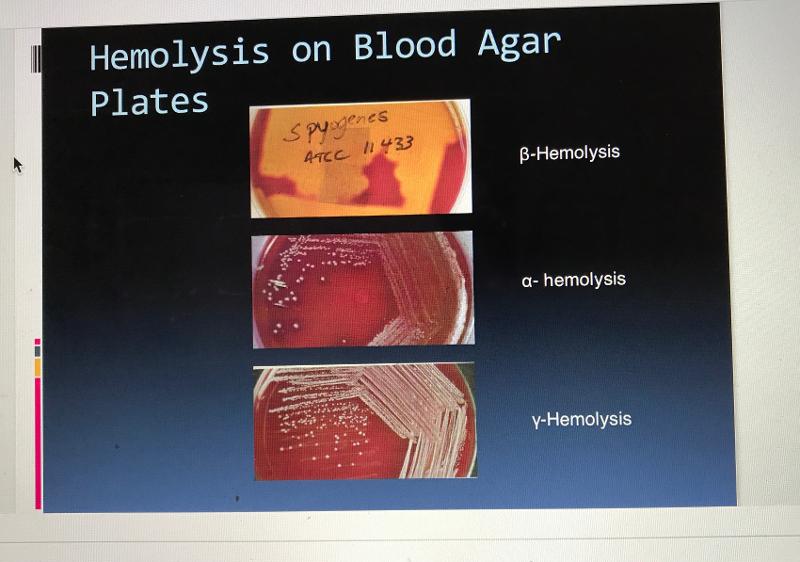 |
front 41 Blood Agar Plate Hemolysis 2 | back 41 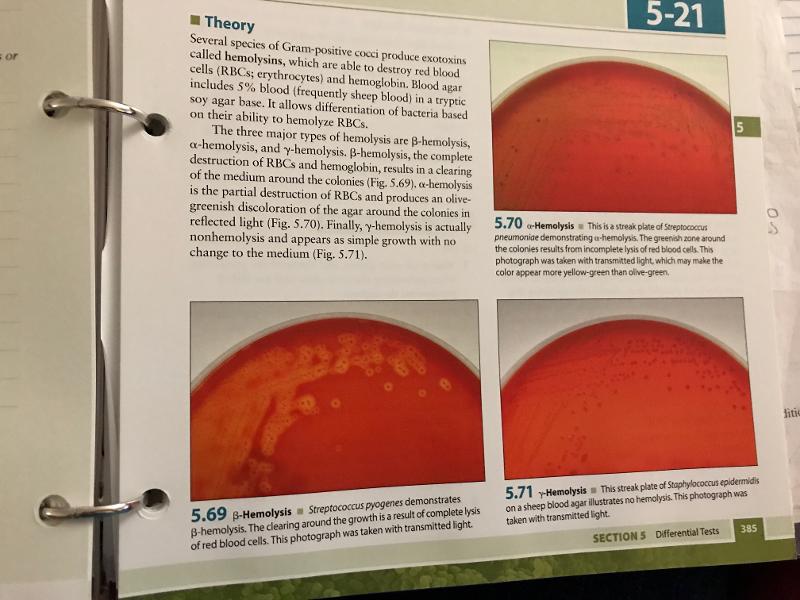 |
front 42 MSA Pos/Neg Colors | back 42 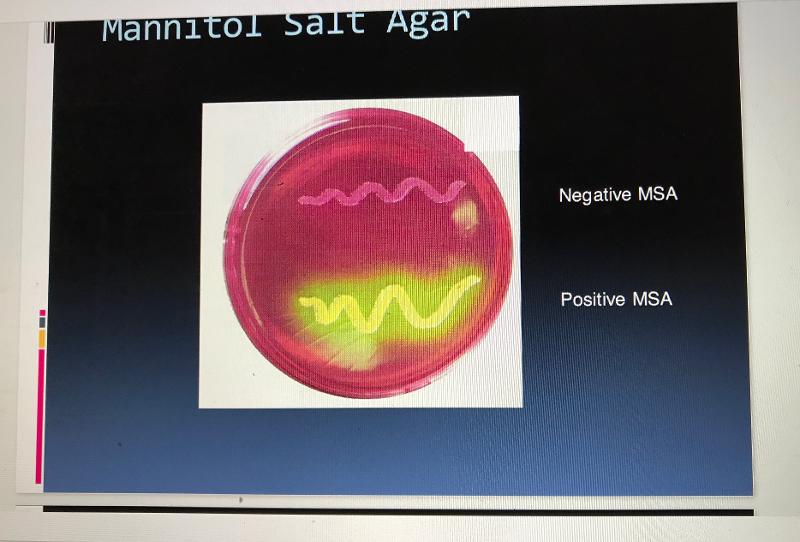 |
front 43 MSA organisms that are pos/neg | back 43 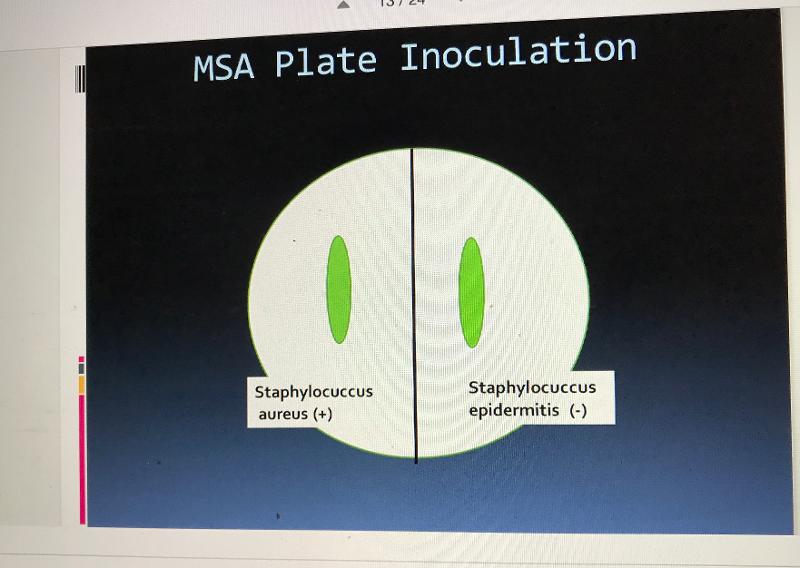 |
front 44 EMB pos/neg | back 44 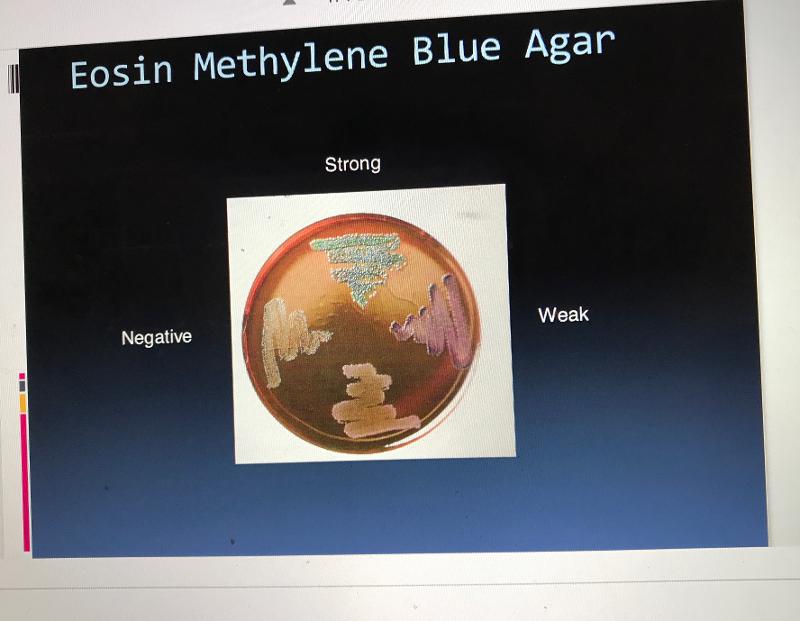 |
front 45 EMB organisms that are pos/neg | back 45 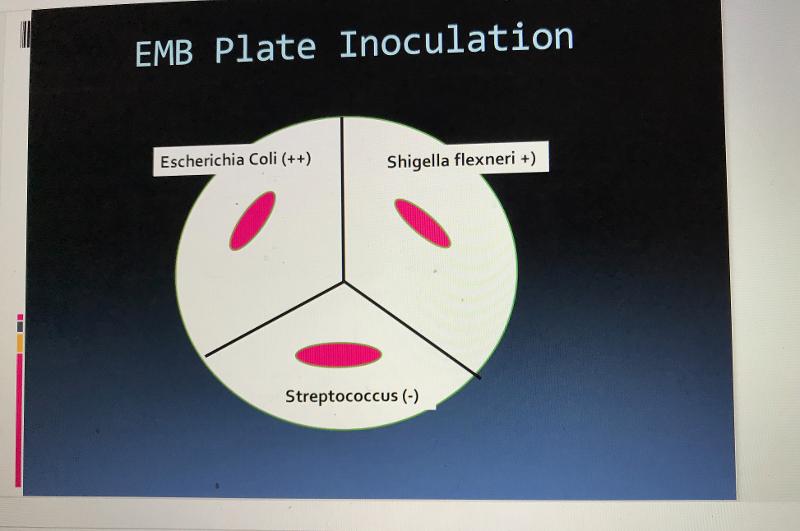 |
front 46 MAC pos/neg | back 46 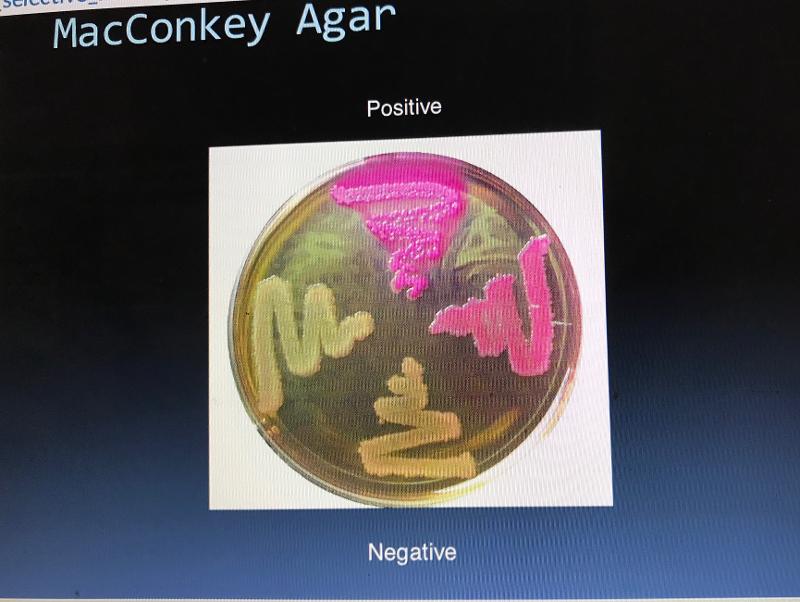 |
front 47 MAC organisms that are pos/neg | back 47 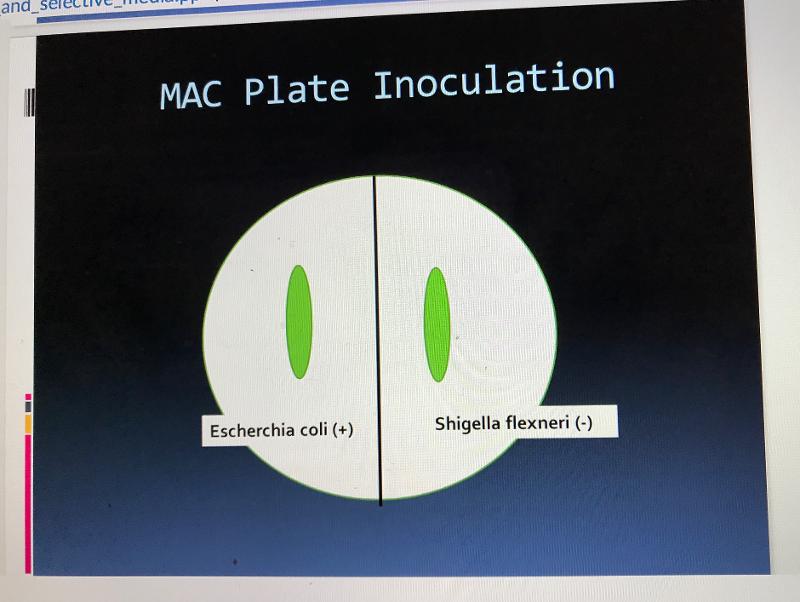 |
front 48 What does a positive Oxidase test look like? | back 48 Dark blue/purple |
front 49 What does a negative Oxidase test look like? | back 49 No color change |
front 50 What is the color indicator in a fermentation test/MSA plate? | back 50 Phenol Red |
front 51 What does a positive Catalase test look like? | back 51 Bubbles |
front 52 What does a negative Catalase test look like? | back 52 No bubbles |
front 53 What does a positive Nitrate Reduction test look like? | back 53 Gas (non fermenter), Red color (after addition of reagents A and B), No color change (after addition of Zinc dust.) |
front 54 What does a negative Nitrate Reduction test look like? | back 54 No gas, Red color (after addition of Zinc dust.) |
front 55 What gas is produced from a fermentation test? | back 55 Carbon Dioxide |
front 56 What does a positive Phenol Red test look like? | back 56 Yellow |
front 57 What does a negative Phenol red test look like? | back 57 Red |
front 58 What does a positive Methyl Red test look like? | back 58 Red |
front 59 What does a negative Methyl Red test look like? | back 59 No color change; yellow |
front 60 What does a positive Voges-Proskauer test look like? | back 60 Red ring; red |
front 61 What does a negative Voges-Proskauer test look like? | back 61 No color change; yellow |
front 62 What does a positive Starch Hydrolysis test look like? | back 62 Halo |
front 63 What does a negative Starch Hydrolysis test look like? | back 63 No halo |
front 64 What does a positive Citrate test look like? | back 64 Blue, or there is no color change but growth is present |
front 65 What does a negative Citrate test look like? | back 65 Green, no growth |
front 66 What does a positive Sulfur Reduction test look like? | back 66 Black |
front 67 What does a negative Sulfur Reduction test look like? | back 67 No black in medium; yellow |
front 68 What does a positive Indole test look like? | back 68 Red ring |
front 69 What does a negative Indole test look like? | back 69 No color change; yellow |
front 70 What does a positive Motility test look like? | back 70 Growth radiating outwards from stab line |
front 71 What does a negative Motility test look like? | back 71 No radiating growth |
front 72 What does a positive Gelatinase test look like? | back 72 Liquid |
front 73 What does a negative Gelatinase test look like? | back 73 Solid |
front 74 What does a positive Urease test look like? | back 74 Fuchsia (pink) |
front 75 What does a negative Urease test look like? | back 75 Yellow |
front 76 Oxidase test | back 76  |
front 77 Catalase test | back 77 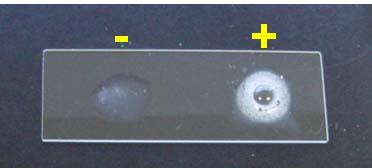 |
front 78 Nitrate Reduction test | back 78  |
front 79 Methyl Red test | back 79  |
front 80 Voges-Proskauer test | back 80  |
front 81 Phenol Red Fermentation test | back 81  |
front 82 Starch Hydrolysis test | back 82 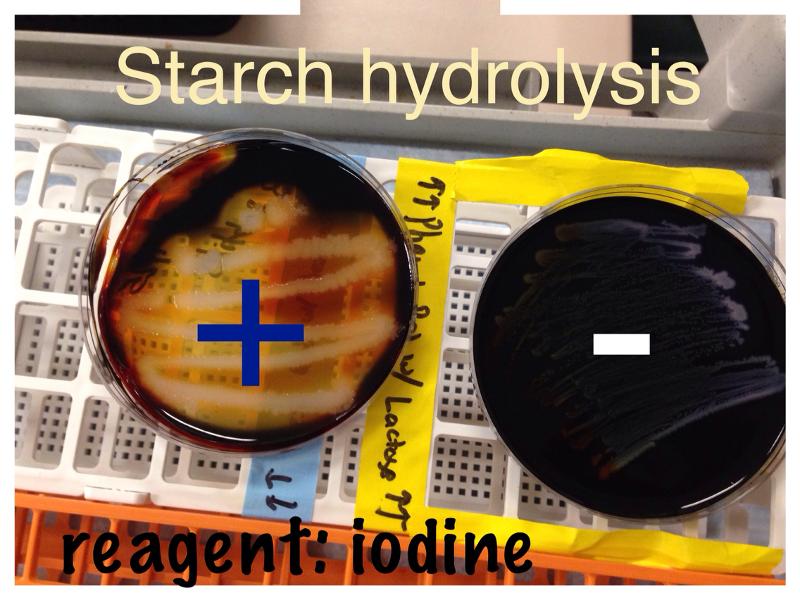 |
front 83 Citrate test | back 83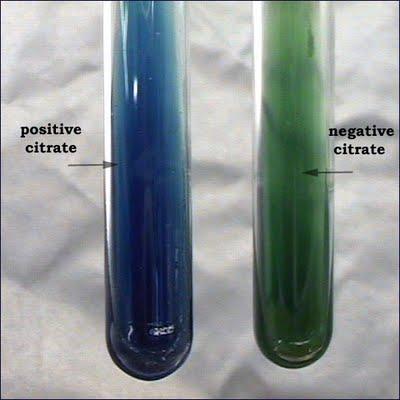  |
front 84 Sulfur test | back 84  |
front 85 Indole test | back 85  |
front 86 Motility test | back 86  |
front 87 Geltinase test | back 87 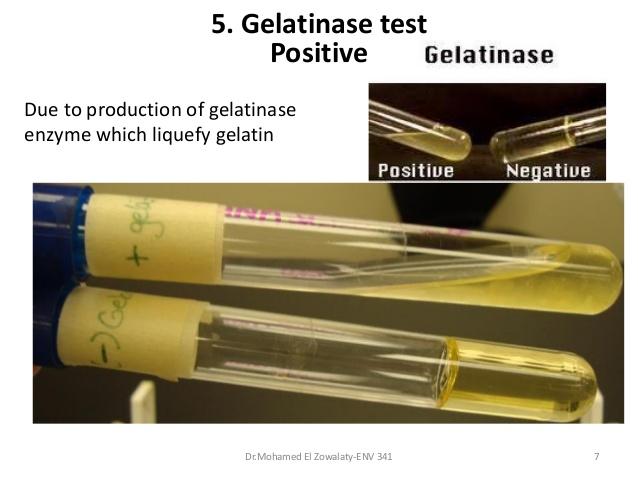 |
front 88 Urease test | back 88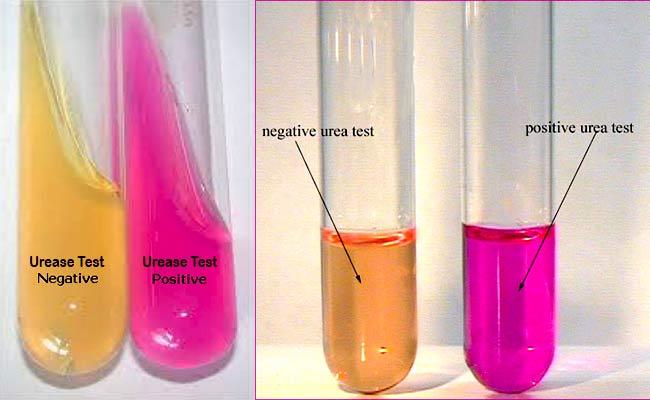  |
front 89  | back 89
|
front 90  | back 90
|
front 91 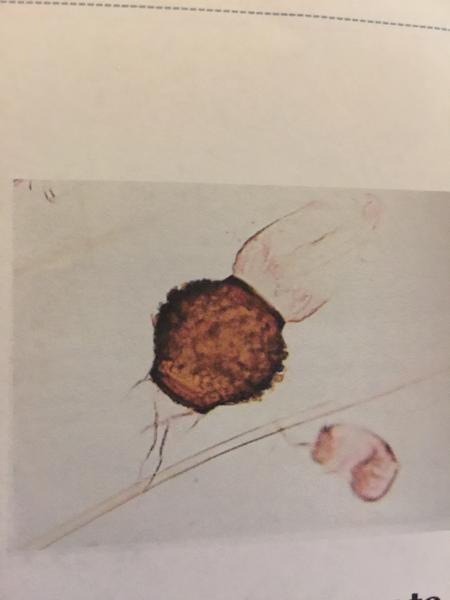 | back 91
|
front 92 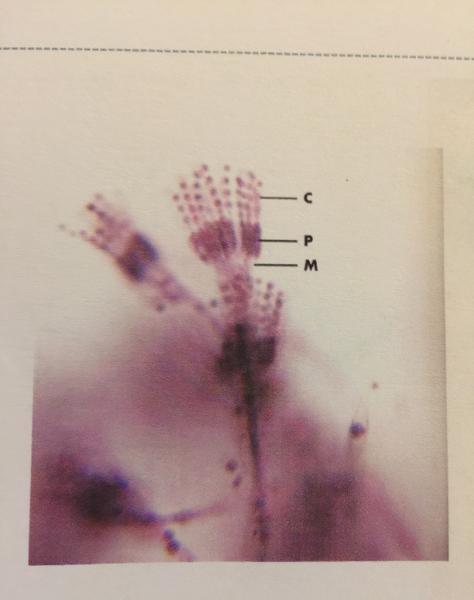 | back 92
|
front 93 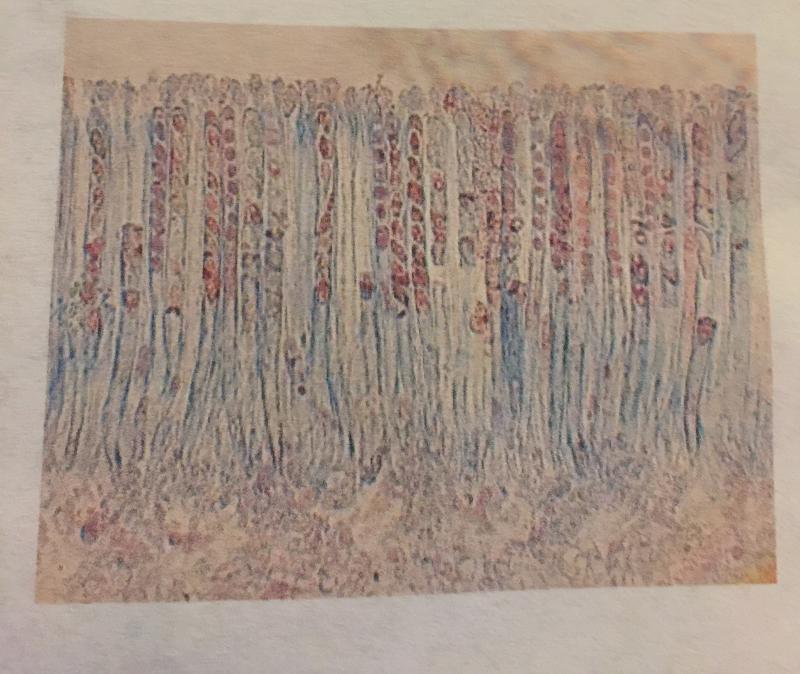 | back 93
|
front 94 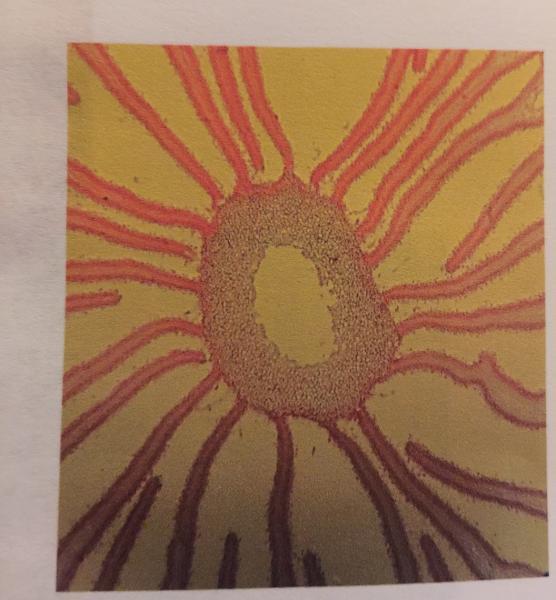 | back 94
|
front 95  | back 95
|
front 96 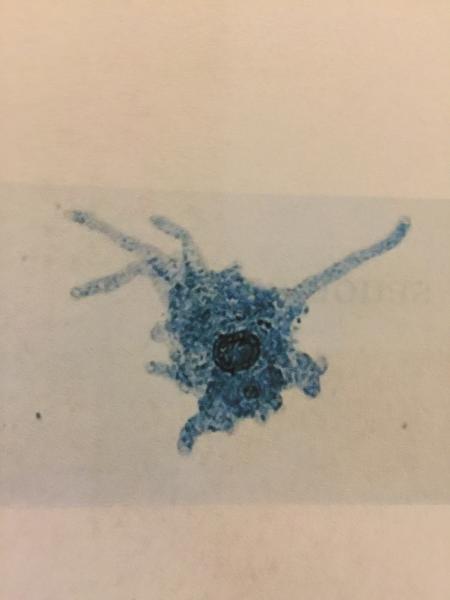 | back 96
|
front 97 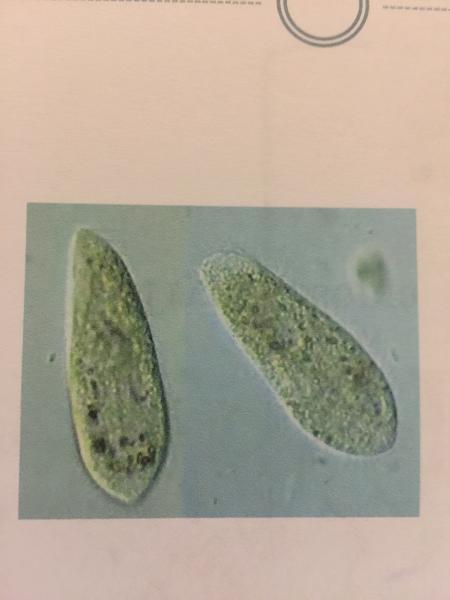 | back 97
|
front 98 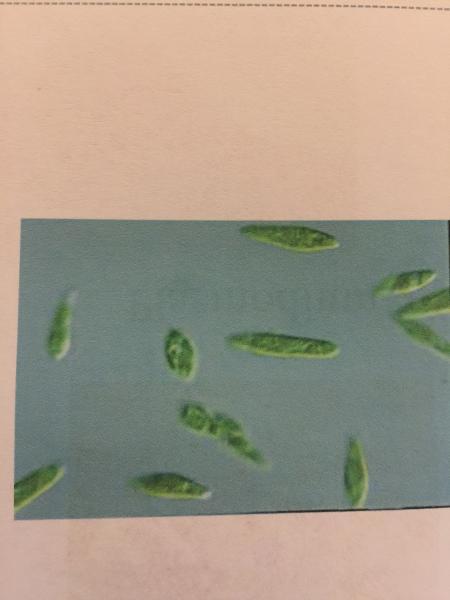 | back 98
|
front 99 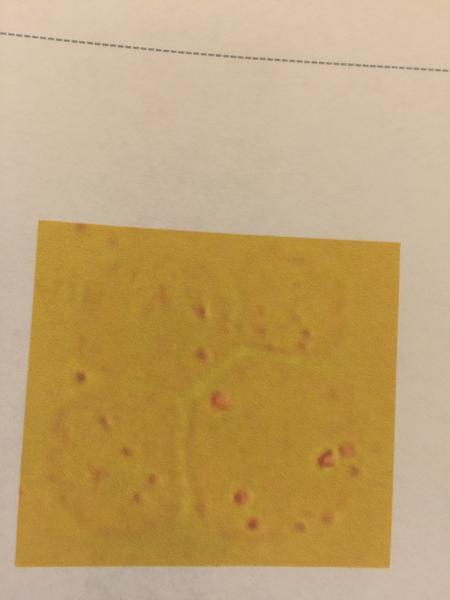 | back 99
|
front 100 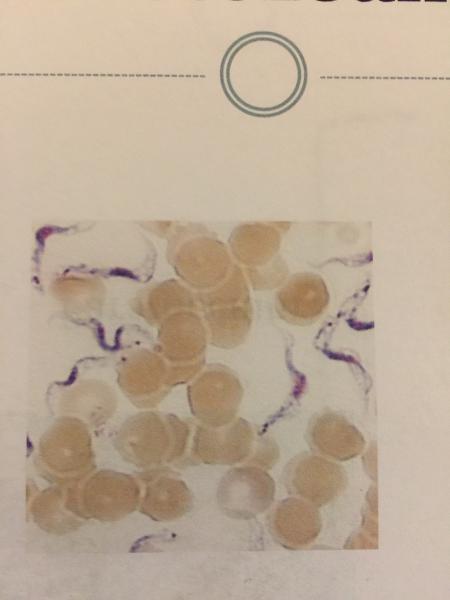 | back 100
|
front 101 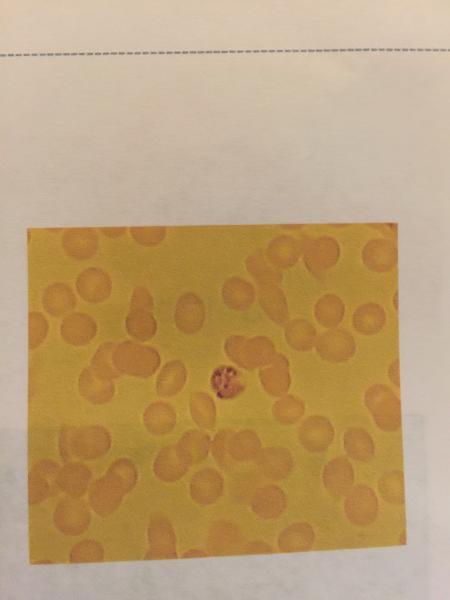 | back 101
|
front 102  | back 102
|
front 103 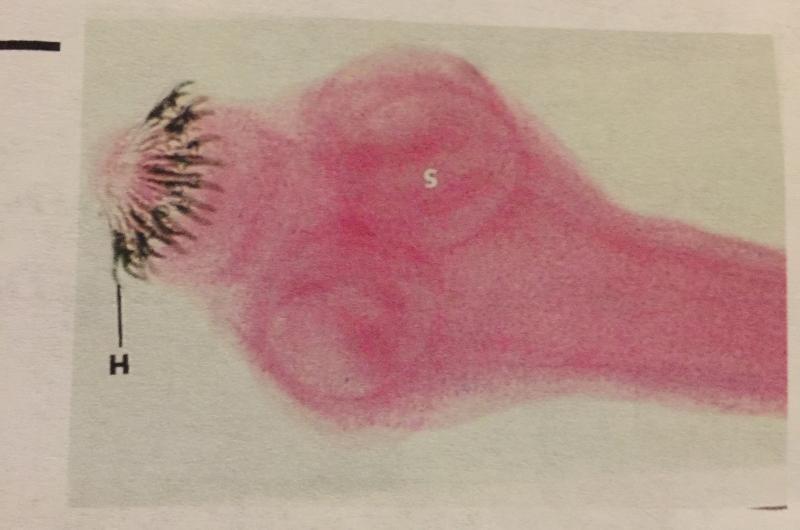 | back 103
|
front 104 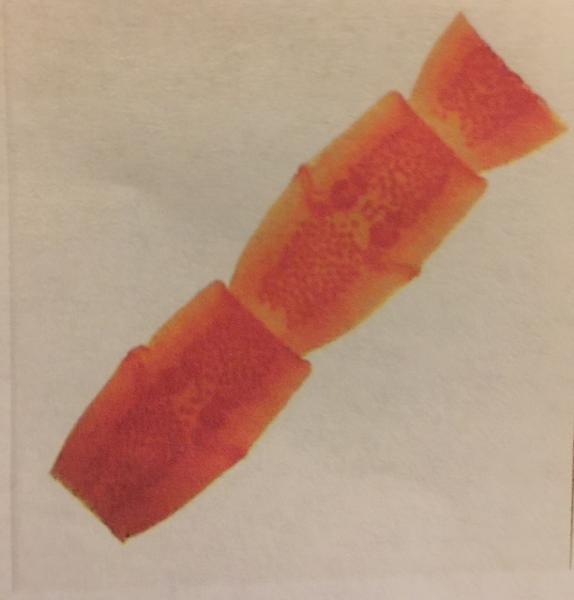 | back 104
|
front 105  | back 105
|
front 106  | back 106
|
front 107 UV light works by Inducting genetic mutations called... | back 107 Thymine Dimmers |
front 108 What kind of Agar does the Kirby-Bauer test use? | back 108 Mueller-Hinton |
front 109 What do you measure in a Kirby-Bauer test? | back 109 Zone of inhibition |
front 110 What do we measure the Zone of Inhibition in? | back 110 Millimeters |
front 111 What does the Membrane Filter Technique use? | back 111 Eosin Methylene Blue agar (EMB) in combination with a membrane filter |
front 112 When is water considered potable in the Membrane Filter Technique? | back 112 If the count is less than 1 coliform per 100 mLs. |
front 113 What color is Methylene blue when it is oxidized? | back 113 Blue |
front 114
What color is Methylene blue when it is reduced? | back 114 Colorless |
front 115 What is an indicator of good quality milk in a Methylene Blue Reductase test? | back 115 It takes more than 6 hours to turn from blue to white. |
front 116 What is the pH indicator in the Snyder test? | back 116 Bromcresol blue |
front 117 What does a positive Snyder test look like? | back 117 Yellow |
front 118 What does a negative Snyder test look like? | back 118 Green |
front 119 The Snyder test is a test to detect... | back 119 The prescience of Lactobacillus in saliva as an indicator of dental care susceptbility. |
front 120 Methylene Blue test | back 120  |
front 121 Snyder test | back 121  Positive is yellow |
front 122 What does color change in less than 24 hours mean on a Snyder test? | back 122 High susceptibility |
front 123 What does color change in less than 48 hours mean on a Snyder test? | back 123 Moderate susceptibility |
front 124 What does no color change 72 hours mean on a Snyder Test? | back 124 Negative result or low susceptibility. |
front 125 The Oxidase test differential for | back 125 Enterobacteriales and Pseudomonas |
front 126 Phenol red differentiates between ______________ and _____________ | back 126 E.Coli and Proteus vulgaris |
front 127 MR/VP differential for | back 127 E.Coli and Enterobacter aerogenes |
front 128 Catalase test differential for | back 128 Staphylococcus areus and Streptococcus |
front 129 Nitrate Reduction differentiates for | back 129 Pseudomonas, Bacillus subtitles, e. coli |
front 130 Citrate test differential for | back 130 E.Coli and Enterobacter aerogenes |
front 131 Starch Hydrolysis differential for | back 131 Bacillus subtitles, pseudomonas arguenosa, e.coli |
front 132 Urease differential for | back 132 Proteus and Enterobacter |
front 133 Gelatinase differential for | back 133 E.Coli and Proteus |
front 134 Sulfur differential for | back 134 E.Coli, Salmonella, Shigella |
front 135 Indole differential for | back 135 E.Coli, Salmonella, Shigella |
front 136 Motility differential for | back 136 E.Coli, Salmonella, Shigella |