The male wasp Campsoscolia ciliata transfers pollen from one orchid
to another orchid of the
same species. What ʺrewardʺ does the
male wasp receive from the orchid plants for helping
with the
orchid pollination?
A) a supply of energy-rich nectar
B)
volatile chemical hormones that help the male wasp find a sexually
receptive female
C) There is no reward. The male wasp is deceived
by the flower shape and odor
D) successful copulation with the
flower
E) a store of nectar that the wasp can use in time of famine
C
For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their
relationship.
(A) The number of cells within the embryo
sac
(B) The number of nuclei within the embryo sac
A) Item
(A) is greater than item (B).
B) Item (A) is less than item
(B).
C) Item (A) is exactly or very approximately equal to item
(B).
D) Item (A) may stand in more than one of the above
relations to item (B).
B
For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their
relationship.
(A) The ploidy of the angiosperm seed
endosperm
(B) The ploidy of the angiosperm seed embryo
A)
Item (A) is greater than item (B).
B) Item (A) is less than item
(B).
C) Item (A) is exactly or very approximately equal to item
(B).
D) Item (A) may stand in more than one of the above
relations to item (B).
A
For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their
relationship.
(A) The percentage of dandelion plants that produce
seeds by apomixis.
(B) The percentage of creosote bushes that
produce seeds by apomixis
A) Item (A) is greater than item
(B).
B) Item (A) is less than item (B).
C) Item (A) is
exactly or very approximately equal to item (B).
D) Item (A) may
stand in more than one of the above relations to item (B)
A
For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their
relationship.
(A) The GABA levels in pop2 mutant Arabidopsis
flowers
(B) The GABA levels in wild-type Arabidopsis
flowers
A) Item (A) is greater than item (B).
B) Item (A) is
less than item (B).
C) Item (A) is exactly or very approximately
equal to item (B).
D) Item (A) may stand in more than one of the
above relations to item (B)
A
For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their
relationship.
(A) The amount of fumonisin in processed maize
products
(B) The amount of fumonisin in processed Bt maize
products
A) Item (A) is greater than item (B).
B) Item (A)
is less than item (B).
C) Item (A) is exactly or very
approximately equal to item (B).
D) Item (A) may stand in more
than one of the above relations to item (B)
B
At the conclusion of meiosis in plants the end products are always
four haploid
A) spores.
B) eggs.
C) sperm.
D)
seeds.
E) gametes.
A
) Which of the following is the correct sequence during the
alternation of generations life
cycle in a flowering
plant?
A)
sporophyte-meiosis-gametophyte-gametes-fertilization-diploid
zygote
B)
sporophyte-mitosis-gametophyte-meiosis-sporophyte
C) haploid
gametophyte-gametes-meiosis-fertilization-diploid sporophyte
D)
sporophyte-spores-meiosis-gametophyte-gametes
E) haploid
sporophyte-spores-fertilization-diploid gametophyte
A
Which of the following is true in plants?
A) Mitosis occurs in
gametophytes to produce gametes.
B) Meiosis occurs in sporophytes
to produce spores.
C) The gametophyte is within the flower in
angiosperms.
D) A and B only
E) A, B, and C
E
) Which of the following are true of most angiosperms?
A) a
triploid endosperm within the seed
B) an ovary that becomes a
fruit
C) a small (reduced) sporophyte
D) A and B
only
E) A, B, and C
D
Based on studies of plant evolution, which flower part is not a
modified leaf?
A) stamen
B) carpel
C) petals
D)
sepals
E) receptacle
E
All of the following floral parts are directly involved in
pollination or fertilization except the
A) stamen.
B)
carpel.
C) petals.
D) sepals.
E) receptacle.
D
Location of the ovary:
A) stamen
B) carpel
C)
petals
D) sepals
E) receptacle
B
Location of the microsporangia:
A) stamen
B) carpel
C)
petals
D) sepals
E) receptacle
A
) Which of the following is the correct order of floral organs from
the outside to the inside of a
complete flower?
A)
petals-sepals-stamens-carpels
B)
sepals-stamens-petals-carpels
C)
spores-gametes-zygote-embryo
D)
sepals-petals-stamens-carpels
E) male gametophyte-female gametophyte-sepals-petals
D
In some angiosperms, other floral parts contribute to what is
commonly called the fruit.
Which of the following fruits is
derived mostly from an enlarged receptacle?
A) pea
B)
raspberry
C) apple
D) pineapple
E) peach
C
All of the following are primary functions of flowers except
A)
pollen production.
B) photosynthesis.
C) meiosis.
D)
egg production.
E) sexual reproduction.
B
) Meiosis occurs within all of the following flower parts except
the
A) ovule.
B) style.
C) megasporangium.
D)
anther.
E) ovary.
B
A perfect flower is fertile, but may be either complete or
incomplete. Which of the following
correctly describes a perfect
flower?
A) It has no sepals.
B) It has fused
carpels.
C) It is on a dioecious plant.
D) It has no
endosperm.
E) It has both stamens and carpels
E
Carpellate flowers
A) are perfect.
B) are complete.
C)
produce pollen.
D) are found only on dioecious plants.
E)
develop into fruits.
E
Which of the following statements regarding flowering plants is
false?
A) The sporophyte is the dominant generation.
B)
Female gametophytes develop from megaspores within the
anthers.
C) Pollination is the placing of pollen on the stigma of
a carpel.
D) The food-storing endosperm is derived from the cell
that contains two polar nuclei
and one sperm nucleus.
E)
Flowers produce fruits within the ovul
B
Which of the following types of plants is not able to
self-pollinate?
A) dioecious
B) monoecious
C)
complete
D) wind-pollinated
E) insect-pollinated
A
) In flowering plants, pollen is released from the
A)
anther.
B) stigma.
C) carpel.
D) filament.
E)
pollen tube.
A
In the life cycle of an angiosperm, which of the following stages is
diploid?
A) megaspore
B) generative nucleus of a pollen
grain
C) polar nuclei of the embryo sac
D)
microsporocyte
E) both megaspore and polar nuclei
D
Where does meiosis occur in flowering plants?
A)
megasporocyte
B) microsporocyte
C) endosperm
D) pollen
tube
E) megasporocyte and microsporocyte
E
Which of the following is a correct sequence of processes that takes
place when a flowering
plant reproduces?
A)
meiosis-fertilization-ovulation-germination
B)
fertilization-meiosis-nuclear fusion-formation of embryo and
endosperm
C) meiosis-pollination-nuclear fusion-formation of
embryo and endosperm
D) growth of pollen
tube-pollination-germination-fertilization
E)
meiosis-mitosis-nuclear fusion-pollen
C
Which of these is incorrectly paired with its life-cycle
generation?
A) anthergametophyte
B)
pollengametophyte
C) embryo sacgametophyte
D)
stamensporophyte
E) embryosporophyte
A
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in a pollen
sac?
A) sporangiameiosistwo haploid cellsmeiosistwo pollen
grains per cell
B) pollen grainmeiosistwo generative cellstwo
tube cells per pollen grain
C) two haploid
cellsmeiosisgenerative cell-tube cellfertilizationpollen
grain
D) pollen grainmitosismicrosporesmeiosisgenerative cell
plus tube cell
E) microsporocytemeiosismicrosporesmitosistwo
haploid cells per pollen grain
E
Which of the following occurs in an angiosperm ovule?
A) An
antheridium forms from the megasporophyte.
B) A megaspore mother
cell undergoes meiosis.
C) The egg nucleus is usually
diploid.
D) A pollen tube emerges to accept pollen after
pollination.
E) The endosperm surrounds the megaspore mother cell.
B
Where and by which process are sperm cells formed in plants?
A)
meiosis in pollen grains
B) meiosis in anthers
C) mitosis in
male gametophyte pollen tube.
D) mitosis in the micropyle
E)
mitosis in the embryo sac
C
In which of the following pairs are the two terms equivalent?
A)
ovuleegg
B) embryo sacfemale gametophyte
C) endospermmale
gametophyte
D) seedzygote
E) microsporepollen grain
B
Which of the following is the male gametophyte of a flowering
plant?
A) ovule
B) microsporocyte
C) pollen
grain
D) embryo sac
E) stamen
C
33) Which of the following would be considered to be a multiple
fruit?
A) apple
B) strawberry
C) raspberry
D)
pineapple
E) corn on the cob
D
In flowering plants, a mature male gametophyte contains
A) two
haploid gametes and a diploid pollen grain.
B) a generative cell
and a tube cell.
C) two sperm nuclei and one tube cell
nucleus.
D) two haploid microspores.
E) a haploid nucleus
and a diploid pollen wall.
C
Three mitotic divisions within the female gametophyte of the
megaspore produce
A) three antipodal cells, two polar nuclei, one
egg, and two synergids.
B) the triple fusion nucleus.
C)
three pollen grains.
D) two antipodal cells, two polar nuclei,
two eggs, and two synergids.
E) a tube nucleus, a generative
cell, and a sperm cell.
A
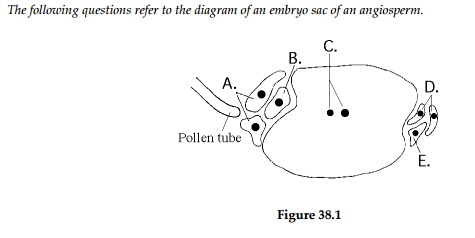
Which cell(s), after fertilization, give(s) rise to the embryo plant?
B

Which cell(s) become(s) the triploid endosperm?
C

Which cell(s) guide(s) the pollen tube to the egg cell?
A
What is the difference between pollination and fertilization in
flowering plants?
A) Fertilization precedes pollination.
B)
Pollination easily occurs between plants of different species,
fertilization is within a
species.
C) Pollen is formed
within megasporangia so that male and female gametes are
near
each other.
D) Pollination is the transfer of pollen
from an anther to a stigma. Fertilization is the
fusion of
haploid nuclei
E) If fertilization occurs, pollination is unnecessary.
D
Recent research has shown that pollination requires that carpels
recognize pollen grains as
ʺself or nonself.ʺ For
self-incompatibility, the system requires
A) rejection of nonself
cells.
B) the rejection of self cells.
C) carpel
incompatibility with the egg cells.
D) that the flowers be
incomplete.
E) the union of genetically identical sperm and egg cells.
B
) Genetic incompatibility does not affect the
A) attraction of a
suitable insect pollinator.
B) germination of the pollen on the
stigma.
C) growth of the pollen tube in the style.
D)
membrane permeability of cells.
E) different individuals of the
same species.
A
You are studying a plant from the Amazon that shows strong
self-incompatibility. To
characterize this reproductive
mechanism, you would look for
A) ribonuclease (RNAase) activity
in stigma cells.
B) RNA in the plants.
C) pollen grains with
very thick walls.
D) carpels that cannot produce eggs by
meiosis.
E) systems of wind, but not insect, pollination.
A
What effects would occur in a mutant of Arabidopsis that cannot
synthesize GABA within its
flowers?
A) Pollen tube growth
would not be directed toward the egg, and fertilization would
not
occur.
B) The seeds from the flowers would be unable to
break dormancy.
C) The pollen grain would not form a pollen tube
due to incompatibility with the pollen
tube.
D) The length
of the style would be increased to the point where the growing pollen
tube
would be unable to reach the synergids.
A
Biofuels are mainly produced by
A) the breakdown of cell wall
biopolymers into sugars that can be fermented.
B) plants that
convert hemicellulose into gasoline.
C) the genetic engineering
of ethanol generating genes into plants.
D) transgenic crops that
have cell walls containing ethylene.
E) plants that are easy to
grow in arid environments.
A
A plant that has small, green petals is most likely to be
A)
bee-pollinated.
B) bird-pollinated.
C)
bat-pollinated.
D) wind-pollinated.
E) moth-pollinated.
D
A seed develops from
A) an ovum.
B) a pollen grain.
C)
an ovule.
D) an ovary.
E) an embryo.
C
A fruit is a(an)
A) mature ovary.
B) mature ovule.
C)
seed plus its integuments.
D) fused carpel.
E) enlarged
embryo sac.
A
Double fertilization means that
A) flowers must be pollinated
twice in order to produce fruits and seeds.
B) every egg must
receive two sperm to produce an embryo.
C) one sperm is needed to
fertilize the egg, and a second sperm is needed to fertilize
the
polar nuclei.
D) the egg of the embryo sac is
diploid.
E) every sperm has two nuclei.
C
Some dioecious species have the XY genotype for male and XX for
female. After double
fertilization, what would be the genotypes
of the endosperm nuclei and embryos?
A) embryo X and endosperm XX
or embryo Y and endosperm XY
B) embryo XX and endosperm XX or
embryo XY and endosperm XY
C) embryo XX and endosperm XXX or
embryo XY and endosperm XYY
D) embryo XX and endosperm XXX or
embryo XY and endosperm XXY
E) embryo XY and endosperm XXX or
embryo XX and endosperm XXY
D
Sources of genetic variability in an asexually propagated species may
involve all of the
following processes except
A) protoplast
fusion.
B) mutation.
C) hybridization.
D) genetic
engineering.
E) apomixis.
C
Plant biotechnologists use protoplast fusion mainly to
A)
culture plant cells in vitro.
B) asexually propagate desirable
plant varieties.
C) introduce bacterial genes into a plant
genome.
D) study the early events following
fertilization.
E) produce new hybrid species.
E
The basal cell formed from the first division of a plant zygote will
eventually develop into
A) the suspensor that anchors the embryo
and transfers nutrients.
B) the proembryo.
C) the endosperm
that nourishes the developing embryo.
D) the root apex of the
embryo.
E) two cotyledons in eudicots, but one in monocots.
A
) The development of Bt crops raises concerns because
A) Bt
crops have been shown to be toxic to humans.
B) pollen from these
crops is harmful to monarch butterfly larvae in the field.
C) if
genes for Bt toxin ʺescapeʺ to related weed species, the hybrid weeds
could have
harmful ecological effects.
D) Bacillus
thuringiensis is a pathogen of humans.
E) Bt toxin reduces the
nutritional quality of crops.
C
ʺGolden Riceʺ is a transgenic variety that
A) is resistant to
various herbicides, making it practical to weed rice fields with
those
herbicides.
B) is resistant to a virus that commonly
attacks rice fields.
C) includes bacterial genes that produce a
toxin that reduces damage from insect pests.
D) produces much
larger, golden grains that increase crop yields.
E) contains
daffodil genes that increase vitamin A content.
E