Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
AP Biology Chapter 38
front 1 The male wasp Campsoscolia ciliata transfers pollen from one orchid
to another orchid of the | back 1 C |
front 2 For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their
relationship. | back 2 B |
front 3 For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their
relationship. | back 3 A |
front 4 For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their
relationship. | back 4 A |
front 5 For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their
relationship. | back 5 A |
front 6 For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their
relationship. | back 6 B |
front 7 At the conclusion of meiosis in plants the end products are always
four haploid | back 7 A |
front 8 ) Which of the following is the correct sequence during the
alternation of generations life | back 8 A |
front 9 Which of the following is true in plants? | back 9 E |
front 10 ) Which of the following are true of most angiosperms? | back 10 D |
front 11 Based on studies of plant evolution, which flower part is not a
modified leaf? | back 11 E |
front 12 All of the following floral parts are directly involved in
pollination or fertilization except the | back 12 D |
front 13 Location of the ovary: | back 13 B |
front 14 Location of the microsporangia: | back 14 A |
front 15 ) Which of the following is the correct order of floral organs from
the outside to the inside of a | back 15 D |
front 16 In some angiosperms, other floral parts contribute to what is
commonly called the fruit. | back 16 C |
front 17 All of the following are primary functions of flowers except | back 17 B |
front 18 ) Meiosis occurs within all of the following flower parts except
the | back 18 B |
front 19 A perfect flower is fertile, but may be either complete or
incomplete. Which of the following | back 19 E |
front 20 Carpellate flowers | back 20 E |
front 21 Which of the following statements regarding flowering plants is
false? | back 21 B |
front 22 Which of the following types of plants is not able to
self-pollinate? | back 22 A |
front 23 ) In flowering plants, pollen is released from the | back 23 A |
front 24 In the life cycle of an angiosperm, which of the following stages is
diploid? | back 24 D |
front 25 Where does meiosis occur in flowering plants? | back 25 E |
front 26 Which of the following is a correct sequence of processes that takes
place when a flowering | back 26 C |
front 27 Which of these is incorrectly paired with its life-cycle
generation? | back 27 A |
front 28 Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in a pollen
sac? | back 28 E |
front 29 Which of the following occurs in an angiosperm ovule? | back 29 B |
front 30 Where and by which process are sperm cells formed in plants? | back 30 C |
front 31 In which of the following pairs are the two terms equivalent? | back 31 B |
front 32 Which of the following is the male gametophyte of a flowering
plant? | back 32 C |
front 33 33) Which of the following would be considered to be a multiple
fruit? | back 33 D |
front 34 In flowering plants, a mature male gametophyte contains | back 34 C |
front 35 Three mitotic divisions within the female gametophyte of the
megaspore produce | back 35 A |
front 36 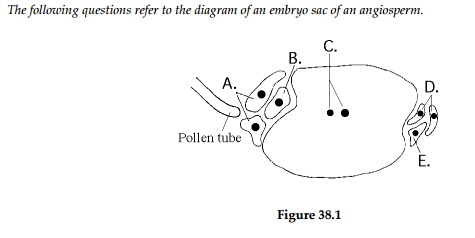 Which cell(s), after fertilization, give(s) rise to the embryo plant? | back 36 B |
front 37  Which cell(s) become(s) the triploid endosperm? | back 37 C |
front 38  Which cell(s) guide(s) the pollen tube to the egg cell? | back 38 A |
front 39 What is the difference between pollination and fertilization in
flowering plants? | back 39 D |
front 40 Recent research has shown that pollination requires that carpels
recognize pollen grains as | back 40 B |
front 41 ) Genetic incompatibility does not affect the | back 41 A |
front 42 You are studying a plant from the Amazon that shows strong
self-incompatibility. To | back 42 A |
front 43 What effects would occur in a mutant of Arabidopsis that cannot
synthesize GABA within its | back 43 A |
front 44 Biofuels are mainly produced by | back 44 A |
front 45 A plant that has small, green petals is most likely to be | back 45 D |
front 46 A seed develops from | back 46 C |
front 47 A fruit is a(an) | back 47 A |
front 48 Double fertilization means that | back 48 C |
front 49 Some dioecious species have the XY genotype for male and XX for
female. After double | back 49 D |
front 50 Sources of genetic variability in an asexually propagated species may
involve all of the | back 50 C |
front 51 Plant biotechnologists use protoplast fusion mainly to | back 51 E |
front 52 The basal cell formed from the first division of a plant zygote will
eventually develop into | back 52 A |
front 53 ) The development of Bt crops raises concerns because | back 53 C |
front 54 ʺGolden Riceʺ is a transgenic variety that | back 54 E |