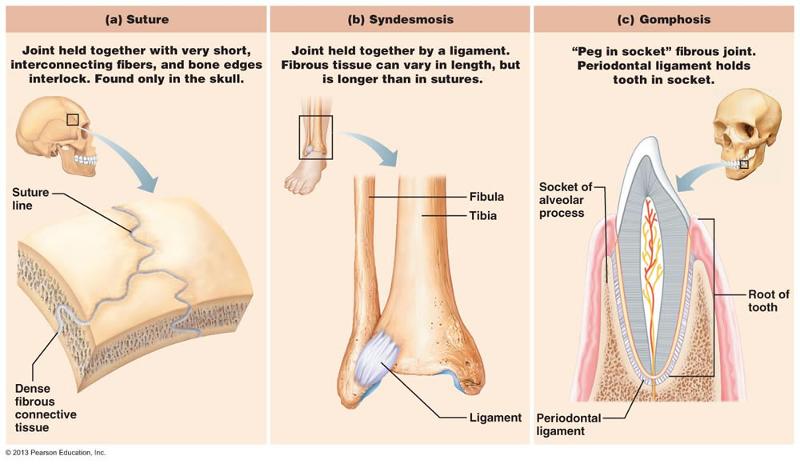
Structural Categories of Joints
Fibrous
Adjoining bones connected by dense regular connective, no joint
cavity.
Types
-suture; between parietal and temporal
bone
-syndesmosis (long fibers) : between tibia and
fibula
-gomphosis: Tooth in bony sockets
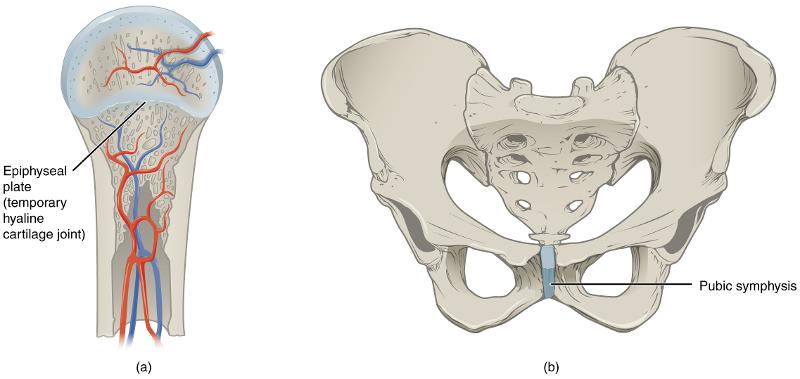
Cartilaginous
adjoining bones united by cartilage, no joint cavity. synchondrosis (hyaline cartilage)- between the coastal cartilage of rib 1 and the sternum and the epiphyseal plate in growing long bones
symphysis - .Inter vertebral discs between adjacent vertebrae and the anterior connection between the pubic bones.
Symphysis (fibrocartilage)
Inter vertebral discs between adjacent vertebrae and the anterior connection between the pubic bones.
synovial (covered in articular cartilage)
Adjoining bones covered in articular cartilage; separated by a joint cavity and enclosed in an articular capsule lined with a synovial membranes.
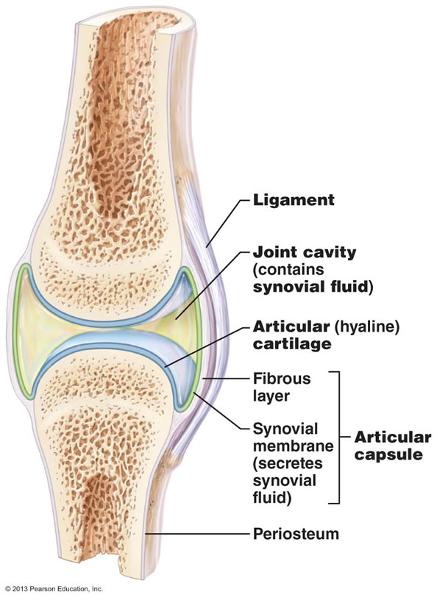
Structural Features of Synovial Joint
joint cavity- space between the articulating
bones.
ligament-located on outsides of articular capsule.
reinforces the joint.
articular cartilage- hyaline cartilage that
covers the surface of the bones forming the joints
articular
capsule - composed of fibrous layer and synovial membrane- secretes
the synovial fluid
synovial fluid- a viscous fluid located in
joint cavity. acts as a lubricant to reduce friction.
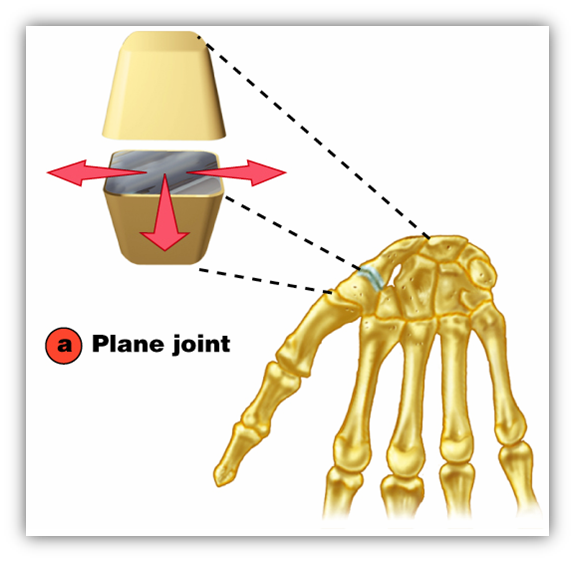
plane
between the carpals of the wrist. Flat or slightly curved bones. Non axial;gliding
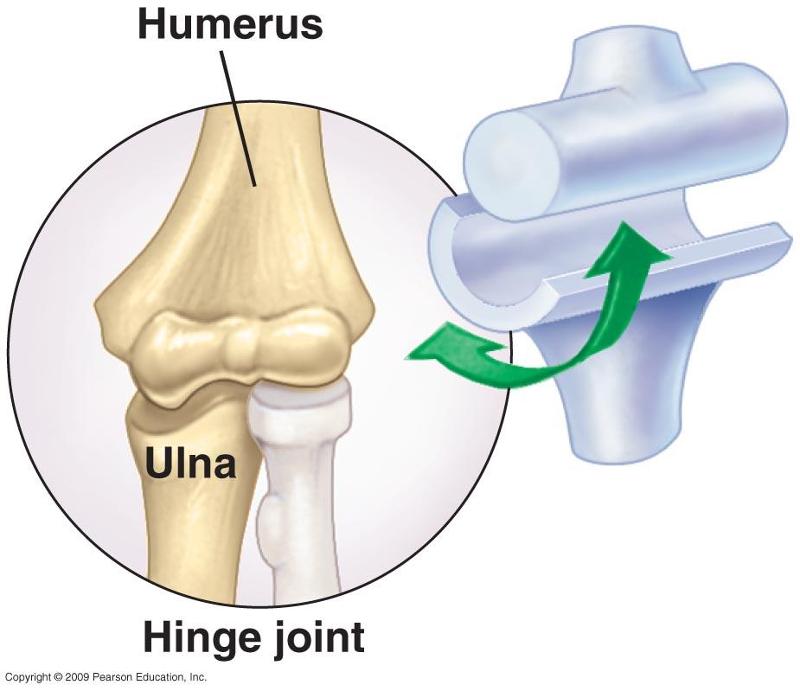
hinge
elbow, a rounded or cylindrical bone fits into a concave surface on the other bone. uni axial; flexion and extension
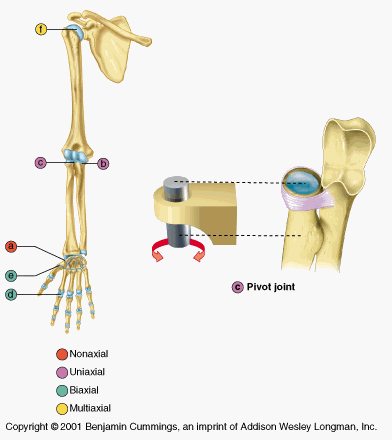
pivot
proximal radio ulnar. a rounded bone fits into a sleeve ( a concave bones plus a ligament)
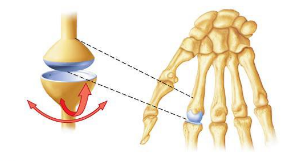
condylar
between the metacarpals and proximal phalanx. An oval condyle fits into an oval depression on the other bone. Bi axial; flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction
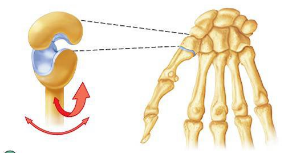
saddle joint
between the trapezium (carpal) and metatarsal 1. articulating surfaces are saddle shaped; one surface concave, the other surface is convex.
ball and socket
shoulder, and hip joints. The ball shaped head of the bone fits into the cup like depression of the other bone. multi axial. flexion extension, adduction, abduction, rotation
insertion
the more movable attachment, moves toward origin during muscle contraction.
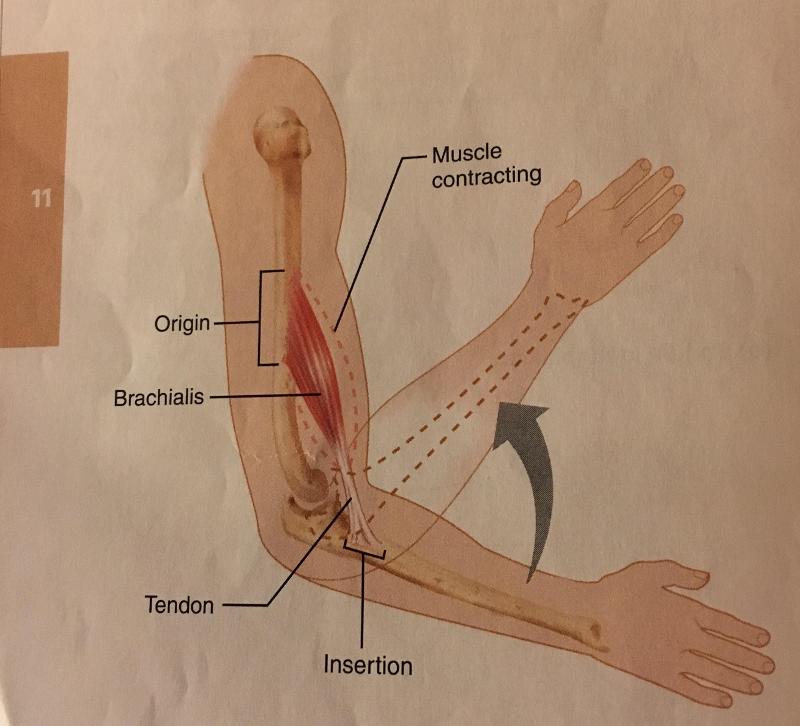
origin
the stationary, immovable, or less movable attachment
flexion
A movement, generally in the sagittal plane, that decrease the angle of the joint and reduces the distance between 2 bones. Common in hinge joints and ball and socket.
extension
increases the angle of a joint and the distance between 2 bones or parts of the body, opposite of flexion. if extension exceeds beyond anatomical position it is considered hyper extension.
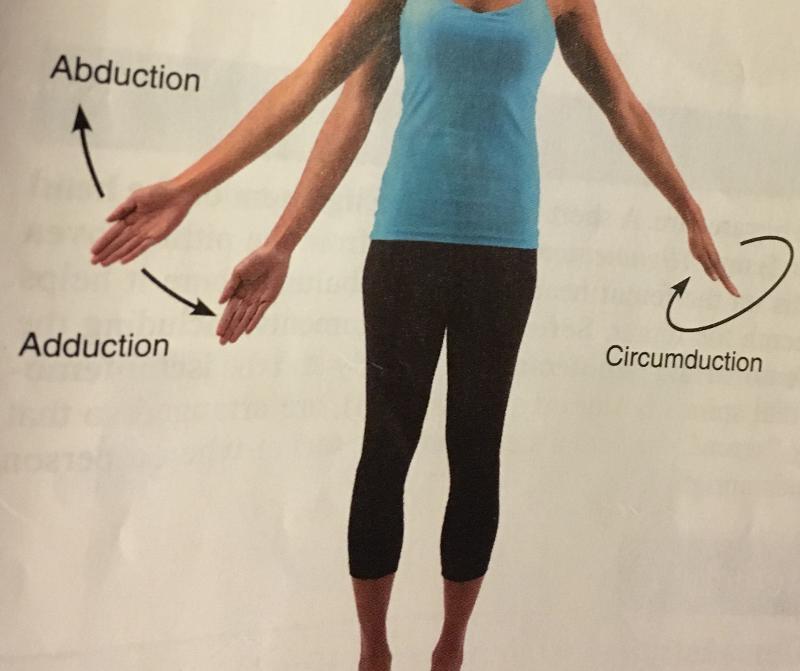
abduction
movement of a limb away from the mid-line of the body, along the frontal plane or the fanning movement of fingers or toes when they're spread.
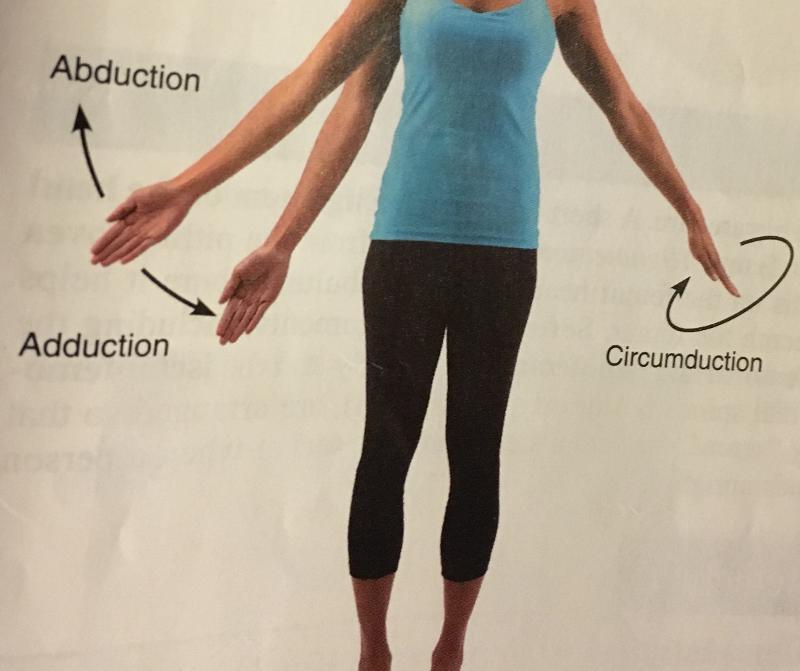
adduction
movement of limb toward the mid line of the body or drawing the fingers or toes together. opposite of abduction
rotation
Bone around its longitudinal axis without lateral or medial displacement. common in ball and socket joints
circumduction
A combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction. common in ball and socket joints
pronation
Movement of palm of the hand from an anterior / upward facing position to a posterior/ downward position.distal end of radius and ulna cross to form a X.
supination
Movement of palm from a posterior position to an anterior position the anatomical position the opposite of pronation. the radius and ulna are parallel.
dorsi flexion
a movement of the ankle joint that lifts the foot so that its superior surface approaches the shin.
plantar flexion
ankle joint in which the foot is flexed downwards as if standing on ones toes or pointing the toes.
inversion
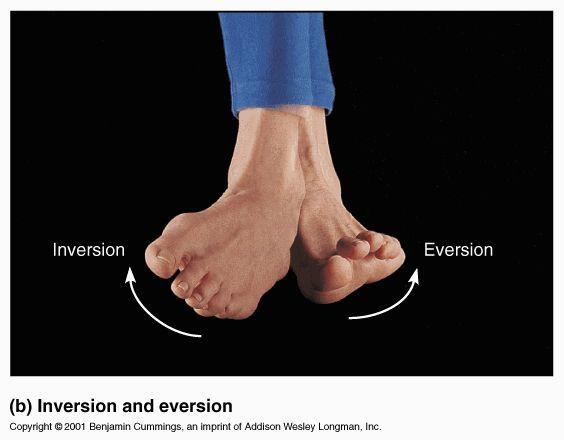
turns the sole of the foot medially
eversion
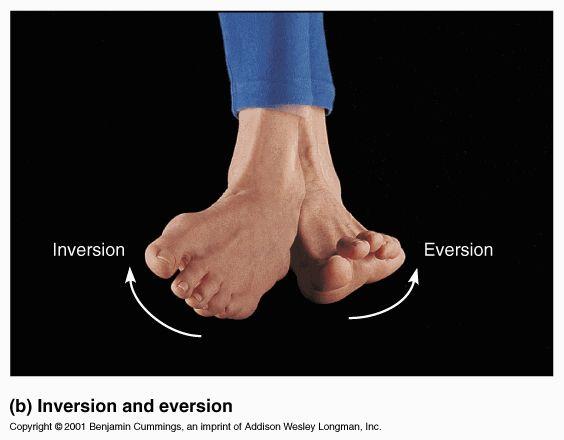
turns the sole of the foot laterally; opposite of inversion