Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Articulation and Body Movement A&P 1 Lab Quiz 3
front 1 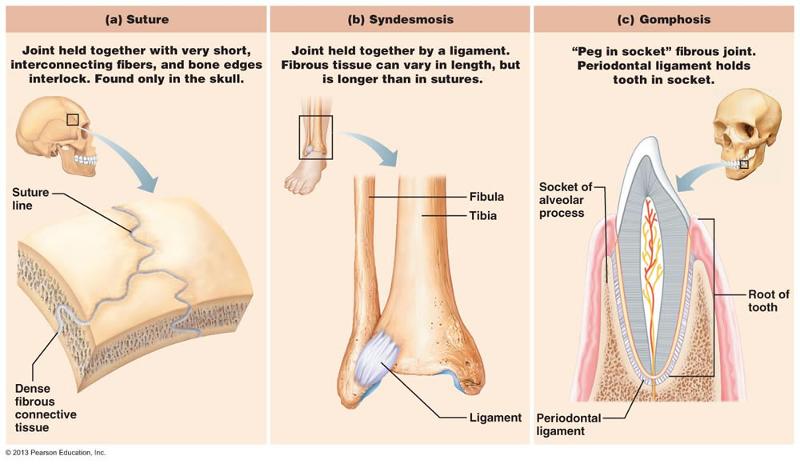 Structural Categories of Joints Fibrous | back 1 Adjoining bones connected by dense regular connective, no joint
cavity. |
front 2 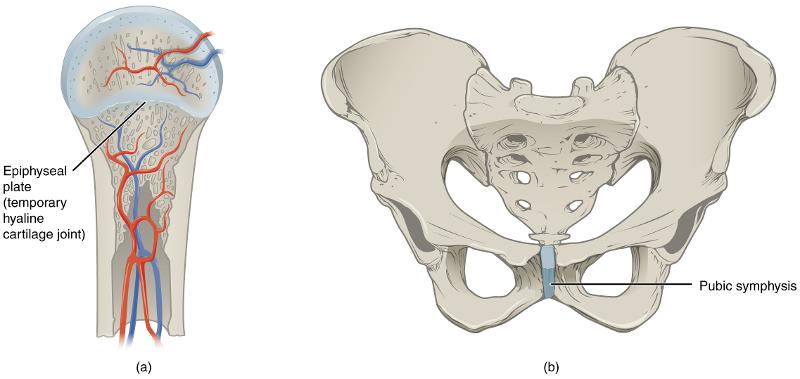 Cartilaginous | back 2 adjoining bones united by cartilage, no joint cavity. synchondrosis (hyaline cartilage)- between the coastal cartilage of rib 1 and the sternum and the epiphyseal plate in growing long bones symphysis - .Inter vertebral discs between adjacent vertebrae and the anterior connection between the pubic bones. |
front 3 Symphysis (fibrocartilage) | back 3 Inter vertebral discs between adjacent vertebrae and the anterior connection between the pubic bones. |
front 4 synovial (covered in articular cartilage) | back 4 Adjoining bones covered in articular cartilage; separated by a joint cavity and enclosed in an articular capsule lined with a synovial membranes. |
front 5 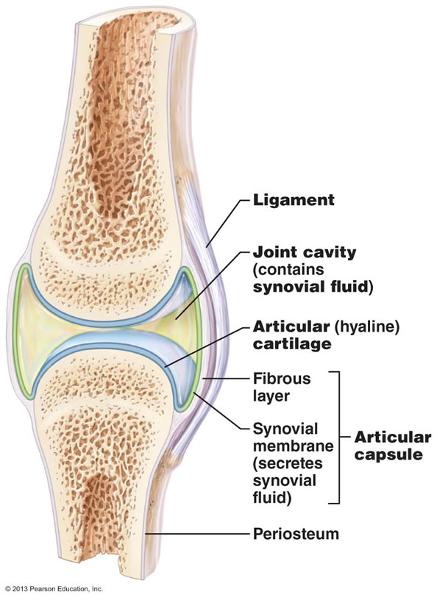 Structural Features of Synovial Joint | back 5 joint cavity- space between the articulating
bones. |
front 6 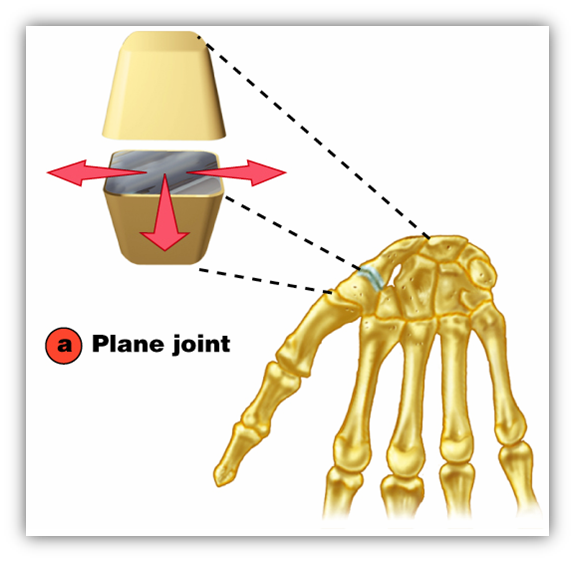 plane | back 6 between the carpals of the wrist. Flat or slightly curved bones. Non axial;gliding |
front 7 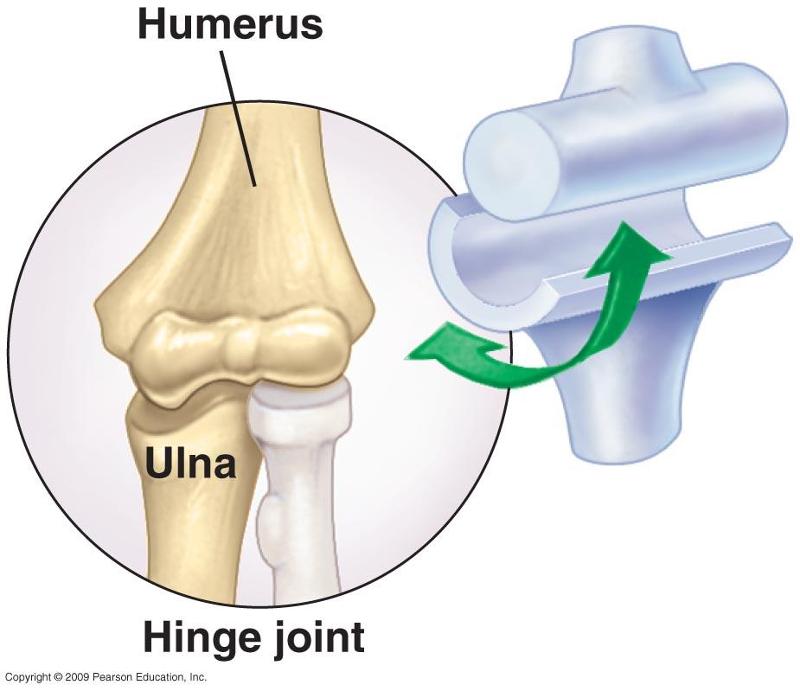 hinge | back 7 elbow, a rounded or cylindrical bone fits into a concave surface on the other bone. uni axial; flexion and extension |
front 8 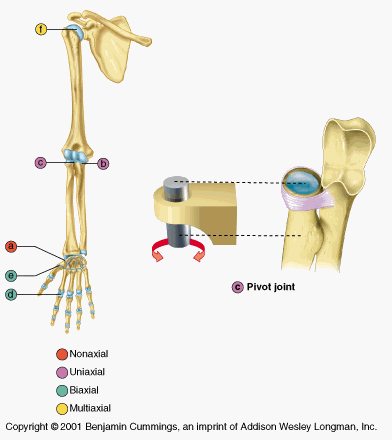 pivot | back 8 proximal radio ulnar. a rounded bone fits into a sleeve ( a concave bones plus a ligament) |
front 9 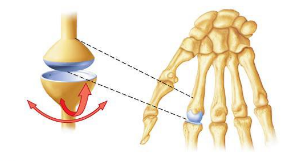 condylar | back 9 between the metacarpals and proximal phalanx. An oval condyle fits into an oval depression on the other bone. Bi axial; flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction |
front 10 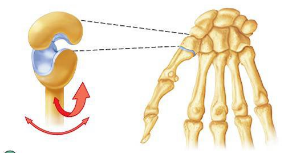 saddle joint | back 10 between the trapezium (carpal) and metatarsal 1. articulating surfaces are saddle shaped; one surface concave, the other surface is convex. |
front 11 ball and socket | back 11 shoulder, and hip joints. The ball shaped head of the bone fits into the cup like depression of the other bone. multi axial. flexion extension, adduction, abduction, rotation |
front 12 insertion | back 12 the more movable attachment, moves toward origin during muscle contraction. |
front 13 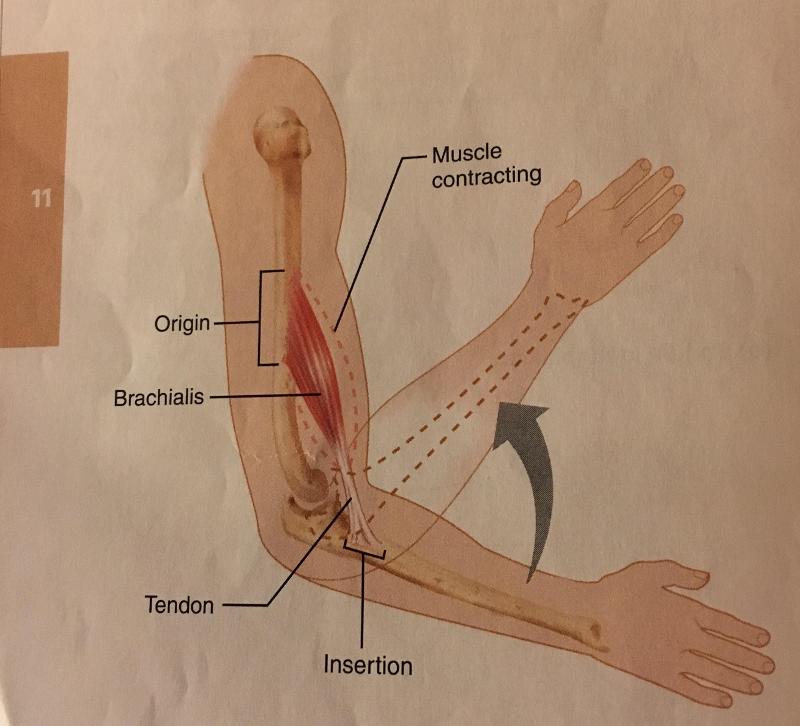 origin | back 13 the stationary, immovable, or less movable attachment |
front 14 flexion | back 14 A movement, generally in the sagittal plane, that decrease the angle of the joint and reduces the distance between 2 bones. Common in hinge joints and ball and socket. |
front 15 extension | back 15 increases the angle of a joint and the distance between 2 bones or parts of the body, opposite of flexion. if extension exceeds beyond anatomical position it is considered hyper extension. |
front 16 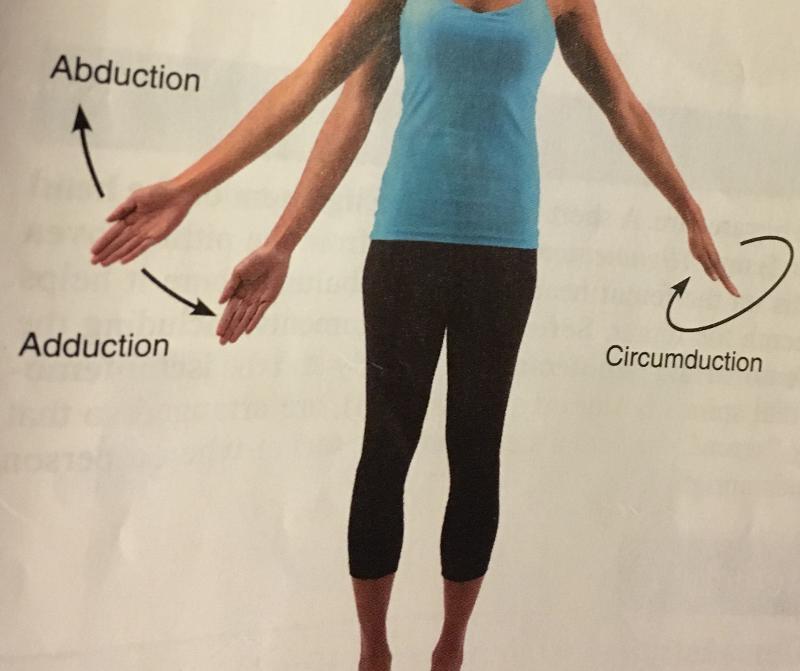 abduction | back 16 movement of a limb away from the mid-line of the body, along the frontal plane or the fanning movement of fingers or toes when they're spread. |
front 17 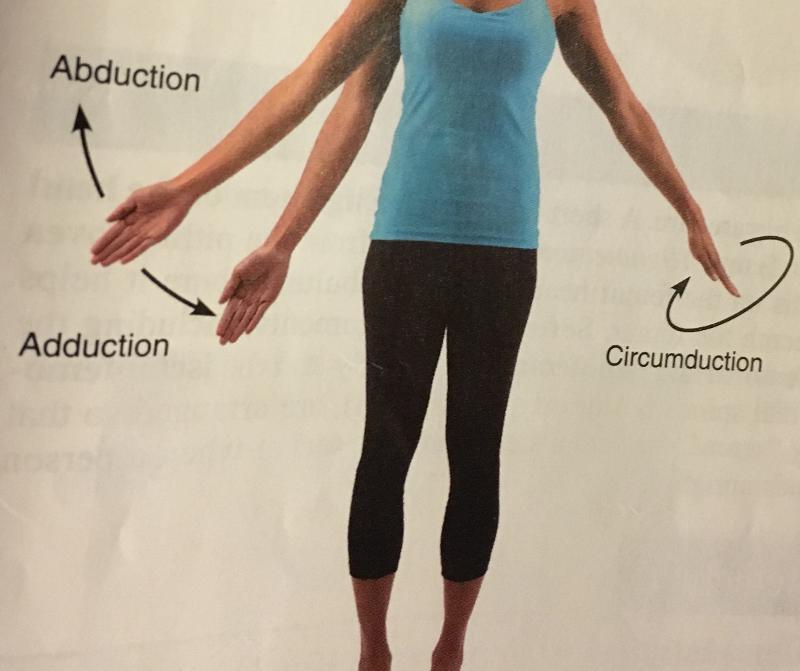 adduction | back 17 movement of limb toward the mid line of the body or drawing the fingers or toes together. opposite of abduction |
front 18 rotation | back 18 Bone around its longitudinal axis without lateral or medial displacement. common in ball and socket joints |
front 19 circumduction | back 19 A combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction. common in ball and socket joints |
front 20 pronation | back 20 Movement of palm of the hand from an anterior / upward facing position to a posterior/ downward position.distal end of radius and ulna cross to form a X. |
front 21 supination | back 21 Movement of palm from a posterior position to an anterior position the anatomical position the opposite of pronation. the radius and ulna are parallel. |
front 22 dorsi flexion | back 22 a movement of the ankle joint that lifts the foot so that its superior surface approaches the shin. |
front 23 plantar flexion | back 23 ankle joint in which the foot is flexed downwards as if standing on ones toes or pointing the toes. |
front 24 inversion | back 24 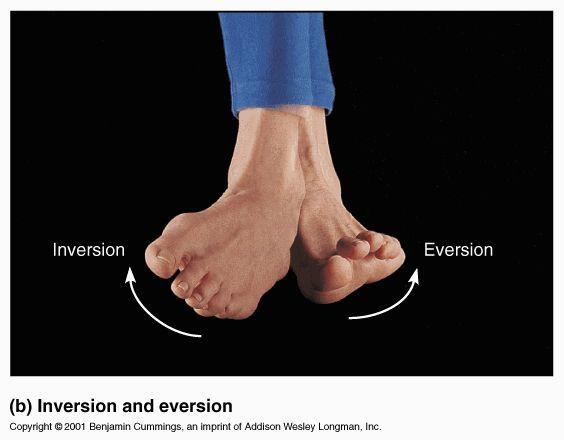 turns the sole of the foot medially |
front 25 eversion | back 25 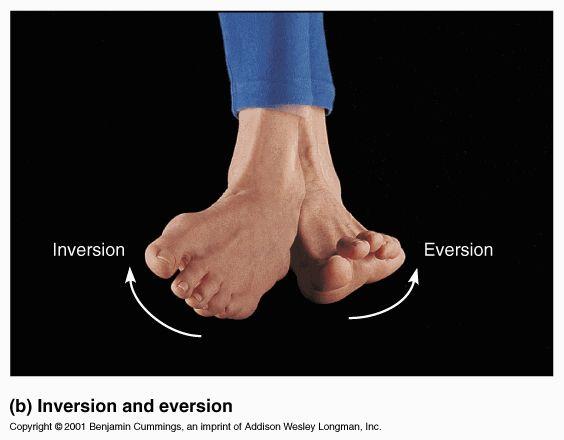 turns the sole of the foot laterally; opposite of inversion |