The peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes the brain and spinal cord.
False
Which of the following is a characteristic of the lens?
The lens focuses light on the retina.
The distance between two consecutive wave crests is the __________.
wavelength
Regeneration within the CNS ________.
is prevented due to growth-inhibiting proteins of oligodendrocytes
Broca's area ________.
is considered a motor speech area
Which of the following is the basic taste quality responsible for the "beef taste" of steak?
umami
Problems in balance may follow trauma to which nerve?
vestibulocochlear
The brain stem consists of the ________.
midbrain, medulla, and pons
Which part of the brain processes inputs received from the cerebral motor cortex, brain stem nuclei, and various sensory receptors, and then uses this information to coordinate somatic motor output so that smooth, well-timed movements occur?
cerebellum
Which middle ear ossicle is attached to, and transmits vibratory motion to, the oval window?
stapes
All processing at the circuit level going up to the perceptual level must synapse in the ________.
thalamus
Which of the following is the correct simple spinal reflex arc?
receptor, afferent neuron, integration center, efferent neuron, effector
The cerebellum and basal nuclei are involved in regulating motor activity, starting and stopping movements, and coordinating postural movements.
True
An essential part of the maculae involved in static equilibrium is (are) the ________.
otoliths
There are three layers of neurons in the retina. The axons of which of these neuron layers form the optic nerves?
ganglion cells
The anterior chamber of the eye is filled with vitreous humor.
False
Somatic reflexes activate __________.
skeletal muscle
What part of the eye constitutes the blind spot?
optic disc
CNS nerve fibers lack the intrinsic capacity to regenerate, while PNS nerve fibers are able to regenerate.
True
The majority of the cranial nerves attach to the __________.
brain stem.
What parts of the brain ultimately plan and coordinate complex motor activities?
cerebellum and basal nuclei
After axonal injury, regeneration in peripheral nerves is guided by ________.
Schwann cells
The arbor vitae refers to ________.
cerebellar white matter
If the ventral root of a spinal nerve were cut, what would be the result in the tissue or region that nerve supplies?
a complete loss of voluntary movement
What structure regulates the amount of light passing to the visual receptors of the eye?
iris
The bending of light rays is called reflection.
False
If retinal detachment occurs in the macula lutea, one can predict that there would be a significant loss of ______.
color vision
Which photoreceptors respond to very dim light?
rods
What is the main function of the rods in the eye?
vision in dim light
There are __________ pairs of cranial nerves.
12
Nerves that carry impulses toward the CNS only are ________.
afferent nerves
Ridges of tissue on the surface of the cerebral hemispheres are called ________.
gyri
Which of the following best describes the hypothalamus?
visceral control center of the body
The receptor organ for hearing is the __________.
spiral organ (of Corti)
Pressure, pain, and temperature receptors in the skin are ________.
exteroceptors
Which of the following generalizations does not describe the cerebral cortex?
The hemispheres are exactly equal in function.
Potentially damaging stimuli that result in pain are selectively detected by ________.
nociceptors
Nerves that only carry impulses away from the central nervous system (CNS) are called __________.
motor nerves
Seventy percent of all sensory receptors are located in the ________.
eye
Conscious perception of vision probably reflects activity in the ________.
occipital lobe of the cortex
Which of the following cranial nerves carries only sensory information?
olfactory
Which of the following is NOT an accessory structure of the eye?
retina
__________ causes a person to lapse abruptly into REM sleep from the awake state.
Narcolepsy
Most taste buds are located __________.
on the tongue
Which part of the brain is the "executive suite" for all brain activity?
cerebral cortex
Which of the following is NOT a function of the hypothalamus?
secretion of the hormone melatonin
Olfactory cells and taste buds are normally stimulated by ________.
substances in solution
Which part of the brain stem houses the reflex centers for respiration and cardiovascular functioning?
medulla oblongata
The receptors for smell are activated when __________.
dissolved odorants bind to receptor proteins in the cilium membranes
Where are equilibrium receptors located?
in the semicircular canals and in the vestibule of the ear
Olfactory cells and taste buds are normally stimulated by ________.
substances in solution
Which brain nucleus is the body's "biological clock"?
suprachiasmatic nucleus
There are __________ pairs of cranial nerves.
12
Which of the following is the basic taste quality responsible for the "beef taste" of steak?
umami
Tremor at rest, shuffling gait, stooped posture, and expressionless face are characteristics of ________.
Parkinson's disease
Which of the following is NOT an accessory structure of the eye?
retina
Nerves that carry impulses toward the CNS only are ________.
afferent nerves
If retinal detachment occurs in the macula lutea, one can predict that there would be a significant loss of ______.
color vision
What part of the eye constitutes the blind spot?
optic disc
The bending of light rays is called reflection.
False
The anterior chamber of the eye is filled with vitreous humor.
False
Which type of white matter fiber tract connects the two cerebral hemispheres?
commissures
Which of the following best describes the hypothalamus?
visceral control center of the body
Patients who have lesions involving Broca's area __________.
can understand language, but have difficulty speaking
The cerebellum and basal nuclei are involved in regulating motor activity, starting and stopping movements, and coordinating postural movements.
True
Problems in balance may follow trauma to which nerve?
vestibulocochlear
Static equilibrium involves linear acceleration as well as changes in head rotation.
False
Spinal nerves are all classified as __________.
mixed nerves
The blood-brain barrier is effective against ________.
metabolic waste such as urea
Which middle ear ossicle is attached to, and transmits vibratory motion to, the oval window?
stapes
Ordinarily, it is not possible to transplant tissues from one person to another, yet corneas can be transplanted without tissue rejection. This is because the cornea ________.
has no blood supply
Which fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres?
longitudinal fissure
Which part of the cerebral cortex is involved in intellect, cognition, recall, and personality?
prefrontal cortex
Where are equilibrium receptors located?
in the semicircular canals and in the vestibule of the ear
Seventy percent of all sensory receptors are located in the ________.
eye
__________ are collections of neuron cell bodies associated with nerves in the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Ganglia
Which part of the brain is considered the "gateway" to the cerebral cortex?
thalamus
Eye color is determined by the amount of brown pigment present in the iris.
True
Regeneration within the CNS ________.
is prevented due to growth-inhibiting proteins of oligodendrocytes
Which of the following is NOT a function of the hypothalamus?
secretion of the hormone melatonin
The arbor vitae refers to ________.
cerebellar white matter
Nerves that only carry impulses away from the central nervous system (CNS) are called __________.
motor nerves
The structure that allows equalization of the pressure in the middle ear with that outside the body is the external auditory meatus.
False
What is the main function of the rods in the eye?
vision in dim light
The vital centers for the control of heart rate, respiration, and blood pressure are located in the ________.
medulla
Dermatomes are skin segments that relate to sensory innervation regions of the spinal nerves.
True
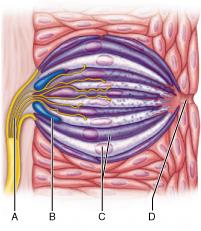
Which of these lettered structures serves as the taste cells?
C
Which meninx is a delicate connective tissue membrane that clings tightly to the brain like cellophane wrap following its every convolution?
pia mater
__________ causes a person to lapse abruptly into REM sleep from the awake state.
Narcolepsy
The majority of the cranial nerves attach to the __________.
brain stem.
Which of the following generalizations does not describe the cerebral cortex?
The hemispheres are exactly equal in function.
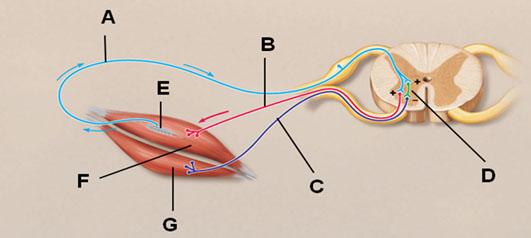
In the figure below, which letter points to an afferent neuron?
A
Which of the following is the receptor organ for hearing?
spiral organ (of Corti)
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes the brain and spinal cord.
False
Which part of the brain processes inputs received from the cerebral motor cortex, brain stem nuclei, and various sensory receptors, and then uses this information to coordinate somatic motor output so that smooth, well-timed movements occur?
cerebellum
The receptor organ for hearing is the __________.
spiral organ (of Corti)
Pressure, pain, and temperature receptors in the skin are ________.
exteroceptors
What cells line the ventricles of the brain?
ependymal cells
What parts of the brain ultimately plan and coordinate complex motor activities?
cerebellum and basal nuclei
Which part of the brain stem houses the reflex centers for respiration and cardiovascular functioning?
medulla oblongata