The larvae of some insects are merely small versions of the adult,
whereas the larvae of other insects look completely different from
adults, eat different foods, and may live in different habitats. Which
of the following most directly favors the evolution of the latter,
more radical, kind of metamorphosis?
A) natural selection of
sexually immature forms of insects
B) changes in the homeobox
genes governing early development
C) the evolution of meiosis
D) the development of an oxidizing atmosphere on Earth
Answer: B
Which tissue type, or organ, is NOT correctly matched with its germ
layer tissue?
A) muscular -mesoderm
B) skin -
ectoderm
C) nervous - mesoderm
D) stomach - endoderm
Answer: C
Among protostomes, which morphological trait has shown the most
variation?
A) type of symmetry (bilateral vs. radial vs.
none)
B) type of body cavity (coelom vs. pseudocoelom vs. no
coelom)
C) type of development (protostome vs.
deutersostome)
D) number of embryonic tissue types (diploblasty
vs. triploblasty)
Answer: B
The protostome developmental sequence arose just once in evolutionary
history, resulting in two main subgroups - Lophotrochozoa and
Ecdysozoa. What does this finding suggest?
A) The protostomes are
a polyphylectic group.
B) Division of these two groups occurred
after the protostome developmental sequence appeared.
C) These
two subgroups have a common ancestor that was a deuterostome.
D)
The lophotrochozoans are monophylectic.
Answer: B
The Hox genes came to regulate each of the following in what
sequence, from earliest to most recent?
1. identity and
position of paired appendages in protostome embryos
2.
anterior-posterior orientation of segments in protostome embryos
3. positioning of tentacles in cnidarians
4.
anterior-posterior orientation in vertebrate embryos
A)
4 → 1 → 3 → 2
B) 4 → 2 → 3 → 1
C) 4 → 2 → 1 → 3
D)
3 → 2 → 1 → 4
Answer: D
The presence of a lophophore in a newly discovered species would
suggest that the species ________.
A) grows by shedding its
external covering
B) is a suspension feeder
C) is
motile
D) has an exoskeleton
Answer: B
Arthropod exoskeletons and mollusk shells both ________.
A) are
secreted by the mantle
B) completely replace the hydrostatic
skeleton
C) help retain moisture in terrestrial habitats
D)
are comprised of the polysaccharide chitin
Answer: C
Which of the following could be considered the most recent common
ancestor of living tetrapods?
A) a sturdy-finned, shallow-water
lobe-fin whose appendages had skeletal supports similar to those of
terrestrial vertebrates
B) an armored, jawed placoderm with two
pairs of appendages
C) an early ray-finned fish that developed
bony skeletal supports in its paired fins
D) a salamander that
had legs supported by a bony skeleton but moved with the side-to-side
bending typical of fishes
Answer: A
Which characteristic is common to all the modern representatives of
all major reptilian lineages (turtles, lepidosaurs, crocodilians, and
birds)?
A) ectothermy
B) presence of a notochord
C)
presence of four walking limbs
D) presence of teeth
Answer: B
What is believed to be the most significant result of the evolution
of the amniotic egg?
A) Tetrapods were no longer tied to the
water for reproduction.
B) Tetrapods can now function with just
lungs.
C) Newborns are much less dependent on their
parents.
D) Embryos are protected from predators.
Answer: A
(DIAGRAM) In the diagram below, point "A" is ________;
point "B" is ________.
A) the most recent species to
evolve on Earth; the last common ancestor of Archaea and
Eukarya
B) the common ancestor of all life; the last common
ancestor of Archaea and Eukarya
C) the most recent species to
evolve on Earth; an ancestor of group "A"
D) the common
ancestor of all life; the common ancestor of Bacteria and Archaea
Answer: B
The various taxonomic levels (for example, phyla, genera, classes) of
the hierarchical classification system differ from each other on the
basis of
A) how widely the organisms assigned to each are
distributed throughout the environment.
B) their inclusiveness.
C) the relative genome sizes of the organisms assigned to each.
D) morphological characters that are applicable to all organisms.
Answer: B
Some beetles and flies have antler-like structures on their heads,
much like male deer do. The existence of antlers in beetle, fly, and
deer species with strong male-male competition is an example of
________.
A) parsimony
B) a synapomorphy
C) convergent
evolution
D) homology
Answer: C
(DIAGRAM) Refer to the figure above. Which of the following forms a
monophyletic group?
A) C and D
B) E, F, and G
C) D, E,
and F
D) A, B, C, D
Answer: B
The duplication of homeotic (Hox) genes has been significant in the
evolution of animals because it ________.
A) caused the
extinction of major groups
B) reduced morphological diversity
into simpler forms of life
C) allowed animals to survive on
significantly fewer calories
D) permitted the evolution of novel forms
Answer: D
What is true of the Cambrian explosion?
A) There are fossils of
animals in geological strata that are older than the Cambrian
explosion.
B) Only the fossils of microorganisms are found in
geological strata older than the Cambrian explosion.
C) The
Cambrian explosion is evidence for the instantaneous creation of life
on Earth.
D) The Cambrian explosion marks the appearance of
filter-feeding animals in the fossil record.
Answer: A
Which of the following is (are) unique to animals?
A)
flagellated gametes
B) the structural carbohydrate, chitin
C) nervous system signal conduction and muscular movement
D) heterotrophy
Answer: C
Both animals and fungi are heterotrophic. What distinguishes animal
heterotrophy from fungal heterotrophy is that only animals derive
their nutrition by
A) preying on animals.
B) ingesting it.
C) consuming living, rather than dead, prey.
D) using
enzymes to digest their food.
Answer: B
The last common ancestor of all animals was probably a
A)
flagellated protist.
B) unicellular yeast.
C) multicellular
algae.
D) multicellular fungus.
Answer: A
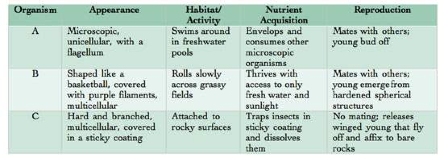
As you are on the way to Tahiti for a vacation, your plane
crash-lands on a previously undiscovered island. You soon find that
the island is teeming with unfamiliar organisms; and you, as a student
of biology, decide to survey them (with the aid of the Insta-Lab
Portable Laboratory you brought along in your suitcase). You select
three organisms and observe them in detail, making the notations found
int he figure above. Which organism would you classify as an
animal?
A) organism A
B) organism B
C) organism C
Answer: C
The most ancient branch point in animal phylogeny is that between
having
A) radial or bilateral symmetry.
B) a well-defined
head or no head.
C) diploblastic or triploblastic embryos.
D) true tissues or no tissues.
Answer: D
In examining an unknown animal species during its embryonic
development, how can you be sure what you are looking at is a
protostome
and not a deuterostome?
A) The animal is
triploblastic.
B) You see a mouth, but not an anus.
C) The
animal is clearly bilaterally symmetrical.
D) There is evidence
of cephalization.
Answer: B
What is the probable sequence in which the following clades of
animals originated, from earliest to most recent?
1.
tetrapods
2. vertebrates
3. deuterostomes
4.
amniotes
5. bilaterians
A) 5 → 3 → 2 → 4 → 1
B) 5 → 3 → 2 → 1 → 4
C) 5 → 3 → 4 → 2 → 1
D) 3 → 5
→ 4 → 2 → 1
Answer: B
Some researchers claim that sponge genomes have homeotic genes, but
no Hox genes. If true, this finding would
A) strengthen sponges'
evolutionary ties to the Eumetazoa.
B) mean that sponges must no
longer be classified as animals.
C) confirm the identity of
sponges as "basal animals."
D) mean that extinct
sponges must have been the last common ancestor of animals and fungi.
Answer: C
Which of the following is most likely to be aquatic?
A)
suspension feeder
B) deposit feeder
C) mass feeder
D)
fluid feeder
Answer: A
Why might researchers choose to use molecular data (such as ribosomal
RNA sequences) rather than morphological data to study the
evolutionary history of animals?
A) Morphological changes usually
do not result from molecular changes.
B) Molecular data can be
gathered in the lab, while morphological data must be gathered in the
field.
C) Some phyla vary too widely in morphological
characteristics to be classified accurately.
D) Sequence data can
be gathered faster than morphological data, and morphological data
provides a different perspective.
Answer: D
You find what you believe is a new species of animal. Which of the
following characterisitics would enable you to argue that it is more
closely related to a flatworm than it is to a roundworm?
A) It is
shaped like a worm.
B) It has a mouth and an anus.
C) it is
a suspension feeder.
D) It has no coelom.
Answer: D
Which characteristic is shared by cnidarians and flatworms?
A)
dorsoventrally flattened bodies
B) a distinct head
C)
radial symmetry
D) a digestive system with a single opening
Answer: D
Which of the following organisms would you expect to have the largest
surface-area-to-volume ratio? Assume that all of the following are the
same total length.
A) a platyhelminth
B) an
arthropod
C) an annelid
D) a mollusk
Answer: A
Nematodes and arthropods both ________.
A) grow by shedding
their exoskeleton
B) are suspension feeders
C) have ciliated
larvae
D) develop an anus from the blastopore (pore) formed in
the gastrula stage
Answer: A
While sampling marine plankton in a lab, a student encounters large
numbers of fertilized eggs. The student rears some of the eggs in the
laboratory for further study and finds that the blastopore becomes the
mouth. The embryo develops into a trochophore larva and eventually has
a true coelom. These eggs probably belonged to a(n) ________.
A)
arthropod
B) echinoderm.
C) mollusc.
D) nematode.
Answer: C
All arthropods ________.
1) undergo complete
metamorphosis
2) have jointed appendages
3) molt
4)
have segmented bodies
5) have an exoskeleton or cuticle
A) 1, 2, and 4
B) 2, 3, 4, 5
C) 1, 4, 5
D) 3 and 5
Answer: B
Which of the following combinations correctly matches a phylum to its
description?
A) Nematoda - segmented worms, closed circulatory
system
B) Platyhelminthes - radial symmetry, polyp and medusa
body forms
C) Echinodermata - bilateral symmetry as a larva,
water vascular system
D) Cnidaria - flatworms, gastrovascular
cavity, acoelomate
Answer: C
Which of the following is a characteristic of all chordates at some
point during their life cycle?
A) post-anal tail
B)
jaws
C) four-chambered heart
D) vertebrae
Answer: A
Which extant chordates are postulated to be most like the earliest
chordates in appearance?
A) lancelets
B) adult tunicates
C) amphibians
D) reptiles
Answer: A
Which of the following characteristics is shared by a hagfish and a
lamprey?
A) paired fins
B) jaws
C) a well-developed
notochord
D) a rasping tongue
Answer: C
Vertebrates and tunicates share
A) a notochord and a dorsal,
hollow nerve cord.
B) a high degree of cephalization.
C)
the formation of structures from the neural crest.
D) an
endoskeleton that includes a skull.
Answer: A
The earliest known mineralized structures in vertebrates are
associated with which function?
A) reproduction
B) feeding
C) locomotion
D) defense
Answer: B
Suppose, while out camping in a forest, you found a chordate with a
long, slender, limbless body slithering across the ground near your
tent. This critter could be ________.
A) a mammal
B) a
lamprey
C) a skate
D) an amphibian
Answer: D
Jaws first occurred in which extant group of fishes?
A)
lampreys
B) chondrichthyans
C) ray-finned fishes
D) lungfishes
Answer: B
It is believed that the coelacanths and lungfish represent a crucial
link between other fishes and tetrapods. What is the major feature in
these fish in support of this hypothesis?
A) Their fins have
skeletal and muscular structures similar to amphibian limbs.
B)
They have highly evolved nervous and circulatory systems.
C) Like
amphibians, they are tied to the water for reproduction.
D) They
have lungs and are able to breathe air when water is scarce.
Answer: A
Which of the following characteristics evolved independently in
mammals and birds?
A) jaws
B) bone
C)
endothermy
D) amniotic eggs
Answer: C
Arrange these groups in order from most inclusive (most general) to
least inclusive (most specific).
1. lobe-fins
2. amphibians
3. gnathostomes
4.
osteichthyans
5. tetrapods
A) 4, 3, 1, 5, 2
B) 4, 3, 2, 5, 1
C) 4, 2, 3, 5, 1
D) 3, 4, 1, 5, 2
Answer: D
Which of these characteristics added most to vertebrate success in
relatively dry environments?
A) the shelled, amniotic egg
B) the ability to maintain a constant body temperature
C)
two pairs of appendages
D) bony scales
Answer: A
Mammals and birds eat more often than reptiles. Which of the
following traits shared by mammals and birds best explains this
habit?
A) endothermy
B) amniotic egg
C)
terrestrial
D) ectothermy
Answer: A
Which of the following are the only extant animals that descended
directly from dinosaurs?
A) lizards
B) crocodiles
C)
snakes
D) birds
Answer: D
Which of these are amniotes?
A) amphibians
B) fishes
C) lungfish
D) turtles
Answer: D
Which of the following is the most inclusive (most general) group,
all of whose members have fully opposable thumbs?
A) apes
B) Homo
C) anthropoids
D) primates
Answer: C
Unlike eutherians, both monotremes and marsupials
A) lack
nipples.
B) have some embryonic development outside the uterus.
C) lay eggs.
D) are found in Australia and Africa.
Answer: B
In what respect do hominins differ from all other
arthropoids?
A) opposable thumbs
B) eyes on the front of the
face
C) bipedal posture
D) lack of a tail
Answer: C
Arrange the following taxonomic terms from most inclusive (most
general) to least inclusive (most specific).
1. apes
2. hominins
3. Homo
4 anthropoids
5. primates
A) 5, 1, 4, 2, 3
B) 5, 4, 1, 2, 3
C) 5, 4, 2, 1, 3
D) 5, 2, 1, 4, 3
Answer: B
With which of the following statements would a biologist be most
inclined to agree?
A) Humans and apes represent divergent lines
of evolution from a common ancestor.
B) Humans evolved directly
from Old World monkeys.
C) Humans represent the pinnacle of
evolution and have escaped from being affected by natural selection.
D) Humans evolved from chimpanzees.
Answer: A
(TABLE) The table above is a comparison of several characteristics of
H. floresiensis to those of nine other hominin species (arranged
roughly from oldest to most recent). What do these data
suggest?
A) Homo floresiensis is most closely related to
Australopithecus afarensis or A. africanus.
B) Hominins first
evolved in and then radiated out from Asia.
C) A large brain is
not necessarily required for toolmaking.
D) Body mass and
braincase volume are completely unrelated.
Answer: C
The evolution of similar insulating skin coverings such as fur, hair,
and feathers in mammals and birds is a result of ________.
A)
shared ancestry
B) homology
C) convergent evolution
D)
evolutionary divergence
Answer: C
As the size of some animals has evolved to greater sizes, the
effectiveness of their adaptations that promote exchanges with the
environment have also increased. For example, in many larger
organisms, evolution has favored lungs and a digestive tract with
________.
A) larger cells
B) decreased blood supply
C)
more branching or folds
D) increased thickness
Answer: C
Much of the coordination of vertebrate body functions via chemical
signals is accomplished by the ________.
A) excretory
system
B) integumentary system
C) respiratory system
D)
endocrine system
Answer: D
If you were to view a sample of animal tissue under a light
microscope and notice an extensive extracellular matrix surrounding a
tissue, which tissue type would you most suspect?
A) striated
muscle
B) nervous
C) connective
D) epithelial
Answer: C
Evolutionary adaptations that help diverse animals directly exchange
matter between cells and the environment include
A) a
gastrovascular activity, a two-layered body, and a torpedo-like body
shape.
B) an external respiratory surface, a small body size,
and a two-cell-layered body.
C) a large body volume; a long,
tubular body; and a set of wings.
D) complex internal
structures, a small body size, and a large surface area.
Answer: B
Most of the exchange surfaces of multicellular animals are lined with
A) connective tissue.
B) smooth muscle cells.
C)
neural tissue.
D) epithelial tissue.
Answer: D
Interstitial fluid is
A) the fluid inside the gastrovascular
cavity of Hydra.
B) the internal environment inside animal
cells.
C) identical to the composition of blood.
D) a
common site of exchange between blood and body cells.
Answer: D
If you gently bend your ear, and then let go, the shape of your ear
will return because the cartilage of your ear contains
________.
A) collagenous fibers.
B) elastic fibers.
C) reticular fibers.
D) adipose tissue.
Answer: B
Environmental influences appear to contribute to cellular mutations
that lead to tumor growth. For example, certain diets lead to higher
incidence of colon cancers, and overexposure to sunlight leads to
higher incidence of skin cancers. The tissues in closest contact with
a carcinogen or mutagen (anything that causes genetic mutations) are
obviously the ones most likely to develop tumors. Carcinomas and
melanomas account for well over half of all cancers. What type of
tissue would you guess the term carcinoma and melanoma is most closely
associated with?
A) muscle
B) connective
C)
nervous
D) epithelial
Answer: D
An elephant and a mouse are running in full sunlight, and both
overheat by the same amount above their normal body temperatures. When
they move into the shade and rest, which animal will cool down
faster?
A) The elephant will because it has the higher
surface-area-to-volume ratio.
B) They will cool at the same rate
because they overheated by the same amount.
C) The mouse will
because it has the higher surface-area-to-volume ratio.
D) The
elephant will because it has the lower surface-area-to-volume ratio.
Answer: C
The body's automatic tendency to maintain a constant and optimal
internal environment is termed
A) balanced equilibrium.
B)
physiological chance.
C) homeostasis.
D) static equilibrium.
Answer: C
Positive feedback differs from negative feedback in that
A)
positive feedback benefits the organism, whereas negative feedback is
detrimental.
B) the positive feedback's effector responses are
in the same direction as the initiating stimulus rather than opposite
to it.
C) the effector's response increases some parameter (such
as body temperature), whereas in negative feedback it can only
decrease the parameter.
D) positive feedback systems have only
effectors, whereas negative feedback systems have only receptors.
Answer: B
In a cool environment, an ectotherm is more likely to survive an
extended period of food deprivation than would an equally sized
endotherm because the ectotherm
A) maintains a higher basal
metabolic rate.
B) expends more energy per kg of body mass than
does the endotherm.
C) invests little energy in temperature
regulation.
D) metabolizes its stored energy more readily than
can the endotherm.
Answer: C
Most land-dwelling invertebrates and all of the amphibians
A)
are ectothermic organisms with variable body temperatures.
B)
alter their metabolic rates to maintain a constant body temperature of
37°C.
C) have a net loss of heat across a moist body surface,
even in direct sun.
D) are endotherms but become
thermoconformers only when they are in water.
Answer: A
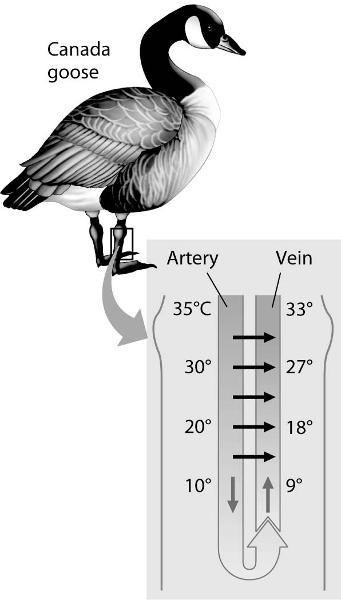
The thin horizontal arrows in the figure above show that the
A)
warmer arterial blood can bypass the legs as needed, when the legs are
too cold to function well.
B) warmer venous blood transfers heat
to the cooler arterial blood.
C) warmer arterial blood transfers
heat to the cooler venous blood.
D) arterial blood is always
cooler in the abdomen, compared to the temperature of the venous blood
in the feet of the goose.
Answer: C
The temperature-regulating center of vertebrate animals is located in
the
A) medulla oblongata.
B) thyroid gland.
C)
hypothalamus.
D) subcutaneous layer of the skin.
Answer: C
Certain nutrients are considered "essential" in the diets
of some animals because
A) only those animals use those
nutrients.
B) the nutrients are subunits of important polymers.
C) these animals are not able to synthesize these
nutrients.
D) the nutrients are necessary coenzymes.
Answer: C
Ingested dietary substances must cross cell membranes to be used by
the body, a process known as
A) ingestion.
B) digestion.
C) hydrolysis.
D) absorption.
Answer: D
In the digestive system, peristalsis is
A) smooth muscle
contractions that move food along the esophagus.
B) voluntary
control of the rectal sphincters regulating defecation.
C) the
transport of nutrients to the liver through the hepatic portal vessel.
D) a common cause of loss of appetite, fatigue, and dehydration.
Answer: A
You discover a new species of bacteria that grows in aquatic
environments with high salt levels. While studying these bacteria, you
note that their internal environment is similar to the salt
concentrations in their surroundings. You also discover that the
internal salt concentrations of the bacteria change as the salt
concentration in their environment changes. The new species can
tolerate small changes in this way, but dies from large changes
because it has no mechanism for altering its own internal salt levels.
What type of homeostatic mechanism is this species using to regulate
its internal salt levels?
A) assimilation
B)
integration
C) regulation
D) conformation
Answer: D
The function of mechanical digestion is to break down large chunks of
food into smaller pieces. Why is this important? Smaller pieces of
food ________.
A) have more surface area for chemical digestion
than do larger pieces of food
B) are more easily stored in the
stomach than are larger pieces of food
C) are easier to excrete
than are larger pieces of food
D) do not taste as good as larger
pieces of food
Answer: A
A zoologist analyzes the jawbones of an extinct mammal and concludes
that it was an herbivore. The zoologist most likely came to this
conclusion based upon ________.
A) the shape of the teeth
B)
the size of the mouth opening
C) the position of muscle
attachment sites
D) the angle of the teeth in the mouth
Answer: A
In a well-fed human eating a Western diet, the richest source of
stored chemical energy in the body is
A) fat in adipose tissue.
B) glucose in the blood.
C) protein in muscle cells.
D) glycogen in muscle cells.
Answer: A
Because the foods eaten by animals are often composed largely of
macromolecules, this requires the animals to have mechanisms for
A) elimination.
B) dehydration synthesis.
C)
enzymatic hydrolysis.
D) regurgitation.
Answer: C
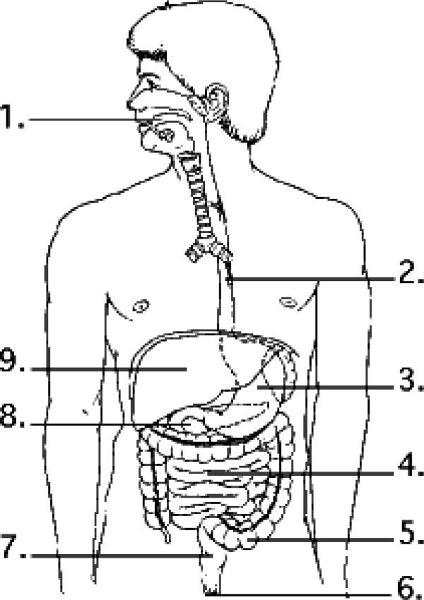
Examine the digestive system structures in the figure above. Bacteria
that produce vitamins as products are residents of location
A)
3.
B) 4.
C) 5.
D) 7.
Answer: C
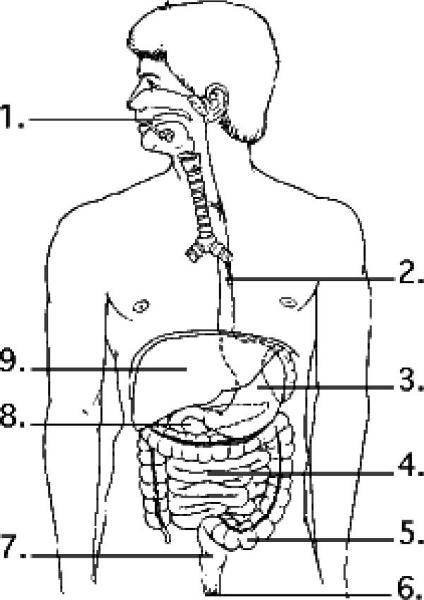
Examine the digestive system structures in the figure above. The
highest rate of nutrient absorption occurs at location(s)
A) 3
only.
B) 4 only.
C) 1 and 4.
D) 3 and 4.
Answer: B
Circulatory systems compensate for
A) temperature differences
between the lungs and the active tissue.
B) the slow rate at
which diffusion occurs over large distances
C) the problem of
communication systems involving only the nervous system.
D) the
need to cushion animals from trauma.
Answer: B
Organisms with a circulating body fluid that is distinct from the
fluid that directly surrounds the body's cells are likely to have
A) an open circulatory system.
B) a closed circulatory
system.
C) a gastrovascular cavity.
D) branched tracheae.
Answer: B
To adjust blood pressure independently in the capillaries of the
gas-exchange surface and in the capillaries of the general body
circulation, an organism would need a(n)
A) open circulatory
system.
B) hemocoel.
C) four-chambered heart.
D)
two-chambered heart.
Answer: C
Atria contract ________.
A) immediately after systole
B)
just prior to the beginning of diastole
C) during systole
D)
during diastole
Answer: C
Which of the following is the correct sequence of blood flow in birds
and mammals?
A) left ventricle → aorta → lungs → systemic
circulation
B) right ventricle → pulmonary vein → pulmocutaneous
circulation
C) pulmonary vein → left atrium → left ventricle →
pulmonary circuit
D) vena cava → right atrium → right ventricle
→ pulmonary circuit
Answer: D
If a molecule of CO₂ released into the blood in your left toe is
exhaled from your nose, it must pass through all of the following
except
A) the pulmonary vein.
B) an alveolus.
C) the
trachea.
D) the right atrium.
Answer: A
The velocity of blood flow is the lowest in capillaries because
A) the capillary walls are not thin enough to allow oxygen to
exchange with the cells.
B) the total cross-sectional area of
the capillaries is greater than the total cross-sectional area of the
arteries or any other part of the circulatory system.
C) the
diastolic blood pressure is too low to deliver blood to the
capillaries at a high flow rate.
D) the systemic capillaries are
supplied by the left ventricle, which has a lower cardiac output than
the right ventricle.
Answer: B
A normal event in the process of blood clotting is the
A)
production of erythropoietin.
B) conversion of fibrin to
fibrinogen.
C) activation of prothrombin to thrombin.
D)
increase in platelets.
Answer: C
For a healthy 20-year-old at rest, arterial blood pressure is
typically ____ mm Hg at systole and ____ mm Hg at diastole.
A)
120; 70
B) 70: 120
C) 140; 90
D) 90; 140
Answer: A
Small swollen areas in the neck, groin, and axillary region are
associated with
A) increased activity of the immune system.
B) a broken limb.
C) blood sugar that is abnormally high.
D) dehydration.
Answer: A
Countercurrent exchange in the fish gill helps to maximize
A)
endocytosis.
B) blood pressure.
C) diffusion.
D)
active transport.
Answer: C