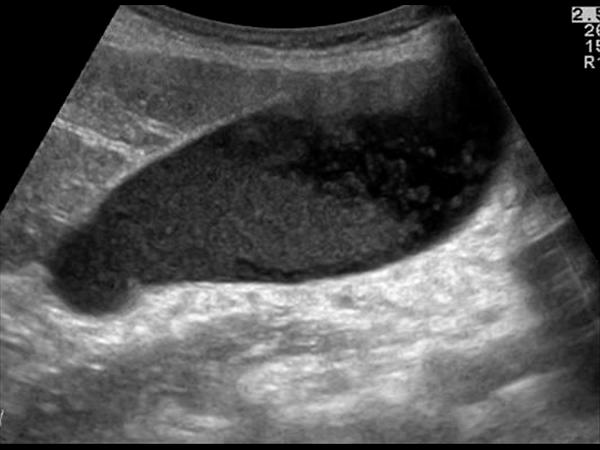
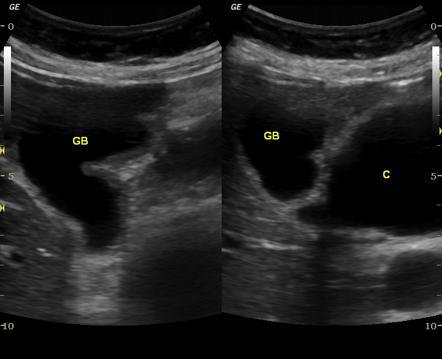
Courvoisier's GB
Distension without wall thickening
due to obstruction distal to the cystic duct
*Panncreatic head mass
* Duodenal papilla mass
*CBD mass
RUQ pain
Jaundice
recurrent cholangitis
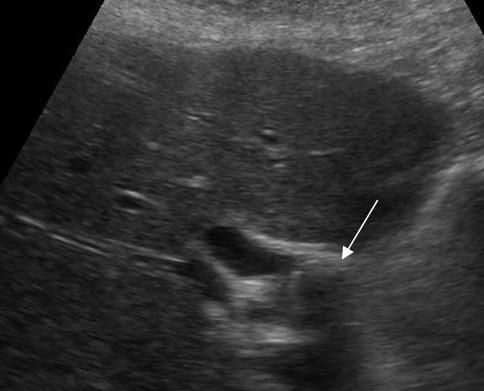
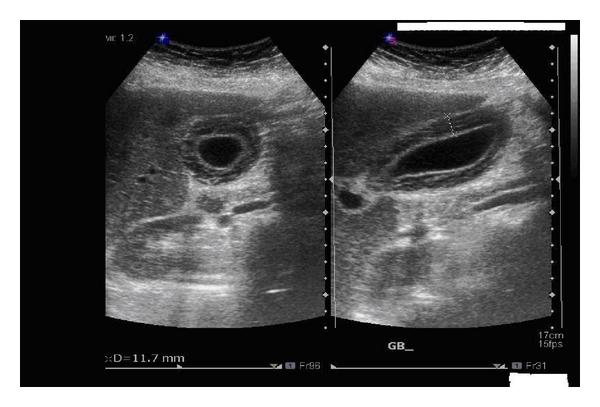
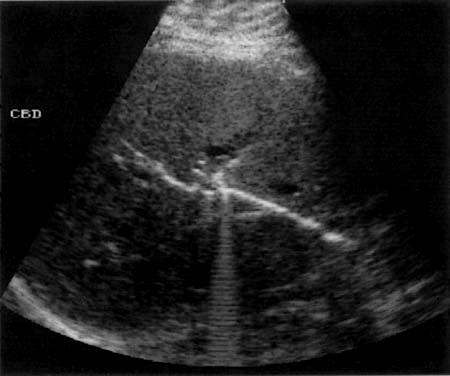
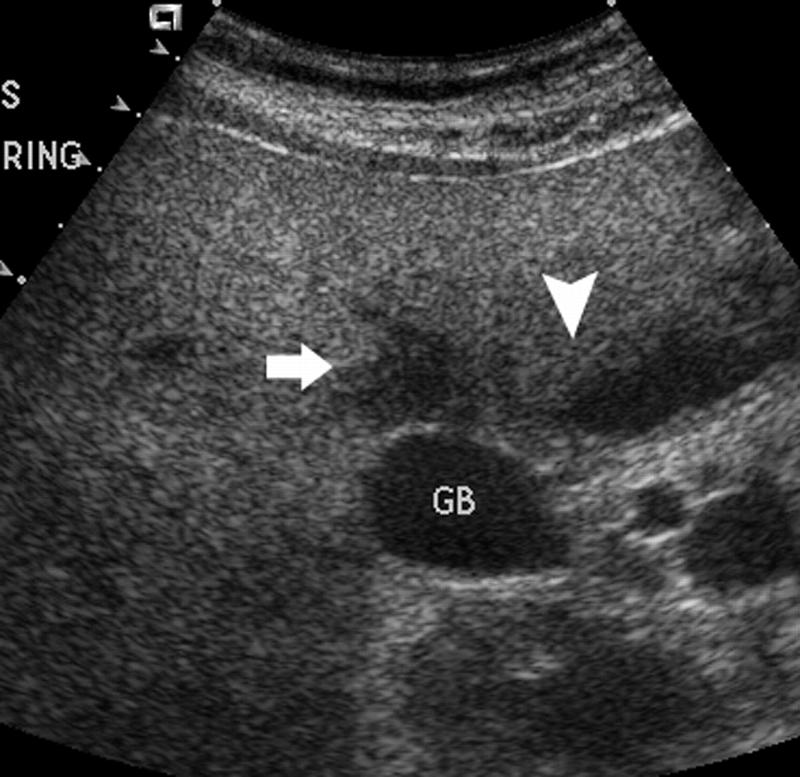
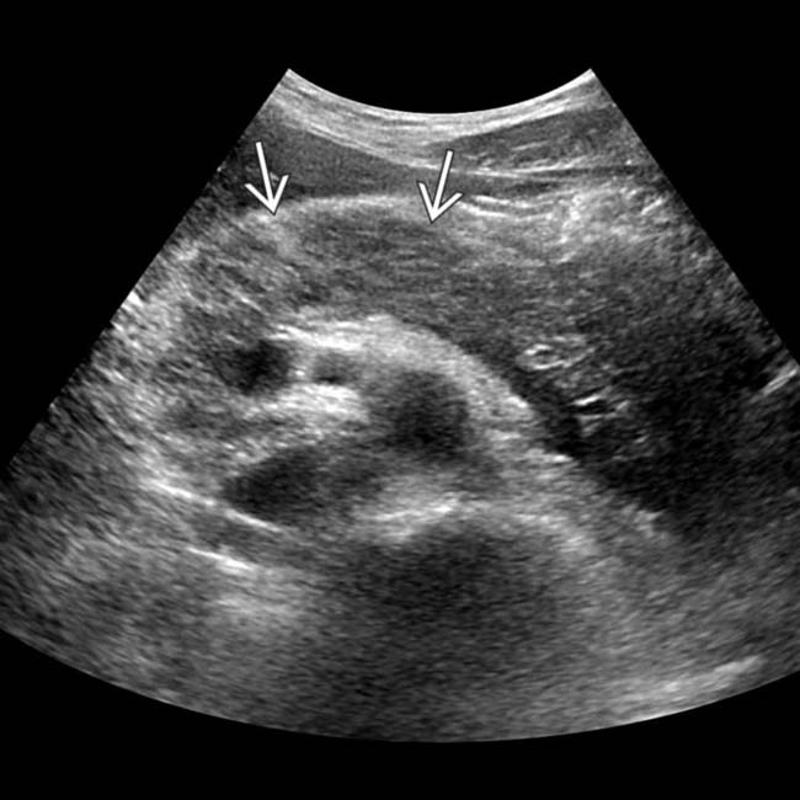
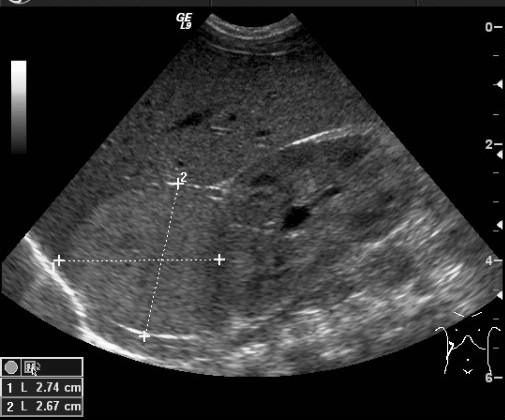
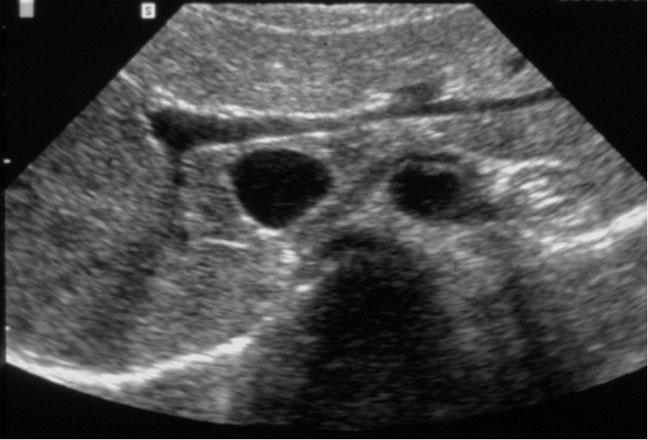
Mirizzi SYndrome
impacted stone in the cystic duct or GB neck
presence of two tubular structures representing the bile duct above the level of the cystic duct
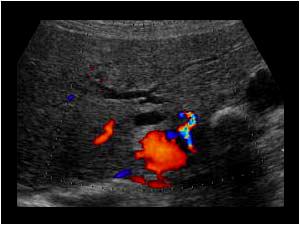
Mirizzi SYndrome
impacted stone in the cystic duct or GB neck
presence of two tubular structures representing the bile duct above the level of the cystic duct

Patient has been fed intravenously for 3 days.
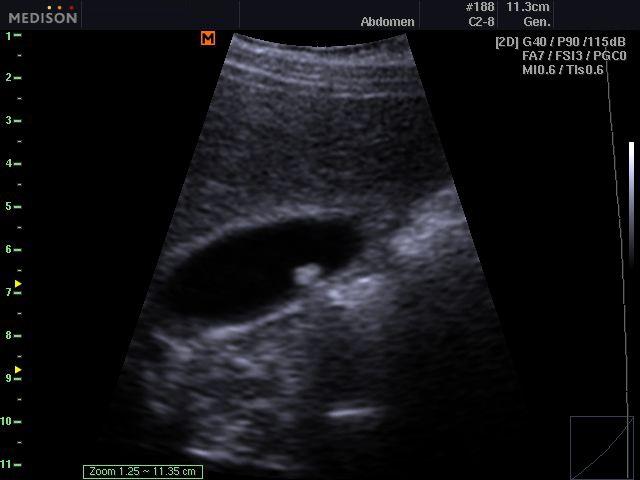
Sludge
highly concentrated bile
Gravity dependent
Cholelithiasis
Mobile, hyperechoic, round or triangular structures casting a well defined posterior acoustic shadowing
Will change when patient’s body position changes (Gravity dependent)
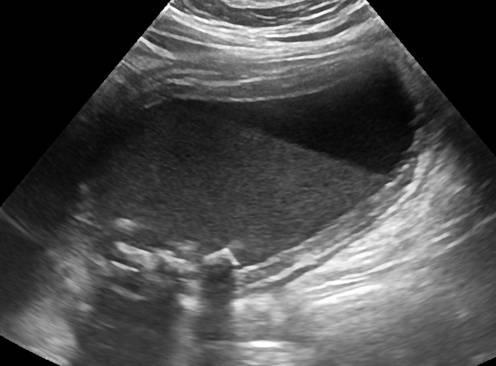
RUQ pain
fever
leukocytosis
Positive Murphy's sign
Acute cholecystitis
inflamation of the GB wall w/ stone
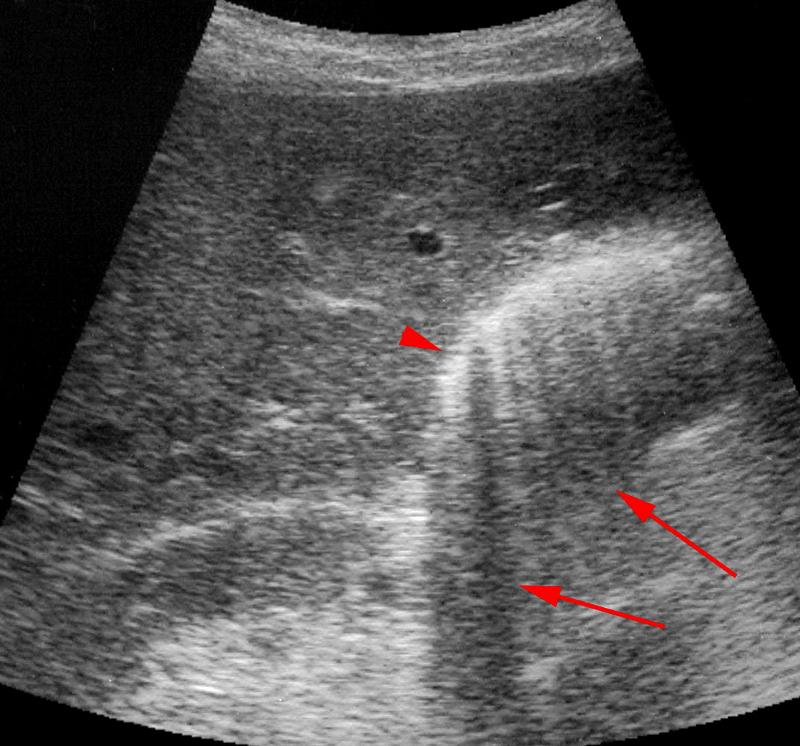
Diabetic
RUQ pain
fever
leukocytosis
Emphysematous Cholecystitis
Gas forming bacteria in gallbladder wall yields to high intensity echoes and comet tail artifact
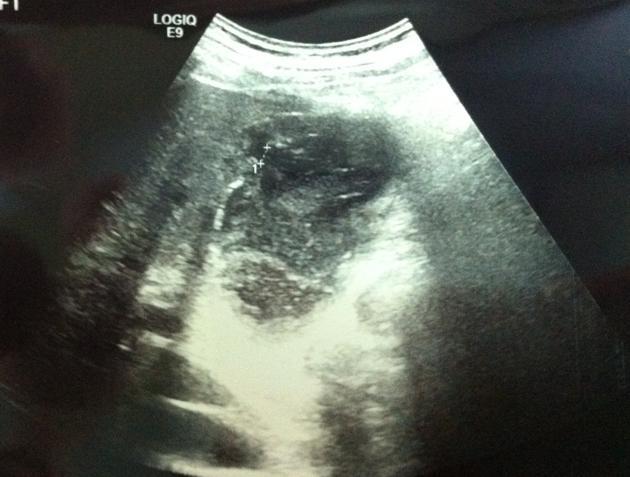
RUQ pain
fever
leukocytosis
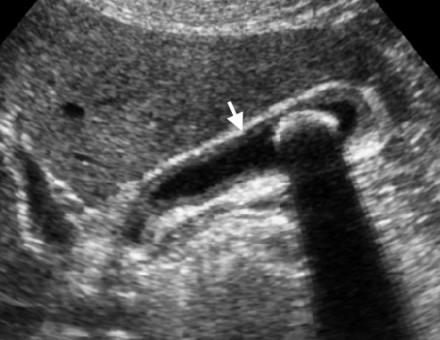
Empyema of the gallbladder
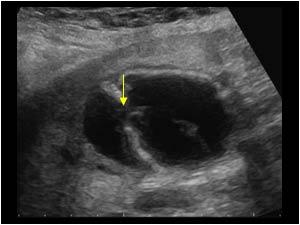
Perforation in the gallbladder wall
Typically secondary event in critically ill
Acalculus Cholecystitis
Inflammation of GB wall without stones
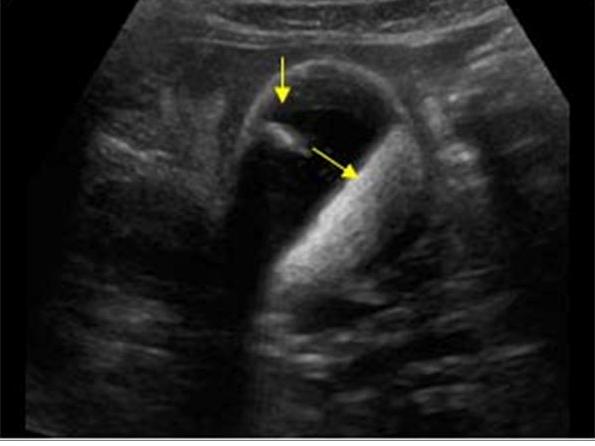
Chronic Cholecystitis
Contracted gallbladder with acoustic shadowing from cholelithiasis
Thick hyperechoic gallbladder wall greater than 4 – 5 mm
Sludge may be present
patient present with chronic Cholecytitis
Milk of calcium Bile (Limy bile)
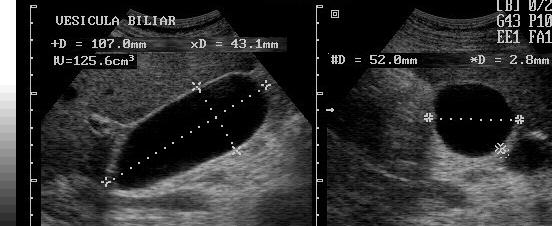
Asymptomatic with palpable RUQ mass
Hydrops GB
Greater than 4cm in diameter
Female patient with Chronic Cholecystitis
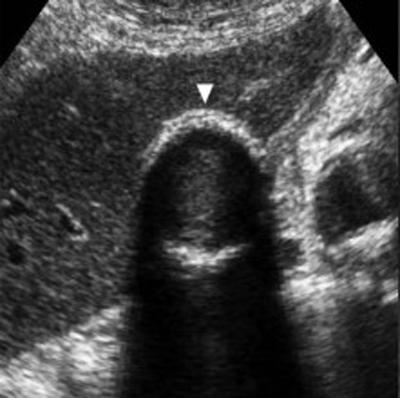
Porcelain GB
Calcification of GB wall due to chronic cholecytitis
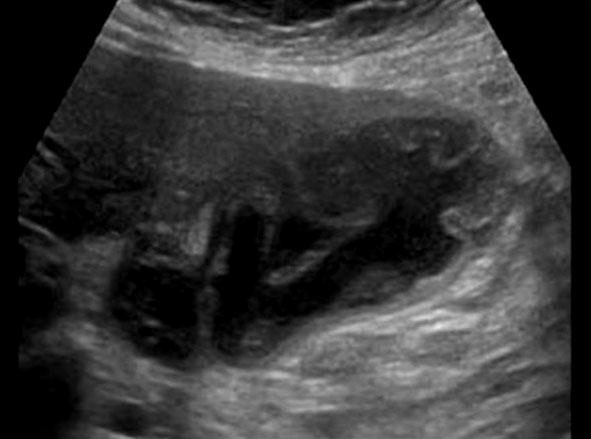
Gangrenous Cholecystitis
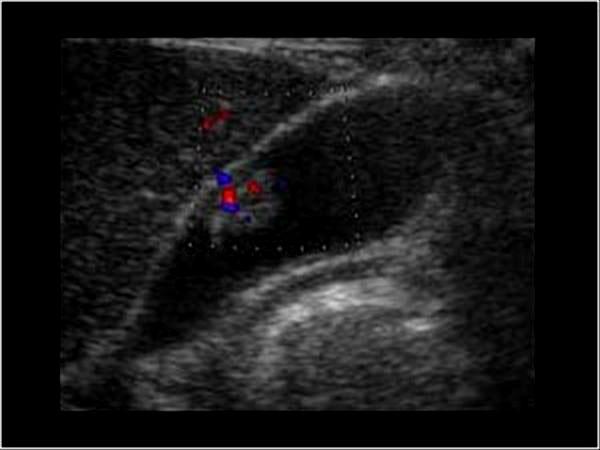
GB Ademoma
epithelial tumor
overgrowth of the lining
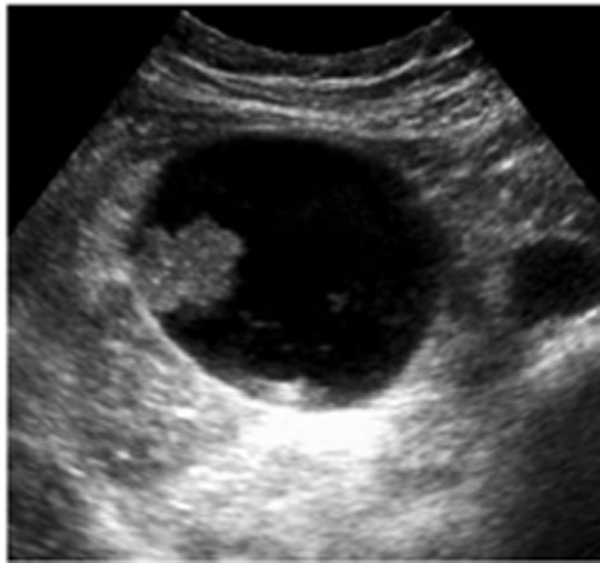
GB Ademoma
epithelial tumor
overgrowth of the lining
Asymptomatic
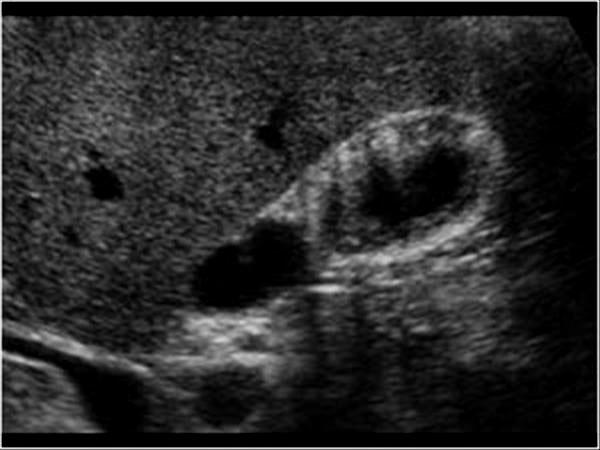
Gallbladder Adenomyomatosis
diverticulum of the GB
Focal, segmental or diffuse smooth muscle proliferation with exaggerated diverticular appearance of the Rokitansky – Aschoff sinuses into the muscular wall
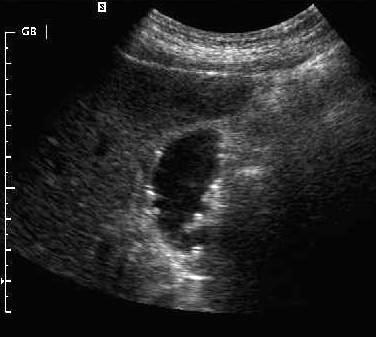
Gallbladder Cholesterolosis
Non shadowing, hyperechoic, polyp
Strawberry GB
Lipids
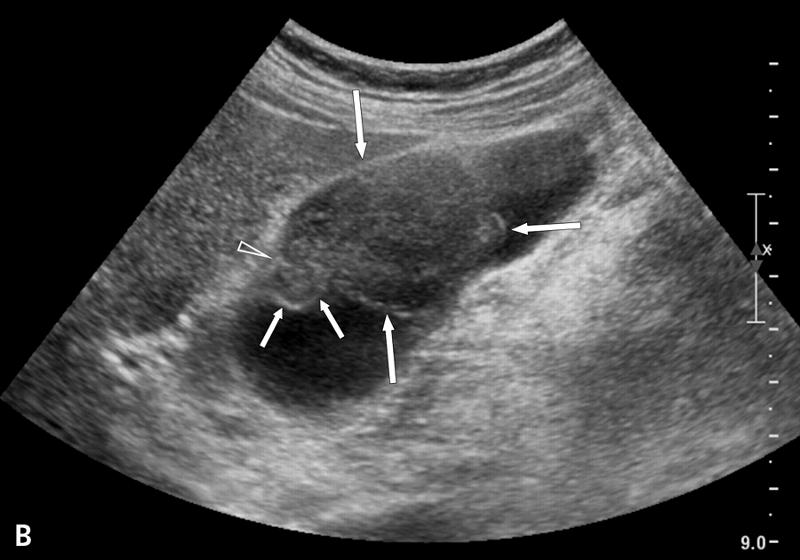
60 year old with long standing cholecystitis
and porcelain GB
Gallbladder Carcinoma
Most commonly a mass from the gallbladder fossa replaces the gallbladder and invades adjacent liver.
Focal or diffuse irregular gallbladder wall thickening
Polypoid intramural lesions with irregular borders
Stage 4 colon cancer
Gallbladder Metastasis
commonly from stomach, pancreas and bile ducts
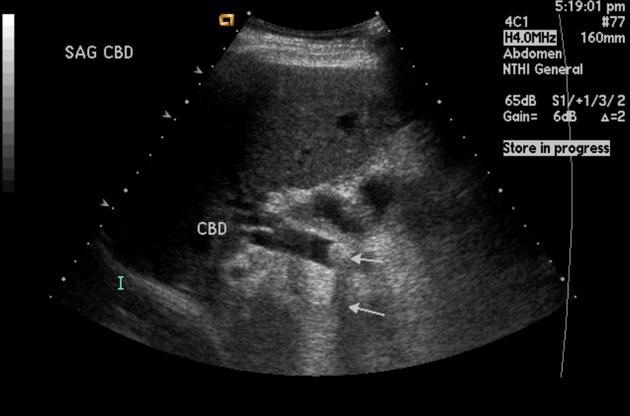
RUQ pain
Jaundice
Elevated Alkaline phosphatase
Elevated conjugated bilirubin
Elevated Gamma gluamyl transpeptidase
Choledocholithiasis
obstrution by biliary stone
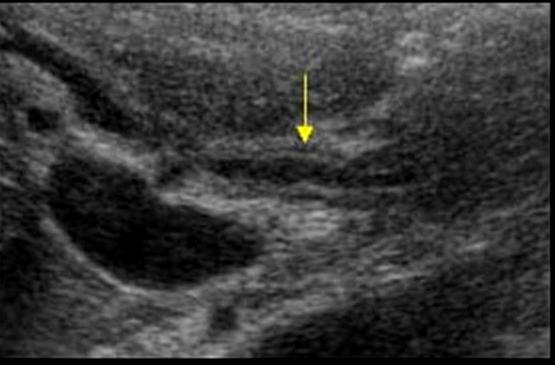
RUQ pain
Fever
Jaundice
Elevated Conjugated bilirubin
Elevated Alkaline phosphatase ALP
Elevated GGT
Elevated amylase and lipase
Elevated white blood count
Cholangitis
inflamation of the duct walls
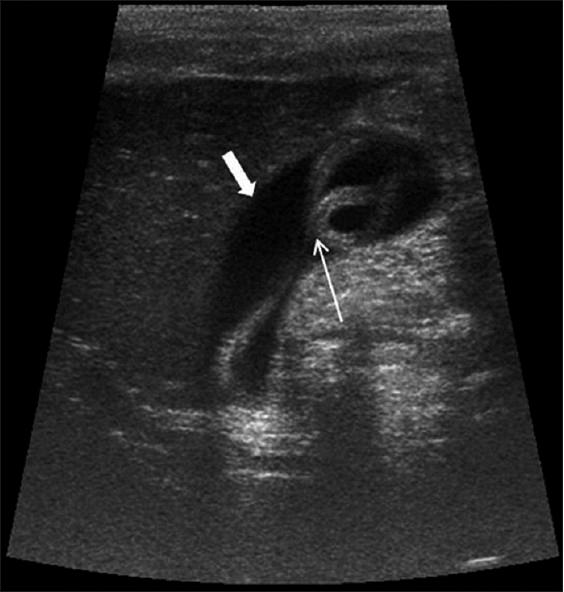
asymptomatic
biliary colic
cholangitis
Poor hygiene
Ascariasis
infection of round worms
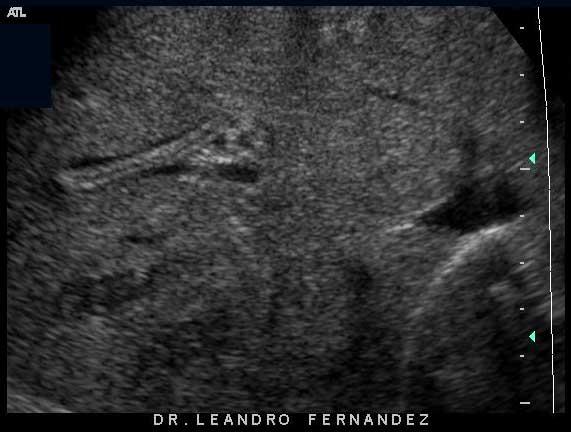
asymptomatic
biliary colic
cholangitis
Poor hygiene
Ascariasis
infection of round worms

Pain
Hematemesis
caused by procedures or biopsy
Hemobilia
blood in the biliary tree
caused by procedures or biopsy
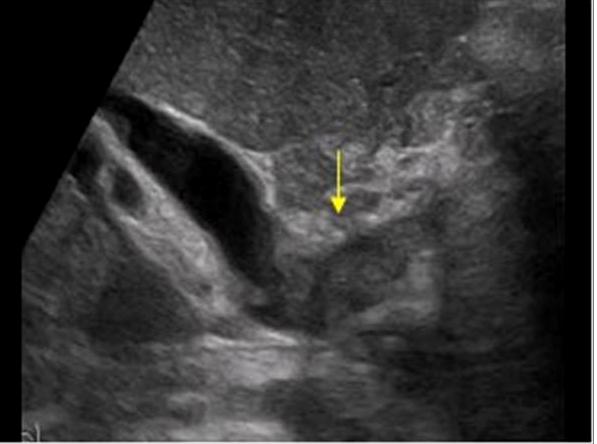
Patient recently had ERCP
pneumobilia
Air within the biliary tree
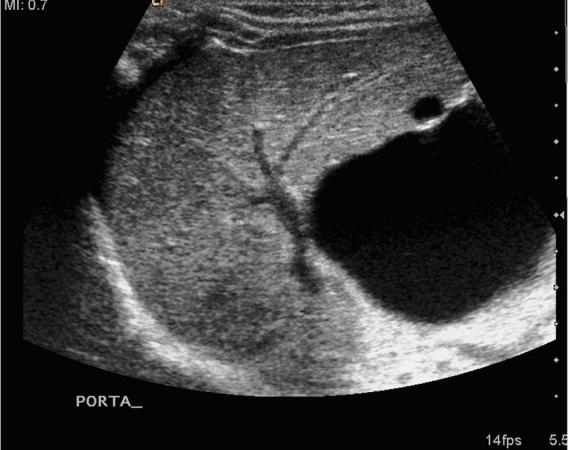
Jaundice
weight loss
abdominal pain
Cholangiocarcinoma
typically originate within the extrahepatic bile ducts
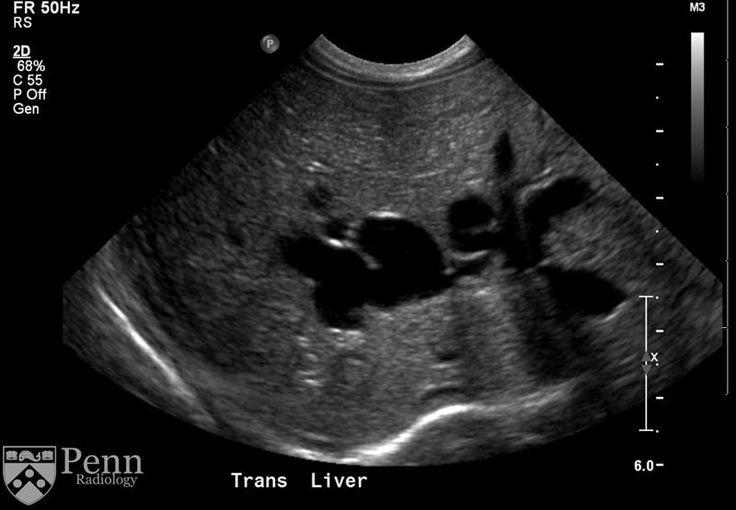
Neonate presents with Jaundice for 14+ days
Biliary Atresia
Congenital
cystic formation without dilated interhepatic ducts
congenital hepatic fibrosis
Portal hypertension
Caroli's Disease
congenital cystic dilatation of the intrahepatic biliary tree
9 year old Japanese patient
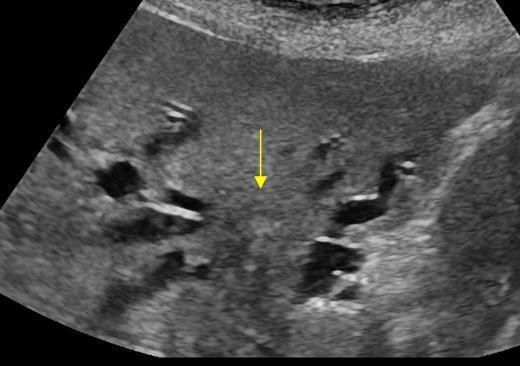
Choledochal Cyst
Congenital cystic dilation of the extrahpatic biliary tree
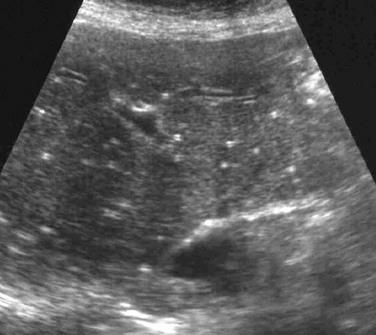
Klatskin Tumor
malignant tumor arising between the left and right hepatic ducts
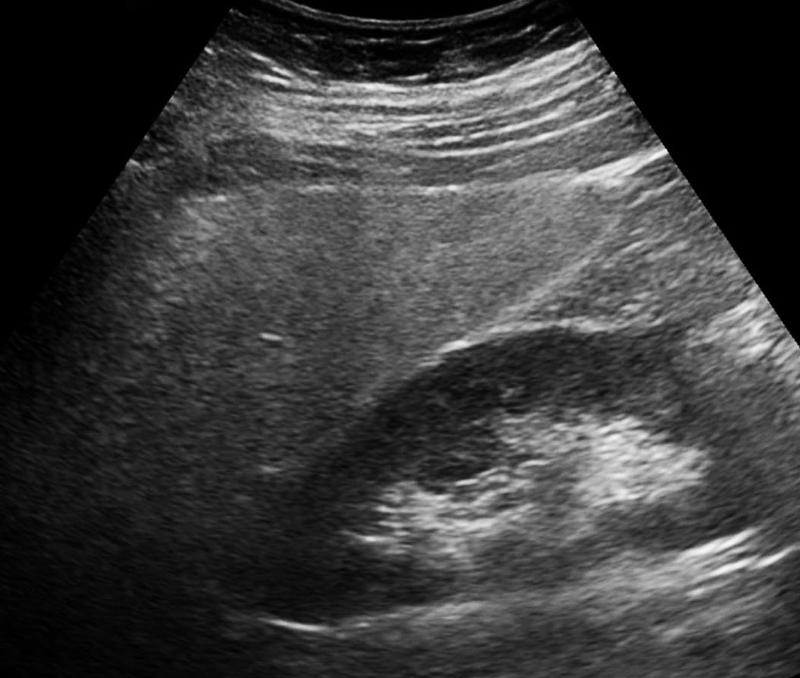
Patient in Great Lakes basin
Liver granulomas
Hypoechoic renal cortex
obese
Type II diabetes
Fatty infiltration
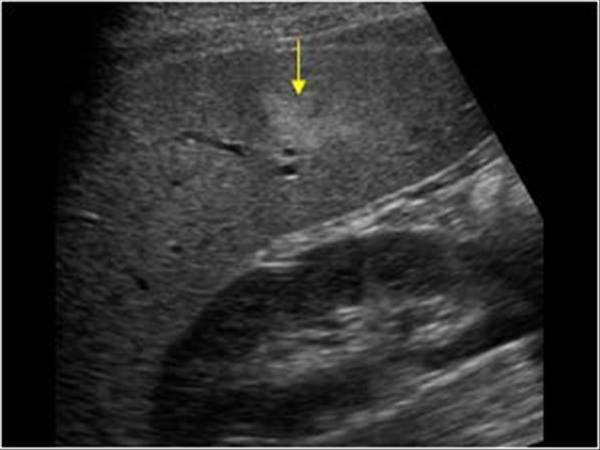
Fat Sparing
- diabetes mellitus
- obesity
- alcohol abuse
- exogenous steroids
- drugs (amiodarone, methotrexate, chemotherapy)
- IV hyperalimentation
focal fatty infiltration
Infant
impaired growth
hypoglycemia
CHF
delayed puberty
osteoporosis
Glycogen Storage Disease
Autosomal recessive disorder of carb metabolism
found in infants
seen with adenomas
Elevated
ALT
AST
Bilirubin con & un
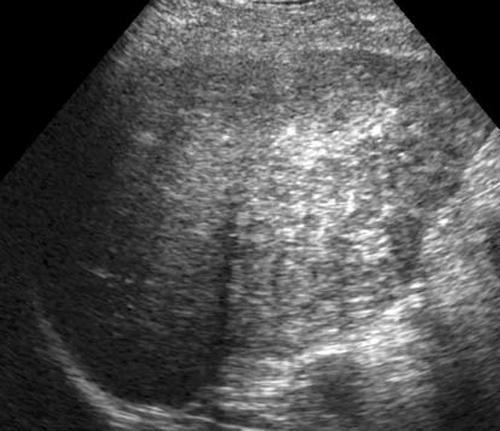
Acute Hepatitis
Generally normal
but can have portal cuffing (starry sky)
Elevated
ALT
AST
Bilirubin con & un
Chronic Hepatitis
course texture
increased echogenicity
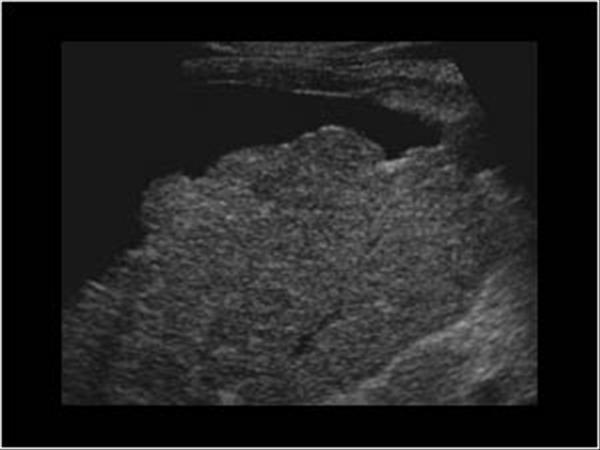
chronic hepatitis
alcoholism
elevated
AST
ALT
GGT
LDH
conjugated bilirubin
Cirrhosis
nodular and course
heterogenic
Ascites
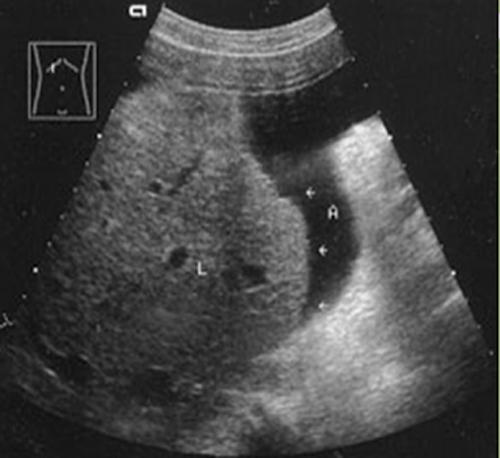
Cirrhosis
nodular and course
heterogenic
Ascites
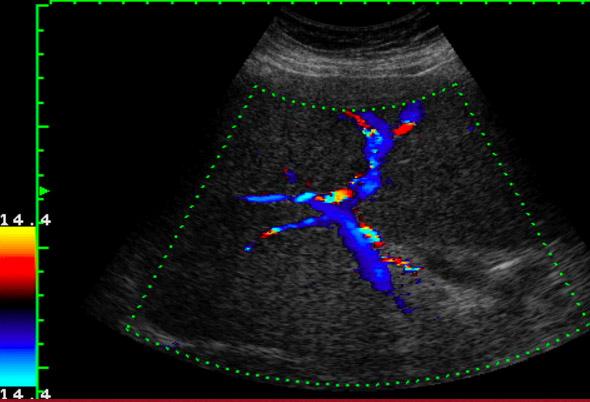
asymptomatic
sudden painless upper GI hemorrhage due to ruptures esophageal varices
Portal Hypertension
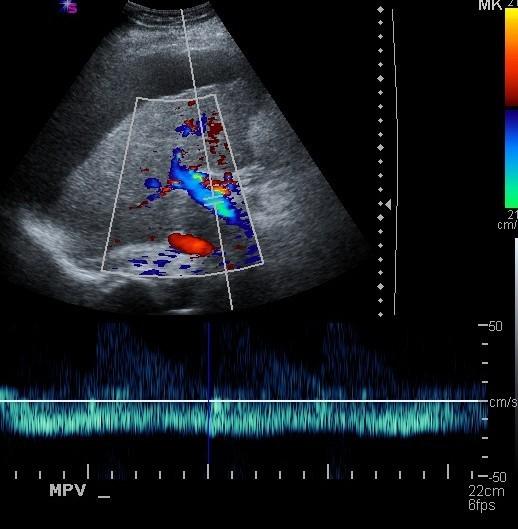
Portal Hypertension
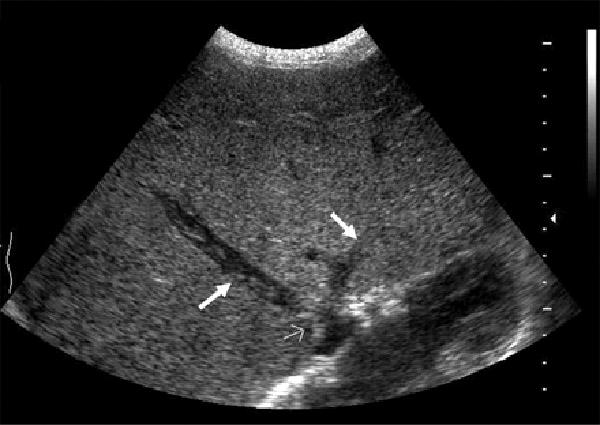
Budd-Chiari
Life threatening emergency
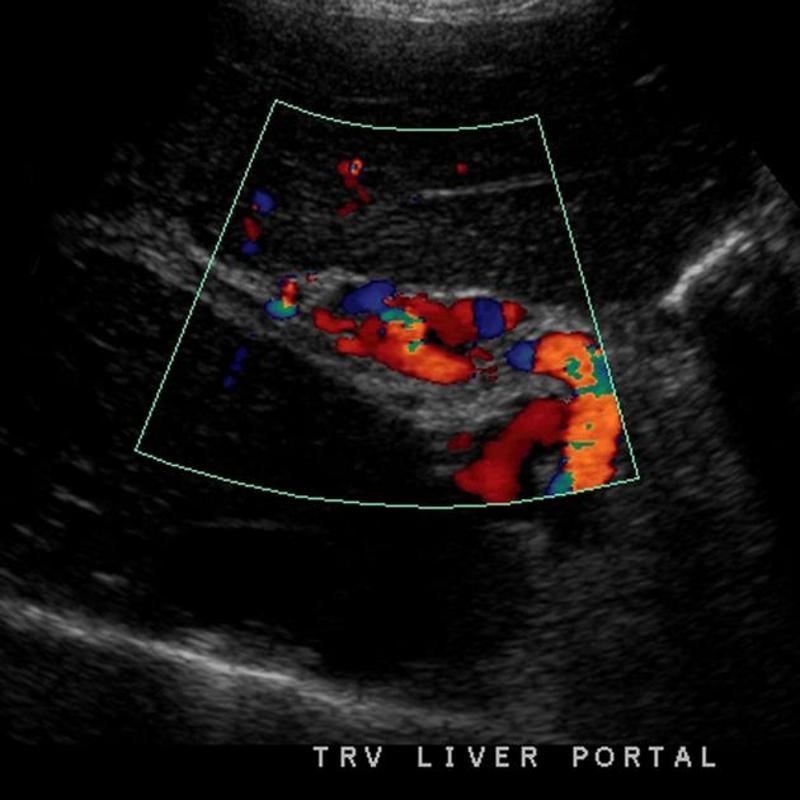
Portal vein Thrombosis - cavernous transformation
replacement of the normal single channel portal vein with numerous tortuous venous channels.
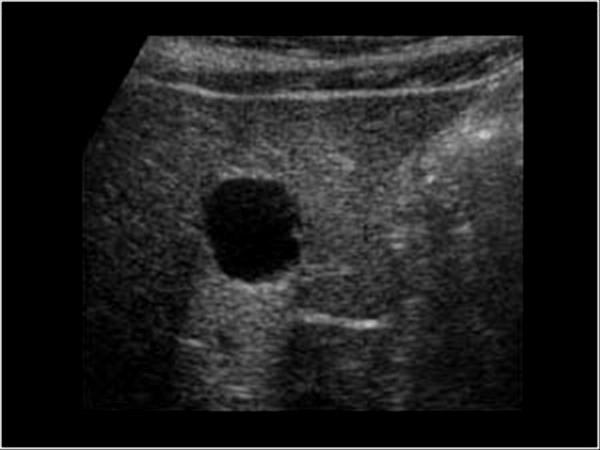
50+
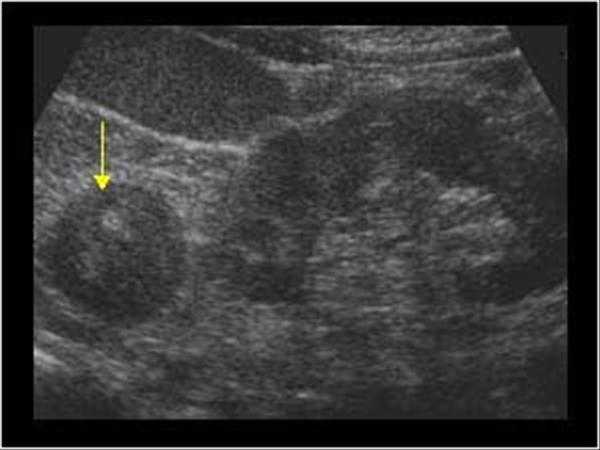
Cysts
True cysts are congenital
other cysts lack an epithelial lining and are not true cysts
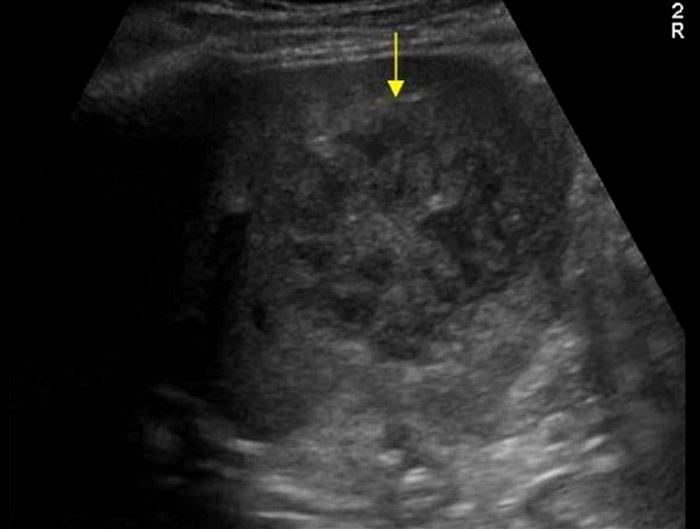
Presentation
Fever
pain
N&V
Leukocytosis
Elevated LFTs
Pyogenic (bacterial) abscess
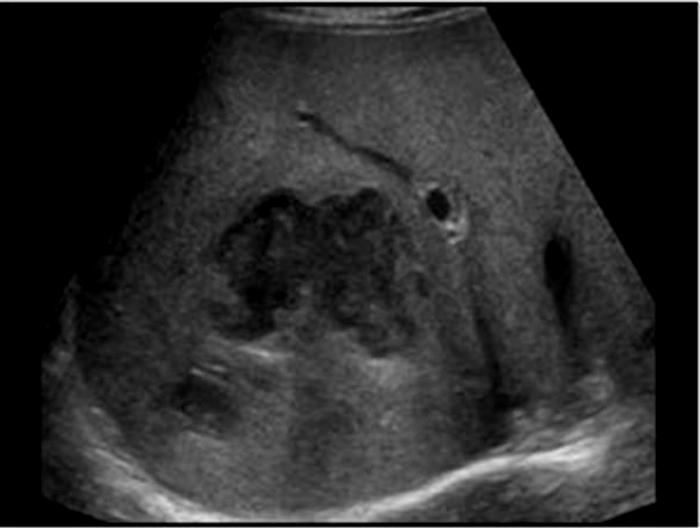
Presentation
fever
pain
diarrhea
Leukocytosis
Elevated LFTs
Amebic abscess
contaminated food or water usually in colon but can invade the liver through the portal vein
fever
pain
diarrhea
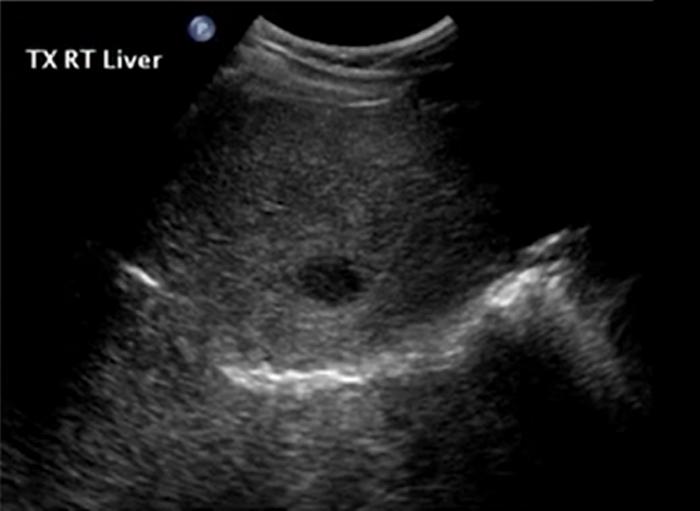
May also present
wheel within a wheel
Bull's eye
Echogenic focus
Candidiasis
early wheel within wheel
later hypoechoic
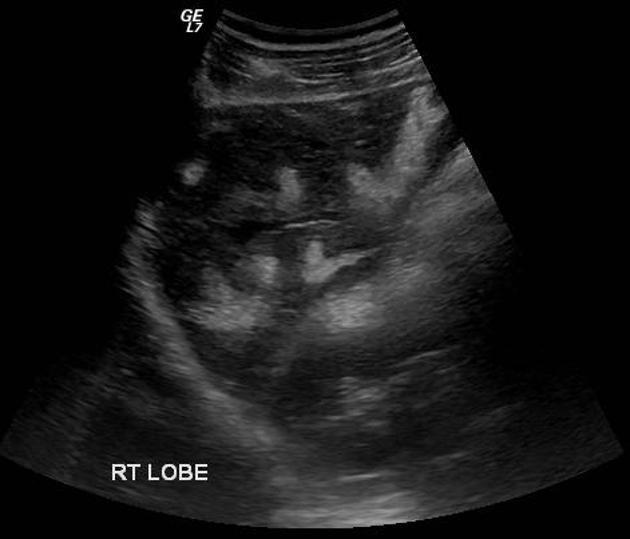
# cause of portal hypertension
Schistosomiasis
#1 cause of portal hypertension in the world. Not common in US but estimated 400,000 infected people have immigrated
parasitic infection mainly in Egypt
- irregular surface of liver
- hyperechoic thickened walls of portal venules giving the "clay-pipestem" pattern of periportal fibrosis
- marked thickening and echogenecity of the gallbladder bed
- splenomegaly
- portal vein and splenic vein dilatation with maintained continuous hepatopetal flow and average velocity
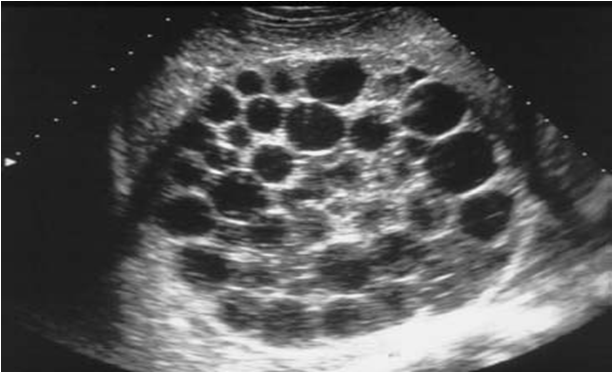
Sheep herder
Echinococcal Cyst
Sheep Herders
AKA Hydatid Cyst
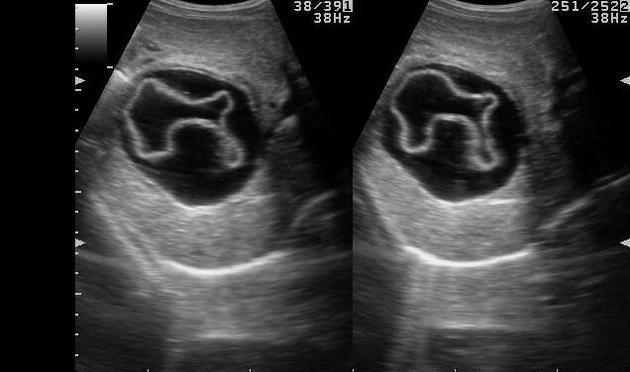
Sheep herder
Echinococcal Cyst
Sheep Herders
AKA Hydatid Cyst
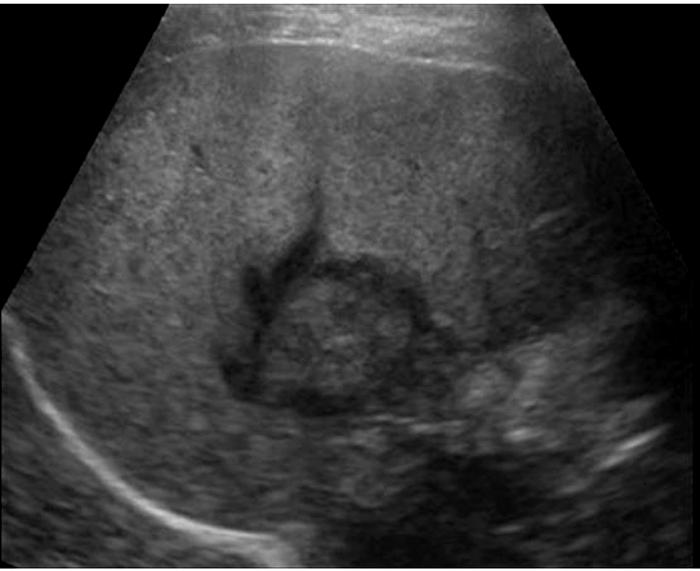
Water lily
Sheep herder
Echinococcal Cyst
Sheep Herders
AKA Hydatid Cyst
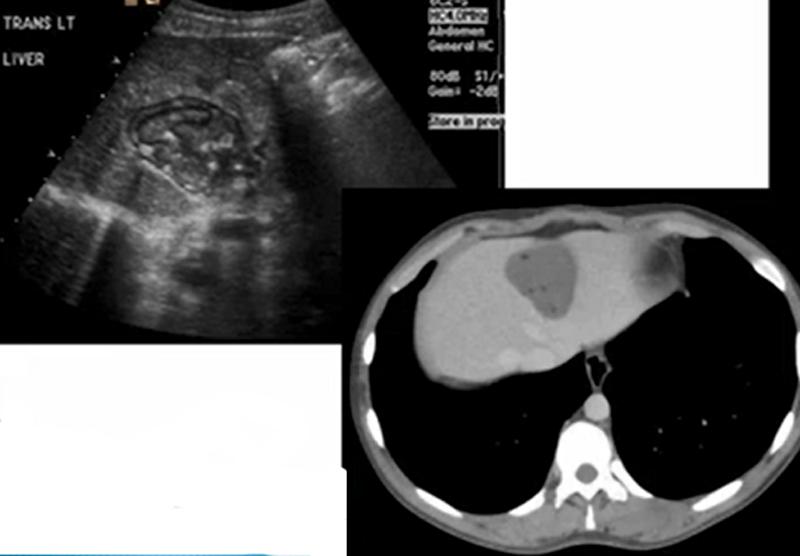
24 year old female on birth control pills
Pain
Liver Adenoma
Females taking birth control
*Hypoechoic
*Hyperechoic
*Isoechoic
*Mixed
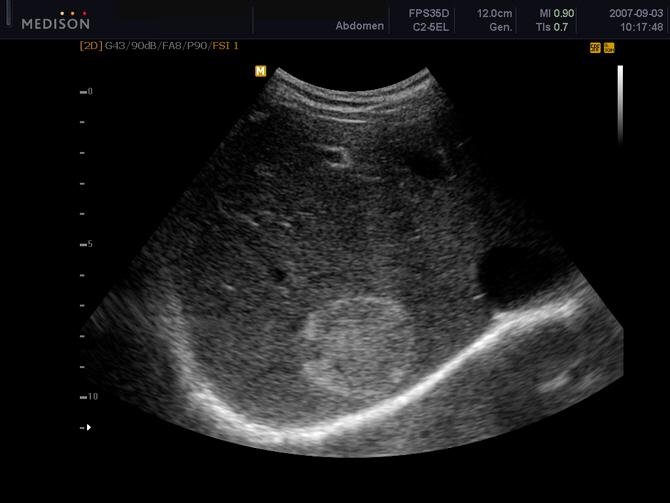
enlarge with pregnancy
Cavernous Hemangioma
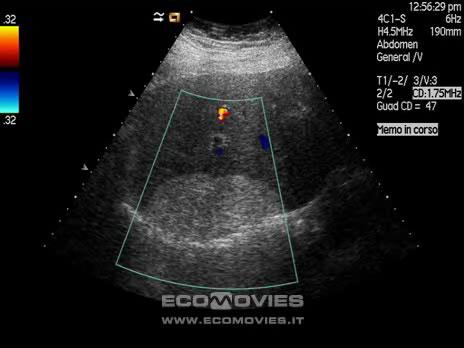
Hepatic lipoma
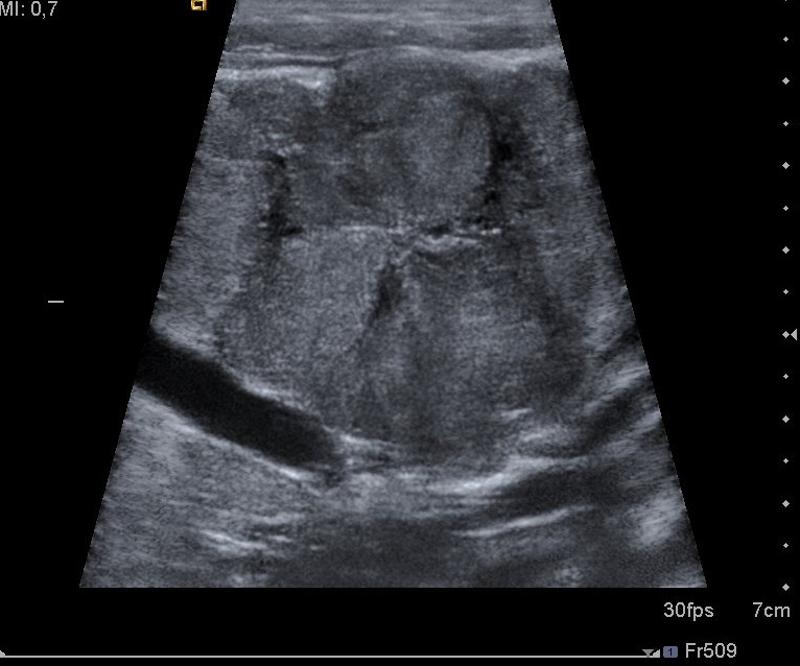
Asymptomatic
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia
abnormally arranged hepatocytes
Second most common benign liver mass
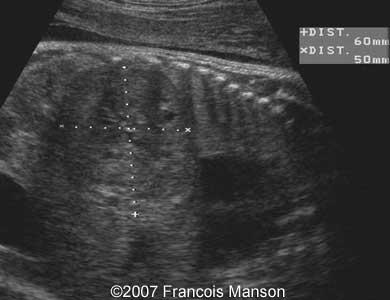
6 month old female
abdominal mass
CHF
Hemangioendothelioma
Benign condition of overgrowth of endothelium of capillaries
Found in infants
Usually seen as hepatic lesions that are predominantly hypoechoic; however, hepatic lesions can also have mixed echotexture or be predominantly hyperechoic.
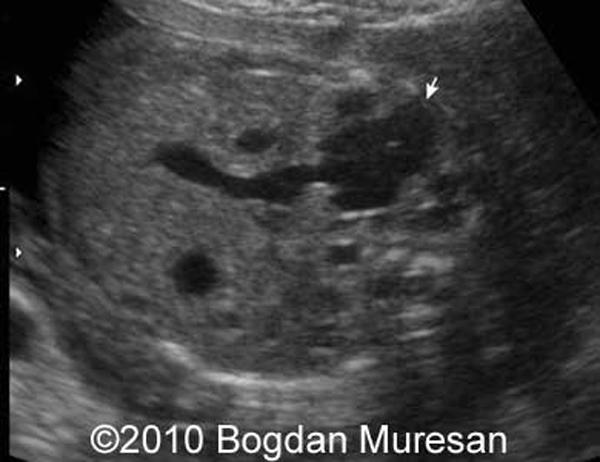
Two year old with palpable mass on right side
Mesenchymal hamartoma
rare developmental cystic tumor of the lover
complex mass
more common in rt lobe
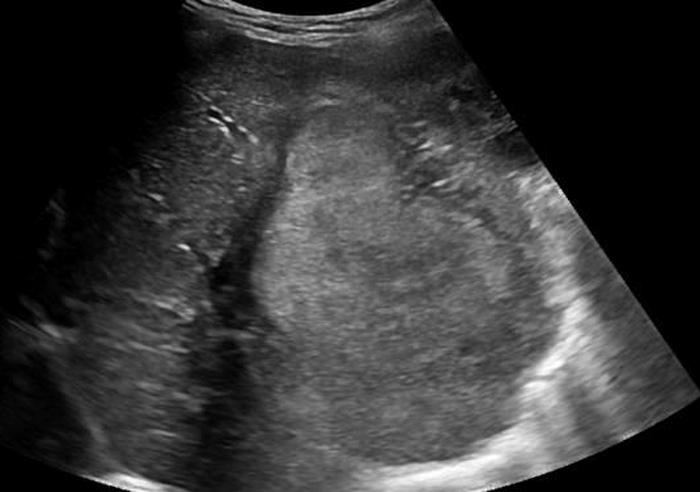
3 year old
abdominal enlargement
weight loss
nausea and vomiting
marked elevation of AFP
Hepatoblastoma
malignant germ cell tumor
most common malignant liver tumor of children under 3
associated with Beckwith Wiedermann
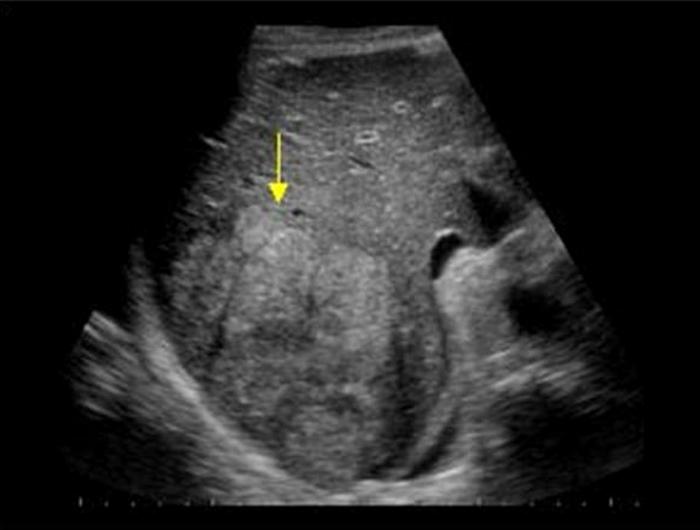
Patient with cirrhosis
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
solid
multiple
diffuse
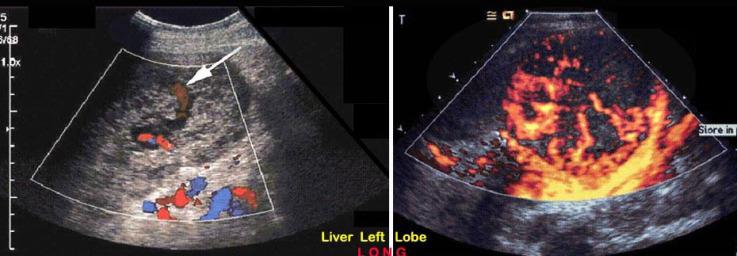
Hemangiosarcoma
rare in 60 - 80
related to exposure of thorotrast, arsenic or polyvinyl chloride
large mixed mass
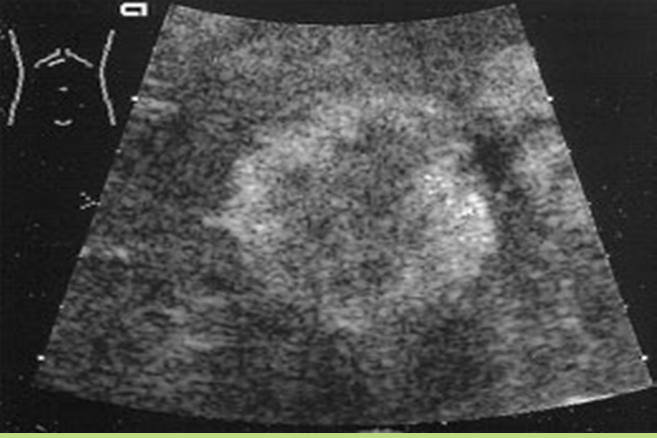
Liver mets from ?
Metastasis to the liver
colon
Most common
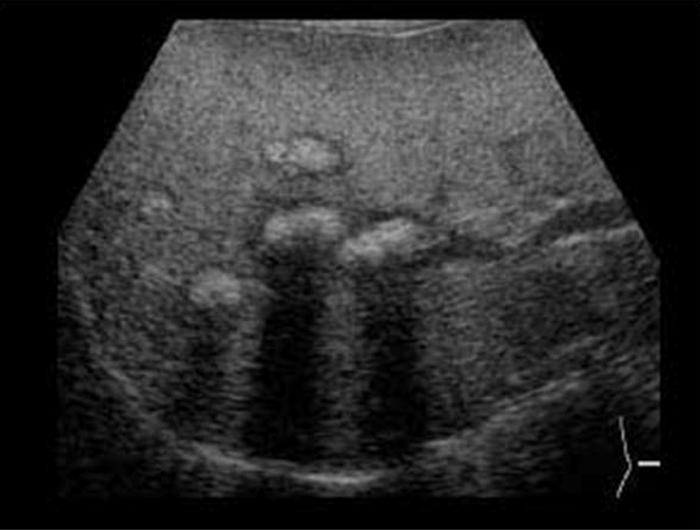
Liver mets from ?
Metastasis to the liver
Breast
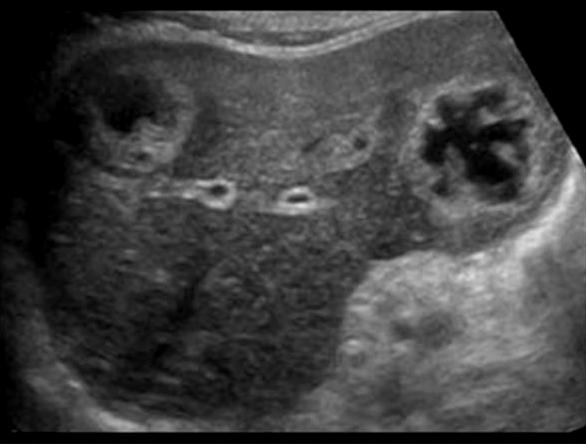
Liver mets from ?
Metastasis to the liver
Lung
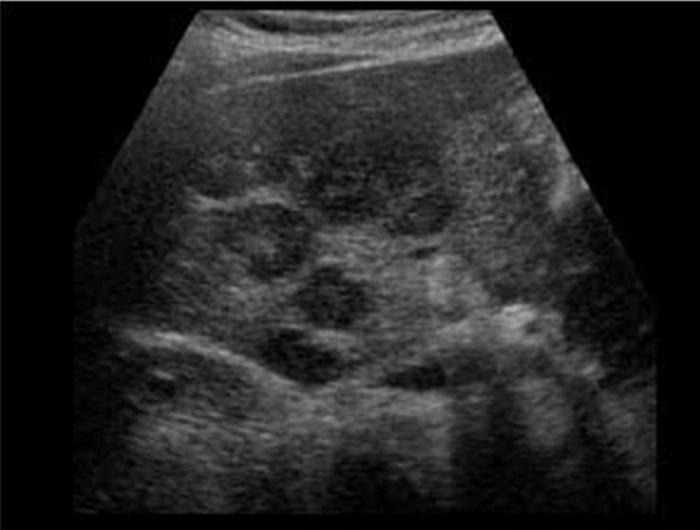
Liver mets from ?
Lymphoma
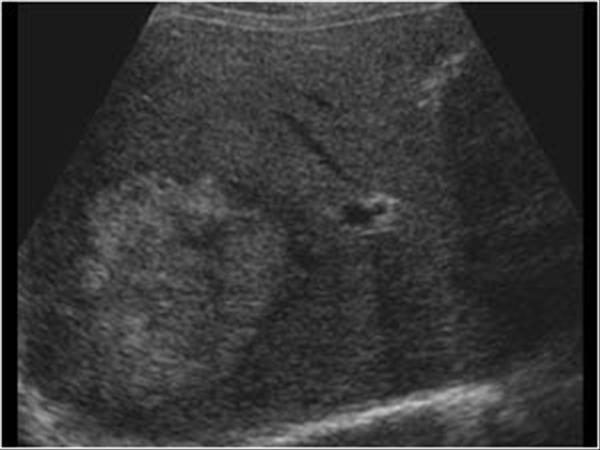
Pain
hypertension
after car accident
Liver hematoma
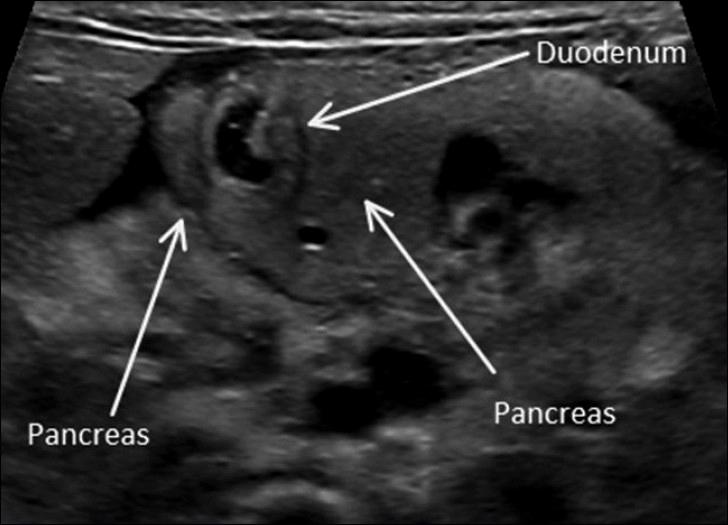
Annular Pancreas
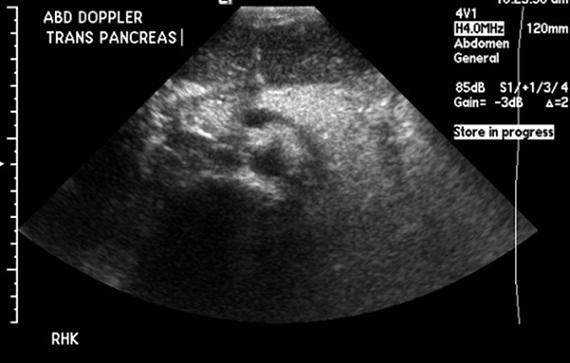
6 year old present
Cystic Fibrosis
autosomal Recessive
Pancreas appears hyperechoic due to microcystic changes, increased fibrotic and fat
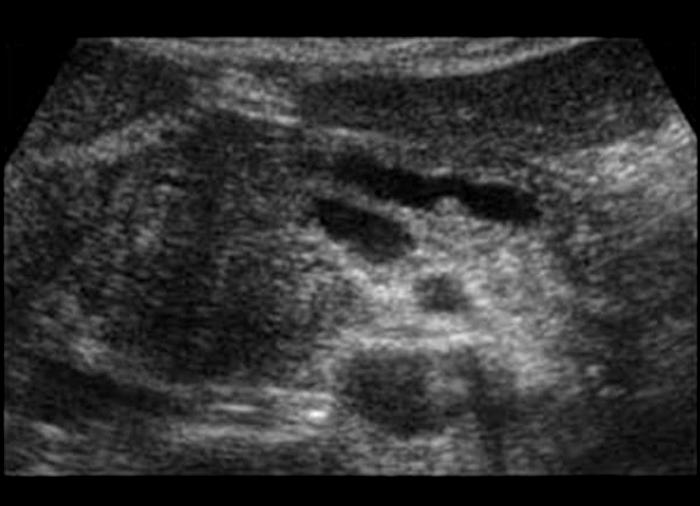
severe constant, intense pain radiating to the back
N & V
fever
sweating
paralytic ilius
elevated amylase 48 - 78 hours
elevated lipase 5 - 7 days
WBC
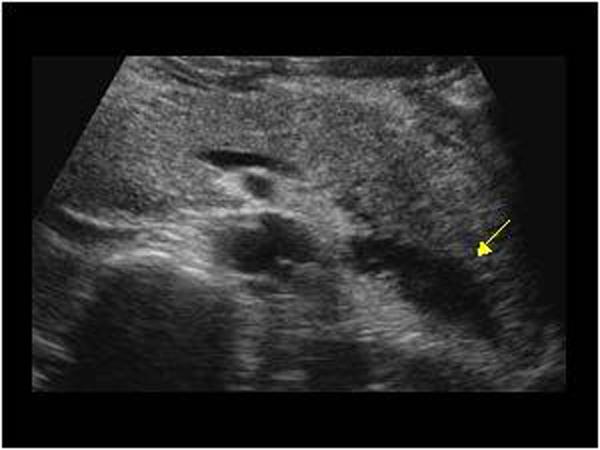
Acute Pancreatitis
severe constant, intense pain radiating to the back
N & V
fever
sweating
paralytic ilius
elevated amylase 48 - 78 hours
decreased hematocrit & calcium
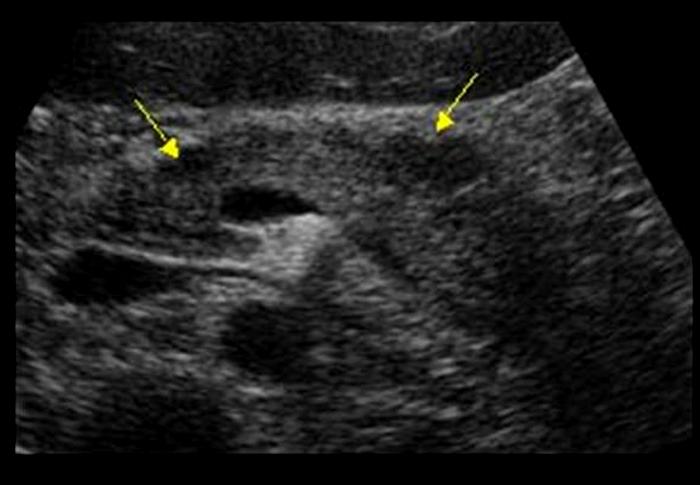
Hemorrhagic Pancreatitis
Type of acute pancreatitis 2% to 5%
significant fat necrosis that results in rupture of pancreatic vessels and secondary hemorrhage
N & V
fever
sweating
paralytic ilius
elevated amylase 48 - 78 hours
elevated lipase 5 - 7 days
WBC
Phlegmonous Pancreatitis
Type of acute pancreatitis 18%
enlarged solid inflammatory mass with retroperitoneal fat necrosis
usually lesser sac is involved
Pancreatic Abscess
infection of necrotic pancreatic and retroperitoneal fat
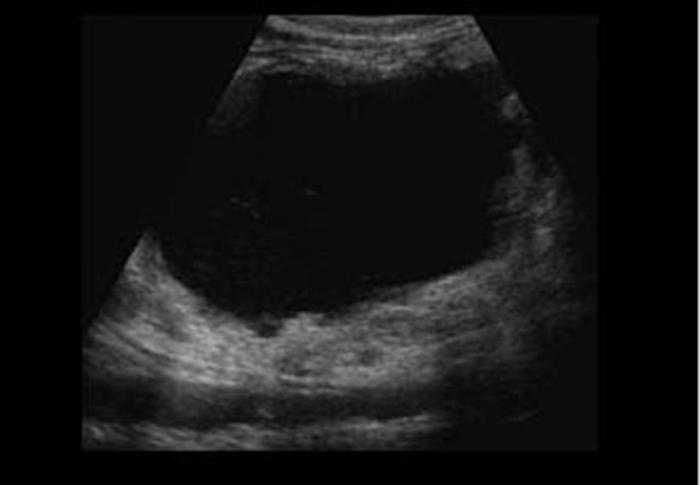
persistently elevated amylase and lipase
Pancreatic Psydocyst
Spherical fluid collection of pancreatic enzymes that arise from inflamatory, necrotic and hemorrhage processes of the pancrreas
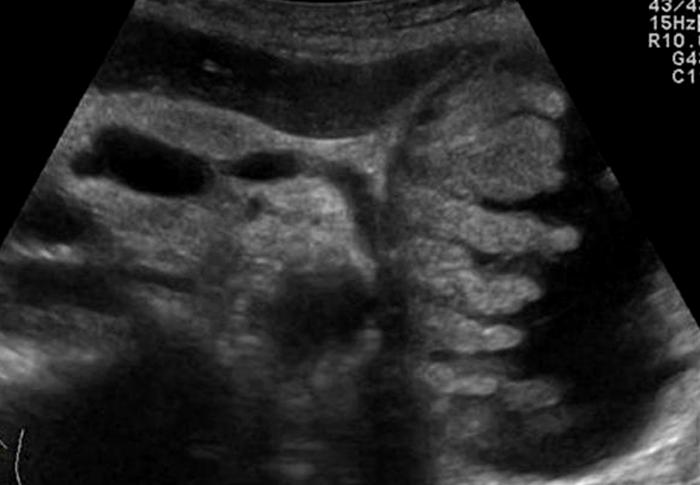
persistently elevated amylase and lipase
Pancreatic Psydocyst
Spherical fluid collection of pancreatic enzymes that arise from inflamatory, necrotic and hemorrhage processes of the pancrreas
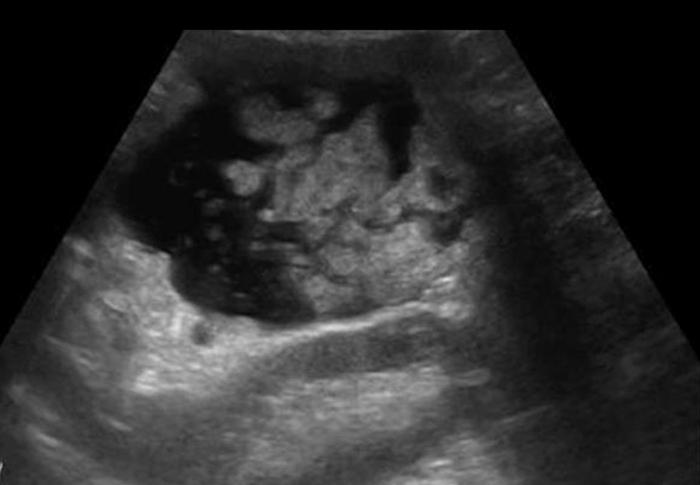
persistently elevated amylase and lipase
Pancreatic Psydocyst
Spherical fluid collection of pancreatic enzymes that arise from inflamatory, necrotic and hemorrhage processes of the pancrreas
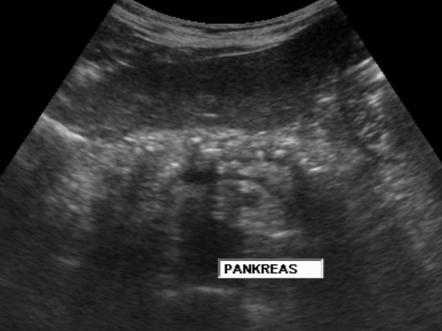
N & V
flatulence
weight loss
Chronic Pancreatitis
Ongoing inflammation that results in permanent damage
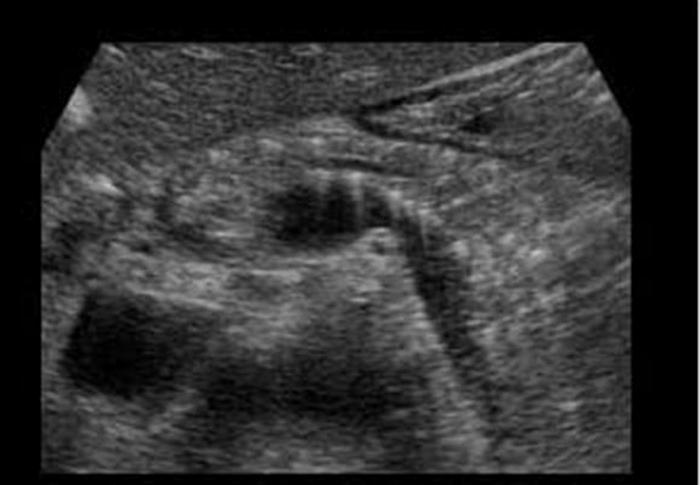
N & V
flatulence
weight loss
Chronic Pancreatitis
Ongoing inflammation that results in permanent damage
Mid epigastric Pain
weight loss
jaundice
palpable mass
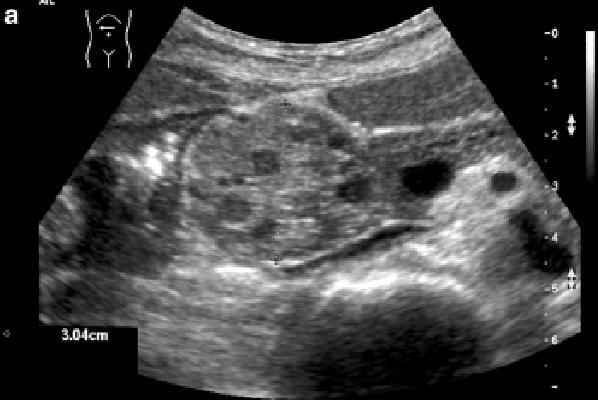
Cystadenoma
multiple cystic masses that contain secreted material
Mid epigastric Pain
weight loss
jaundice
palpable mass
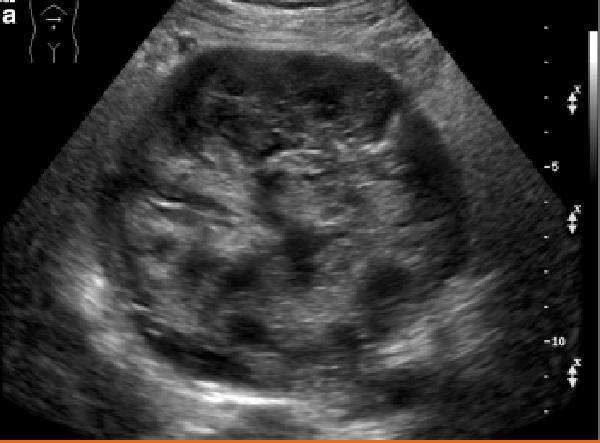
Mucinous Cystic / Cystadenocarcinoma
malignant tumor from glandular tissue in which secretions are oobtained
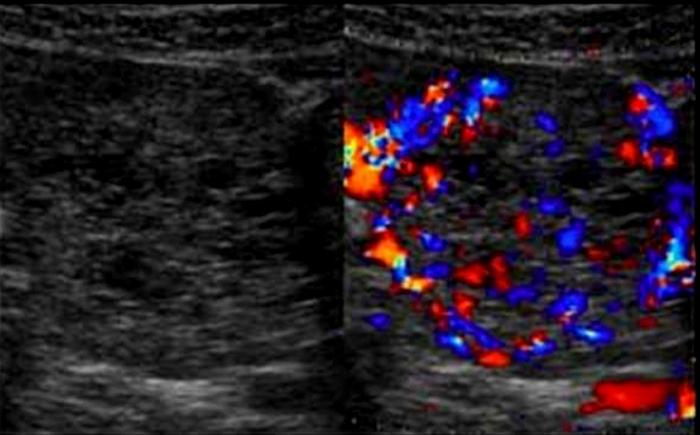
25 year old female with vague abdominal pain
Serious Cystadenoma / Microcystic adenoma
type of serous cystadenoma
lobulated mass of numerous small cysts
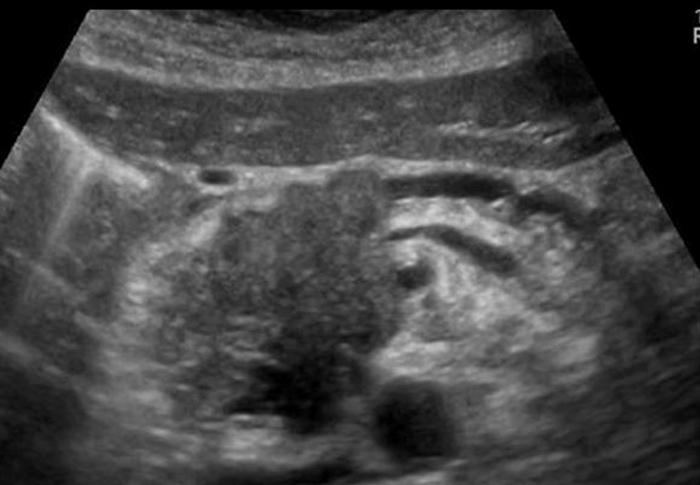
Most common cause of malignant neoplasm
abdominal / back pain
jaundice
weight loss
Adenocarcinoma
arises from the epithelium and involves the exocrine portion of the pancreas
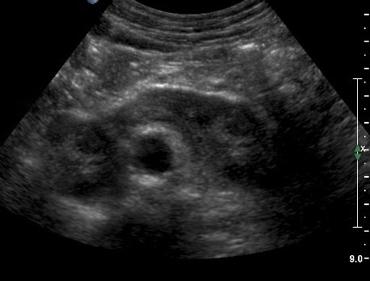
The most common form of fusion anomaly of the kidneys
Horseshoe Kidneys
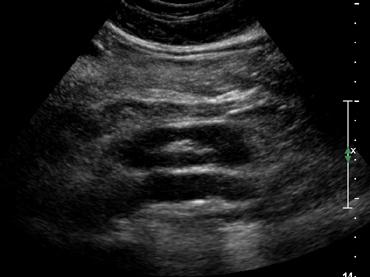
The most common form of fusion anomaly of the kidneys
Horseshoe Kidneys
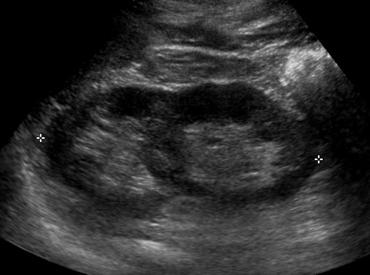
Crossed fused Renal Ectopia
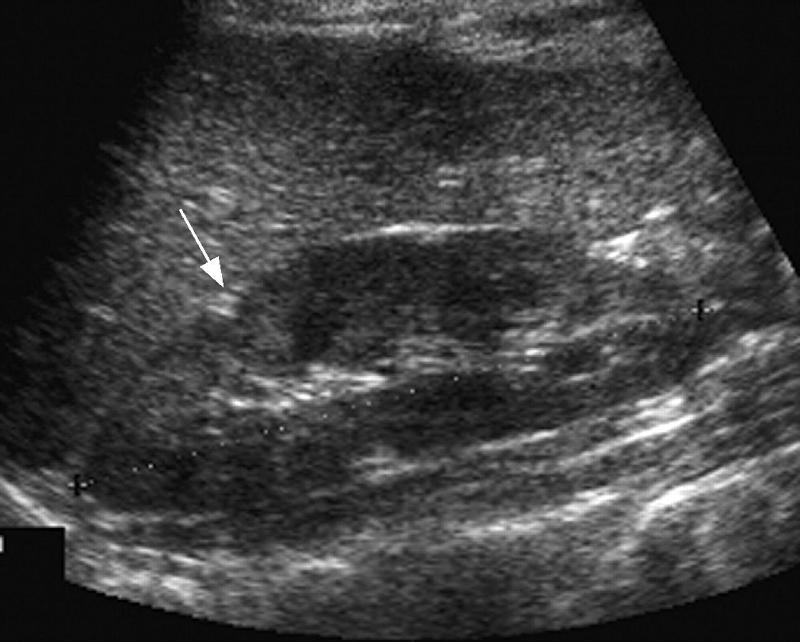
Right kidney
Junctional Parenchymal Defect
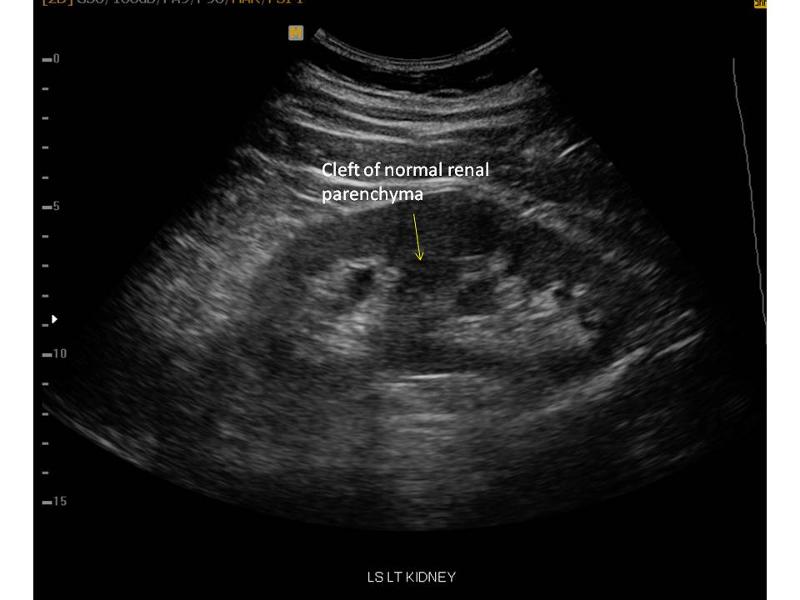
often seen with hydronephrosis in the upper pole
Duplex Kidney
Seen in 15% of population
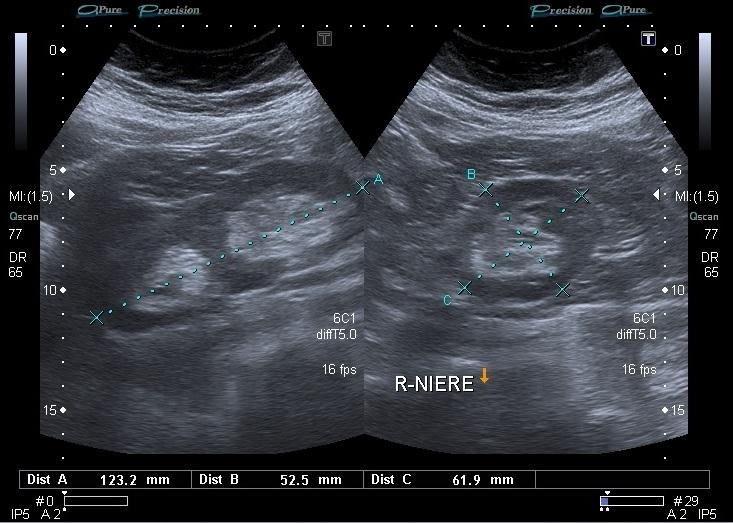
Duplex Kidney
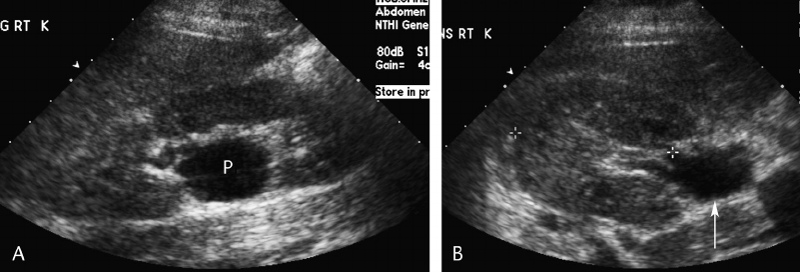
Extrarenal Pelvis
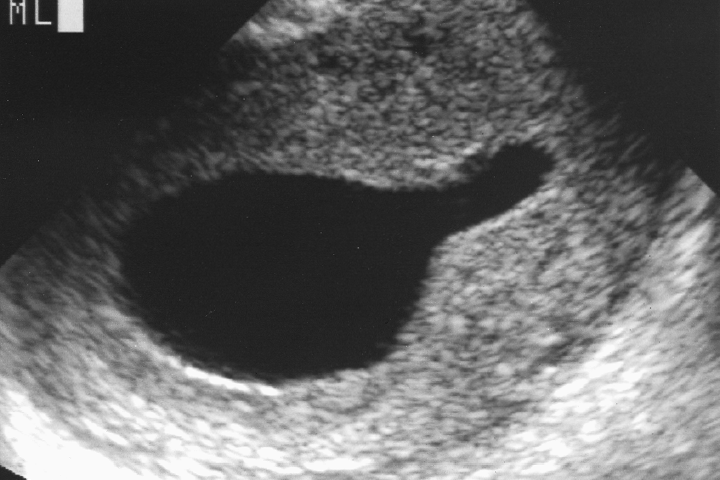
Male neonate
Posterior Urethral valves
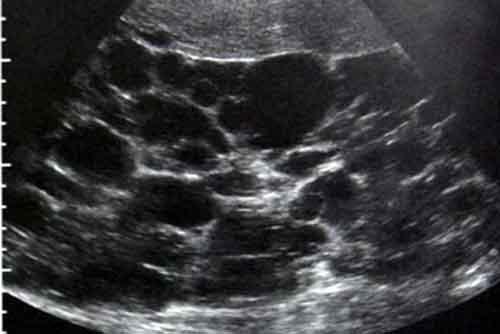
30 year old male presents for a renal ultrasound
liver & spleen cysts
Adult Polycystic Kidney Disease

infant presents with renal dysfunction
Infantile Polycystic Kidney Disease
results from cystic dilation of the collecting tubules
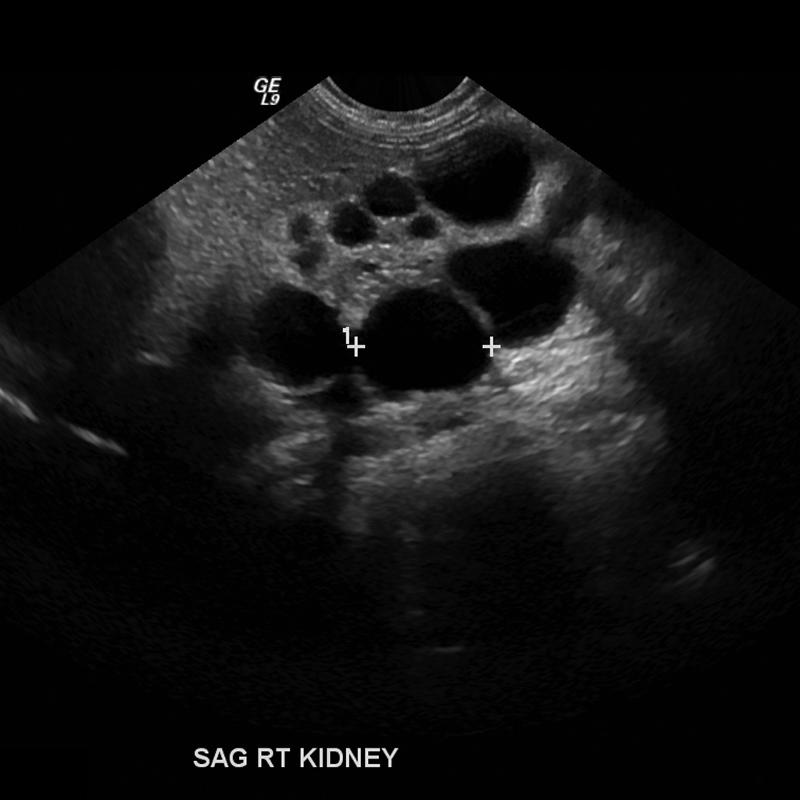
Most common cause of abdominal mass in newborns
unilateral
Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney
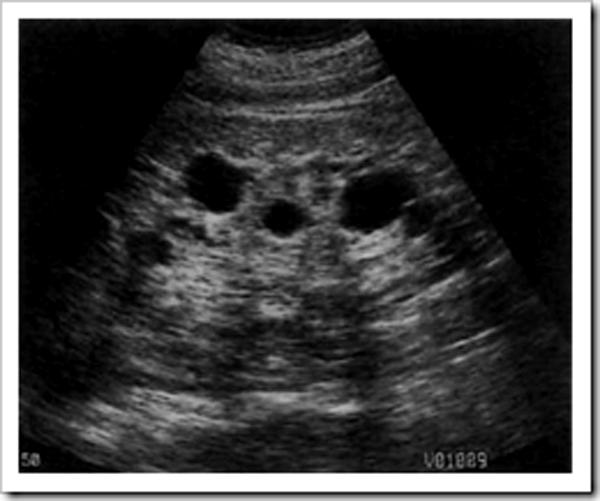
chronic renal failure
hemodialysis
Aquired Cystic Disease
multiple cysts in failing kidney during long term hemodialysis
hemorrhage often occurs
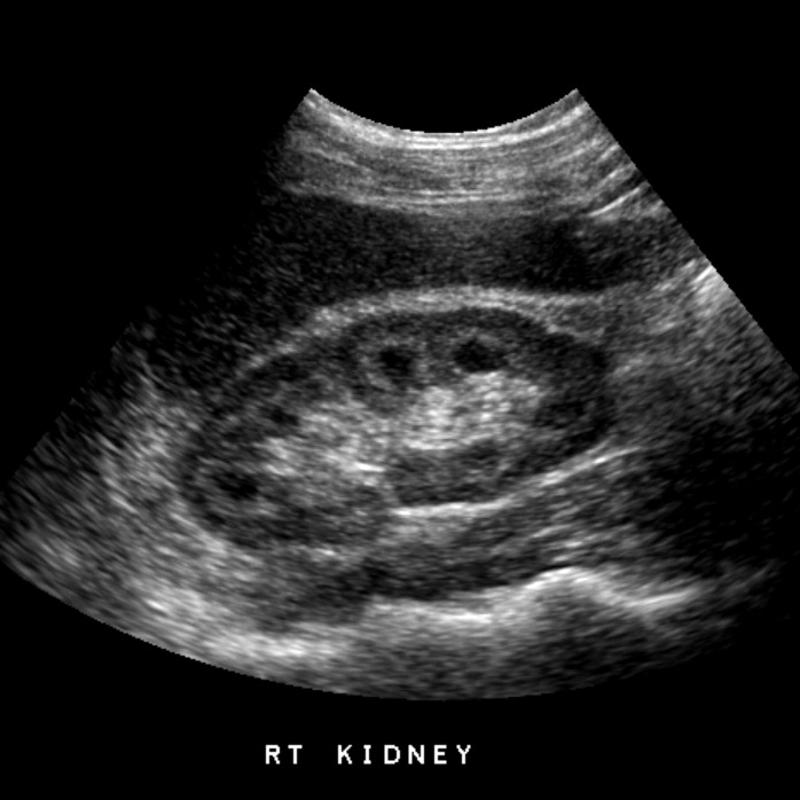
Medullary Sponge Kidney
congenital dysplastic dilatation of the medullary pyramids due to tubular ectasia or dysplasia
medullary neprocalcinosis
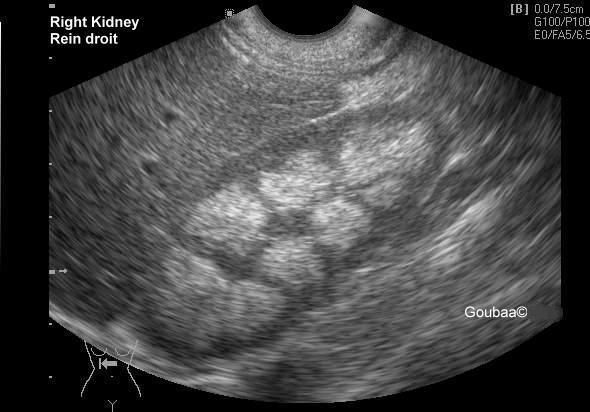
medullary neprocalcinosis
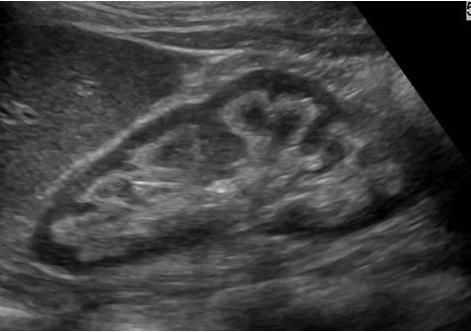
hypercalcemia
hypercalciuria
Nephrocalcinosis
20 year old presents with visual impairments
Von Hippel-Lindau Disease
inhearited usually present in 2nd to 3rd decade
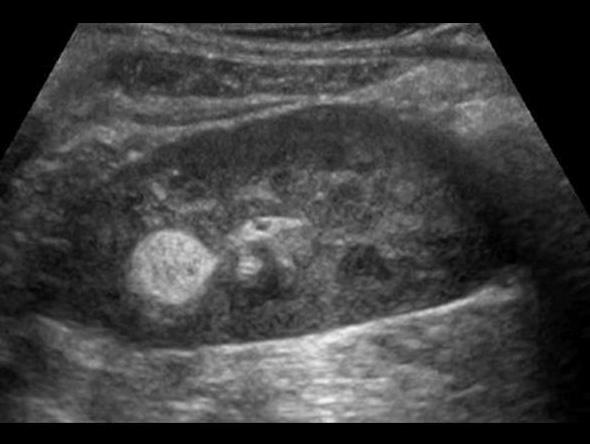
right kidney
Angiomyolipoma
benign fatter renal tumor
80% involve right kidney
echogenicity is gretr than of equal to the renal sinus
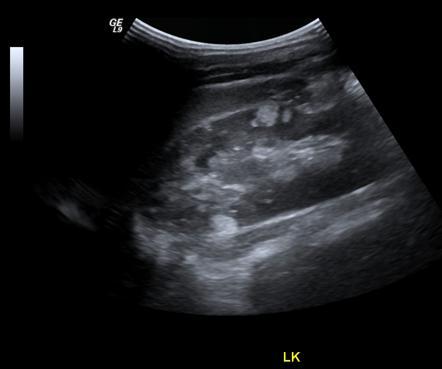
right kidney
Angiomyolipoma
benign fatter renal tumor
80% involve right kidney
echogenicity is gretr than of equal to the renal sinus
seizures
mental retardation
facial angiofibroma
bilateral Angiomyolipomas
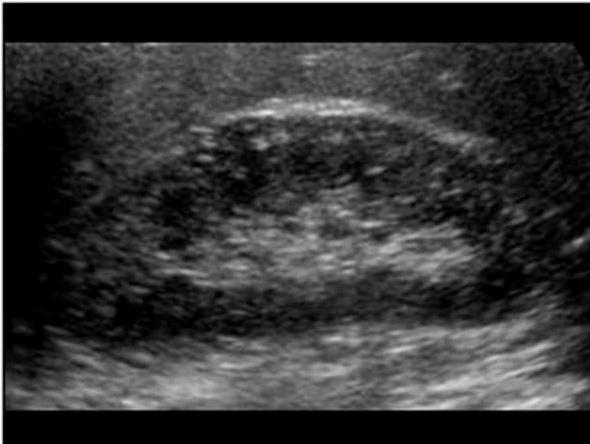
Tuberous Sclerosis
genetic
Most common solid renal mass in adults
hematuria
flank pain
palpable mass
lung mets
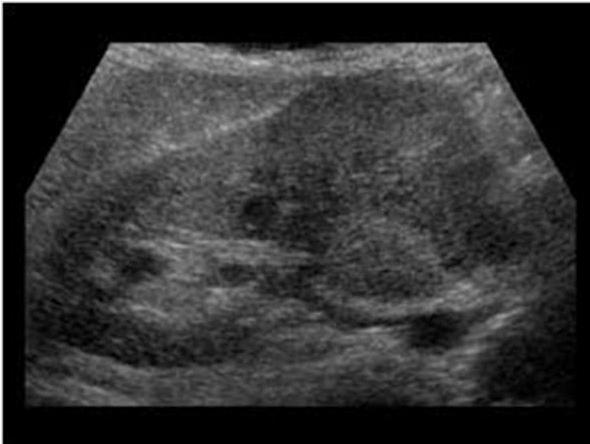
Renal Cell Carcinoma
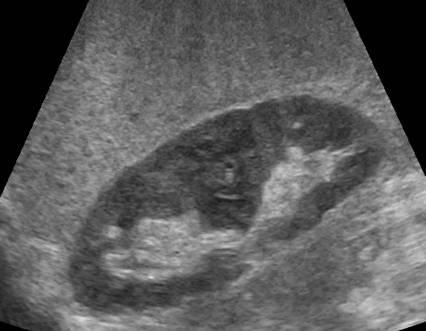
Most common solid renal mass in adults
hematuria
flank pain
palpable mass
lung mets
Renal Cell Carcinoma
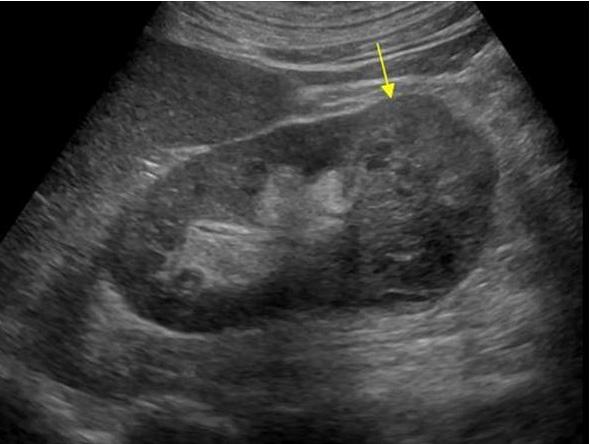
generally appear as hypoechoic or diffuse enlargement
Renal Metastases
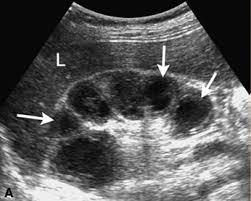
3 years
large asymptomatic flank amss
hypertension
fever
hematuria
Wilm's Tumor
3 years
90% survival
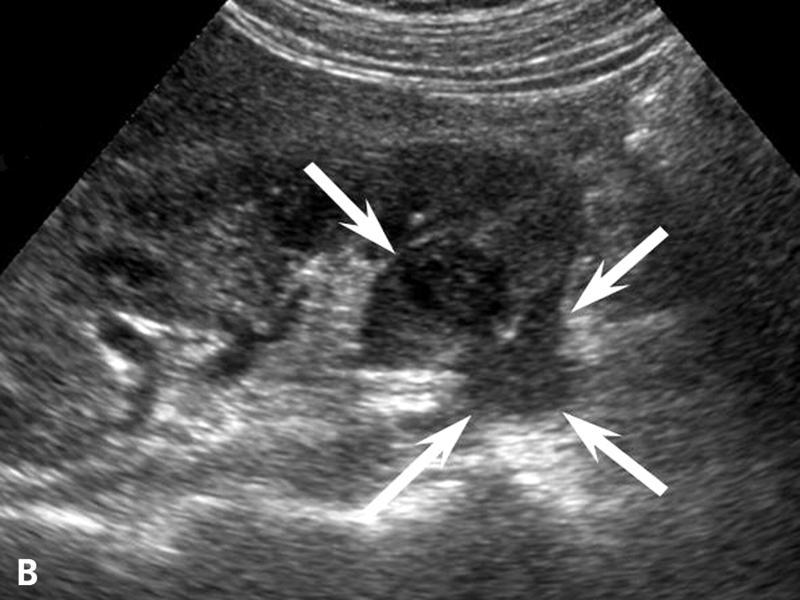
Acute Pyelonephritis
travel from bladder
AKA acute focal bateria nephritis / lobar nephritis
Acute Pyelonephritis
travel from bladder
AKA acute focal bateria nephritis / lobar nephritis
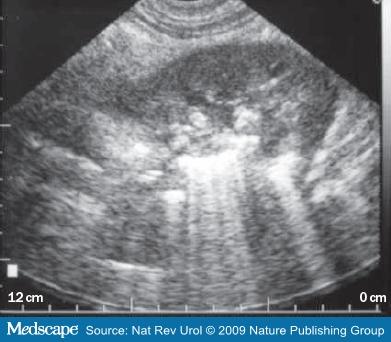
diabetic
Emphysematous pyelonephritis
Gas in the kidney
nephroectomy is usually required
small hyperechoic kidneys with cortical thinning
Chronic Pyelonephritis
due to recurrent renal infection
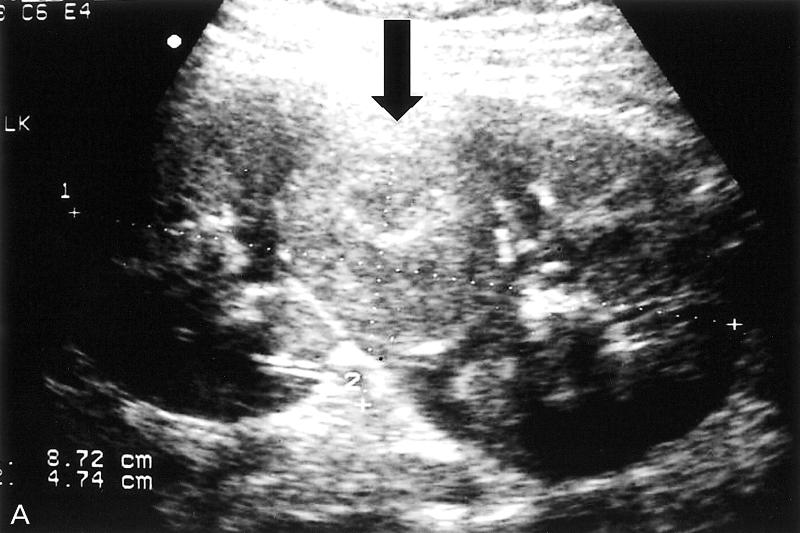
type of Chronic Pyelonephritis
Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis XGPN
Chronic Pyelonephritis due to stone
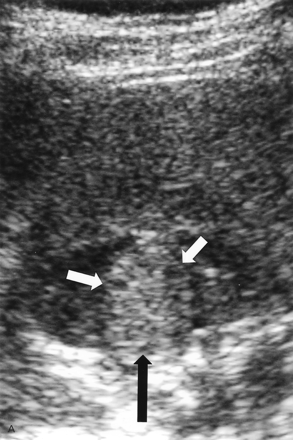
type of Chronic Pyelonephritis
Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis XGPN
Chronic Pyelonephritis due to stone
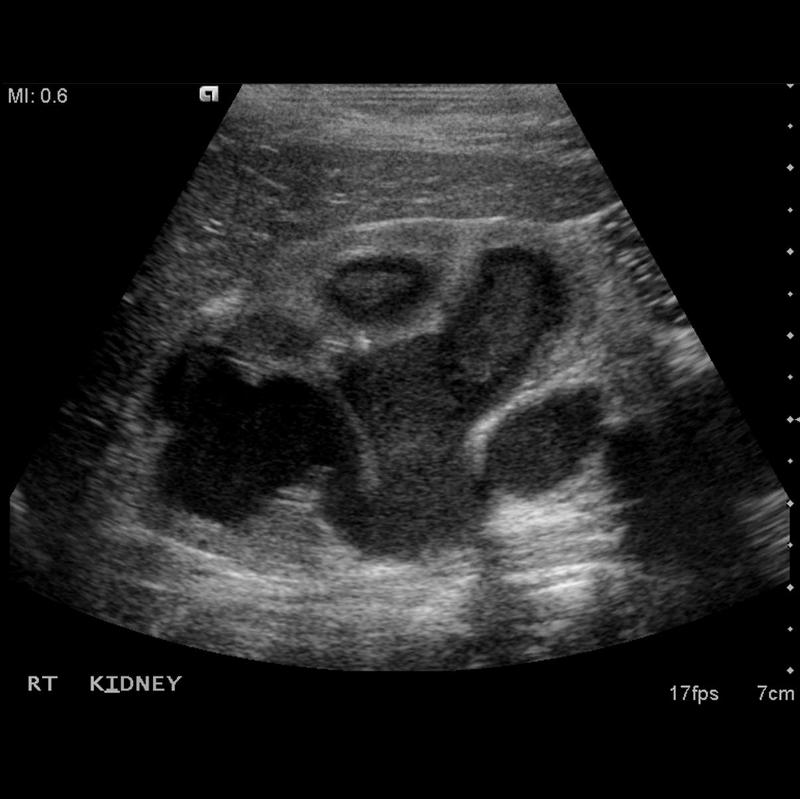
due to secondary infection from renal obstrution
Pyonephrosis
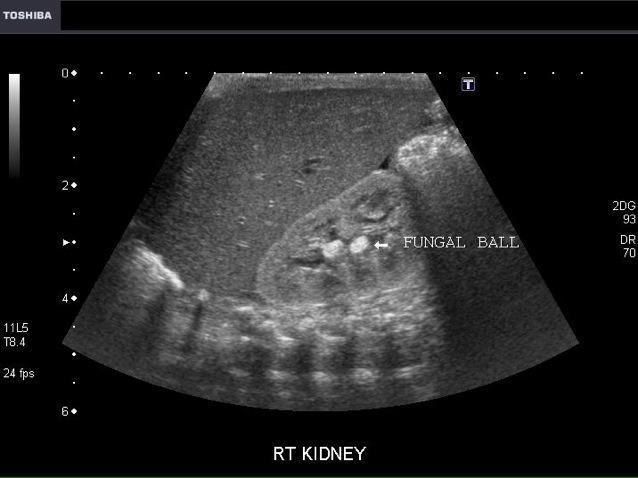
Mycetoma (fungal ball)
candidiasis is the most common
Non shadowing hyperechoic mass
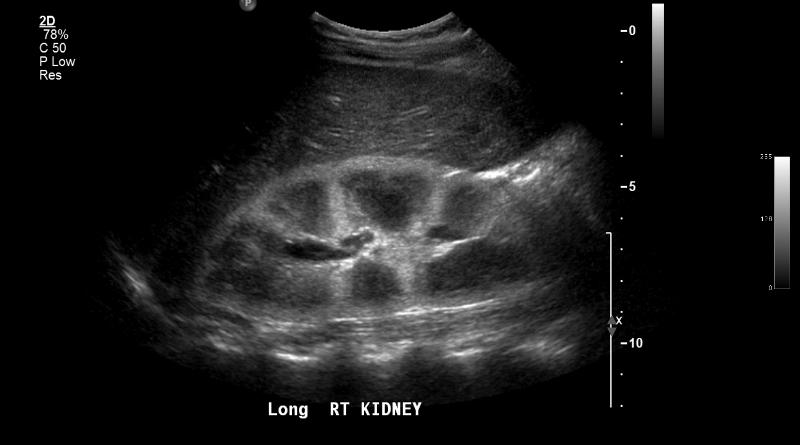
Most common cause of acute renal failure
prolonged drugs or contrast agents
Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
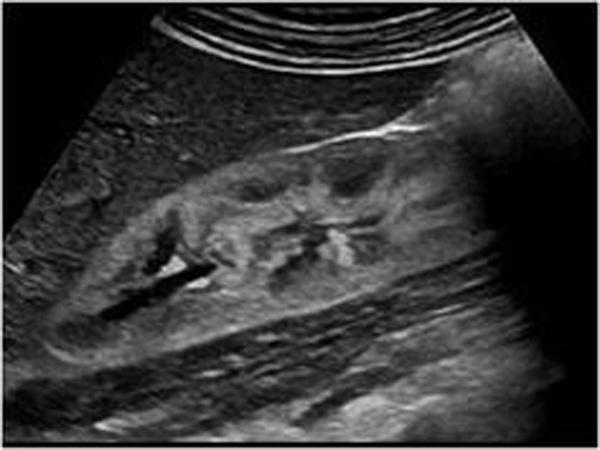
hematuria
proteinuria
azotemia
red blood cell casts in urine
Acute Glomerulonephritis
gomerular damage
caused by
autoimmune
infection
toxins

anagesic abuse
diabetes mellitus
UTI and obstruction
sickle cell
CHF
Papillary Necrosis
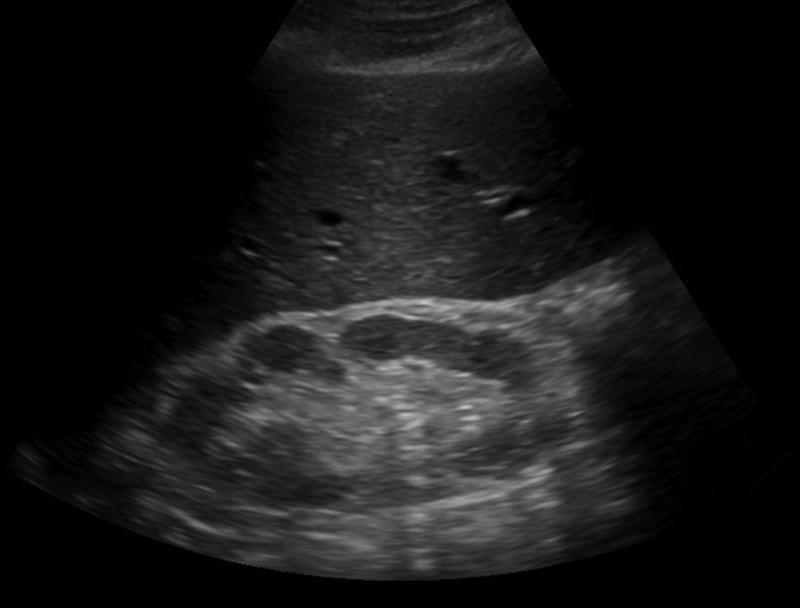
Renal Sinus Lipomatosis
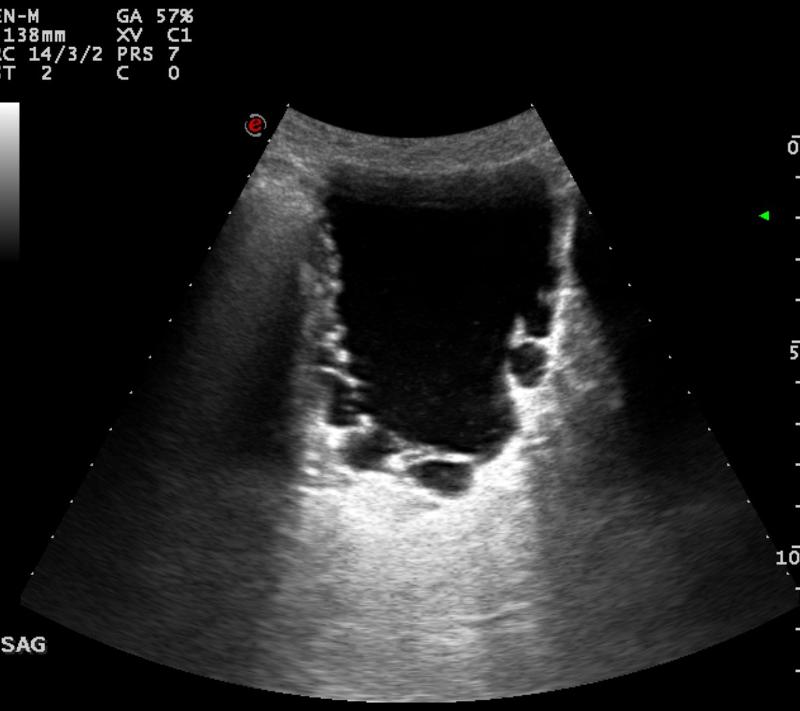
benign prostatic hypertrophy
Bladder diverticula
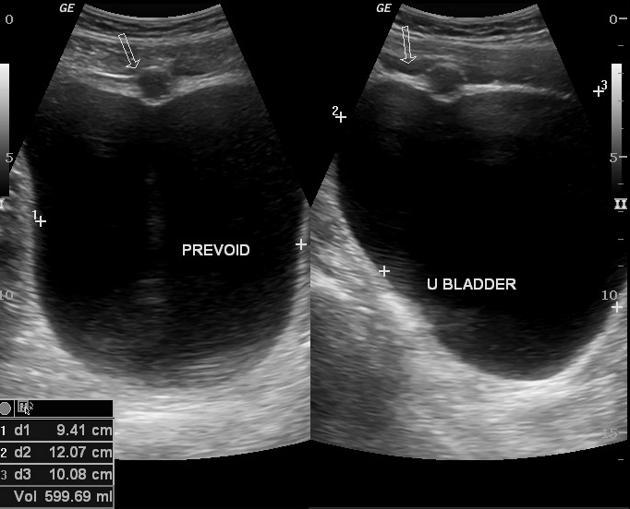
Urachal Cyst
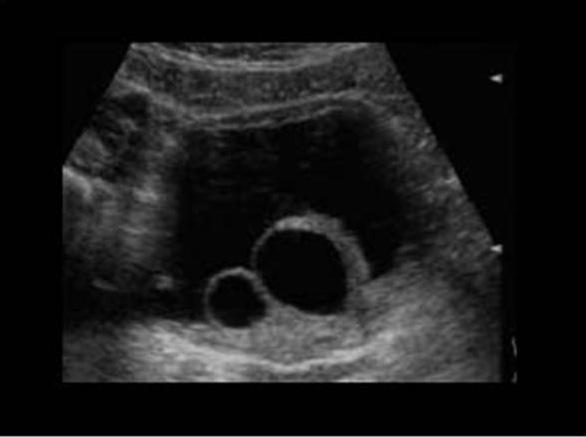
Ureteroceles
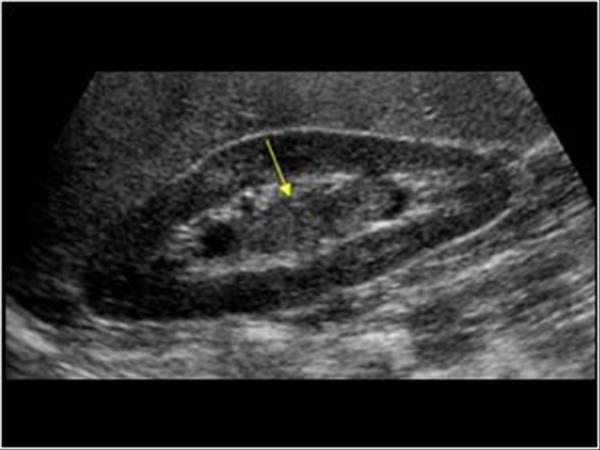
Most common bladder neoplasm
hematuria
hydronephrosis
Transitional Cell Carcinoma
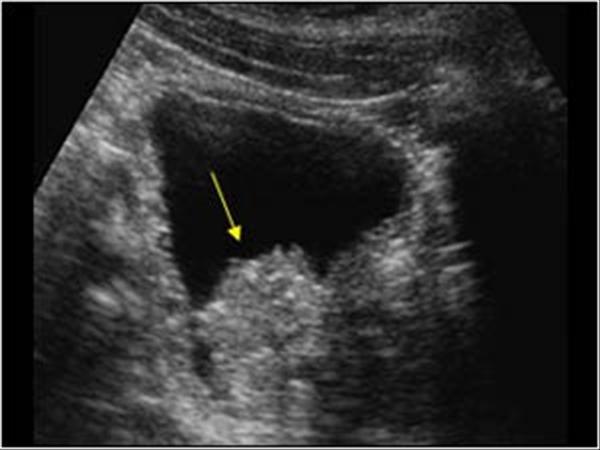
Most common bladder neoplasm
hematuria
hydronephrosis
Transitional Cell Carcinoma
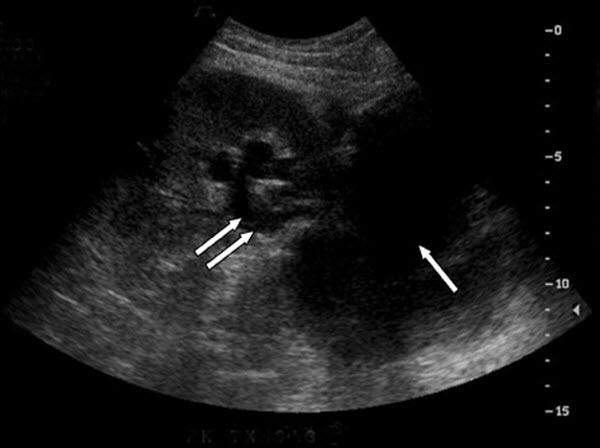
Lymphocele

most common germ cell tumor
white male smoker
infertility
Seminoma
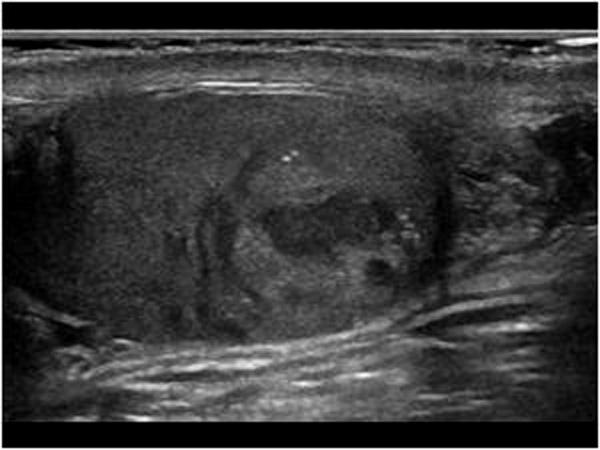
25 - 35 year olds
most aggressive testicular cancer
elevated beta-hcg
elevated AFp
Embryonal Cell carcinoma
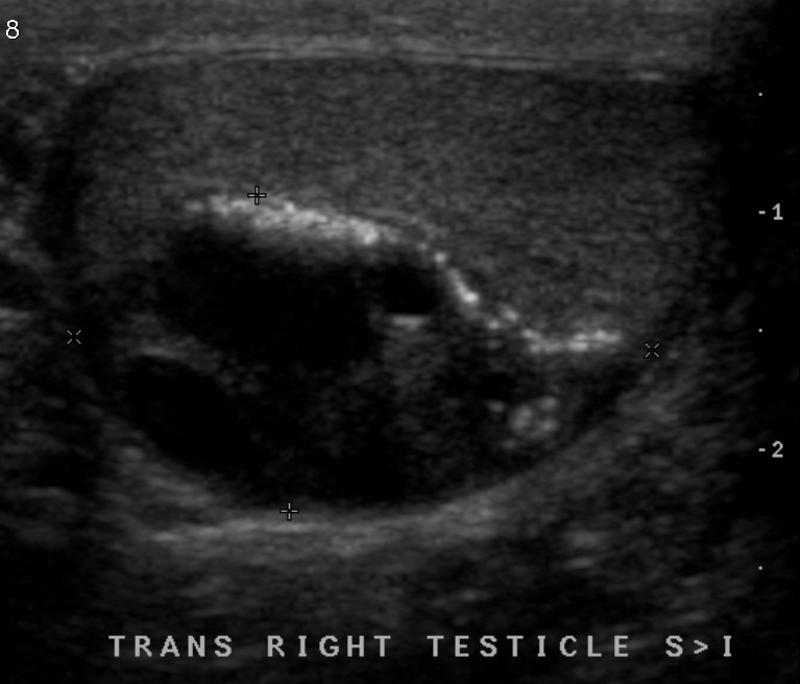
common in infants
25 - 35 year olds
Testicular Teratoma
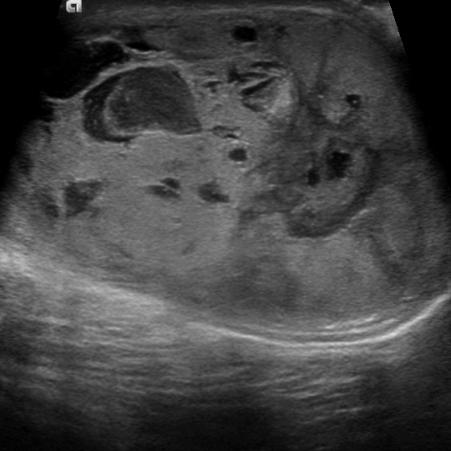
most common testicular tumor in infants and young children
elevated afp
Yolk sac tumors
20 - 30 year old
elevated beta-Hcg
Choriocarcinoma
5-10 year old - benign
precocious puberty
feminizing features (gynecomastia)
Leydig Cell tumors
appears in 10% of population
Epidermoid Cysts
benign testicular cyst
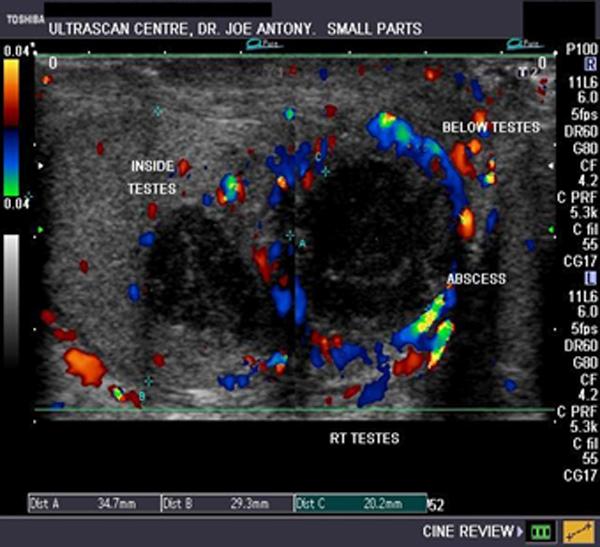
fever
scrotal pain
swelling
untreated orchitis
Testicular abscess
co
Testiular Pearls
testicular calcification
40% have neoplasm asscoiation
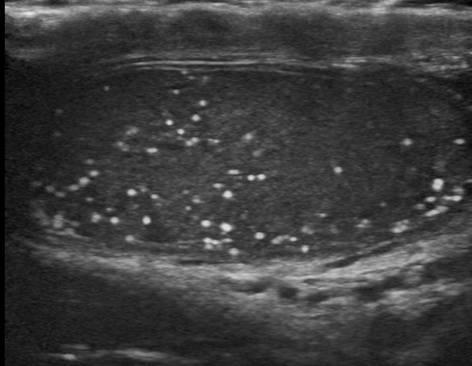
Microlithiasis

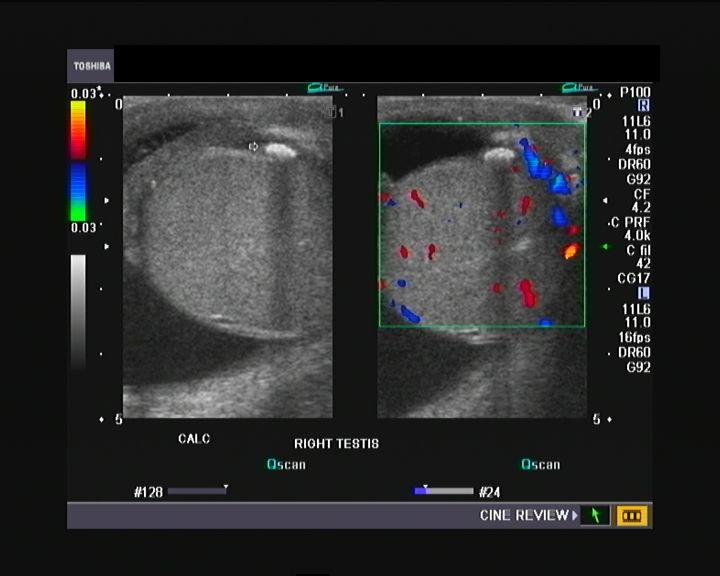
trauma
torsion
Testicular infarct
trauma
pain
scrotal Hematocele
trauma
pain
swelling
fever
leukocytosis
scrotal pyocele
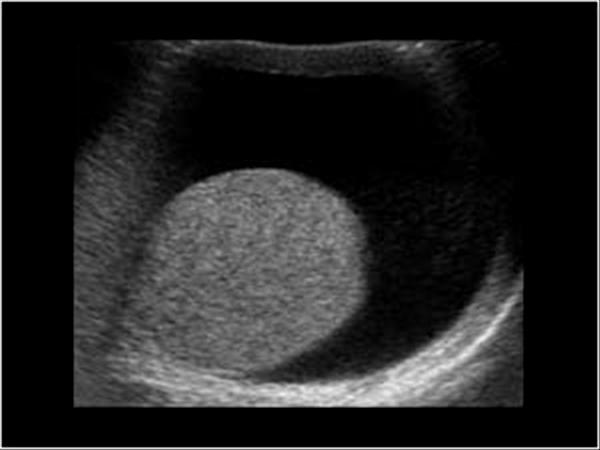
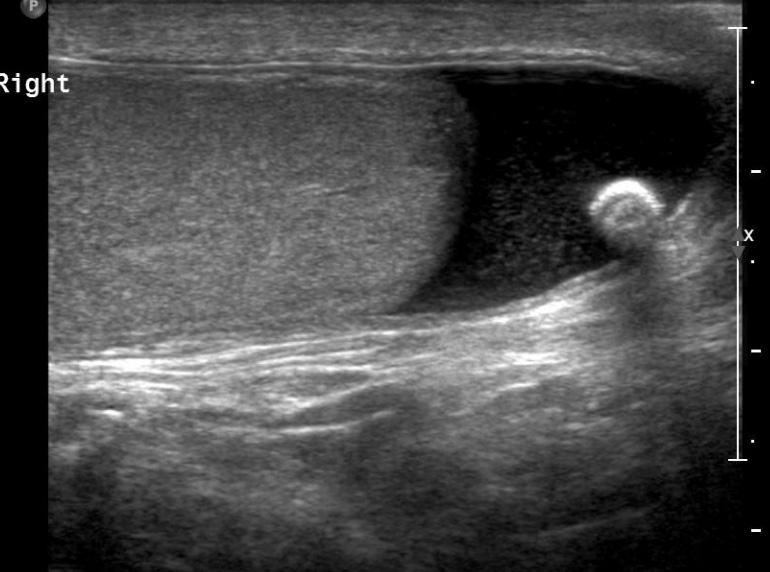
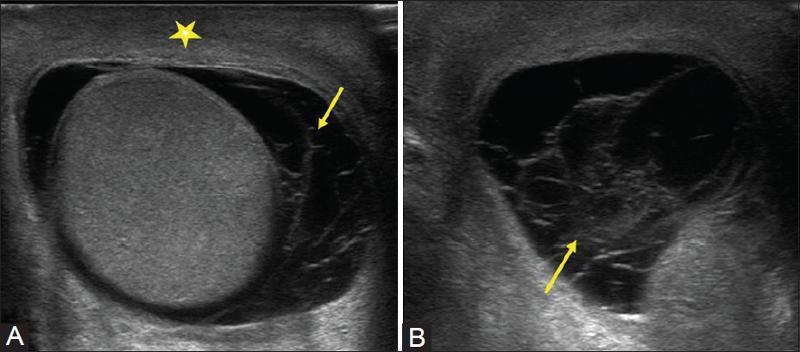
most common fluid collection of the testicle
Hydrocele
serious fluid between the tunica vaginalis

left side
most common correctible cause of male infertility
Varicocele
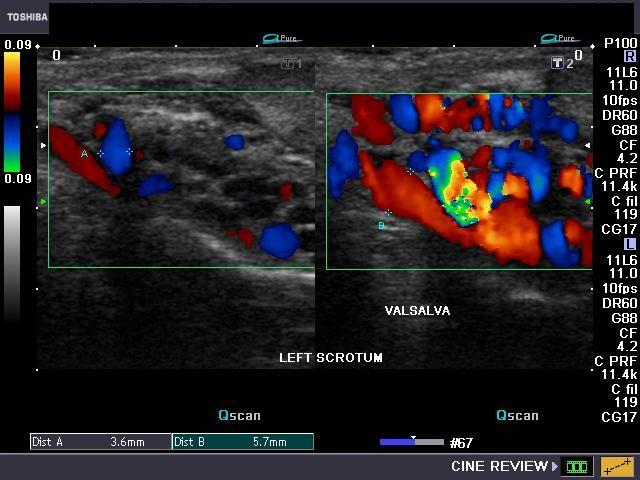
left side
most common correctible cause of male infertility
Varicocele
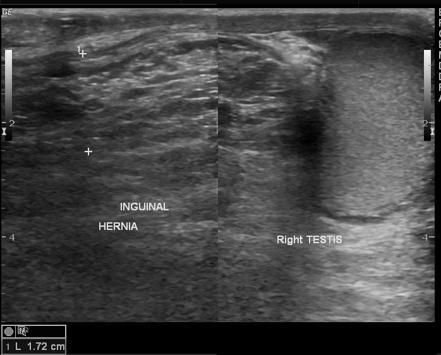
swollen scrotum
persistent or intermittent palpable mass
abdominal pain
blood in stool
Scrotal Hernia
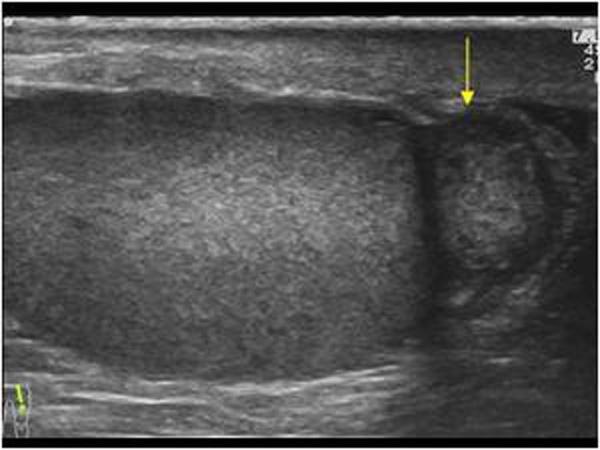
most common extratesticular tumor
adenomatoid tumor
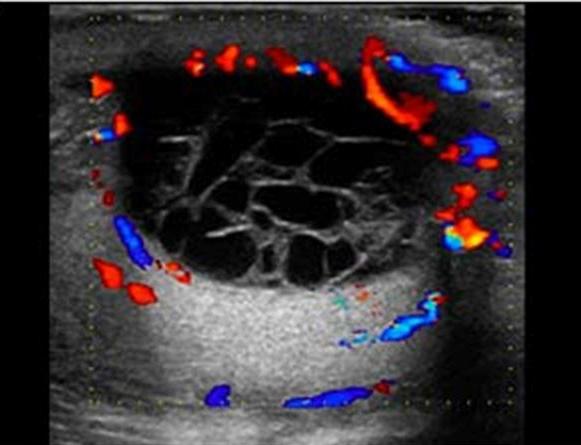
Spermatoceles
AKA Epididymal Cysts
result of dilation of the epididymal tubules
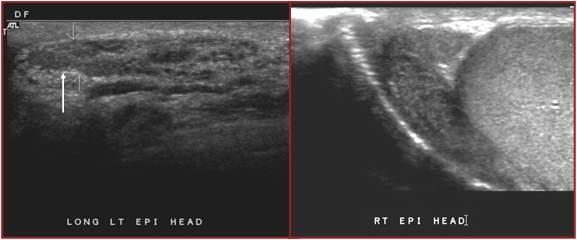
most common condition that causes scrotal pain
possible fever
pyuria
STD
UTI
Epididymitis
inflammation of epididymis usually due to UTI
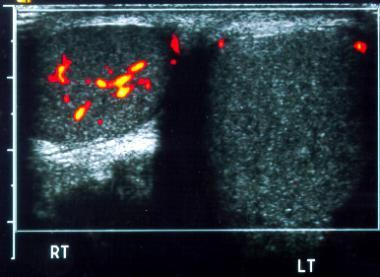
pain usually during rest or sleep
N & V
torsion
less than 6 hours 80% + salvage
6 - 12 hours 70% salvage
12 + hours :(
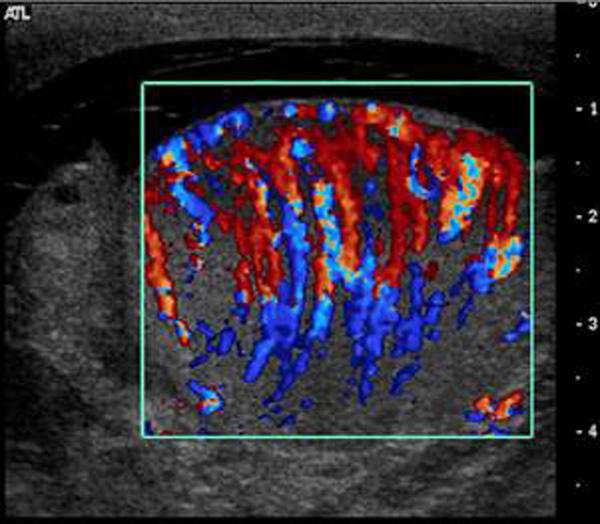
most common cause of mender 35 is chlamidia
pain
elevated WBC
Orchitis
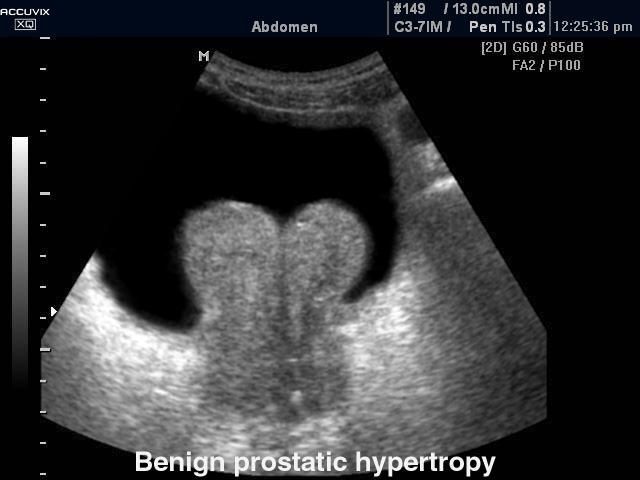
50+ year old man
difficult voiding
urinary frequency
small stream
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
usually in transitional zones
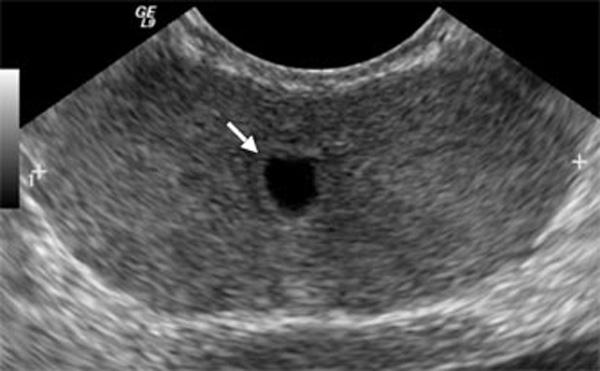
Mullerian Duct Cyst
usually midline
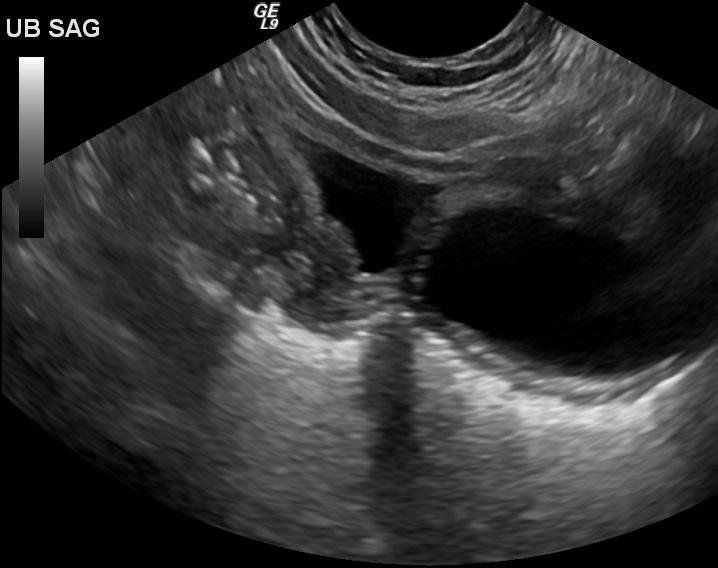
Utricle Cysts
usually midline
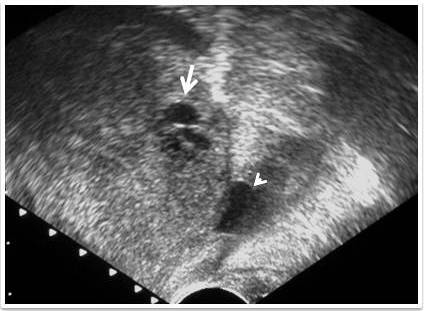
Retention cyst
usually lateral
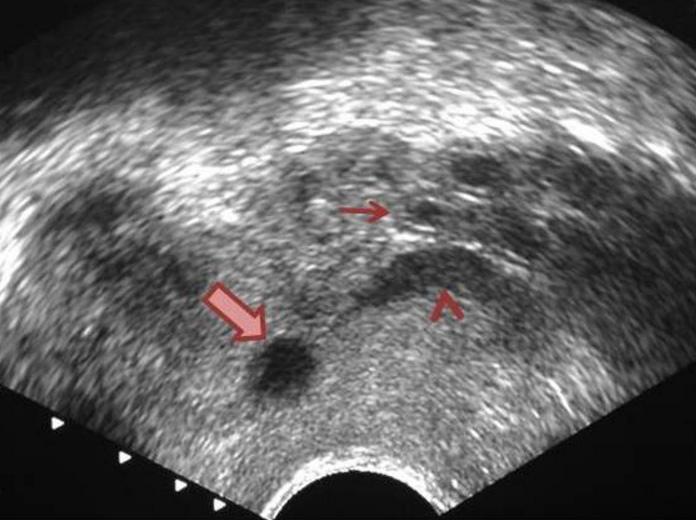
Ejaculatory duct cyst
Usually lateral & central

pain
rectal and prostate tenderness
Fever
Prostatitis
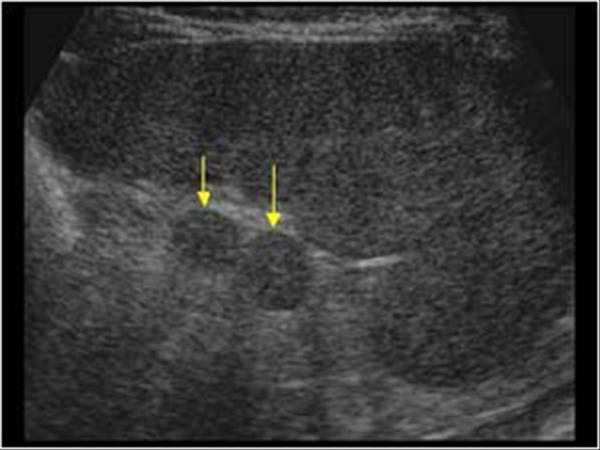
Accessory Spleen
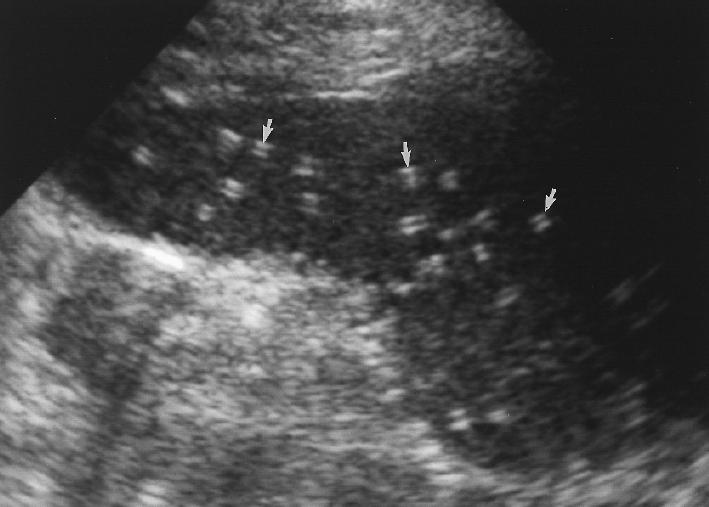
Splenic granulomas
focal lesions resulting from previous infection
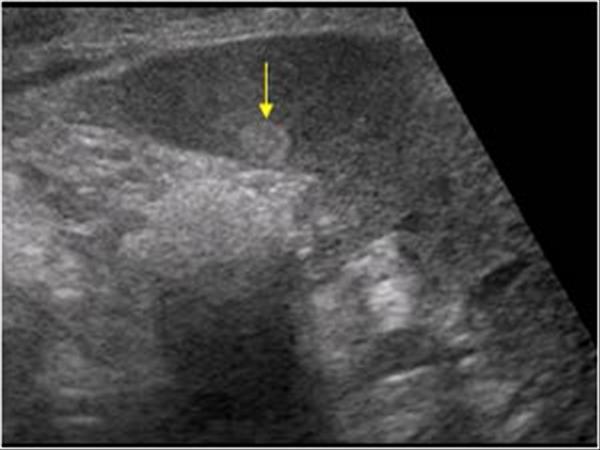
Hemangioma
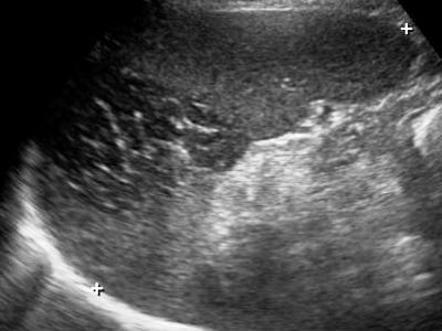
Splenic infarct
common in patients with bacterial endocarditis and splenic artery aneurysms
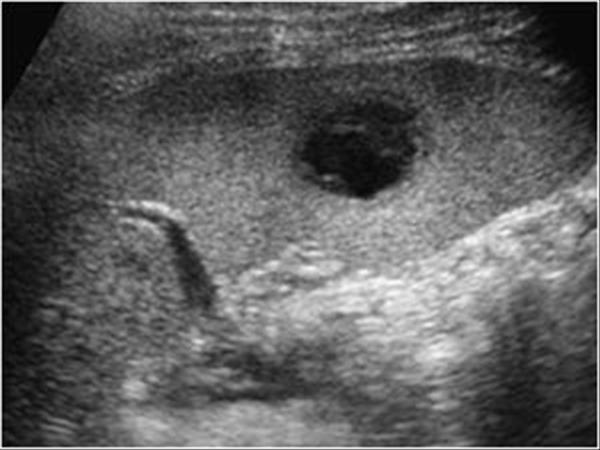
general abdominal sepsis
Splenic Abscess
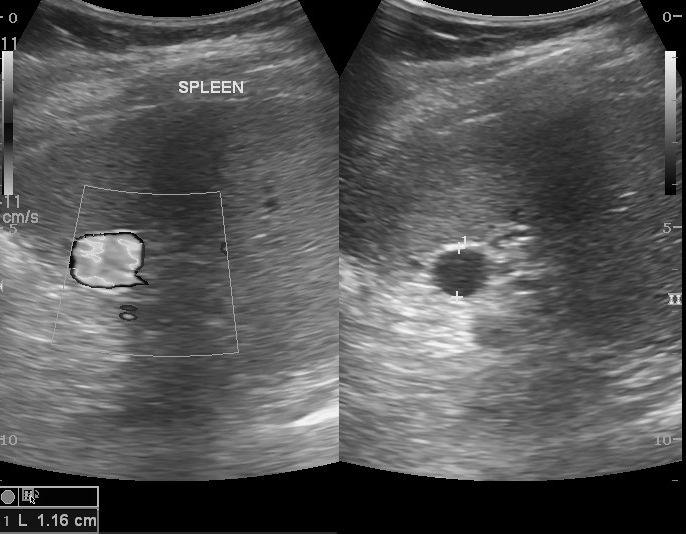
Splenic Artery Aneurysm
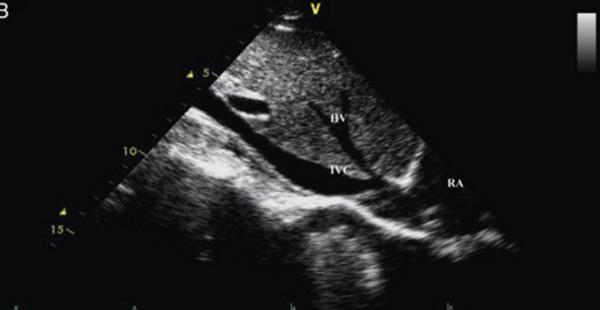
Crus of the diaphragm
Crus of the diaphragm
Crus of the diaphragm
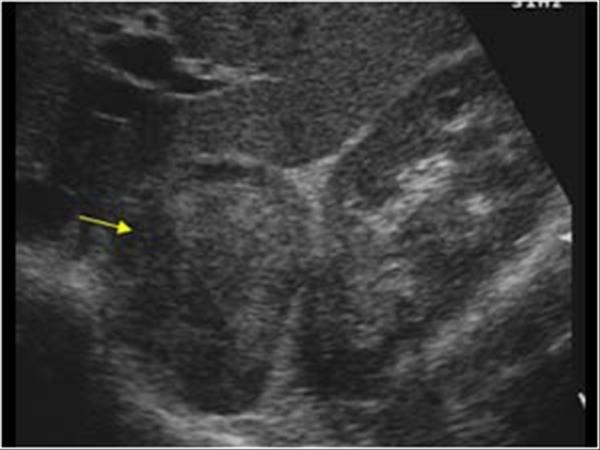
asymptomatic
cushing's
conn's
Adreanal Adenoma
cushing's
Adrenal Cortical Carcinoma
hypertension
headache
palpitations
tachycardia
anxiety
excessive persperation
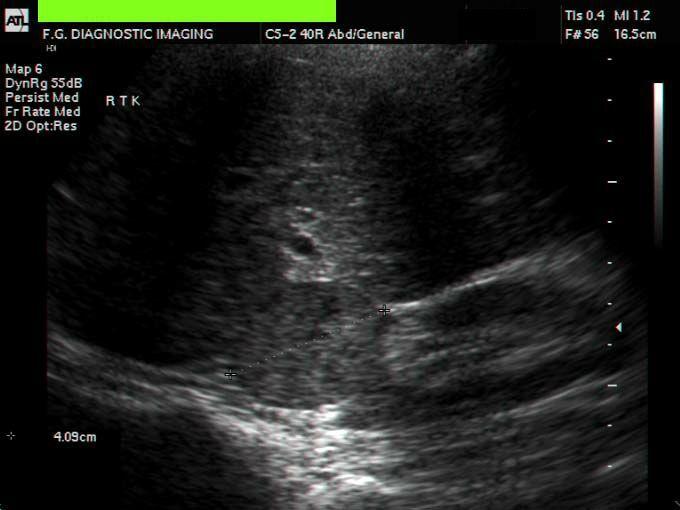
Pheochromocytoma
tumor arising from the adrenal medusa
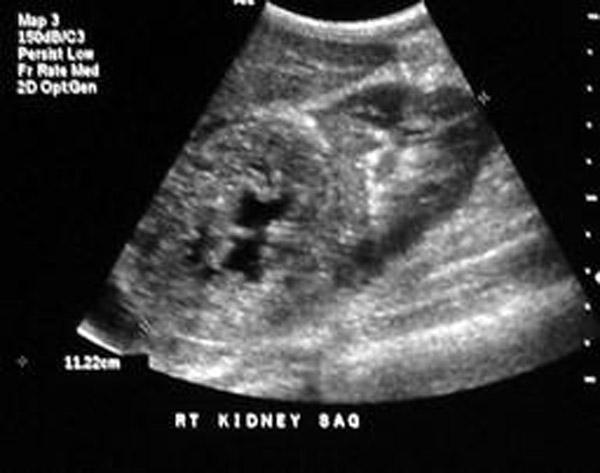
most common childhood adrenal mass
Adrenal Neuroblastoma
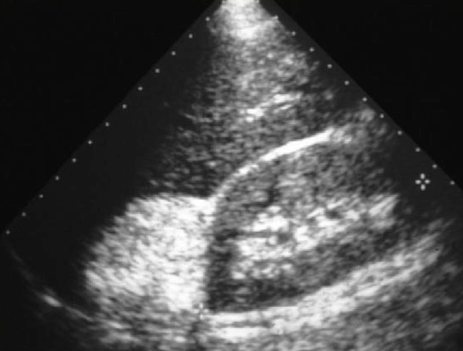
Myelolipoma
benign, nonfunctioning adrenal masses that contain fat
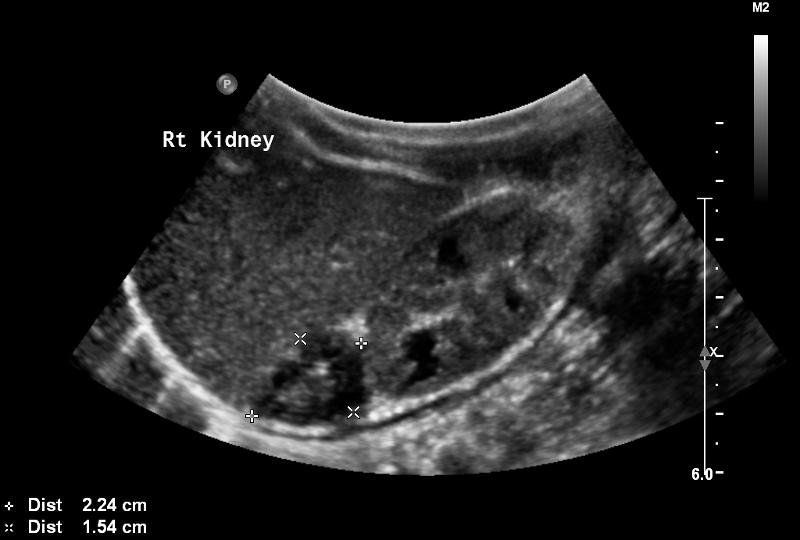
large neonate
difficult birth
Adrenal Hemorrahage
Caucasian male
75 year old
hypertension
abdominal, back and leg pain
palpable abdominal mass
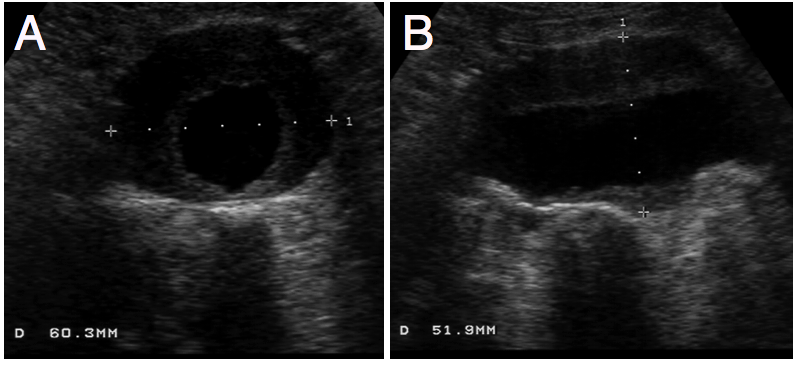
Fusiform aneurysms
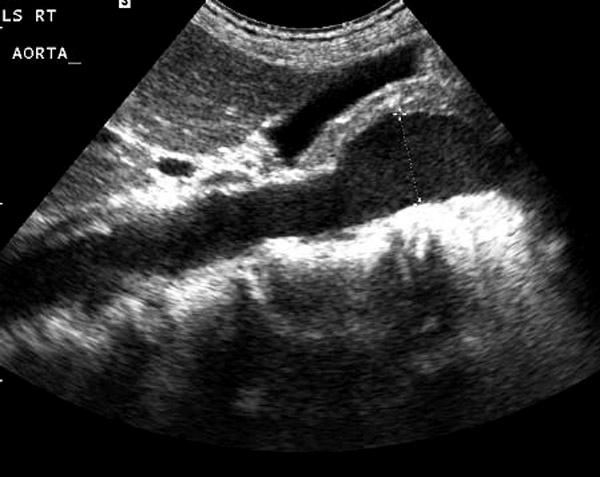
Sacular aneurysms
rare
Pseudoaneurysm
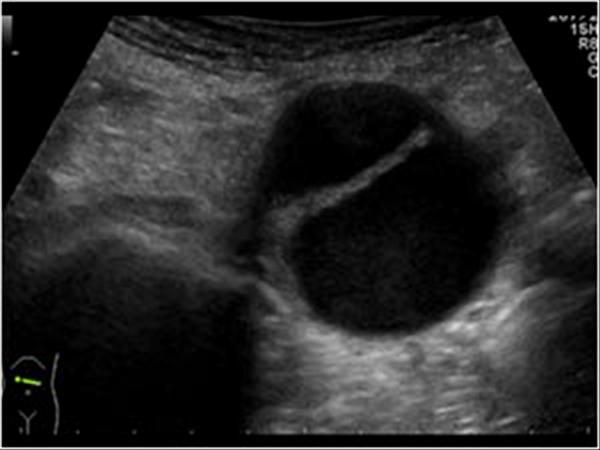
tearing back pain
shock
headache
abdominal pain
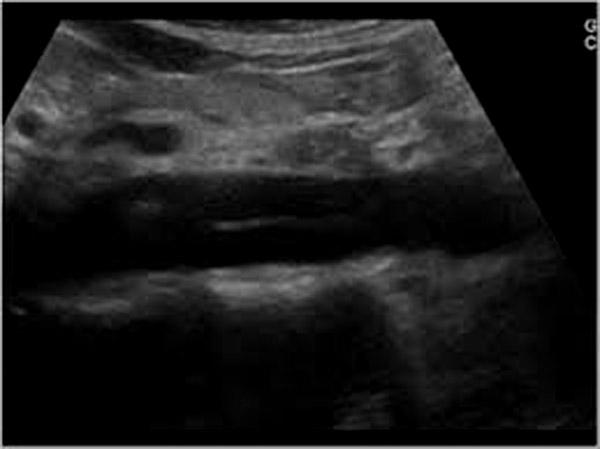
Aortic Dissection
tearing back pain
shock
headache
abdominal pain
Aortic Dissection
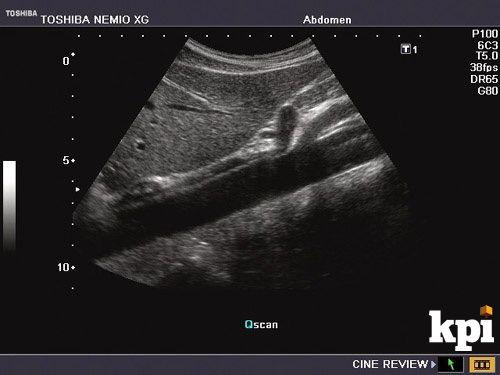
Gastoesophageal Junction
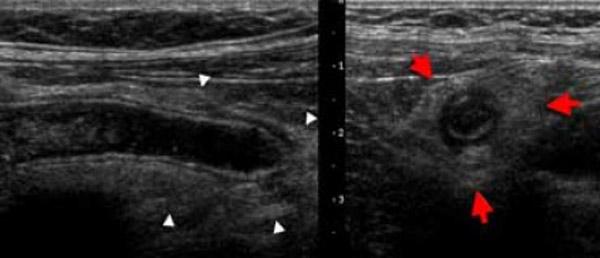
Pain over McBurney's point
umbilical pain shifting to RLQ
loss of appetite
leukocytosis
rebound tenderness
Acute appendicitis
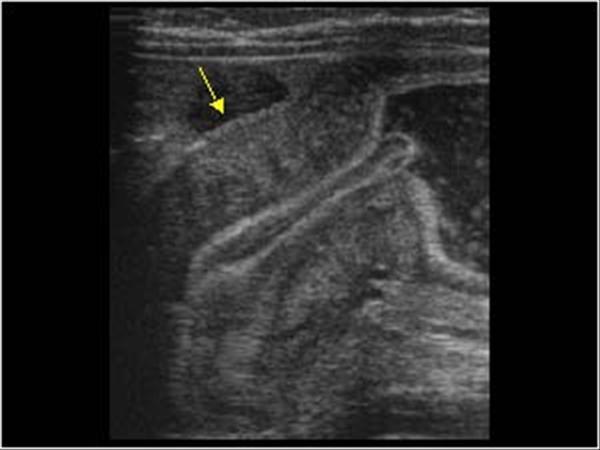
3 - 6 months old
projectile vomiting
palpable olive shaped abdominal mass
Hypertrophic Pyoric Stenosis
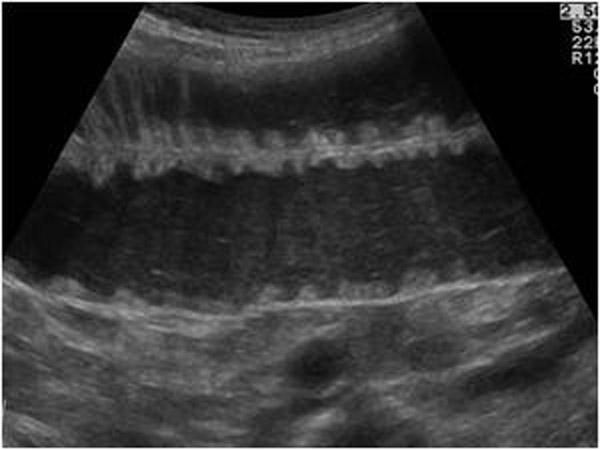
Fever
leukocytosis
LLQ pain
Diverticulitis
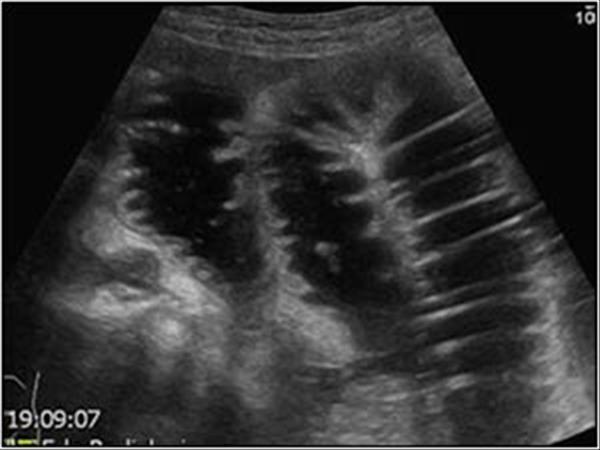
abdominal distension
pain
vomiting
hypotension
leukocytosis
Small bowel Obstruction
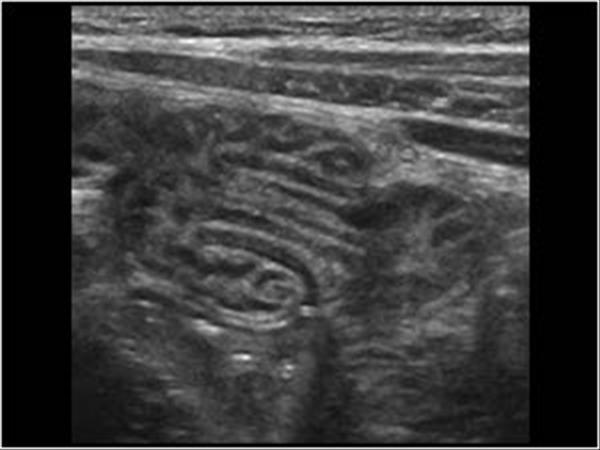
Colon obstruction

vomiting
abdominal pain
rectal bleeding
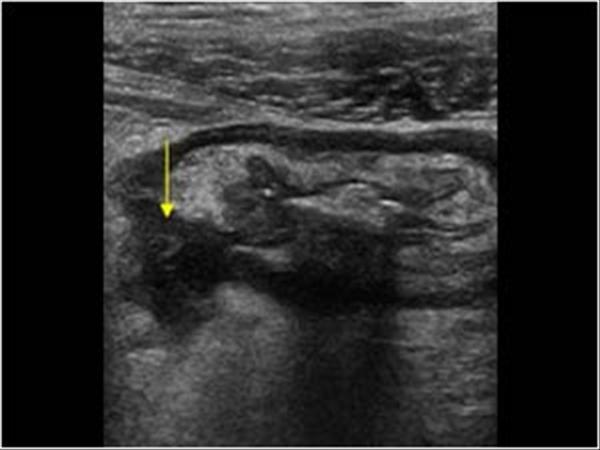
Intussception
vomiting
abdominal pain
rectal bleeding
Intussception
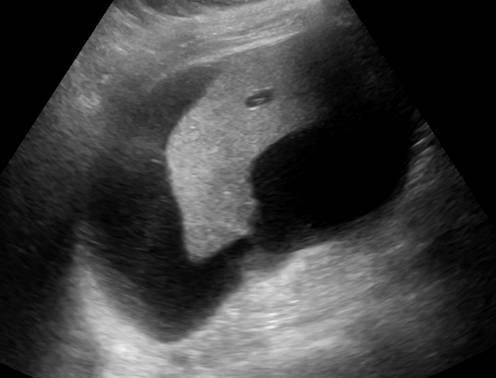
Biloma
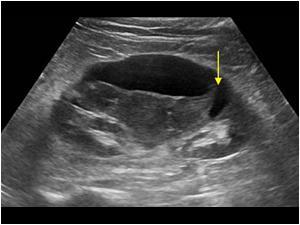
renal trauma
renal transplant
Urinoma
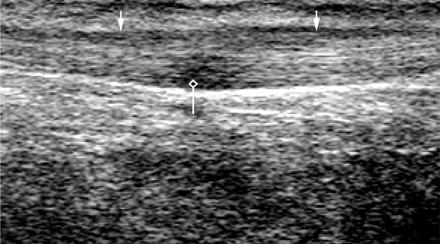
failed thompson test
Achilles Tendon Rupture
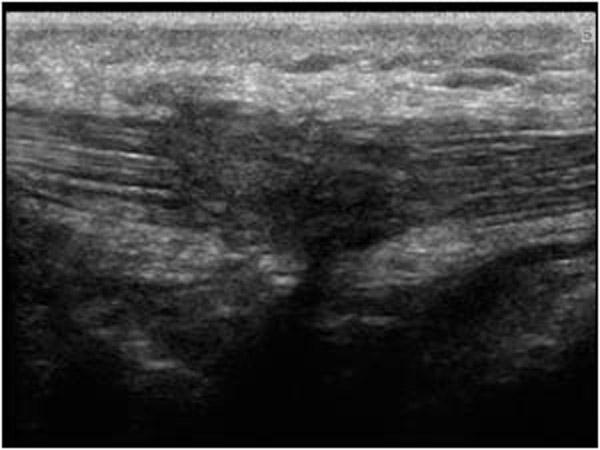
inability to extend knee
Patellar tendon Rupture
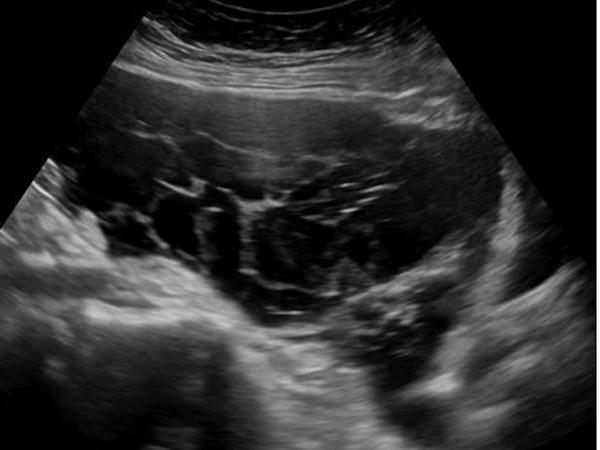
matted bowel loops
malignant ascites
Pseudomyxoma Peritonel
...
Hematoma
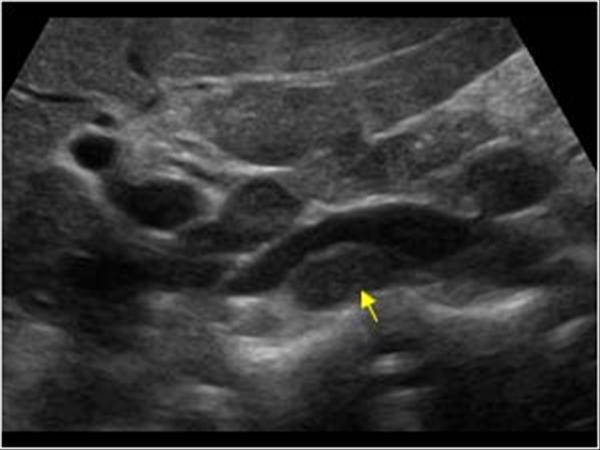
sandwich sign
Lymphadenopathy

carpet layer
Baker's Cyst
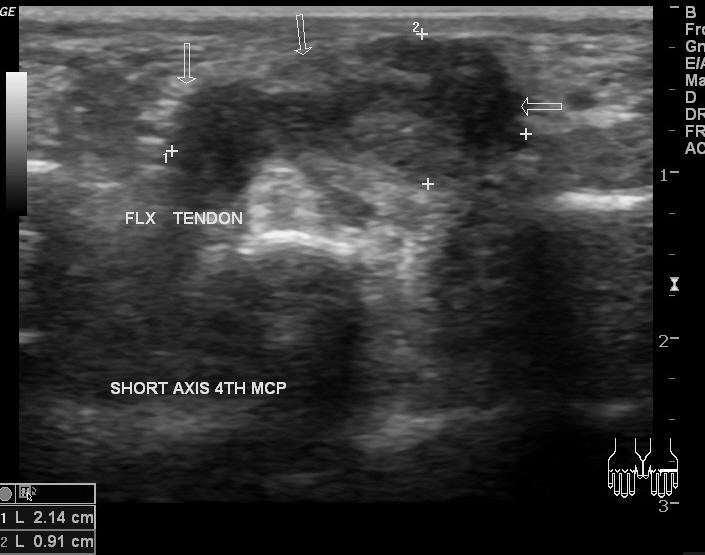
2nd most common tumor of the hand and wrist
Giant Cell tumor (ganglion cyst)
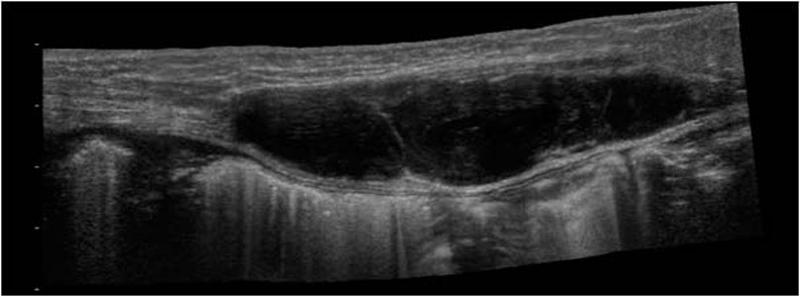
Rectus Sheath Hematoma