TRUE / FALSE
The skin is the largest organ of the body?
~True~
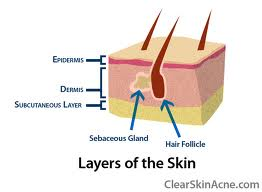
The skin consists of 2 layers:
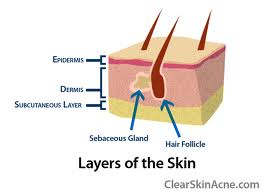
1. Epidermis (outermost protective layer of dead keratinized epithelial cells).
2. Dermis (the underlying layer of connective tissue w/blood vessels, nerve endings & the associated skin structures.
TRUE / FALSE
The dermis rests on the subcutaneous tissue that connects the skin to the superficial muscles.
~True~
The layers of the epidermis, from the OUTER layer to the INNER layer are

Stratum corneum (most outer layer), Stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum & the (inner most)stratum germinativum (basal).
*DISREGARD THE SPINOSUM LAYER FOR NOW*
TRUE/FALSE
In stratum germinativum (inner most layer of the epidermis)is where MITOSIS occurs.
~True~
Epidermal cells contain the protein pigment called
Melanin
What is melanin's function?
Protect against radiation from the sun
Dermis
inner layer of the skin
What are the 4 things that makeup the Dermis?
Fibrous connective tissue w/blood vessels, sensory nerve endings, hair follicles & glands.
What are the 2 types of sweat glands?
Eccrine & Apocrine
Eccrine sweat glands
They are distributed all over the body (except for the lips, tip of penis and clitoris). Regulates body temperature by releasing a water secretion that evaporates from the surface of the skin.
Apocrine sweat glands
mainly in the armpits & groin area, display apocrine secretion.
TRUE/FALSE
Apocrine secretion contains bits of cytoplasm from the secreting cells; this cell debris attracts bacteria & the presence of the bacteria on the skin results in in BODY ODOR.
~True~
Sebaceous glands
release an oily secretion (sebum) through the hair follicles that lubricates the skin & prevents drying.
Oil is produced by
holocrine secretion, in which whole cells of the gland are part of the secretion. *These glands are susceptible to becoming clogged & attracting bacteria, particularly during adolescence.
The appendages of the skin include
hair & nails.
Hair and nails are composed of a strong protein called
keratin
True/False
Hair,nails & skin may show changes in disease that may be used to diagnosis of clinical conditions.
~True~
For example, skin cancer is a clinical condition that is associated w/the skin.
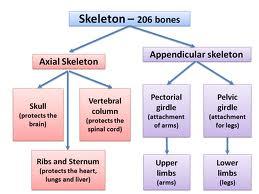
Skeletal System
Skeletal System
What does the body framework consist of?
Bone, cartilage & ligaments, plus the joints between the bones.
Functions of the skeletal system include
support, permission of movement, blood cell formation (hemopoiesis), protection of internal organ, detoxification (removal of poisons), provision for muscle attachment & mineral storage.
Calcium & Phosphorus are minerals stored in the
bone
TRUE / FALSE
Individual bones are classified by shape
*There are long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones & sesamoid bones, such as the patella.
~True~
Long bones
Long bones: relatively long, slender; found in the arms, legs, thighs, palms, soles, fingers and toes. Has an irregular epiphysis @ each end, composed of mainly spongy (cancellous) bone & a shaft or diaphysis composed mainly of compact bone.
Short bones
Short bones: somewhat cube-shaped; of nearly equal length and width.
Carpals (bones of the wrist), tarsals (bones of the ankle)
Flat bones
Flat bones: thin, flat surfaces, no marrow cavity, but spongy bone sandwiched between an upper and lower layer of compact bone.
Irregular bones
Irregular bones: complex shapes; notched, or with ridges; not easily classified into any other category. Example: vertebrae; some facial bones (like the ethmoid or sphenoid); pelvic bones = ischium and pubis; calcaneus (heel bone); mandible
Sesamoid bones
Sesamoid bones: develop in tendons where there is considerable pressure, tension or friction.
largest example patella (knee cap) is best known,
The cells that form compact bone are called
Osteoblasts
*when they become fixed in the dense bone matrix, they stop dividing, but continue to maintain bone tissue as osteocytes.
The axial skeleton / appendicular skeleton
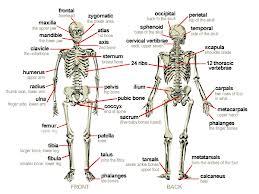
The axial skeleton consists of ___ bones of the skull.
28
The 28 skull bones are separated into the ___ facial bones and the ___ bones of the cranium.
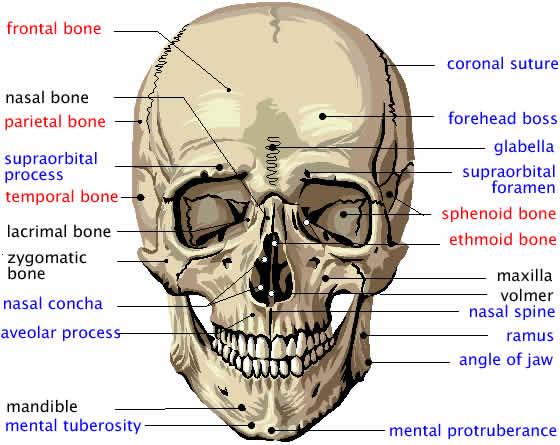
14 & 14
The facial bones are
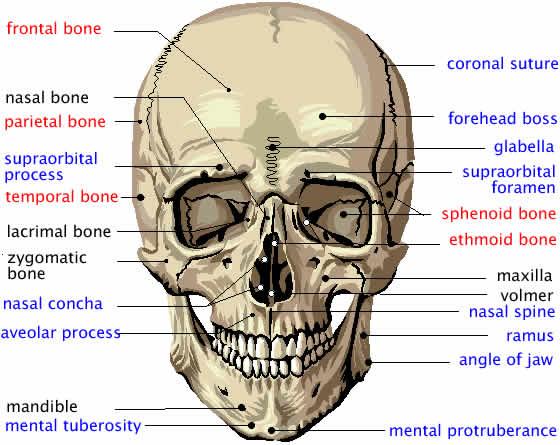
2 nasal bones, 2 maxillary bones, 2 zygomatic bones, 1 mandible (the only moveable bone of the skull), 2 palatine bones, 1 vomer, 2 lacrimal bones & 2 inferior nasal conchae
Bones of the cranium
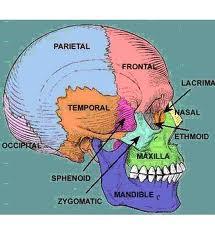
SINGLE occipital, frontal, ethmoid & sphenoid & the PAIRED parietal, temporal & ossicles of the ear (malleus, incus & stapes.
Single bones of the cranium
occipital, frontal, ethmoid & sphenoid
Paired bones of the cranium
parietal, temporal & ossicles of the ear (Malleus, incus & stapes).
Ossicle of the ear are
malleus, incus & stapes
The axial skeleton has how many bones in the vertebal column?
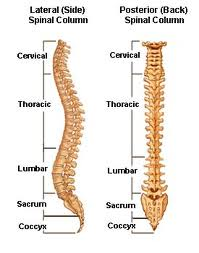
33
Bones of the vertebra are
Cervical= 7
Thoracic= 12
Lumbar= 5
Sacral= 5 (fused to form the sacrum)
Coccygeal= 4 (fused to form the tailbone)
The final portion of the axial skeleton consists of the bones of the
thorax, sternum & the 12 pairs of ribs.
How many ribs does the human skeleton have?
12 pairs totaling 24.
The appendicular skeleton
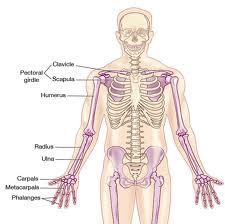
includes the girdles & the limbs.
The upper portion (of the append. skeleton) consists of the
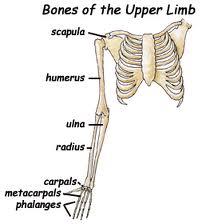
pectoral or shoulder girdle, the clavicle, the scapula & the upper extremity (bones of the arm).
The bones of the arm are
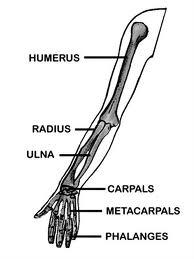
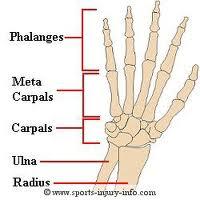
humerus, the radius, ulna, the carpals (wrist bones), the metacarpals (bones of the hand) & phalanges (bones of the finger).
What are phalanges?
bones of the fingers
What are metacarpals?
bones of the hand
What are carpals?
bones of the wrist
Image of the hand bones
The appendicular skeleton includes the ________ girdle or os coxae.
pelvic
Each of the os coxae consists of a
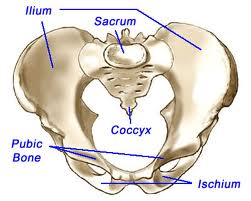
fused ilium, ischium & pubis.
Bones of the lower extremity include the
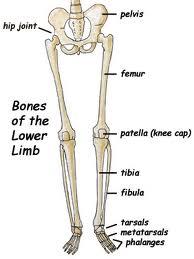
femur (thigh bone)
tibia/fibula
tarsals (ankle bones)
metarsals (bones of the foot)
phalanges (toes)
Thank you for viewing my note cards; please leave comments..I enjoy feedback. I got this information right out of the Hesi 2nd edition book I added a lot more info than the book offers. With these notes you won't need the Anatomy portion in the hesi book at ALL!! ;-)
Please add notecards of your own. We need Chemistry & Microbiology~
Labled skeleton
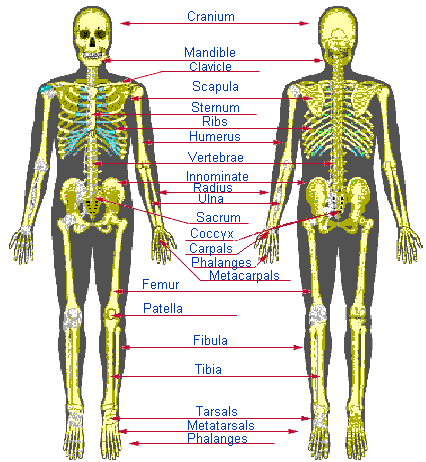
Visual of the entire skeleton