The process of sperm production is known as what?
Spermatogenisis
Spermatogenesis begins at the outermost layer in the ????? tubules and proceeds toward the ????.
Seminiferous
lumen
These stem cells divide by mitosis to produce two daughter cells.
Spermatogonia
When spermatogonia divide to produce two daughter cells, what do the two daughter cells do?
one remains as a spermatogonium
second differentiates into primary spermatocyte
A primary spermatocyte begins meiosis and forms a what?
Secondary spermatocytes
Secondary spermatocytes differentiate into what?
Spermatids
Spermatids differentiate into what?
spermatozoa
Spermatozoa lose contact with the wall of the ???? and enter fluid in the ????.
Seminiferous tubule
Lumen
The contents of the seminiferous tubules include what?
Spermatogonia
Spermatocytes (at various stages of meiosis)
Spermatids
Spermatozoa
Large nurse cells
Spermatogenesis involves three integrated processes. List them.
1. Mitosis
2. Meiosis
3. Spermiogenesis
At spermiation, a spermatozoon loses attachments to ???? and enters the ?????? of the seminiferous tubules
Nurse cells
lumen
Nurse cells, or sertoli cells, affect what?
Mitosis
Meiosis
Spermiogenesis
Nurse cells have 6 major functions. what are the?
1. Maintain a blood-testes barrier
2. Support mitosis and meiosis
3. Support spermiogenesis
4. Secrete inhibin
5. Secrete ABP
6. Secrete MIF
The anatomy of a spermatozoon is fairly simple. give the 4 parts.
Head
Neck
Middle piece
Tail
A mature spermatozoon lacks many organelles such as?
RER
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
peroxisomes
The loss of organelles in a mature spermatozoon results in what?
Reduces sperm size and mass
Where do mature spermatozoon get their nutrients from?
Fructose from surrounding fluids
The testes produce physically mature spermatozoa. Are these cells able to fertilize an oocyte?
No
Other parts besides the testes play a role in sperm maturation. What kind of tasks do they preform?
functional maturation
nourishment
storage
transport
As sperm mature in the testes they detach from the ????? and become free in the lumen of the ??????.
Nurse cells
seminiferous tubule
While the sperm is in the lumen of the seminiferous tubules, they are incapable of locomotion. How are the then moved to the next location?
Moved by cilia lining the efferent ductules
This is the first organ after the testes that is the start of the male reproductive tract.
Epididymis
What are the three parts of the Epididymis?
The head
The body
The tail
What is the function of the epididymis?
Monitors and adjusts fluid produced by seminiferous tubules
recycles damaged spermatozoa
Stores and protects spermatozoa
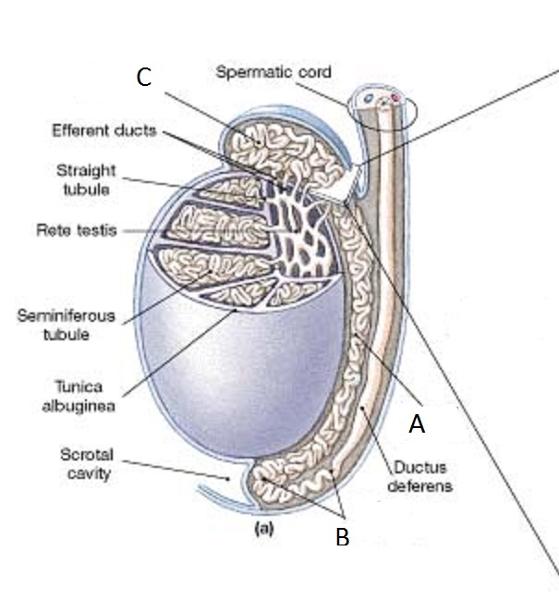
Identify A
Body of the epididymis
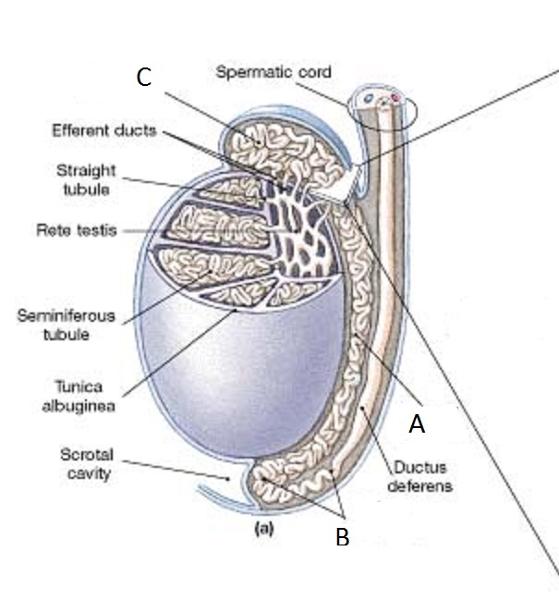
Identify B
Tail of the Epididymis
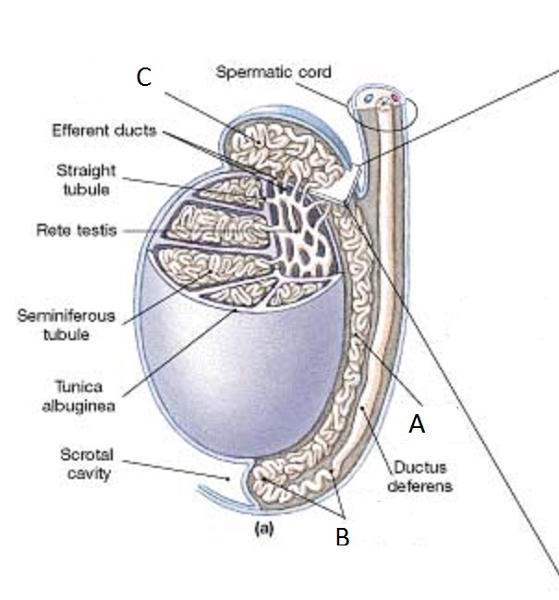
Identify C
Head of the Epididymis
Even though the spermatozoa that leave the epididymis are mature, they remain ?????.
Immobile
To become motile, spermatozoa undergo what?
Capacitation
What are the two steps in capacitation?
1. Spermatozoa become mobilized when mixed with secretions of seminal glands
2. Spermatozoa become capable of fertilization when exposed to female reproductive tract
What is another name for the Vas Deferens?
Ductus Deferens
The Vas deferens begins at the tail of the ???? and as a part of the spermatic cord, ascends through the ?????.
tail of the epididymis
inguinal canal
The vas deferens passes along what two glands that add to the sperm?
prostate gland
seminal gland
The lumen of the vas deferens larges into a what?
ampulla
The wall of ampulla of the vas deferens contains a thick layer of what?
smooth muscle
The ductus deferens is lined by what?
ciliated epithelium
Spermatozoa and other fluids are propelled through the ductus deferens by what?
Peristaltic contractions
The ductus deferens can store spermatozoa for several months in a state of what?
suspended animation (low metabolic rates)
This is a short passageway at the junction of ampulla and the seminal gland duct.
The ejaculatory duct
The ejaculatory duct penetrates the wall of what gland?
the prostate gland
The urethra is used by what two systems?
Urinary and reproductives
The urethra is divided into what three regions?
1. Prostatic
2. Membranous
3. Spongy
List the three accessory gland to the male reproductive system.
1. Seminal glands
2. Prostate glands
3. Bulbo-urethral glands
The male reproductive accessory glands have 4 main functions. what are they?
1. Activating spermatozoa
2. Providing nutrients
3. Propelling spermatozoa (mainly by peristaltic contractions)
4. Producing buffers
The seminal glands produce what kind of secretions?
Very alkaline and makes up about 60% of semen volume
The secretion produce by the seminal gland has 4 defining characteristics. what are they?
1. Rich in fructose
2. Contains Prostaglandin
3. Contains fibrinogen
4. Is alkaline
Why is the fructose produce by the seminal gland important?
it gives the spermatozoa nutrients
Why is the prostaglandin that is produced by the seminal gland important?
It increases smooth muscle contractions
Why is the fibrinogen produced the seminal gland important?
It forms a temporary clot in the vagina
Why is the alkaline produced by the seminal gland important?
to neutralize acids from the prostate gland and vagina
The first step in capacitation is initiated by what?
seminal fluid
This gland is a small, muscular organ that encircles the proximal portion of the urethra found below the urinary bladder.
The prostate gland
Prostatic fluid, in terms of pH, is very what?
Acidic
Prostatic fluid has what effect on sperm?
Helps to activate them
Prostatic fluid contains an antibiotic known as what?
Seminalplasmin
What is another name for the Bulbo-urethral gland?
Cowpers gland
The bulbo-urethral gland secretes what?
Thick, alkaline mucus
What is the function of the secretions of the bulbo-urethral gland?
Helps to neutralize acids in urethra
lubricates the glans (penis tip)
The typical amount of semen ejaculated is what?
2-5 mL
What is the normal range of spermatozoa that is ejaculated
20-100 Million/mL
This is the volume of fluid produced by ejaculation
Ejaculate
The ejaculate contains what three things?
1. Spermatozoa
2. Seminal fluid
3. Enzymes
What is the main external male genitalia and what is its function?
Penis
introduces semen into females vagina
These hormones that are released by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland play a part in male reproduction.
FSH
LH
FSH and LH are released in response to what other hormone?
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone)
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) is synthesized where?
In the hypothalamus
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) is carried to the pituitary by what?
hypophyseal portal system
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) is secreted in pulses at ????? minute intervals.
60-90
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) controls the rate of secretion of what two hormones?
FSH and LH
LH stimulates the release of what hormone?
testosterone
FSH and testosterone target what cells of the seminiferous tubules?
The nurse cells
Nurse cells promote what two things?
Spermatogenesis
Spermiogenesis
Nurse cells secrete what?
androgen-binding protein (ABP)
Spermatogenesis is regulated by what three things?
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone)
FSH
inhibin
As spermatogenesis accelerates, inhibin secretion does what?
Increases
Inhibin does what two things?
inhibits FSH production in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland
Suppresses secretion of GnRH at the hypothalamus
When FSH levels goes up, what happens to inhibin production?
An increase of inhibin production
If FSH levels decline, what happens to inhibin production?
Inhibin production falls
LH targets what cells of what organs?
Interstitial cells of the testes
LH induces the secretion of what hormone?
testosterone and other androgens
What is the most important androgen hormone?
Testosteron
This testosterone stimulates what?
Spermatogenesis
What affect does testosterone on CNS functions?
Increases libido and related behaviors
What effect does testosterone have on the metabolism?
stimulates metabolism
especially protein synthesis
stimulates blood cell formation and muscle growth
What kind of secondary sex characteristics are started by testosterone?
Distribution of facial hair
Increased muscle mass and body size
Characteristic adipose tissue deposits
Around what week of fetal development does the production of testosterone develop and when does it reach prenatal peak?
around the 7th week
6 months
The secretion of this factor by nurse cells leads to regression of what ducts?
Mullerian-inhibiting factor
Mullerian ducts
An early surge in testosterone levels stimulates differentiation of ??????? system and ????? and affects ????? development.
male duct
accessory organs
CNS
Testosterone programs hypothalamic centers that control what three things?
1. GnRH, FSH, and LH
2. Sexual behaviors
3. Sexual drive
This hormone is produced in relatively small amounts, 70% is converted from circulating testosterone and the other 30% is secreted by interstitial nurse cells.
Estridol