DNA Bases
Polymer of Nucleotides
A- adenine
G-guanine
T- thymine
C- cytosine
RNA polymerase
enzyme that produces primary transcript RNA. In cells, RNAP is necessary for constructing RNA chains using DNA genes as templates, a process called transcription.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid o
DNA
deoxyribose nucleic acid
three major classes of cellular RNAs
(i) ribosomal RNA (rRNA),
(ii) messenger RNA (mRNA)
(iii) transfer RNA (tRNA).
transcription
these three types of molecules originate as complementary copies of one of the two strands of a DNA segment that constitutes a gene
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
structural component of ribosomes, the sites where translation occurs during protein synthesis (machinery of protein synthesis)
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
responsible to carry the genetic message from DNA to the ribosome. Their length and sequence vary depending upon the gene which is being transcribed into m RNA
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
the smallest of the three types. It carries amino acids to the ribosomes (protein) during translation.
RNA Bases
A-
G -
C-
U - uracil
Pair DNA with RNA
A
G
T
C
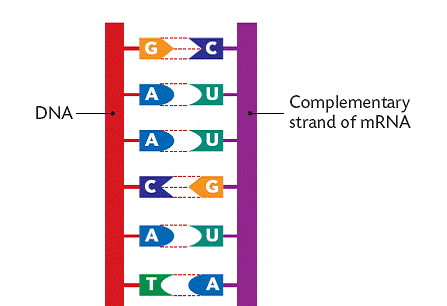
RNA
U
C
A
G
Where does replication occur in DNA
at the replication fork
how many replication forks are in bacteria
two replication forks in bacteria
in which directions do the replication forks move in bacteria
opposite directions
what are the two replication forks called in bacteria
bi-directional
what direction does synthesis occur in DNA
5'- 3'
What is the 5'- 3' strand called
leading strand
what is the non synthesizing strand called
lagging strand 3'- 5'
what are the short pieces on the lagging strand called
okazaki fragments
what does RNA require to begin each fragment
primers
what closes the gaps in the strands
DNA ligase
genetics
study of genes
gene
segment of DNA that encodes a functional product usuall a protein
The three essential macromolecules of life are
DNA
RNA
Protein
Phenotype
expression of gene (protein that can be seen)
Semiconservative replication
describes the mechanism by which DNA is replicated
1 strand of old and one strand of new DNA
DNA to RNA is called what....
RNA to Protein is called
transcription
translation
all RNA is transcribed from DNA by
RNA polymerase
DNA is
double helix (double strand)
RNA is
mono strand
codon
a sequence of three nucleotides that together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule
what forms codons
triplets of bases in mRNA
what does each triplet correspond to
a specific amino acid
what determines which amino acid goes with which codon
genetic code
how many codons for amino acid
61
how many stop codons
3
what is the sequence based on the genetic code chart
from left, top, to right side (top to bottom)
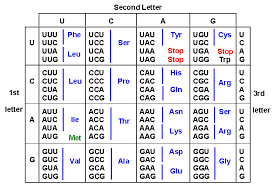
UCAG left (top to bottom), UCAG top (left to right), UCAG, UCAG, UCAG (right top to bottom 4x's) 4 columns
how many bases are genetic in genetic code
3 bases
is there a concern if there is a mutation in the 3rd base
no, only time there is a concern is if there is mutation in base 1 or 2
what is RNA start codon
A U G
what are the most common stop codons
UAA, UAG, UGA
what marcomolecule do disenfectants normally effect in bacteria
disenfectants normally effect PROTEINS in bacteria which prevents metabolism
how many stages are there in translation
there are 3 stages in translation
- initation
- elongation
- termination
what do these three translation stages require to be functional
enzymes and proteins
what are the 3 steps in elongation translation
- codon recognition
- peptide bond formation
- translocation
where does mutation occur
mutation occurs in DNA
what is mutation
a change in genetic material (beneficial, netural, harmful)
ex. beneficial mutation- evolution
harmful mutation- cancer
netural mutation- no effect
what causes mutation
mutagen
what is a mutagen
a gene that causes a mutation
nonsense mutation
a sequence of DNA that results in a premature stop codon, or a nonsense codon in the transcribed mRNA
frameshift mutation
insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotide pairs
*shorten or extend frame of DNA, RNA
ionizing radiation
x-rays and gamma rays that cause the formation of ions that can react with nucleotides and DNA phosphate backbone
what does UV radiation cause
thymine dimers
thymine dimers (t-dimers)
A pair of abnormally chemically bonded adjacent thymine bases in DNA, resulting from damage by ultra-violet irradiation. The cellular processes that repair this lesion often make errors that create mutations. (cancer)
transformation
naked dna from environment transfers to another bacteria
conjugation
transfer of genetic material (plasmid) between bacterial cells by direct cell-to-cell contact or by a bridge-like connection between two cells...... through pilli (gram negative)
-phage
virus
Transposons
jumping gene
transduction
the process by which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus
sterilization
completely destroys all forms of microbial life
disinfection
- destroys VEGETATIVE cells on SURFACE
- reduces # of viable organisms in material
antisepsis
the chemical disinfection of living tissue, such as skin or
mucous membrane
- removal of pathogens from living tissue
degerming
physical removal(mechanical cleansing) of microbes via alcohol, swab, soap
ex. cleaning the skin with alcohol prior to injection
asepsis
the absence of significant contamination
bactericidal (-cidal, to kill)
kill ALL bacterial
bacteriostatic (-static, to stop)
halt (inhibit) the growth of bacteria for as long as the inhibitory substance is present, NO DUPLICATION
ex. freezing food method
once inhibitor is removed, growth begins
ex. removing food from freezer
Thermal Death Time (TDT)
the TIME at a given temperature in which all the micoorganisms in a liquid culture will be killed
- time is the variable (it changes)
- temp is the constant (remains the same)
- ex. temp is 50 degrees celcius but bacteria may not die at 5, 10 or 15 mins but may die at 30 mins
Thermal Death Point (TDP)
the lowest temperature at which all microorganisms in a liquid suspension are killed in 10 mins
- temperature is the varaiable (it changes)
- time is the constant (it remains the same)
Pasteuriztion
heat (below boiling) for short period of time to kill pathogens and reduce bacteria count, does not kill all bacteria- some useless ones survive
flash pasteurization
high heat at a short period of time
tyndallization
method used to destroy spores
consists of heating the substance to boiling point and holding it there for 15 minutes, three days in succession. After each heating, the resting period will allow spores that have survived to germinate into bacterial cells; these cells will be killed by the next day's heating. During the resting periods the substance being sterilized is kept in a moist environment at a warm room temperature, conducive to germination of the spores (favorable environment for bacteria). When the environment is favourable for bacteria, it is conducive to the germination of cells from spores, and spores do not form from cells in this environment
autoclave
a pressure chamber used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to high pressure saturated steam at 121 °C (249°F) for around 15–20 minutes
KILLS SPORES
non ionizing radiation
NO PENETRATION (ex. sound waves, visiable light)
ionizing radiation
PENETRATION (ex. gamma rays, Xrays, electron beams)
filtration
the passage of a liquid or gas (air) through a filter with pores small enough to remain microbes
pore size .45 or .2 micron
used with heat liable samples
photophosphorylation
light reactions
2 kinds of photophosphorylation
cyclic (mostly found in bacteria, used by cyanobacteria)
non-cycllic (found in green plants and cyanobacteria)
dark reaction
the cycle of reactions (the Calvin cycle) that occurs in the second phase of photosynthesis and does not require the presence of light
It involves the fixation of carbon dioxide
oxygenic photosynthesis
produces oxygen
carbon dioxide + water + light energy → carbohydrate + oxygen.
Anoxygenic photosynthesis
process where light energy is captured and converted to ATP, without the production of oxygen
water is not the electorn donor
photosynthesis
light energy transformed into chemical energy
2 parts.....
- light reactions (require light)
- dark reactions (no light required)
minimum temperature
lowest temperature where growth can occur
optimum temperature
temperature where species grows the best
maximum temperature
highest temperature where growth can occur
what are the PHYSICAL growth requirements for microbacterial growth
ph, osmotic pressure, food
psychrophiles
cold-loving, grow at 0 to 20 degrees celsius,
- (optimum cold-loving temp 15 degrees Celsius)
mesophiles
middle temperature loving, human body temp, 20 degrees to 45 degrees celsius,
- (optimum middle-loving temp 20 - 37 degrees celsius) PATHOGEN
thermophiles
heat loving, grow at 37 to 65 degrees celsius
psychrotrophs
A psychrotroph can survive at a similar, but larger range than a psychrophile. It can survive from 0 - 35 degrees celsius but (optimally at 20 - 30 degrees celsius) These organisms can be found in refrigerated spoiled food.
what is the optimum ph for bacteria to grow
6.5- 7.5
what pH is favorable for molds and yeasts
5 & 6
acidophiles
- grow in acidic enviroments such as: digestive tracts, dairy foods (yogurt), vagina
- considered probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus (L. acidophilus) lactic acid bacteria
basophiles
basic loving grown in intestines
optimum pH 8.5
hoe can organisms change the culture media
due to their own waste products may be toxic due to pH change
pH change is due to
bacterial metabolism
what percentage of cells are water
80-90%
hypotonic
water will move INTO cell (can cause cell to BURST)
hypertonic
water will move OUT of the cell (can cause cell to SHRINK)
halophiles
salt loving
facultative halophiles
organism that can grow at high salt concentrations but DO NOT require high salt concentrartons
obligate halophile
REQUIRES high salt concentration for growth
macro-nutrients
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
trace elements
inorganic elements required in small amounts (usually enzyme co-factors)
oxygen effects
organisms produce more energy when growing in oxygen but toxic byproducts can be fatal to cells
example of oxygen byproducts
superoxide radical (superoxide dismutase)
hydrogen peroxide (catalase, peroxidase)
what do AEROBES require for growth
oxygen
facultative ANArobes
grow with or without oxygen
ANArobes
can NOT survive in oxygen environments
microAEROphiles
require SMALL (micro) or low amounts of oxygen
what enzyme do AERObes require
- superoxide dismutase
- catalase
- peroxidase
obligate AERobes
REQUIRE oxygen
facultative ANAerobes
can grow with or without oxygen
obligate ANAerobes
can NOT live with oxygen
AEROtolerant
tolerate oxygen
synthetic or defined medium
medium made of KNOWN amounts of chemicals
complex medium
some ingredients are of unknown composition or amounts (extracts of plants, yeast, or meat) ex. nutrient broth tryptic soy broth
selective medium
encourages the growth of certain organisms while discouraging the growth of others
- (ex. crystal violet, or basic dyes selective for Gram- against Gram+ (2 groups)
- MacConkey
differential medium
distinguishes between different groups of bacteria. medium contains constituents which cause an OBSERVABLE change (color or pH change)
- ex: MacConkey contains lactose and netural red, lactose fermenters appear pink
generation time
the time required for cells to divide (and double the population) can be a short as 20 mins or longer than a day
2 bacteria to one culture equals how many generations at 64
5 generations
what phase does bacterial begin to adjust to environment
lag phase
based on the chart, what phase should antibiotics be added
log phase
what phase of microbial growth is the gram stain performed
log phase
direct methods of measuring bacterial growth
- plate counts
- filtration
- most probable number (statistical method)
- direct microscopic count
turbidity (indirect method)
cloudy (turbid) broth indicates greater bacterial population; estimate number of bacteria by analyzing turbidity with spectrophotometer (measures the amount of light passing through a culture); transmission of light is inversely proportional to population size of bacteria
does not distinguish between living and dead cells
Metabolic Activity (indirect method)
estimates number of cells in a culture by measuring changes in metabolic processes (e.g., nutrient utilization, waste production, pH) ......ADD GLUCOSE
Dry Weight (Biomass)
involves filtering mo's from culture medium, drying and then weighing; suitable for broth cultures, useful when there is an abundance of mo's; growth cannot be followed over time b/c mo's are killed in the process
What are the sources of antibiotics
more than half from Streptomyces and Bacillus and molds (fungi)
What does the term broad-spectrum antibiotic refer to
an antibiotic that acts against a wide range of disease-causing bacteria. A broad-spectrum antibiotic acts against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
- binds 50s subunit, inhibits peptide bond formation
What does the term narrow-spectrum antibiotic refer to
an antibiotic effective against specific families of bacteria.
(small range of pathogens they are effective against)
Give an example of a narrow-spectrum antibiotic
penicillin (affects Gram positive bacteria)
Is there any danger in using broad-spectrum antibiotics
Yes, broad-spectrum antibiotics can destroy the normal microbial flora.
Define selectively toxic
highly effective against the microbe but have minimal or no toxicity to humans (host).
Discoverer of penicillin
Alexander Fleming 1928
Who performed the first clinical trial of penicillin
(when was penicillin first used)
Howard Florey and Ernst Chain 1940
What fungus does penicillin originate from
Penicillum
What is spectrum of activity in antibiotics
mode of action and which pathogen it is effective against
What can happen as a result of the normal microbial flora being destroyed
destruction of normal microbial flora can lead to a superinfection in which a survivng organism overgrows
What is a superinfection
A superinfection is generally defined as a second infection superimposed on an earlier one, especially by a different microbial agent of exogenous or endogenous origin, that is resistant to the treatment used against the first infection. An example of this in bacteriology is the overgrowth of endogenous Clostridium difficile which occurs following treatment with a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
What are some examples of a superinfection from antibiotic use
- Clostridium difficle (c-diff)
- Candida albicans (yeast)
What is the criteria for ideal antibiotics
- selectively toxic
- soluble
- resists excretion (breakdown)
- shelf life
- does NOT lead to resistance
- cost
Describe: Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
Peptidoglycan is found only in bacterial cell walls (animals do not
have PGC/cell walls).
-Penicillin prevents the synthesis of PGC,
weakening the walls and the cell undergoes lysis.
penicillins common core is called
b-lactum ring
penicillinases
enzymes produced by some bacteria that provide resistance to β-lactam antibiotics like penicillins
what interferes with cross-linking
penicillin and cephalosporin
what prevents stand synthesis
vancomyicin
is penicilinase resistant to penicillin
yes penicilinase is resistant to penicillin
What is synergism
occurs when the effect of two drugs together is greater than the effect of either alone
What is antagonism
occurs when the effect of two drugs together is less than the effect of either alone
ex. penicillin does not worl well with tetracycline because cells are not growing
Misuse of antibiotics include
- using outdated (weakened) antibiotics
- using antibiotics for common cold and other inappropiate conditions
- using antibiotics in animal feed
- faliure to complete subscribed regimen of antibiotics
- using someone else's leftover prescription
Antibiotic resistance
occurs when bacteria change in some way that reduces or eliminates the effectiveness of drugs, chemicals, or other agents designed to cure or prevent infections. The bacteria survive and continue to multiply causing more harm
Compare the terms bacteriocidal and bacteriostatic
Bactericidal: kills the bacteria.
-Bacteriostatic: inhibits the
growth of the bacteria.
what percentage of Americans get a viral disease each year
90%
are anti-virals limited in the groups they are effective against
yes
nucleoside analogs
synthetic nucleosides which interfere with DNA and RNA synthesis
Enzyme inhibitors
inactivate reverse transcriptase
what is transcriptase needed for
to make DNA from RNA viral genome
what are the tests used to guide chemotherapy
Kirby-Bauer
Broth dillution
Vancomycin (last resort)
is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections.
effective mostly against gram-positive (cell wall) bacteria
Kirby-Bauer antibiotic testing
test which uses antibiotic-impregnated wafers to test whether bacteria are affected by antibiotics. In this test, wafers containing antibiotics are placed on an agar plate where bacteria have been placed, and the plate is left to incubate. If an antibiotic stops the bacteria from growing or kills the bacteria, there will be an area around the wafer where the bacteria have not grown enough to be visible. This is called a zone of inhibition.
minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC)
the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible g rowth of a microorganism after overnight incubation.
minimal bactericidal concentration
the lowest concentration of an antibacterial agent required to kill a particular bacterium.
how can minimal bactericidal concentration be determined
from both dilution
the major modes of antimicrobial drugs
- inhibition of cell wall synthesis
- inhibition of protein synthesis
- inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis
- injury to plasma membrane
- inhibit the synthesis of essential metabolites
chloramphenicol
- simple structure
- easily manufactured
- broad spectrum
- SERIOUS SIDE EFFECTS (used only as last resort)
macrolides
contain macrocyclic lactone ring
ex. erythromycin (not able to penetrate most Gram negative cell walls
what is alternative to penicillin
erythromycin (macrolides)
side effects of streptomycin (bactericidal)
- auditory nerve damage
- kidney damage
tetracyclines (broad spectrum) is produced by (protein synthesis)
streptomyces
disadvantages and side effects of tetracyclines (protein synthesis)
supress normal flora (causing superinfection)
not advised to:
children-brownish teeth
pregnant women-liver damage
sulfonamides
stop folic acid synthesis (broad spectrum)
ciprofloxacin
stops DNA gyrase (urinary tract infections)
polymyxin B
topical
combined with bacitracin and neomycin in O-T-C preparation
why are quinolones and fluoroquinolones not given to children
they stop cartilage development
Describe: Injury to plasma membrane
Antibacterial & anti-fungal drugs.
Polymyxin B and
bacitracin cause damage to plasma membranes.