What is the length of the testis?
3-5 cm
What is the width of the testis?
2-3 cm
What is the volume of the testis
25 ml
Which gene determines sex?
Y
What what age do embryos look the same?
up to 8 weeks
what drives structural changes?
hormones
boys get a testosterone bath
Where do the testes develop?
near the kidneys
At what time do the testes descend?
7 months (28 weeks)
where do the testis drop?
through the inguinal canal into the scrotum
Name the 2 parts of the testis
outer sac
internal contents
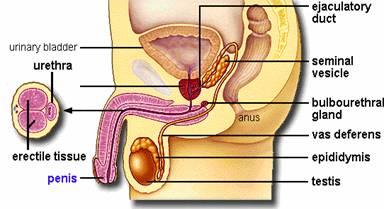
Name the external genitalia
scrotum
penis
name the internal genitalia
prostate
seminal vesicles
Bulbourethral gland
vas
deferens
testes
Explain the layers of the scrotum from out to in
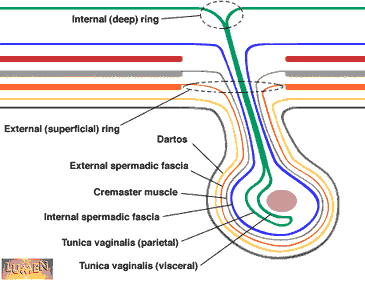
skin
tunica dartos
external spermatic fascia
cremaster muscle
internal spermatic fascia
tunica
vaginalis X2
tunica albuginea
what does the external spermatic fascia cover?
the cremaster muscle
explain the significance of the tunica vaginalis
it is an double walled covering with a visceral and parietal layer
What type of gland is the testi?
endocrine - testosterone
exocrine - sperm
what is the outer coat of the testis
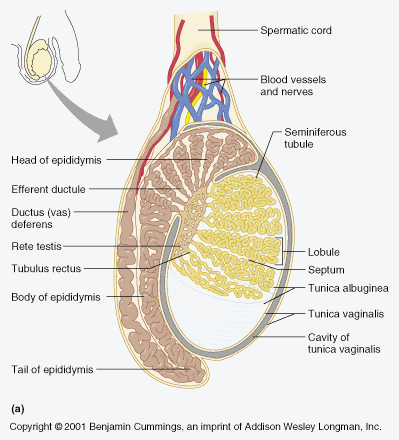
tunica albuginea
what does the tunica albuginea form?
extends into the testi to form the mediastinum
What is the mediastinum testis?
formed from the extension of the tunica albuginea the mediastinum testis radiates into the testi to form 200-300 lobules containing seminiferous tubules
what is the function of seminiferous tubules
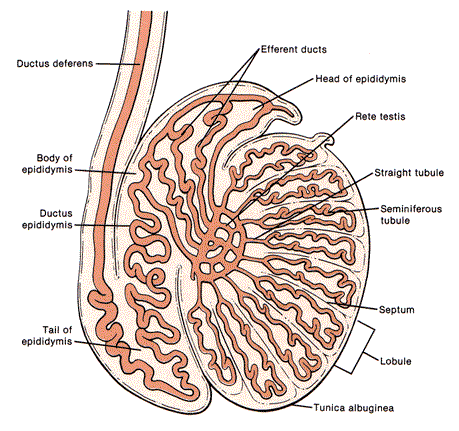
spermatogenesis
explain the path of sperm after leaving the seminiferous tubules
straight tubules
Rete testis
efferent ducts - head epididymis
What arteries supply the testis?
testicular arteries off the aorta
what veins drain the testis?
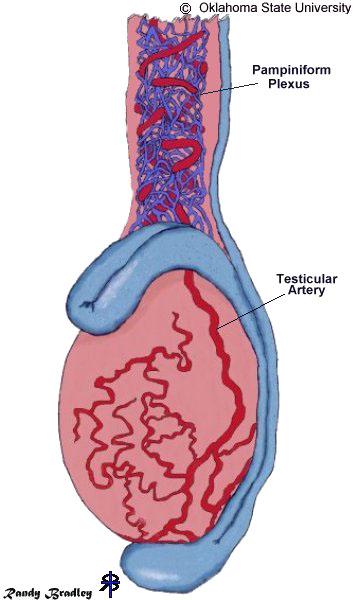
pampiniform plexus
testicular veins
Rt - IVC
Lt -
Lt renal vein
Describe the shape of the epididymis
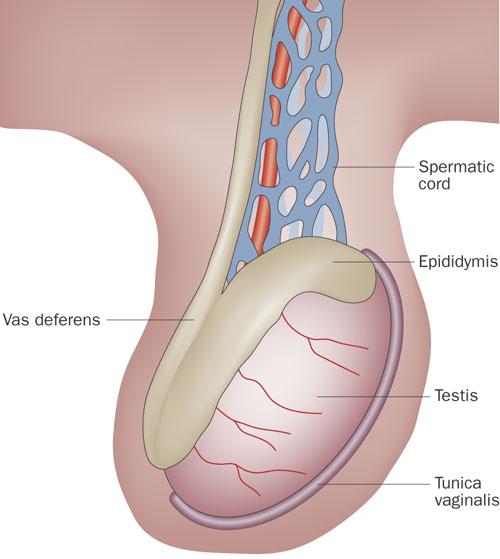
comma shape
single long convoluted tube
How long is the epididymis tube?
20 feet
6 meters
Which part of the epididymis is the largest?
head
Where does the head lie
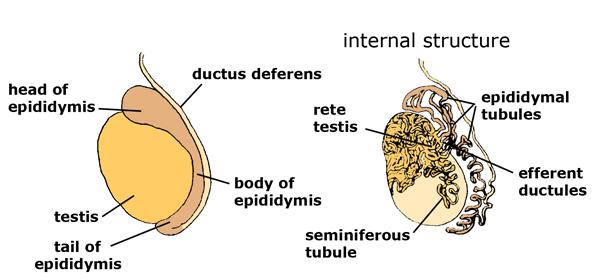
most superior
where does the body of the epididymis lie?
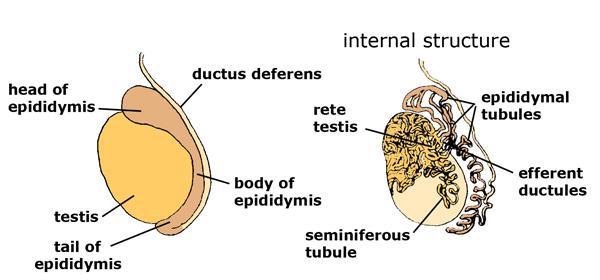
extends along the posterior aspect
Where is the tail of the epididymis
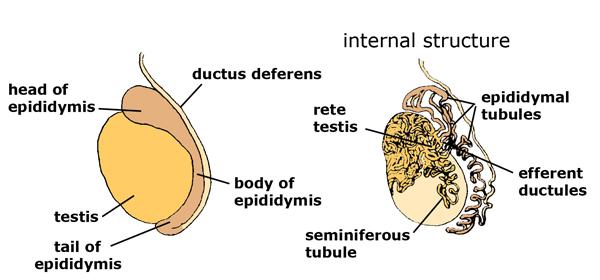
thinnest most inferior part
What is problematic of the inguinal canal?
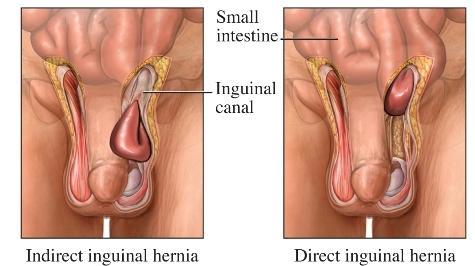
tends to be weak
common place for hernia
What is the spermatic cord composed of?
vas deferens
arteries
veins
nerves
lymphatics
cremaster muscle
What is the function of the cremaster muscle?
temperature regulation
Seminal vesicles VS seminiferous tubules
seminiferous tubules - spermatogenous
Seminal vesicles -
What is the function of the vas deferens?
connect the tail of the epididymis to the prostate
How long is the vas deferens?
18 inches
Explain the route of the vas deferens.
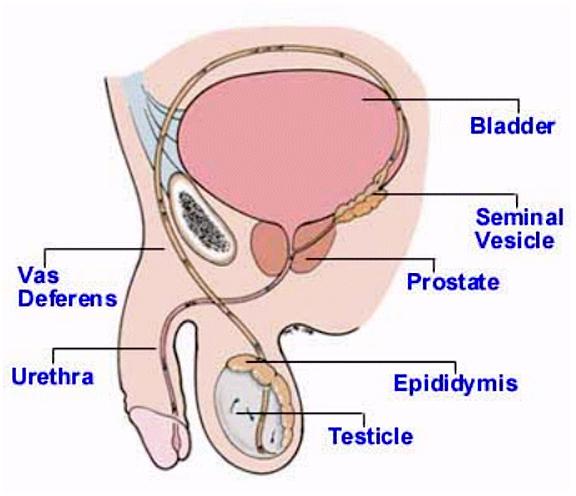
travels through the inguinal canal
travels over the top of the
pubic bone
swings around to the back side of the bladder
dilates distally to form the ampulla of deferens
joins the seminal vesicles
into the superior section of
the prostate
What does the epididymis consist of?
3 smooth muscles
what is the ampulla of deferens
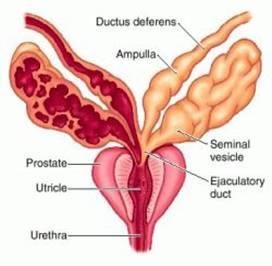
dilation of the vas deferens just before it enters the prostate
What is the ejactlatory duct?
vas deferens joins the seminal vesicles
What is the function of the seminal vesicles?
secretes 60% of seminal fluid
What is the function of the prostate?
produces 30 % of seminal fluid
what is the shape of the prostate?
cone shaped
base and apex
What does the Prostate consist of?
various regions and zones
levator ani muscles
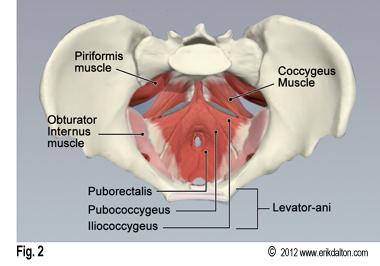
pelvic floor muscles
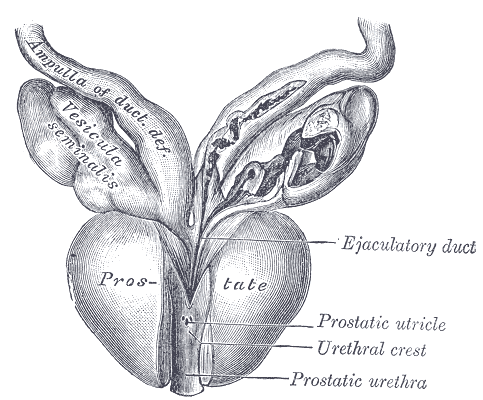
What is the prostate urethra?
part of the urethra that runs through the prostate
bulbourethral gland
5% of seminal fluid
clear and thick
lubricant;
flushing agent that washes out the urethra
What is the Cowper’s Gland?
another name for bulbourethral gland
Seminal Fluid
60% seminal vesicles
30% prostate
5% bulbourethral gland
Appearance of the prostate
hetergenous
What are the regions of the prostate?
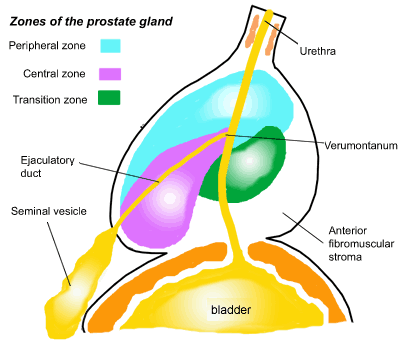
veramontanum - prostatic portion of the urethra where the seminal
ducts enter
Peripheral zone (PZ)
Central
zone (CZ)
Transition zone (TZ)
fibromuscular zone (or stroma)
periurethral zone
What is the penis consist of?
3 cylinder masses
2 corpus cavernosum
1 corpus spongiosum
Where does the urethra run through the penis?
within the posterior spongiosum
what bounds and divided the the three cylinder masses of the penis
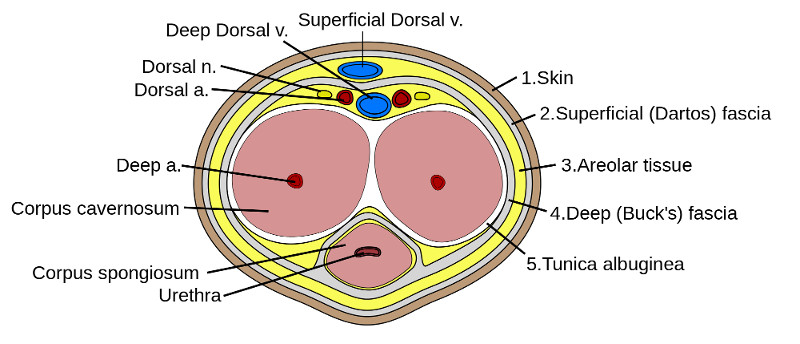
tunica albuginea
buck's fascia - fibrous envelope
What type of blood engorges penis during erection
venous blood
Explain the flow of penile arteries
internal iliacs
internal pudendal
- deep
artery of the penis
- corpus cavernosum
-
bulbourethral artery
- corpus spongiosum , glans penis
Explain venous flow of the penis
superficial and deep dorsal vein
pudendal venous plexus
internal pudendal vein
internal iliac vein
...
What do Reproduction organs begin from?
2 urogenital folds
What does the urogenital folds consist of?
- gonad
- mesonephros
What does the mesonephos develop into
- metanephos
- urogential sinus
What does the gonad develop into
- mesonephric duct
- paramesonephric duct
What does the paramesonephric duct develop into?
female genitalia
- vagina
- uterus
- fallopian tubes
What does the mesonephric duct develop into?
male genitalia
- testis
- penis
What is the wolfian duct
mesonephric duct
What is the mullerian duct
paramesonephric duct
Which gender has mullerian and wolfian ducts?
both
What is the sonographic appearance of the scrotum & testes?
homogeneous
medium level echoes
bilaterally equal in size
echogenic midline
epididymis superior posteriorly to the testicle
slightly more echogenic
more course texture
Blood flow is evident on color Doppler
through out the parenchyma
What transducer should be used on a scrotal exam?
5 - 7 MHz Linear transducer
What should the patient be dressed during a scrotal exam?
maintain patient dignity
What techniques should be used during a scrotal exam?
place towel under testis for support
What are the required images for a scrotal exam?
- longitudinal
upper
mid
mid with measurement
lower
- transverse
med
mid
mid with measurement
lateral
- comparison
What are the reasons for a scrotal scan?
R?O torsion
trauma
pain
size change
nodularity on physical exam
possible varicocele
R/O Hernia
locate undescended testicle
F/U Hydrocele
inflamation
infection
At what age do the testicle descend into the sac?
28 weeks
What drives the descent of the testicles?
gonatrophins
What happens if the testicles do not descend?
orchiopexy
surgery to correct
What is the medical intervention for a hematoma on a testicle?
let it heal on its own
What happens if a testicle gets ruptured?
medical emergency
within 72 hours the testicle can be saved
What is the sonographic appearance of a epididymal cyst?
hypoechoic
What is a spermatic cyst?
AKA epididymal cyst
What is a spermatocele?
AKA epididymal cyst
What causes a epididymal cyst?
obstruction of efferent ductile
old sperm
How dangerous are the large epididymal cyst?
usually benign
How dangerous are the small rigid epididymal cyst?
cause a lot of pain
What is the normal epididymal A/P measurement?
8 mm
What is the normal skin measurement of the skin surrounding the testicle?
2 mm
What is epididymitis?
inflammation of the epididymis
What is the most common cause of acute scrotal pain and tenderness?
epididymitis
What is the treatment for epididymitis?
responds well to antibiotics
What is the presentation of epididymitis?
fever
painful urination
What is the sonographic appearance of epididymitis?
enlarged epididymis (more than 8 mm)
increased flow
What is orchitis?
inflammation of a testicle
complication of epididymitis
What is the sonographic appearance of orchitis?
heterogenius
hyperechoic
reactive hydrocele
What is the presentation of orchitis?
elevated WBC
enlarged
skin thickening
What is a bell clapper?
narrow or absent bare area of the testicle
tunica albuginea closes all the way around testicle
What is the problem with a bell clapper?
when tunica albuginea closes all the way or most of the way there is no bare area and no place for the testicle to attach to scrotal wall
What is the common age for testicular torsion?
12 - 18
What is the peak age for testicular torsion?
13
What is testicular torsion?
testicle twists blocks blood flow
congenital
What is the sonographic appearance of testicular torsion?
No flow
contralateral to normal
enlarged
hypoechoic
What happens when a patient has testicular torsion?
24 hours
emergency
will become necrotic after 24 hours
What is hydrocele?
accumulation of serous fluid between the tunica vaginalis
What is the most common cause of painless scrotal swelling?
hydrocele
What is congenital hydrocele?
vaginalis usually closes after testis descend
if open fluid can leak into scrotum
What is acquired hydrocele?
abdominal secretions leak through
What happens to congenital hydrocele?
by 24 months usually resides
What causes acquired hydrocele?
infection
infarction
neoplasm - 60%
trauma - 25%
What is Varicocele?
abnormal enlargement of the pampiniform venous plexus in the scrotum
What is the sonographic appearance of varicocele?
pampiniform plexus larger than 2 mm
pampiniform usually not seen in U/S
What side is a varicocele on?
left because left spermatic cord drains into the left renal vein and causes reverse flow when valves are not created
What causes 40% of infertility in men?
varicocele
What is the biggest problem with varicocele?
increased flow causes testis to get to HOT and cause infertility
What are techniques to prove varicocele?
ask the patient to take a deep breath
or stand and pampiniform should dilate
What is a scrotal hernia?
bowel comes through when older men get loose
What is the sonographic appearance of varicocele?
bowel in the scrotum
peristalsis
What is testicular microlithiasis?
tiny micro fications without shadow
What is the sonographic appearance of testicular microlithiasis?
tiny micro fications without shadow
What does testicular microlithiasis cause?
infertility
precursor for testicular cancer
Names the solid malignant masses.
seminoma
embryonal cell carcinoma
yolk sac tumors
teratomas
What make up 95% of all testicular tumors?
germ cell tumors
What is a germ cell tumor?
highly malignant tumor associated with
elevated AFP
elevated HGC
What is AFP?
alpha fetal proteins
What is HCG?
human chorionic gonadotropin
What is 40-50% of solid malignant testicular masses?
seminoma
What is 25% of solid malignant testicular masses?
embryonal cell carcinoma
What is 60% of solid malignant testicular masses in infants?
yolk sac tomors
What is 5-10% of solid malignant testicular masses?
teratomas
What is a seminoma?
Solid malignant mass
generally found in 30 - 40 year olds
What is embryonal cell carcinoma?
malignant testicular tumor
less common but more aggressive
What is the most common germ cell tumor in infants?
yolk sac tumors
What is a teratoma?
malignant testicular tumor in adults
*generally benign in children
What is the sonographic appearance of a seminoma?
hypoechoic
single mass
How sensitive is ultrasound in diagnosing testicular tumors?
100%
Where are most malignant testicular masses found?
intratesticular
Where are most benign testicular masses found?
extratesticular