ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS
Chemotherapy
Treatment of disease with chemical substances.
ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS
Antimicrobial drugs
Act by killing or by interfering with the growth of microorganisms.
ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS
Selective toxicity
The property of some antimicrobial agents to be toxic for a microorganism and nontoxic for the host.
ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS
Antibiotic
A substance produced by microorganisms that in small amounts inhibits another microorganism.
ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS
1928
Fleming discovered penicillin, produced by Penicillium.
ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS
1940
Howard Florey and Ernst Chain performed first clinical trials of penicillin.
THE SPECTRUM OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY
Narrow Spectrum of microbial activity
Range of different microbial types they affect; affects either gram-positive OR gram-negative bacteria; one or the other, but not both.
THE SPECTRUM OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
Antibiotics that affect a broad range of
gram-positive or
gram-negative bacteria; both.
THE SPECTRUM OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY
Superinfection
Growth of a target pathogen that has developed resistance to antibiotics; overgrowth; broad-spectrum antibiotic.
THE ACTION OF ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS
Bactericidal
Kills microbes directly
THE ACTION OF ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS
Bacteriostatic
Prevent microbes from growing; inhibits growth
MAJOR ACTION MODES OF ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS
5 TYPES:
1. INHIBITION OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS:
Penicillins,
Cephalosporins, Bacitracin,
Vancomycin.
2. INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS:
Chloramphenicol,
Erythromycin, Tetracyclines,
Streptomycin.
3. INHIBITION OF NUCLEIC ACID REPLICATION AND
TRANSCRIPTION:
Quinolones, Rifampin.
4. INJURY TO THE PLASMA MEMBRANE:
Polymyxin B
5. INHIBITION OF ESSENTIAL METABOLITE
SYNTHESIS:
Sulfanimide, Trimethoprim.
ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS
Para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA)
PABA is the substrate for an enzymatic reaction leading to the synthesis of folic acid, a vitamin that functions as a coenzyme for the synthesis of the purine and pyrimidine bases of nucleic acids and many amino acids.
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Penicillin
A group of 50 chemically related antibiotics produced either by Penicillium (natural penicillins) or by adding side chains to the beta-lactam ring (semisynthetic penicillins); inhibitors of cell wall synthesis.
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
What are the three types of penicillins?
1. Natural penicillin
2. Semisynthetic penicillin
3. Extended-spectrum penicillin
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Natural penicillin
Penicillin extracted from cultures of the mold Penicillium exists in several closely related forms.
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
What are the 2 types of natural penicillin?
1. Penicillin G:
against gram-positive bacteria,
*REQUIRES INJECTION.
2. Penicillin V:
against gram-positive bacteria,
*ORAL ADMINISTRATION.
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Semisynthetic penicillins
Part of the penicillin is produced by the mold, and part is added synthetically; attempts to overcome the disadvantages of natural penicillins.
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Extended-spectrum penicillins
Changes made to the narrow spectrum of activity of natural penicillins giving them a broader-spectrum making them effective against both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, although they are not resistant to penicillinases.
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Augmentin
An approach to the proliferation of penicillinase to combine penicillins (Amoxicillin) with potassium clavulanate (clavulanic acid), which is a noncompetitive inhibitor of penicillinase with no antimicrobial activity of its own. It is a product of a Streptomycete; Penicillins + β-lactamase inhibitors (combo drug).
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
What are the 2 types of semisynthetic penicillins?
1. OXACILLIN:
narrow spectrum, only gram-positives, but
resistant to penicillinase.
2. AMPICILLIN:
Extended (broad)spectrum, many
gram-negatives.
β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS
Penicillin
1. Penicillinase-resistant penicillins.
2. Penicillins + β-lactamase inhibitors.
β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS
Carbapenems
Substitute a Carbon atom for a Sulfur and add a double bond to the penicillin nucleus.
β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS
Monobactam
A Single ring.
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Cephalosporins: First Generation
Narrow spectrum; act against gram-positive bacteria.
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Cephalosporins: Second Generation
Extended spectrum includes gram-negative bacteria
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Cephalosporins: Third Generation
Includes pseudomonads; injected
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Cephalosporins: Fourth Generation
Oral
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Polypeptide antibiotics:
1. BACITRACIN:
topical application; against gram-positives
2. VANCOMYCIN:
glycopeptide; important "last
line" against
antibiotic-resistant S. aureus.
INHIBITOR OF CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Antimycobacterial antibiotics
1. ISONIAZID (INH):
inhibits mycolic acid synthesis.
2. ETHAMBUTOL:
inhibits incorporation of mycolic acid.
THE INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY ANTIBIOTICS
30s subunit portions of the 70s prokaryotic ribosomes.
STREPTOMYCIN:
changes shape of 30s portion, causing code on
mRNA to be read incorrectly.
THE INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY ANTIBIOTICS
50s subunit portions of the 70s prokaryotic ribosomes.
CHLORAMPHENICOL:
binds to 50s portion and inhibits formation of
peptide bond.
THE INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY ANTIBIOTICS
Tetracyclines
Interfere with attachment of tRNA to mRNA-ribosome complex.
THE INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY ANTIBIOTICS
70s prokaryotic ribosome
Occurs in translation.
INHIBITORS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Chloramphenicol
Broad spectrum; binds 50s subunit; inhibits peptide bond formation.
INHIBITORS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Aminoglycosides
Streptomycin, Neomycin, Gentamicin; broad spectrum; change shape of 30s subunit.
INHIBITORS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Tetracyclines
Broad spectrum; interfere with tRNA attachment.
INHIBITORS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Glycylcyclines
MRSA and Acinetobacter baumanii; bind 30s subunit; inhibit translation.
INHIBITORS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Macrolides
Gram-positives; bind 50s subunit; prevent translocation.
INHIBITORS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Streptogramins
Gram-positives; bind 50s subunit; inhibit translation.
INHIBITORS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Oxazolidinones
Linezolid; MRSA; binds 50s subunit; prevent formation of 70s ribosome.
INHIBITORS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Pleuromutilins
From the mushroom Pleurotis Mutilus; MRSA; binds 50s; prevent translocation.
INJURY TO THE PLASMA MEMBRANE
Lipopeptides
Structural changes in the membrane, followed by arrest of the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and protein; MRSA.
INJURY TO THE PLASMA MEMBRANE
Polymyxin B
Topical; Combined with Bacitracin and Neomycin in over-the-counter preparation.
INHIBITORS OF NUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS
Rifamycin
Inhibits RNA synthesis; anti-tuberculosis.
INHIBITORS OF NUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS
Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones
Nalidixic Acid (urinary infections); Ciprofloxacin; Inhibit DNA gyrase; urinary tract infections.
COMPETITIVE INHIBITORS
Sulfonamides (sulfa drugs)
Inhibit folic acid synthesis; broad spectrum.
ACTIONS OF THE ANTIBACTERIAL SYNTHETICS TRIMETHOPRIM AND
SULFAMETHOXAZOLE
Sulfamethoxazole
A Sulfonamide that is a structural analog of PABA, competitively inhibits the synthesis of Dihydrofolic Acid from PABA.
ACTIONS OF THE ANTIBACTERIAL SYNTHETICS TRIMETHOPRIM AND
SULFAMETHOXAZOLE
Trimethoprim
A structural analog of a portion of Dihydrofolic Acid, competitively inhibits the synthesis of Tetrahydrofolic Acid.
ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS: INHIBITION OF ERGOSTEROL SYNTHESIS
Polyenes
Amphotericin B.
ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS: INHIBITION OF ERGOSTEROL SYNTHESIS
Azoles
Miconazole; Triazole.
ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS: INHIBITION OF ERGOSTEROL SYNTHESIS
Allylamines
For Azole-resistant infections.
ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS: INHIBITING CELL WALL SYNTHESIS
Echinocandins
Inhibit synthesis of β-glucan; Cancidas is used against Candida and Pneumocystis.
INHIBITION OF NUCLEIC ACIDS
Flucytosine
Cytosine analog interferes with RNA synthesis.
INHIBITION OF NUCLEIC ACIDS
Pentamidine isethionate
Anti-Pneumocystis; may bind DNA.
OTHER ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS
Griseofulvin
Inhibits microtubule formation; superficial dermatophytes.
OTHER ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS
Tolnaftate
Action unknown.
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE ANTIVIRAL DRUG ACYCLOVIR
A) Acyclovir structurally resembles the nucleoside deoxyguanosine.
B) The enzyme thymidine kinase combines phosphates with
nucleosides to form nucleotides, which are then incorporated into DNA.
C) Acyclovir has no effect on a cell not infected by a virus,
that is, with normal thymidine kinase. In a virally infected cell, the
thymidine kinase is altered and converts the acyclovir (which
resembles the nucleoside deoxyguanosine) to a false nucleotide, which
blocks DNA polymerase.
ANITVIRAL DRUGS
Protease inhibitors
Indinavir:
HIV
ANITVIRAL DRUGS
Integrase inhibitors
HIV
ANITVIRAL DRUGS
Entry inibitors
Amantadine:
influenza
ANITVIRAL DRUGS
Fusion inhibitors
1. Zanamivir:
influenza
2. Block CCR5:
HIV
ANITVIRAL DRUGS: INTERFERONS
1. Prevent spread of viruses to new cells.
2. Alpha interferon:
viral Hepatitis
ANITVIRAL DRUGS: INTERFERONS
Imiquimod
Promotes interferon production.
ANTIPROTOZOAN DRUGS
Chloroquine
Inhibits DNA synthesis; Malaria.
ANTIPROTOZOAN DRUGS
Artemisinin
Kills Plasmodium sporozoites.
ANTIPROTOZOAN DRUGS
Metronidazole
Interferes with anaerobic metabolism; Trichomonas an Giardia.
ANTIHELMINTHIC DRUGS
Niclosamide
Prevents ATP generation; tapeworms.
ANTIHELMINTHIC DRUGS
Praziquantel
Alters membrane permeability; flatworms.
ANTIHELMINTHIC DRUGS
Mebendazole and Albendazole
Interfere with nutrient absorption; intestinal roundworms.
ANTIHELMINTHIC DRUGS
Ivermectin
Paralysis of helminthes; intestinal roundworms.
ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
1. A variety of mutations can lead to antibiotic
resistance.
2. Resistance genes are often on plasmids or
transposons
that can be transferred between
bacteria.
BACTERIAL RESISTANCE TO ANTIBIOTICS
4 STEPS:
1. Blocking entry.
2. Inactivation by enzymes.
3. Alterations of target molecule.
4. Efflux of antibiotic.
ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
Misuse of antibiotics
1. Misuse of antibiotics selects for resistance
mutants.
2. Misuse includes:
a) Using outdated or weakened
antibiotics.
b) Using antibiotics for the common cold and
other
inappropriate conditions.
c) Using antibiotics in animal feed.
d) Failing to complete the prescribed regimen
e) Using someone else's left over prescription.
EFFECTS OF COMBINATIONS OF DRUGS
Synergism
Occurs when the effect of two drugs together is greater than the effect of either one alone; work with each other.
EFFECTS OF COMBINATIONS OF DRUGS
Antagonism
Occurs when the effect of two drugs together is less than the effect of either one alone; work against each other.
ANTIBIOTIC SAFETY
Therapeutic index:
risk versus benefit
FUTURE CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENT
Antimicrobial peptides
Broad spectrum antibiotics:
a) Nisin (lactic acid bacteria)
b) Defensins (human)
c) Magainin (frogs)
d) Squalamine (sharks)
FUTURE CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENT
Phage therapy
GENE SILENCING COULD PROVIDE TREATMENTS FOR A WIDE RANGE OF DISEASES
4 STEPS:
1. An abnormal gene, cancer gene, or virus gene is
transcribed in a host cell.
2. siRNA binds mRNA.
3. RISC breaks down the RNA complex.
4. No protein expressions occur.
The first antibiotic discovered was:
Salvarsan.
Penicillin.
Quinine.
Streptomycin.
Sulfa drugs.
Penicillin.
Which of the following antibiotics inhibits cell wall synthesis?
Chloramphenicol
Trimethoprim
Rifampin
Cephalosporin
Erythromycin
Cephalosporin.
Which of the following antibiotics inhibits protein synthesis?
Vancomycin
Streptomycin
Rifampin
Cephalosporin
Isoniazid
Streptomycin.
Which of the following is not used for treating bacterial infections?
Methicillin
Griseofulvin
Rifampin
Ampicillin
Tetracycline
Griseofulvin.
Which antimicrobial works by inhibiting the synthesis of mycolic
acid?
Methicillin
Penicillin
Vancomycin
Chloramphenicol
Isoniazid
Isoniazid.
Which of the following antibiotics should be prescribed as a first
choice for a streptococcal infection?
Tetracycline
Amoxicillin
Trimethoprim
Rifampin
Neomycin
Amoxicillin.
Which of the following antibiotics inhibits folic acid synthesis?
Chloramphenicol
Ampicillin
Sulfanilamide
Neomycin
Tetracycline
Sulfanilamide.
Which of the following drugs inhibits the synthesis of mRNA in
bacteria?
Polymyxin B
Ampicillin
Rifampin
Ethambutol
Trimethoprim
Rifampin.
Which of the following antibiotics frequently used as an alternative
for those who are allergic to penicillin?
Ethambutol
Vancomycin
Erthryomycin
Streptomycin
Amoxicillin
Erthryomycin.
All of the following antibiotics inhibit protein synthesis except:
Erthromycin.
Bacitracin.
Tetracycline.
Chloramphenicol.
Streptomycin.
Bacitracin.
Which drug would be used to treat athlete's foot?
Amantadine
Neomycin
Clotrimazole
Polymyxin B
Chloroquine
Clotrimazole.
Which antifungal drug is commonly used for systemic fungal
infections?
Clotrimazole
Tolnaftate
Miconazole
Fluconazole
Amphotericin B
Fluconazole.
Tetracyclines are effective against all of the following except:
Gram-negative bacteria.
intracellular chlamydias.
Gram-positive bacteria.
fungi.
intracellular rickettsias.
Fungi.
A nucleoside analog used to treat HIV infection is:
Ribavirin.
Zidovudine.
Praziquantel.
Acyclovir.
Amantidine.
Zidovudine.
All of the following are anti-protozoan drugs except:
Mefloquine.
Metronidazole.
Mebendazole.
Quinacrine.
Chloroquine.
Mebendazole.
Which drug is not a nucleoside analog?
Lamivudine
Zidovudine
Neviraprine
Acyclovir
Ribavirin
Neviraprine.
Which is the drug of choice for the treatment of malaria?
Iodoquinol
Flagyl
Quinacrine
Nifurtimox
Chloroquine
Chloroquine.
The drug, Flagyl, is commonly used to treat an STD caused by:
Trichomonas vaginalis.
Herpesvirus.
HIV.
Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Treponema pallidum.
Trichomonas vaginalis.
Which of the following mechanisms is antifungal?
Inhibit ergosterol synthesis
Interfere with anaerobic
metabolism
Cause muscle spasms
Inhibit peptidoglycan
synthesis
Inhibit 70S ribosomes
Inhibit ergosterol synthesis.
Which of the following is used for treating influenza infections?
Indinivir
Acyclovir
Oseltamivir
Pentamidine isethionate
Interferon
Oseltamivir.
Antibiotic resistance can be minimized by the discriminating use of
drugs in appropriate dosages.
True
False
True
The MIC is the lowest concentration of drug capable of preventing
microbial growth.
True
False
True
It is relatively easy to find drugs that are effective against
eukaryotic pathogens.
True
False
False
Bacteriostatic agents are ineffective as antibiotics.
True
False
False
Some drug combinations are antagonistic, therefore, when taken
together they are more effective.
True
False
False
Semisynthetic penicillins are more effective antibiotics than natural
penicillin.
True
False
True
In 1928, Alexander Fleming observed that the growth of the bacterium
Staphylococcus aureus was inhibited by a mold thereby discovering the
first antibiotic.
True
False
True
Because antifungal drugs like amphotericin B target sterols in the
plasma membrane they are ineffective as antibacterial drugs.
True
False
True
Ivermectin is an anti-protozoan drug.
True
False
False
A drug that inhibits translation at 70S ribosomes can be used to
treat human viral infections.
True
False
False
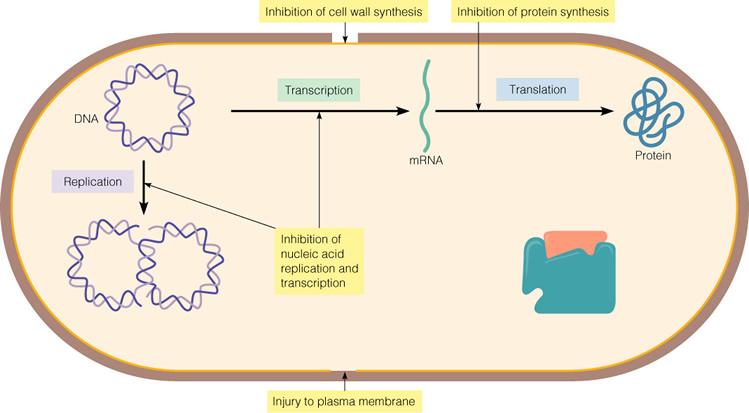
Which mode of antibiotic activity is the most selective target for
antibiotics since it will not affect eukaryotic cells?
A) Inhibition of transcription
B) Inhibition of cell wall
synthesis
C) Inhibition of translation
D) Inhibition of
DNA replication
E) Injury to the plasma membrane
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
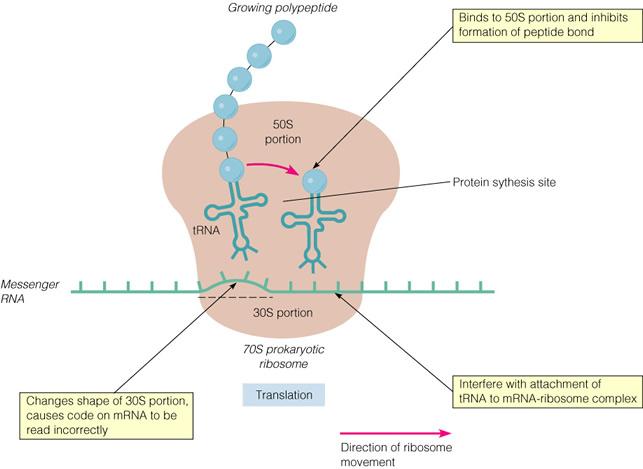
Which of these antibiotics exerts its activity by changing the shape
of 30S portion, causing the code on mRNA to be read incorrectly?
A) Tetracycline
B) Streptomycin
C) Erythromcyin
D) Chloramphenicol
Streptomycin
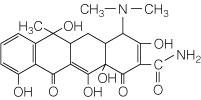
Which antibiotic pictured is not recommended for children due to
possible discolorations of their teeth?
A) Penicillin
B) Amphotericin B
C) Tetracycline
D) Chloramphenicol
Tetracycline
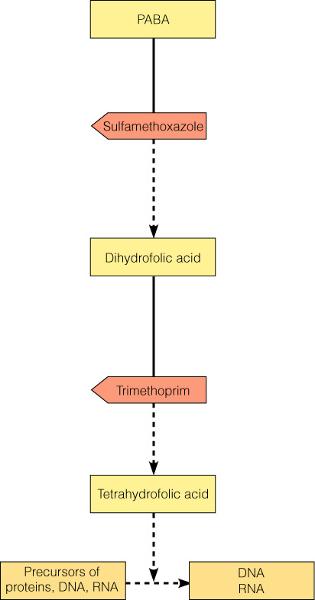
All of the following are correct about the combination of
trimethoprim and sufamethoxazole (TMP-SMZ) EXCEPT:
A) The combination reduces the emergence of
resistant
strains.
B) The drugs in combination have a broad spectrum.
C) The drugs in combination are antagonistic.
D) When
used together, less of the drugs are
needed, compared to when
each drug is used
alone.
The drugs in combination are antagonistic.
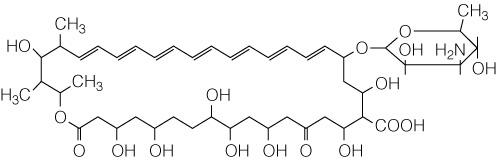
Which of the following is correct about amphotericin B shown in the
figure?
A) The drug belongs to the polyene group of
antifungals.
B) The drug is effective against gram-positive
bacteria
only.
C) The drug has no side effects.
D) The drug
targets protein synthesis.
The drug belongs to the polyene group of antifungals.
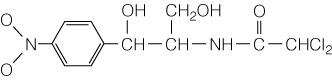
Which antibiotic shown in the figure appears to cause aplastic anemia
in 1 in 500,000 individuals?
A) Penicillin
B) Amphotericin B
C) Erythromycin
D) Chloramphenicol
E) Streptomycin
Chloramphenicol
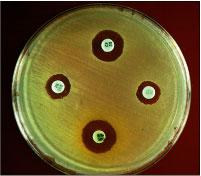
In the disk-diffusion assay shown in the photo, what do the clear
areas around the discs represent?
A) It is impossible to determine from the
information
given.
B) Where bacterial growth has been inhibited.
C)
Where drug-resistant mutants are located.
D) Where the bacteria
are growing the fastest.
Where bacterial growth has been inhibited.
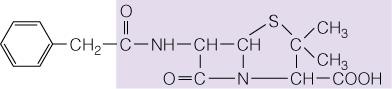
FIGURE A
Which of the following chemical structures is of erythromycin?
PICTURE A, B OR C
A) Figure a
B) Figure b
C) Figure c
D) None
of these figures are of erythromcyin
Figure B
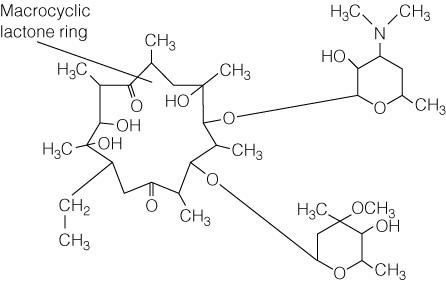
FIGURE B
SEE QUESTION 116
FIGURE C
SEE QUESTION 116
A disk-diffusion test identifies:
bacteriostatic agents.
agents to which a test culture
is susceptible.
bactericidal agents.
MBC.
Agents to which a test culture is susceptible.
A chemical that kills gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative
bacteria is described as:
selectively toxic.
inhibitory.
broad spectrum.
narrow spectrum.
Broad spectrum.
A drug that inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis is:
antibacterial.
antifungal.
antiprotozoal.
antiviral.
Antibacterial.
A drug that inhibits mitosis might be useful against all of the
following infections except which type?
helminthic
protozoal
fungal
bacterial
Bacterial.
Clindamycin binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit to inhibit
translocation. This antibiotic stops:
transcription in eukaryotes.
translation in
prokaryotes.
transcription in prokaryotes.
translation
in eukaryotes.
Translation in prokaryotes.
Gentamicin binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit to cause misreading of
mRNA. This antibiotic stops:
transcription in prokaryotes.
translation in
prokaryotes.
transcription in eukaryotes.
translation
in eukaryotes.
Translation in prokaryotes.
A drug that binds with sterols would injure:
fungal cell walls.
eukaryotic plasma membranes.
bacterial cell walls.
DNA.
Eukaryotic plasma membranes.
The method of action of nucleoside analogs is:
disruption of plasma membrane.
inhibition of cell wall
synthesis.
competitive inhibition.
inhibition of
protein synthesis.
Competitive inhibition.
Ethambutol inhibits incorporation of mycolic acid into:
plasma membranes.
DNA.
enzymes.
cell walls.
Cell walls.
Ethambutol inhibits incorporation of mycolic acid, therefore it is
effective against:
mycoplasmas.
gram-positive bacteria.
mycobacteria.
fungi.
Mycobacteria.
You have a 200 mg/ml antibiotic solution. You prepare serial
dilutions (1:2, 1:4, etc.) of the antibiotic; the first tube contains
100 mg/ml. You then inoculate each tube with Salmonella. Bacteria grow
in tubes 4, 5, and 6. You subculture bacteria from tubes 1 through 3
to nutrient broth. Growth occurs in the tube 3 subculture. You can
conclude that the MIC is:
200 mg/ml.
cannot tell from the information provided.
25 mg/ml.
50 mg/ml.
25 mg/ml.
You have a 200 mg/ml antibiotic solution. You prepare serial
dilutions (1:2, 1:4, etc.) of the antibiotic; the first tube contains
100 mg/ml. You then inoculate each tube with Salmonella. Bacteria grow
in tubes 4, 5, and 6. You can conclude that the MBC is:
cannot tell from the information provided.
50 mg/ml.
12.5 mg/ml.
25 mg/ml.
Cannot tell from the information provided.
You have a 200 mg/ml antibiotic solution. You prepare serial
dilutions (1:2, 1:4, etc.) of the antibiotic; the first tube contains
100 mg/ml. You then inoculate each tube with Salmonella. Bacteria grow
in tubes 4, 5, and 6. You subculture bacteria from tubes 1 through 3
to nutrient broth. Growth occurs in tubes 2 through 3. You can
conclude that the MBC is:
100 mg/ml.
12.5 mg/ml.
50 mg/ml.
25 mg/ml.
100 mg/ml.
Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
Ciprofloxacin-inhibit cell wall synthesis
Defensin-makes membrane channels
RNAi-blocks protein synthesis
Griseofulvin-blocks microtubule formation
Ciprofloxacin-inhibit cell wall synthesis.
You obtain the following zones of inhibition (ZI) from a
disk-diffusion test on Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotic A, ZI = 0 mm;
Antibiotic B, ZI = 23 mm; Antibiotic C, ZI = 16 mm. Which antibiotic
is bacteriostatic?
cannot tell from the information provided
antibiotic C
antibiotic A
antibiotic B
Cannot tell from the information provided.
Rifampin blocks RNA polymerase to inhibit:
transcription.
translation.
DNA synthesis.
cell wall synthesis.
Transcription.
Antisense DNA will combine with a pathogen's DNA to:
inhibit translation.
inhibit cell wall synthesis.
inhibit peptide bond formation.
inhibit transcription.
Inhibit transcription.
Polyenes, azoles, and allyamines interfere with sterol synthesis.
These drugs will affect:
fungi.
gram-positive bacteria.
viruses.
gram-negative bacteria.
Fungi.
Which of the following statements is true about superinfections?
They are caused by endospore-forming bacteria.
They are
caused by antibiotic-resistant
bacteria.
They only
occur in people with
immunodeficiencies.
They inhibit
protein synthesis.
They are caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Sulfa drugs are selective against bacteria for all of the following
reasons except which?
Bacteria synthesize folic acid.
Sulfa drugs inhibit a
bacterial enzyme.
Humans have a dietary requirement for folic
acid.
Sulfa drugs cause production of
antimetabolites.
Sulfa drugs cause production of antimetabolites.