Group of cells combine to form
Tissue
The example of Jack rabbit exchanging heat with the environment and maintaining constant body temperature shows which living characteristic of living organisms?
Regulation
Viruses that infect and takeover bacteria are called?
Bacteriophage
What type of data involve descriptions rather than measurements?
Qualitative
Name the organisms that can only replicate/divide when inside its host
Viruses
The branch of science that helps in naming, identification and classification of species is called?
Taxonomy
Kingdom is the broadest unit of classification. True or False
False
The Kingdom Fungi is grouped under which domain?
domain Eukarya
What is the total number of domains under which all living organisms are classified into?
Three
Give any example of an Ecosystem
Desert, Rainforest, Deciduous forest, grassland, ocean, tundra, coral reef etc...
Name the characteristics of life
Order
Regulation
Energy processing
Evolutionary adaptation
Growth/development
Response to the environment
Reproduction
What are characteristics of Viruses?
A borrowed life
What is the name of the largest virus discovered?
Mimivirus
How many species are identified and named to date?
approx. 1.8 million
Name the three domains
domain Bacteria
domain Eukarya
domain Archaea
What kingdoms are included in domain Eukarya?
Plantae, Fungi, Animalia
Biology
scientific study of life
Levels of organization in ascending order
Atoms
Molecules
Organelles
Cell
Tissues
Organ
Organ systems
Organisms
Populations
Communities
Ecosystems
Biosphere
Communities
entire array of organism inhabiting a particular ecosystem
Populations
all individuals of a species living within the bounds of specified area
Organisms
individual living things
Organ systems
various organ constitutes to from organ system
Organ
carries particular function in the body
Tissues
group of similar cells
Cells
fundamental unit of structure and function
Organelles
various functional components that make up the cell
Molecule
chemical structure consisting of two or more atoms
Levels of classification is descending order
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
What are Darwin's two points?
- species showed evidence of "descent with modification" from common ancestors
- natural selection is the mechanism behind "descent with modification"
What are Darwin's observations?
- individuals in a population have traits that vary
- many of these traits are heritable
- more offspring are produced that survive
- competition is inevitable
- species generally suit their environment
What are Darwin's inferences?
- individuals that are best suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce
- over time, more individuals in a population will have the advantageous traits
What are two main types of scientific inquiry?
discovery science (inductive) and hypothesis-based science(deductive)
Discovery science
describes natural structures and processes
Data
recorded observations or items of information
Name the two categories of data
Qualitative and Quantitative
Qualitative data
descriptions rather than measurements
Quantitative data
recorded measurements
Inductive reasoning
deriving general principles from particular facts or instances
Hypothesis
a tentative answer to a well-framed question
Deductive reasoning
uses general premises to make specific predictions
Why do we need controlled experiments?
to cancel the effects of unwanted variables
Limitations of Science
-observations and experimental results must be repeatable
- cannot support or falsify supernatural explanations
What is a theory
- broader in scope than a hypothesis
- general, can lead to new testable hypotheses
- supported by large body of evidence in comparison to a hypothesis
What are models?
representations of natural phenomena
Diagrams, 3D objects, Computer programs, mathematical equations are examples of?
Models
How do scientists communicate with each other?
seminars, publications, and websites
Substance consisting of two or more elements in fixed ratio is called
compound
How many electrons are there in valence shell of oxygen
six
Atomic number
number of protons in the nucleus
Goiter is caused by the deficiency of which trace element?
Iodine
Covalent bond
formed by sharing pairs of valence electrons
Sodium chloride is formed by which bond?
Ionic bond
Chemical equilibrium
the forward and reverse reaction rates are equal
Give an example of polar molecule
Water, Methane etc..
Water molecules are hold together by which type of bond?
Hydrogen bond
An oxygen molecule is formed by non-polar covalent bond. True or False
True
Element
a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reaction
Matter
anything that has mass and takes up space
Name the four essential elements that constitute 96% of living matter
hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen
Name the elements that constitute 4% of living matter
calcium, phosphorous, potassium, and sulfur
Name the subatomic particles that an atom is composed of
proton, neutron, and electron
Trace elements
elements required in minute quantities
Isotopes
two atoms of an element that differ in number of neutrons
Mass number
number of protons + number of neutrons
Radioactive isotopes
decay spontaneously giving of particles and energy
Applications of radioactive isotopes
dating fossils
tracing atoms through metabolic processes
diagnosing medical disorders
Valence electrons
electrons in the outer most shell of an atom
Electron shell
electron's state of potential energy
Energy
capacity to cause change
Potential energy
the energy that matter has because of its location or structure
Orbital
3D space where an electron is found 90% of the time
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
Structural formula
H-H
Molecular formula
H2
Nonpolar covalent bond
equal sharing of electrons
Polar covalent bond
unequal sharing of electrons
Ionic bond
transfer of electrons
Anions
ions with a negative charge
Cations
ions with a positive charge
Electronegativity
atom's attraction for the electrons in a covalent bond
Chemical reactions
making and breaking of chemical bonds
Reactants
starting molecules of a chemical reaction
Products
final molecules of a chemical reaction
Hydrogen bonds
forms when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom
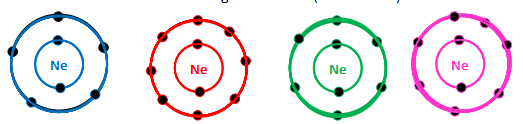
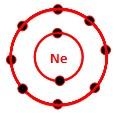
Which of the following is the electron distribution diagram of Neon (Atomic #10)
Four properties of water
cohesive behavior
ability to moderate temperature
expansion upon freezing
versatility as a solvent
Cohesion
hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together
Adhesion
attraction between different substances
Moderation of temperature
Heat is absorbed
Heat is released
Evaporating cooling
Evaporating cooling
as liquid evaporates its remaining surface cools
Name the property that helps transport of water against gravity in plants
cohesion
A solution in which water is a solvent is called
aqueous solution
A mixture that is homogeneous mixture of substances
solution
Dissolving agent of the solution
solvent
Substance that is dissolved
solute
Type of substance that does not have an affinity for water are called?
Hydrophobic
Type of substance that does have an affinity for water are called?
Hydrophilic
Stable suspension of fine particles in a liquid
colloid
A substance that reduces H+ ion concentration
Base
pH for neutral solution
pH 7
A substance which has less OH- conc and more H+ conc is ?
acid
Substances that minimize changes in concentrations of H+ and OH- in a solution
Buffers
HCl, NaOH are examples of
Buffers
Between pH 10 and pH 2, which one has more OH- ions concentration
pH 10
Acid precipitation
refers to rain, snow, or fog with a pH lower than 5.6
What makes large, complex molecules possible?
tetravalence
Frequent partners of carbon
hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen

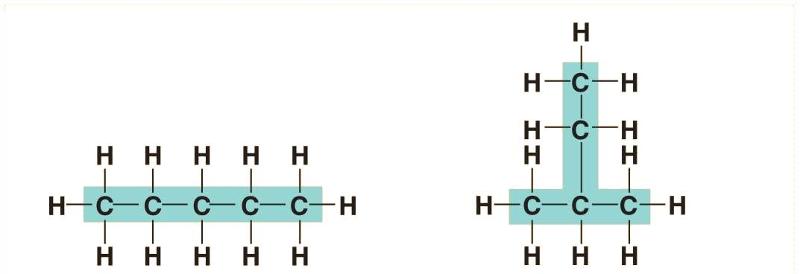
In figure above, in which way do the carbon skeleton differ between the two organic compounds?
Length
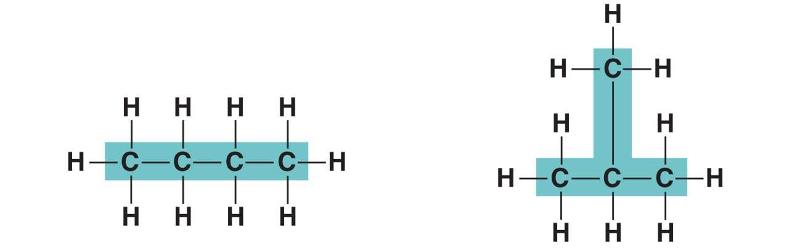
In figure above, in which way do the carbon skeleton differ between the two organic compounds?
Branching
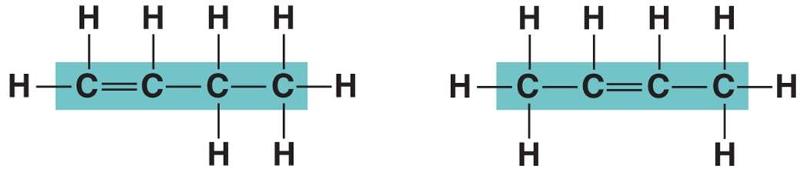
In figure above, in which way do the carbon skeleton differ between the two organic compounds?
Double bonds
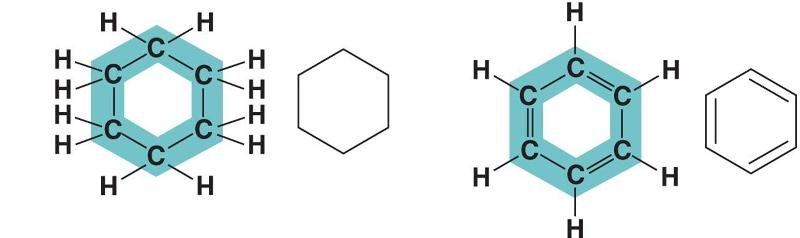
In figure above, in which way do the carbon skeleton differ between the two organic compounds?
Rings
Isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures
The above structure is an example of what type of isomer?
Structural isomers

The above structure is an example of what type of isomer?
Geometric isomers
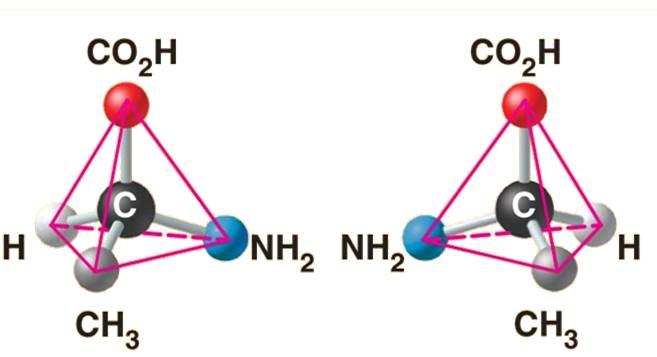
The above structure is an example of what type of isomer?
Enantiomers
Name the seven functional groups discussed in class
Hydroxyl
Carbonyl
Carboxyl
Amino
Sulfhydryl
Phosphate
Methyl
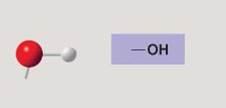
Hydroxyl
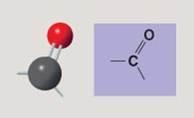
Carbonyl
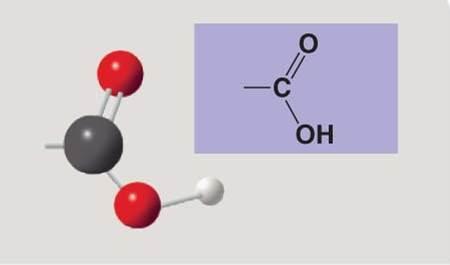
Carboxyl
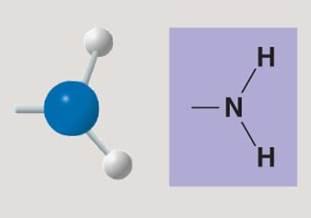
Amino
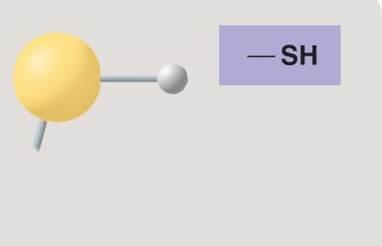
Sulfhydryl
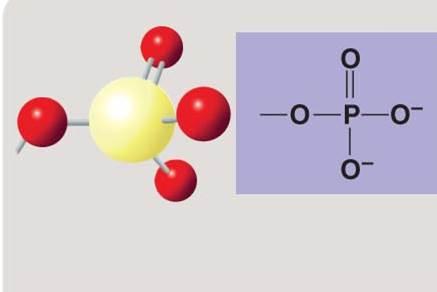
Phosphate
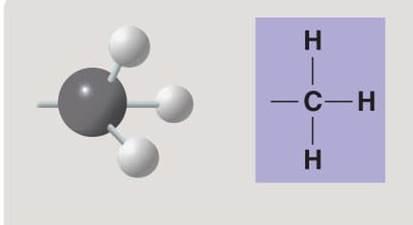
Methyl
Carboxylic group is found in what type of chemical compound?
acid
Macromolecules
large molecules composed of thousands of monomers
Polymer
long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Monomers
the small building block molecules
Condensation reaction
two monomers bonding (loss of water molecule)
Hydrolysis
polymers are broken down into monomers (addition of water)
Name the subgroups of Carbohydrates
Monosaccharide
Disaccharide
Polysaccharide
Name the types of monosaccharide
ketoses
aldoses
Is glucose aldose or ketose
aldose
Is fructose aldose or ketose
ketose
Name the different types of polysaccharides
storage polysaccharides
structural polysaccharides
Carbohydrates are formed by what kind of bonds?
glycosidic linkage
Function of carbohydrates
energy source
Name the subgroups of lipids
fats
phospholipids
steroids
Lipids are formed by what kind of bonds?
ester linkages
Building blocks of lipids
glycerol + fatty acids
Building blocks of phospholipids
phosphate group + fatty acids
Building blocks of steroids
four fused carbon rings
Functions of lipids
long term energy storage
membranes
insulation
sex hormones
Saturated fats
fatty acids containing no double bonds
Unsaturated fats
fatty acids containing one or more double bonds
Where are phospholipids found?
cell membranes
Cholesterol
a steroid in animal cell membrane
What are subgroups of proteins?
Enzymatic
Structural
Storage
Transport
Hormonal
Receptor
Contractile and motor
Defenisve
Proteins are formed by which bonds?
peptide bonds
What are building blocks of proteins?
amino acids
Transthyretin is an example of?
protein
What are amino acids
organic molecules with carboxyl, and amino groups
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine are examples of?
Nonpolar amino acids
Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Tyrosine, Asparagine, Glutamine are examples of?
Polar amino acids
Four levels of protein structure
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
Primary structure
the sequence of amino acids in a protein
Secondary structure
result from hydrogen bond between repeating constituents of the polypeptide backbone
α helix and β pleated sheet are examples of?
secondary structure
Tertiary structure
determined by interactions between R groups
Disulfide bridges
reinforce the protein structure
Quaternary structure
two or more polypeptide chains form one macromolecules
Hemoglobin results from which level of protein structure?
quaternary protein structure
Chitin is an example of?
structural polysaccharide
Polypeptides
polymers built from the same set of 20 amino acids
Name the subgroups of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
Nucleic acids are formed by which kind of bonds
hydrogen bonds
What are building blocks for nucleic acids
Nucleotide
What is nucleotide made up of
Phosphate + pentose sugar + nitrogenous base
What is nucleoside
pentose sugar + nitrogenous base
What are functions of nucleic acids?
genetic material
Name all nitrogenous bases
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine (DNA), Uracil (RNA)
Which bases are pyrimidines?
Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil
Which bases are purines?
Adenine and Guanine
Adenine pairs with? (DNA)
Thymine
Guanine pairs with?
Cytosine
Adenine pairs with? (RNA)
Uracil
How do RNA and DNA differ
RNA has one more oxygen then DNA in the pentose sugar