Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Test #1 Review
front 1 Group of cells combine to form | back 1 Tissue |
front 2 The example of Jack rabbit exchanging heat with the environment and maintaining constant body temperature shows which living characteristic of living organisms? | back 2 Regulation |
front 3 Viruses that infect and takeover bacteria are called? | back 3 Bacteriophage |
front 4 What type of data involve descriptions rather than measurements? | back 4 Qualitative |
front 5 Name the organisms that can only replicate/divide when inside its host | back 5 Viruses |
front 6 The branch of science that helps in naming, identification and classification of species is called? | back 6 Taxonomy |
front 7 Kingdom is the broadest unit of classification. True or False | back 7 False |
front 8 The Kingdom Fungi is grouped under which domain? | back 8 domain Eukarya |
front 9 What is the total number of domains under which all living organisms are classified into? | back 9 Three |
front 10 Give any example of an Ecosystem | back 10 Desert, Rainforest, Deciduous forest, grassland, ocean, tundra, coral reef etc... |
front 11 Name the characteristics of life | back 11 Order
|
front 12 What are characteristics of Viruses? | back 12 A borrowed life |
front 13 What is the name of the largest virus discovered? | back 13 Mimivirus |
front 14 How many species are identified and named to date? | back 14 approx. 1.8 million |
front 15 Name the three domains | back 15 domain Bacteria
|
front 16 What kingdoms are included in domain Eukarya? | back 16 Plantae, Fungi, Animalia |
front 17 Biology | back 17 scientific study of life |
front 18 Levels of organization in ascending order | back 18 Atoms
|
front 19 Communities | back 19 entire array of organism inhabiting a particular ecosystem |
front 20 Populations | back 20 all individuals of a species living within the bounds of specified area |
front 21 Organisms | back 21 individual living things |
front 22 Organ systems | back 22 various organ constitutes to from organ system |
front 23 Organ | back 23 carries particular function in the body |
front 24 Tissues | back 24 group of similar cells |
front 25 Cells | back 25 fundamental unit of structure and function |
front 26 Organelles | back 26 various functional components that make up the cell |
front 27 Molecule | back 27 chemical structure consisting of two or more atoms |
front 28 Levels of classification is descending order | back 28 Domain
|
front 29 What are Darwin's two points? | back 29 - species showed evidence of "descent with modification" from common ancestors
|
front 30 What are Darwin's observations? | back 30 - individuals in a population have traits that vary
|
front 31 What are Darwin's inferences? | back 31 - individuals that are best suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce
|
front 32 What are two main types of scientific inquiry? | back 32 discovery science (inductive) and hypothesis-based science(deductive) |
front 33 Discovery science | back 33 describes natural structures and processes |
front 34 Data | back 34 recorded observations or items of information |
front 35 Name the two categories of data | back 35 Qualitative and Quantitative |
front 36 Qualitative data | back 36 descriptions rather than measurements |
front 37 Quantitative data | back 37 recorded measurements |
front 38 Inductive reasoning | back 38 deriving general principles from particular facts or instances |
front 39 Hypothesis | back 39 a tentative answer to a well-framed question |
front 40 Deductive reasoning | back 40 uses general premises to make specific predictions |
front 41 Why do we need controlled experiments? | back 41 to cancel the effects of unwanted variables |
front 42 Limitations of Science | back 42 -observations and experimental results must be repeatable
|
front 43 What is a theory | back 43 - broader in scope than a hypothesis
|
front 44 What are models? | back 44 representations of natural phenomena |
front 45 Diagrams, 3D objects, Computer programs, mathematical equations are examples of? | back 45 Models |
front 46 How do scientists communicate with each other? | back 46 seminars, publications, and websites |
front 47 Substance consisting of two or more elements in fixed ratio is called | back 47 compound |
front 48 How many electrons are there in valence shell of oxygen | back 48 six |
front 49 Atomic number | back 49 number of protons in the nucleus |
front 50 Goiter is caused by the deficiency of which trace element? | back 50 Iodine |
front 51 Covalent bond | back 51 formed by sharing pairs of valence electrons |
front 52 Sodium chloride is formed by which bond? | back 52 Ionic bond |
front 53 Chemical equilibrium | back 53 the forward and reverse reaction rates are equal |
front 54 Give an example of polar molecule | back 54 Water, Methane etc.. |
front 55 Water molecules are hold together by which type of bond? | back 55 Hydrogen bond |
front 56 An oxygen molecule is formed by non-polar covalent bond. True or False | back 56 True |
front 57 Element | back 57 a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reaction |
front 58 Matter | back 58 anything that has mass and takes up space |
front 59 Name the four essential elements that constitute 96% of living matter | back 59 hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen |
front 60 Name the elements that constitute 4% of living matter | back 60 calcium, phosphorous, potassium, and sulfur |
front 61 Name the subatomic particles that an atom is composed of | back 61 proton, neutron, and electron |
front 62 Trace elements | back 62 elements required in minute quantities |
front 63 Isotopes | back 63 two atoms of an element that differ in number of neutrons |
front 64 Mass number | back 64 number of protons + number of neutrons |
front 65 Radioactive isotopes | back 65 decay spontaneously giving of particles and energy |
front 66 Applications of radioactive isotopes | back 66 dating fossils
|
front 67 Valence electrons | back 67 electrons in the outer most shell of an atom |
front 68 Electron shell | back 68 electron's state of potential energy |
front 69 Energy | back 69 capacity to cause change |
front 70 Potential energy | back 70 the energy that matter has because of its location or structure |
front 71 Orbital | back 71 3D space where an electron is found 90% of the time |
front 72 Molecule | back 72 two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds |
front 73 Structural formula | back 73 H-H |
front 74 Molecular formula | back 74 H2 |
front 75 Nonpolar covalent bond | back 75 equal sharing of electrons |
front 76 Polar covalent bond | back 76 unequal sharing of electrons |
front 77 Ionic bond | back 77 transfer of electrons |
front 78 Anions | back 78 ions with a negative charge |
front 79 Cations | back 79 ions with a positive charge |
front 80 Electronegativity | back 80 atom's attraction for the electrons in a covalent bond |
front 81 Chemical reactions | back 81 making and breaking of chemical bonds |
front 82 Reactants | back 82 starting molecules of a chemical reaction |
front 83 Products | back 83 final molecules of a chemical reaction |
front 84 Hydrogen bonds | back 84 forms when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom |
front 85 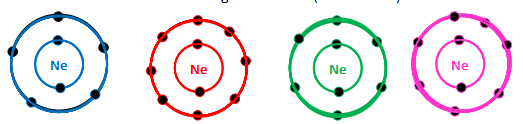 Which of the following is the electron distribution diagram of Neon (Atomic #10) | back 85 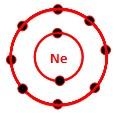 |
front 86 Four properties of water | back 86 cohesive behavior
|
front 87 Cohesion | back 87 hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together |
front 88 Adhesion | back 88 attraction between different substances |
front 89 Moderation of temperature | back 89 Heat is absorbed
|
front 90 Evaporating cooling | back 90 as liquid evaporates its remaining surface cools |
front 91 Name the property that helps transport of water against gravity in plants | back 91 cohesion |
front 92 A solution in which water is a solvent is called | back 92 aqueous solution |
front 93 A mixture that is homogeneous mixture of substances | back 93 solution |
front 94 Dissolving agent of the solution | back 94 solvent |
front 95 Substance that is dissolved | back 95 solute |
front 96 Type of substance that does not have an affinity for water are called? | back 96 Hydrophobic |
front 97 Type of substance that does have an affinity for water are called? | back 97 Hydrophilic |
front 98 Stable suspension of fine particles in a liquid | back 98 colloid |
front 99 A substance that reduces H+ ion concentration | back 99 Base |
front 100 pH for neutral solution | back 100 pH 7 |
front 101 A substance which has less OH- conc and more H+ conc is ? | back 101 acid |
front 102 Substances that minimize changes in concentrations of H+ and OH- in a solution | back 102 Buffers |
front 103 HCl, NaOH are examples of | back 103 Buffers |
front 104 Between pH 10 and pH 2, which one has more OH- ions concentration | back 104 pH 10 |
front 105 Acid precipitation | back 105 refers to rain, snow, or fog with a pH lower than 5.6 |
front 106 What makes large, complex molecules possible? | back 106 tetravalence |
front 107 Frequent partners of carbon | back 107 hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen |
front 108  In figure above, in which way do the carbon skeleton differ between the two organic compounds? | back 108 Length |
front 109 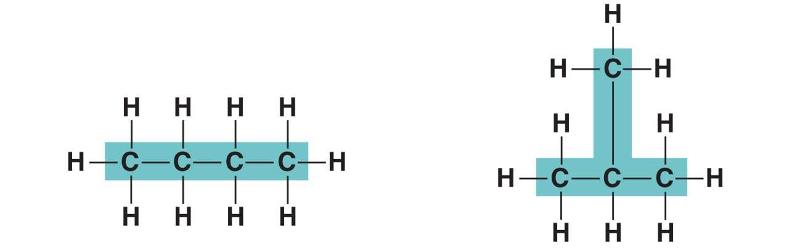 In figure above, in which way do the carbon skeleton differ between the two organic compounds? | back 109 Branching |
front 110 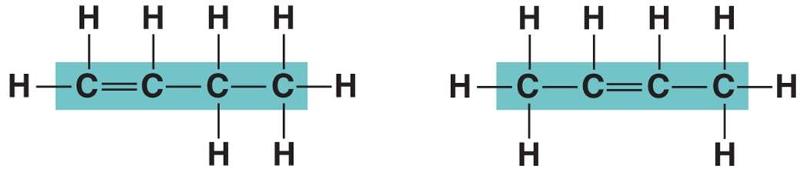 In figure above, in which way do the carbon skeleton differ between the two organic compounds? | back 110 Double bonds |
front 111 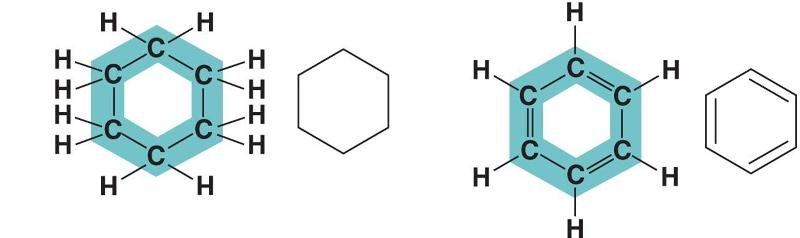 In figure above, in which way do the carbon skeleton differ between the two organic compounds? | back 111 Rings |
front 112 Isomers | back 112 compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures |
front 113 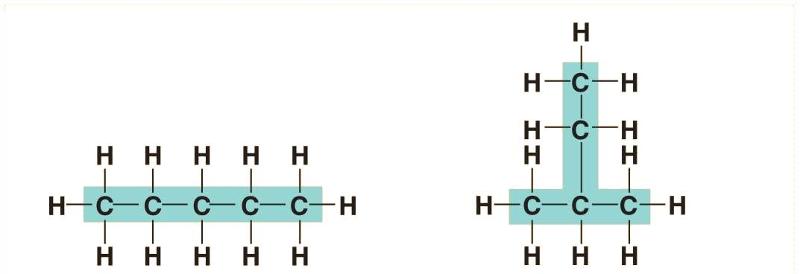 The above structure is an example of what type of isomer? | back 113 Structural isomers |
front 114  The above structure is an example of what type of isomer? | back 114 Geometric isomers |
front 115 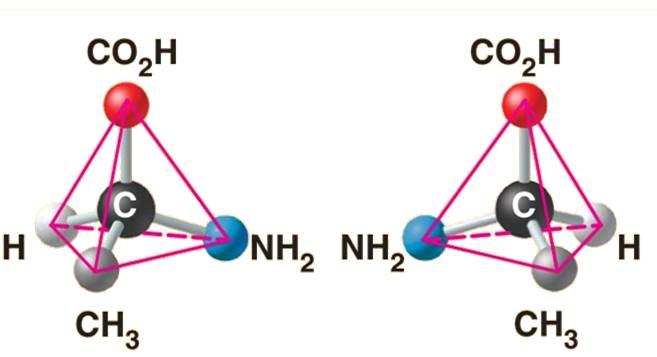 The above structure is an example of what type of isomer? | back 115 Enantiomers |
front 116 Name the seven functional groups discussed in class | back 116 Hydroxyl
|
front 117 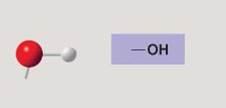 | back 117 Hydroxyl |
front 118 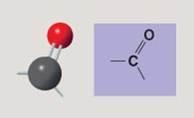 | back 118 Carbonyl |
front 119 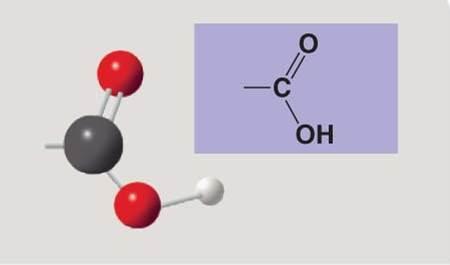 | back 119 Carboxyl |
front 120 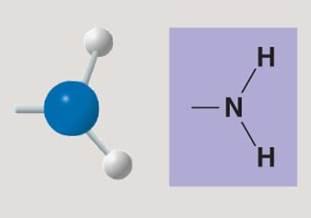 | back 120 Amino |
front 121 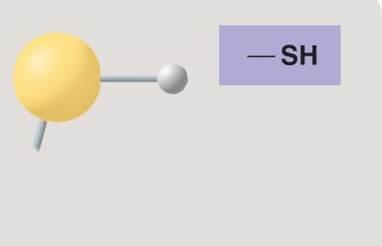 | back 121 Sulfhydryl |
front 122 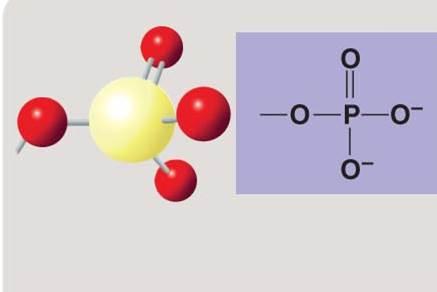 | back 122 Phosphate |
front 123 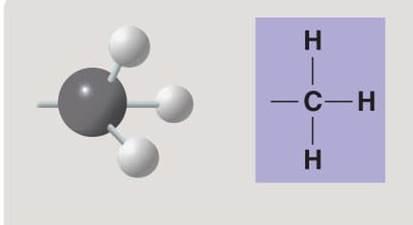 | back 123 Methyl |
front 124 Carboxylic group is found in what type of chemical compound? | back 124 acid |
front 125 Macromolecules | back 125 large molecules composed of thousands of monomers |
front 126 Polymer | back 126 long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks |
front 127 Monomers | back 127 the small building block molecules |
front 128 Condensation reaction | back 128 two monomers bonding (loss of water molecule) |
front 129 Hydrolysis | back 129 polymers are broken down into monomers (addition of water) |
front 130 Name the subgroups of Carbohydrates | back 130 Monosaccharide
|
front 131 Name the types of monosaccharide | back 131 ketoses
|
front 132 Is glucose aldose or ketose | back 132 aldose |
front 133 Is fructose aldose or ketose | back 133 ketose |
front 134 Name the different types of polysaccharides | back 134 storage polysaccharides
|
front 135 Carbohydrates are formed by what kind of bonds? | back 135 glycosidic linkage |
front 136 Function of carbohydrates | back 136 energy source |
front 137 Name the subgroups of lipids | back 137 fats
|
front 138 Lipids are formed by what kind of bonds? | back 138 ester linkages |
front 139 Building blocks of lipids | back 139 glycerol + fatty acids |
front 140 Building blocks of phospholipids | back 140 phosphate group + fatty acids |
front 141 Building blocks of steroids | back 141 four fused carbon rings |
front 142 Functions of lipids | back 142 long term energy storage
|
front 143 Saturated fats | back 143 fatty acids containing no double bonds |
front 144 Unsaturated fats | back 144 fatty acids containing one or more double bonds |
front 145 Where are phospholipids found? | back 145 cell membranes |
front 146 Cholesterol | back 146 a steroid in animal cell membrane |
front 147 What are subgroups of proteins? | back 147 Enzymatic
|
front 148 Proteins are formed by which bonds? | back 148 peptide bonds |
front 149 What are building blocks of proteins? | back 149 amino acids |
front 150 Transthyretin is an example of? | back 150 protein |
front 151 What are amino acids | back 151 organic molecules with carboxyl, and amino groups |
front 152 Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine are examples of? | back 152 Nonpolar amino acids |
front 153 Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Tyrosine, Asparagine, Glutamine are examples of? | back 153 Polar amino acids |
front 154 Four levels of protein structure | back 154 primary
|
front 155 Primary structure | back 155 the sequence of amino acids in a protein |
front 156 Secondary structure | back 156 result from hydrogen bond between repeating constituents of the polypeptide backbone |
front 157 α helix and β pleated sheet are examples of? | back 157 secondary structure |
front 158 Tertiary structure | back 158 determined by interactions between R groups |
front 159 Disulfide bridges | back 159 reinforce the protein structure |
front 160 Quaternary structure | back 160 two or more polypeptide chains form one macromolecules |
front 161 Hemoglobin results from which level of protein structure? | back 161 quaternary protein structure |
front 162 Chitin is an example of? | back 162 structural polysaccharide |
front 163 Polypeptides | back 163 polymers built from the same set of 20 amino acids |
front 164 Name the subgroups of nucleic acids | back 164 DNA and RNA |
front 165 Nucleic acids are formed by which kind of bonds | back 165 hydrogen bonds |
front 166 What are building blocks for nucleic acids | back 166 Nucleotide |
front 167 What is nucleotide made up of | back 167 Phosphate + pentose sugar + nitrogenous base |
front 168 What is nucleoside | back 168 pentose sugar + nitrogenous base |
front 169 What are functions of nucleic acids? | back 169 genetic material |
front 170 Name all nitrogenous bases | back 170 Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine (DNA), Uracil (RNA) |
front 171 Which bases are pyrimidines? | back 171 Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil |
front 172 Which bases are purines? | back 172 Adenine and Guanine |
front 173 Adenine pairs with? (DNA) | back 173 Thymine |
front 174 Guanine pairs with? | back 174 Cytosine |
front 175 Adenine pairs with? (RNA) | back 175 Uracil |
front 176 How do RNA and DNA differ | back 176 RNA has one more oxygen then DNA in the pentose sugar |