The functional and structural unit of the kidneys is the ________.
capsular space
glomerular capsule
nephron loop
nephron
nephron
List and describe three pressures operating at the filtration membrane, and explain how each influences net filtration pressure.
Glomerlar hydrostatic is the main force pushing water across the filtration membrane.Glmelar Osmotic pressure of the plama in the blood drive fluids back into thecappilaries. The third would be the Glumealar capsule also is with osmotic pushing substances into the capillaries.
The urinary bladder is composed of ________ epithelium.
transitional
pseudostratified columnar
simple squamous
stratified squamous
transitional
Which of the following is the correct sequence of kidney development from embryo to fetus?
mesonephros, pronephros, metanephros
pronephros, metanephros, mesonephros
pronephros, mesonephros, metanephros
mesonephros, metanephros, pronephros
pronephros, mesonephros, metanephros
The single most important blood buffer system is the bicarbonate buffer system.
True
False
True
Molecules that can act reversibly as acids or bases depending upon the pH of their environment are called ________.
amphoteric
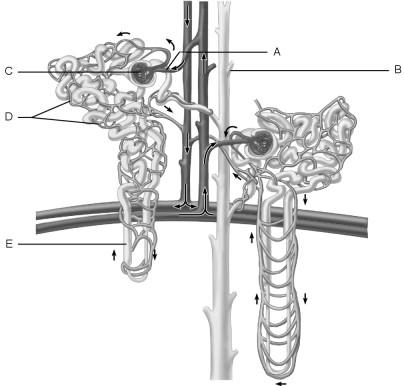
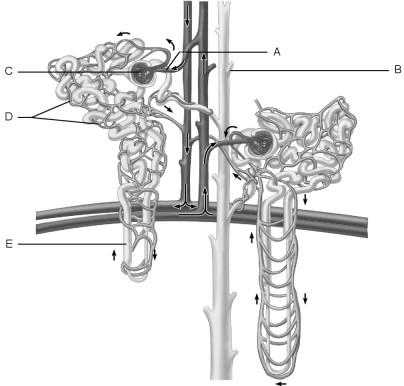
Afferent arteriole.
A
Which of the following is not a chemical buffer system?
phosphate
nucleic acid
protein
bicarbonate
nucleic acid
What hormone reduces blood pressure and blood volume by inhibiting nearly all events that promote vasoconstriction and sodium ion and water retention?
aldosterone
atrial natriuretic peptide
thyroxine
atrial natriuretic peptide
Respiratory acidosis results when lungs are obstructed and gas exchange is inefficient.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
When does a person experience greater thirst, during periods when ADH release is elicited or during periods when aldosterone release is elicited?
ADH is released to tell the body there is not enough water and to conserve and hold onto it. It tell you are thirsty because you are dehydrated and need to drink water to replenish your body
Aldosterone is secreted in response to low extracellular potassium.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Whereas sodium is found mainly in the extracellular fluid, most ________ is found in the intracellular fluid.
bicarbonate
potassium
iron
chloride
potassium
Thirst is always a reliable indicator of body water need.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Atrial natriuretic peptide reduces blood pressure and blood volume by inhibiting nearly all events that promote vasodilation and potassium and water retention.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Problems with fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance are particularly common in infants because of their ________.
low rate of insensible water loss
comparatively low metabolic rates
low daily rate of fluid exchange
inefficient kidneys
inefficient kidneys
Which of the following does not depend on the presence of electrolytes?
membrane polarity
maintenance of osmotic relations between cells and ECF
amount of body fat
neuromuscular excitability
amount of body fat
The electrolyte deficiency condition where the individual may crave substances like clay, chalk, starch or burnt match tips is called ________.
PICA
When aldosterone release is inhibited, sodium reabsorption cannot occur beyond the distal convoluted tubule.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
Which cells of the kidney are chemoreceptors that respond to changes in solute content of the filtrate?
juxtaglomerular cells
macula densa cells
mesangial cells
podocytes
macula densa cells
In the kidneys, the countercurrent mechanism involves the interaction between the flow of filtrate through the nephron loop of the juxtamedullary nephrons (the countercurrent multiplier) and the flow of blood through the limbs of adjacent blood vessels (the countercurrent exchanger). This relationship establishes and maintains an osmotic gradient extending from the cortex through the depths of the medulla that allows the kidneys to vary urine concentration dramatically.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The fatty tissue surrounding the kidneys is important because it ________.
produces vitamin D and other chemicals needed by the kidney
stabilizes the position of the kidneys by holding them in their normal position
is necessary as a barrier between the adrenal glands and kidneys
ensures adequate energy for the adrenal glands to operate efficiently
stabilizes the position of the kidneys by holding them in their normal position
An important characteristic of urine is its specific gravity or density, which is ________.
less than water
much higher than water
slightly higher than water
the same as water
slightly higher than water
Angiotensin II is a substance made by the body to lower blood pressure during stress.
FALSE
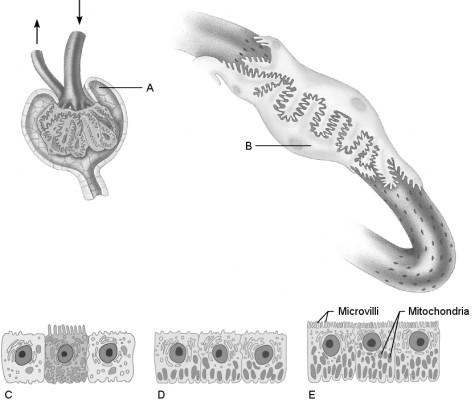
Cells that are most affected by ADH.
C
Blood pressure in the renal glomerulus is lower than in most parts of the body in order to conserve body water.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits sodium reabsorption.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
Having a kinked ureter is called renal ptosis.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Which of the following is not associated with the renal corpuscle?
a fenestrated capillary
a podocyte
a vasa recta
an efferent arteriole
a vasa recta
Select the correct statement about urinary system development.
The pronephros (first tubule system) develops during the tenth week of gestation.
The mesonephros will develop into the kidneys.
Kidneys develop from urogenital ridges.
The metanephric ducts will become the urethras.
Kidneys develop from urogenital ridges.
In the ascending limb of the nephron loop the ________.
thick segment moves ions out into interstitial spaces for reabsorption
thick segment is permeable to water
thin segment is not permeable to sodium and chloride
thin segment is freely permeable to water
thick segment moves ions out into interstitial spaces for reabsorption
The collecting duct is impermeable to water in the presence of ADH.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
The descending limb of the nephron loop ________.
pulls water by osmosis into the lumen of the tubule
is not permeable to water
contains fluid that becomes more concentrated as it moves down into the medulla
is freely permeable to sodium and urea
contains fluid that becomes more concentrated as it moves down into the medulla
Incontinence is the inability to control voluntary micturition.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
A disease caused by inadequate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) by the pituitary gland with symptoms of polyuria is ________.
diabetes mellitus
diabetes insipidus
coma
diabetic acidosis
diabetes insipidus
Humans can survive for a period of time without water thanks to the ability of the kidneys to produce concentrated urine. Briefly explain the factors that allow this to happen.
Reabsorption depends on the presence of the antidiuretic hormone, with it the porins of the collecting tubule filter water with osmosis and increases as it goes down. So water is conserved and becomes concentrated…….it continues and is why it gets dehydrated trying to save water.
The function of angiotensin II is to ________.
constrict arterioles and increase blood pressure
decrease arterial blood pressure
decrease the production of aldosterone
decrease water absorption
constrict arterioles and increase blood pressure
The fluid in the glomerular (Bowman's) capsule is similar to plasma except that it does not contain a significant amount of ________.
glucose
electrolytes
plasma protein
hormones
plasma protein
Which of the following does not describe the justaglomerular complex?
It regulates the rate of filtrate formation.
Its macula densa cells produce aldosterone.
It helps control systemic blood pressure.
Its granular cells produce rennin.
Its macula densa cells produce aldosterone.
The proximal convoluted tubule is the portion of the nephron that attaches to the collecting duct.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Which of the choices below is the least important role of tubular secretion?
eliminating undesirable substances such as urea and uric acid that have been reabsorbed by passive processes
ridding the body of excessive potassium ions
disposing of substances not already in the filtrate, such as certain drugs
ridding the body of bicarbonate ions
ridding the body of bicarbonate ions
If the GFR is too low, needed substances may pass so quickly through the renal tubules that they are not absorbed and instead are lost in the urine.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
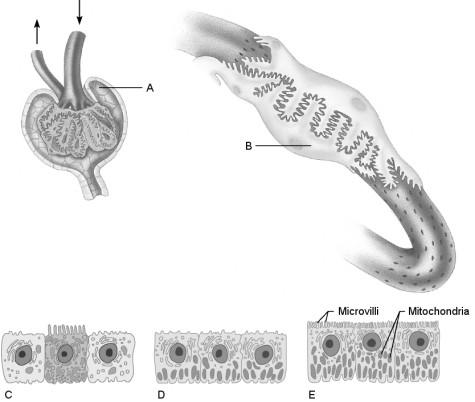
Cells that are the most active in reabsorbing the filtrate.
E
The act of emptying the bladder is called voiding.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
Sodium-linked water flow across a membrane not under hormonal control is called ________ water reabsorption.
obligatory
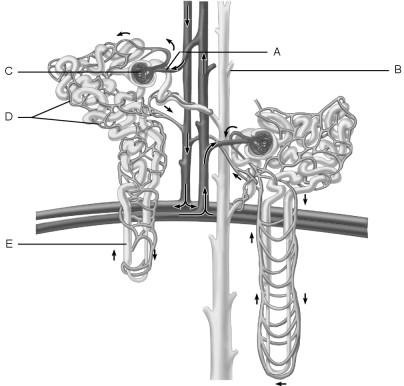
Medulla of the kidney.
E
Which of the following is not a part of the juxtaglomerular complex?
mesangial cells
macula densa
granular cells
podocyte cells
podocyte cells
Both the male and female urethras serve the urinary and the reproductive systems.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
ADH activated water channels called ________ are essential for water reabsorption in the collecting duct.
aquaporins
Reabsorption of high levels of glucose and amino acids in the filtrate is accomplished by ________.
facilitated diffusion
secondary active transport
countertransport
passive transport
secondary active transport
Which of the choices below are the most important hormone regulators of electrolyte reabsorption and secretion?
angiotensin II and ADH
angiotensin I and atrial natriuretic peptide
angiotensin II and aldosterone
angiotensin I and epinephrine
angiotensin II and aldosterone
The ________ artery lies on the boundary between the cortex and medulla of the kidney.
interlobar
cortical radiate
lobar
arcuate
arcuate
Glomerular filtration is an ATP-driven process.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Which of the choices below is not a method by which the cells of the renal tubules can raise blood pH?
by secreting hydrogen ions into the filtrate
by producing new bicarbonate ions
by secreting sodium ions
by reabsorbing filtered bicarbonate ions
by secreting sodium ions
Which of the following is the least important influence on reabsorption of a substance in the nephron?
molecule size relative to fenestrations.
molecular complexity
lipid solubility.
number of carriers.
molecular complexity
Which of the choices below is not a glomerular filtration rate control method?
electrolyte levels
renal autoregulation
hormonal regulation
neural regulation
electrolyte levels
Explain what is meant by the terms cotransport process and transport maximum.
Cotransport means the active transport process of one solute, meaning against the concentration gradient. Transport maximum means the number of carriers in the renel tubes to a certain substance.
The presence of pus in the urine is a condition called ________.
pyuria
The ________ mechanism is the general tendency of vascular smooth muscle to contract when stretched.
myogenic
Most electrolyte reabsorption by the renal tubules is ________.
hormonally controlled in distal tubule segments
in the distal convoluted tubule
not limited by a transport maximum
accomplished after the nephron loop is reached
hormonally controlled in distal tubule segments
The mechanism that establishes the medullary osmotic gradient depends most on the permeability properties of the ________.
glomerular filtration membrane
nephron loop
distal convoluted tubule
collecting duct
nephron loop
Glomerulus.
C
Which of the hormones below is responsible for facultative water reabsorption?
ADH
aldosterone
atrial natriuretic peptide
thyroxine
ADH
Urea is reabsorbed in the nephron loop.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
What would happen if the capsular hydrostatic pressure were increased above normal?
Capsular osmotic pressure would compensate so that filtration would not change.
Net filtration would increase above normal.
Net filtration would decrease.
Filtration would increase in proportion to the increase in capsular pressure.
Net filtration would decrease.
The chief force pushing water and solutes out of the blood across the filtration membrane is ________.
glomerular hydrostatic pressure (glomerular blood pressure)
the size of the pores in the basement membrane of the capillaries
protein-regulated diffusion
the ionic electrochemical gradient
glomerular hydrostatic pressure (glomerular blood pressure)
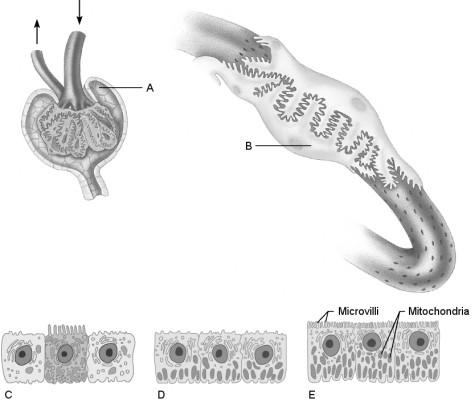
Is composed of simple squamous epithelium.
A
Proximal convoluted tubule.
Site at which most of the tubular reabsorption occurs
Glomerulus.
Site of filtrate formation.
Peritubular capillaries.
Blood supply that directly receives substances from the tubular cells.
Collecting duct.
Site that drains distal convoluted tubule
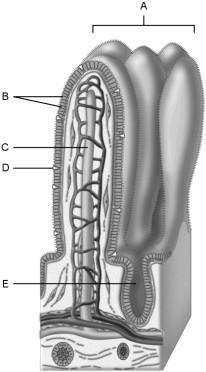
Identify three ways the small intestine is modified to increase the surface area for digestion and absorption.
Villi and microvilli are modifications of the small intestine for digestion and absorption.
Villi increase suface area. Micorvili are projections of plama membrane-enhance absorption and area.
(Pili circulates)Cicular folds of the mucosa and submuscosa, force chyme to move through the lumen.
Which of the following is an essential role played by large intestine bacteria?
synthesize vitamins C and D
synthesize vitamin K and B-complex vitamins
absorb bilirubin
produce gas
synthesize vitamin K and B-complex vitamins
Ionic iron is actively transported into the mucosal cells, where it binds to the protein ferritin, a phenomenon called the mucosal iron barrier.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
How is digestive activity provoked after eating? What activates the secretion of digestive juices into the lumen or hormones into the blood?
Mecanoreceptors and chemorecptors that are in the walls of the gastrointsonal tract. Mecanoreptors and (barorecptors) respond to stretching from the food being added. The pH change and new concentrations are detected by chemoreceptors and aid in digestion.
What stomach secretion is necessary for normal hemoglobin production in RBCs?
intrinsic factor
pepsinogen
HCl
gastric lipase
intrinsic factor
Pepsinogen is the precursor to the gastric enzyme for protein digestion and is secreted by the parietal cells.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
If an incision has to be made in the small intestine to remove an obstruction, the first layer of tissue to be cut is the ________.
serosa
submucosa
muscularis externa
mucosa
serosa
Short-chain triglycerides found in foods such as butterfat molecules in milk are split by a specific enzyme in preparation for absorption. Which of the following enzymes is responsible?
rennin
cholecystokinin
lipase
pepsin
lipase
Cell type specialized to secrete mucus into the lumen of the intestinal tract.
D
The intrinsic ability of visceral smooth muscle to exhibit the stress-relaxation response is termed plasticity.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The ducts that deliver bile and pancreatic juice from the liver and pancreas, respectively, unite to form the ________.
pancreatic acini
hepatopancreatic ampulla
portal vein
bile canaliculus
epatopancreatic ampulla
There are three phases of gastric secretion. The cephalic phase occurs ________.
before food enters the stomach and is triggered by aroma, sight, or thought
at the end of a large meal, and the juices secreted are powerful and remain in the GI tract for a long period of time
immediately after food enters the stomach, preparing the small intestine for the influx of a variety of nutrients
when the meal is excessively high in acids and neutralization is required
before food enters the stomach and is triggered by aroma, sight, or thought
Smooth muscle layer.
C
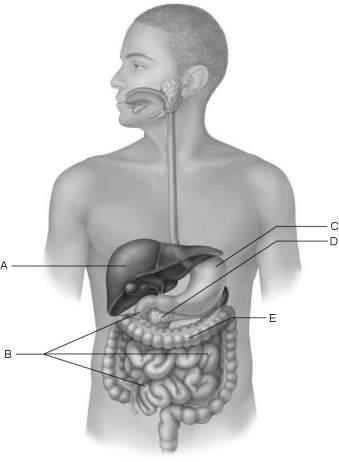
Bacteria process undigested chyme from the small intestine.
E
The solutes contained in saliva include ________.
electrolytes, digestive enzyme, mucin, lysozyme, wastes, and IgA
only salts and minerals
mucin, lysozyme, electrolytes, salts, and minerals
only proteases and amylase
electrolytes, digestive enzyme, mucin, lysozyme, wastes, and IgA
The circular folds of the small intestine enhance absorption by causing the chyme to spiral, rather than to move in a straight line, as it passes through the small intestine.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
Compare and contrast the structure and function of a premolar and a molar.
Pre-molars- have a broader crown and only one root.
Molars- have broad crowns but are larger in size and have at least 2 roots.
The layer of the digestive tube that contains blood vessels, lymphatic nodes, and a rich supply of elastic fibers is the ________.
muscularis externa
submucosa
mucosa
serosa
submucosa
Select the correct statement about the regulation of gastric secretion.
Gastric secretion can be stimulated before food has entered the mouth.
Gastric secretion is enhanced by very low pH (below a pH of 2).
The presence of food in the stomach prevents hormonal control of gastric secretion.
Vagus stimulation of the stomach results in decreased secretion of gastric juice.
Gastric secretion can be stimulated before food has entered the mouth.
The protective outermost layer of the esophagus is the ________.
adventitia
In addition to storage and mechanical breakdown of food, the stomach ________.
is the only place where fats are completely digested
is the first site where absorption takes place
is the first site where chemical digestion of starch takes place
initiates protein digestion and denatures proteins
initiates protein digestion and denatures proteins
The pancreas has both an endocrine and an exocrine function.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
What are chylomicrons?
They are little fat drops, and have fatty acids and cholesterol.
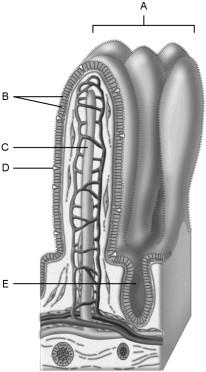
Structures that increase the absorptive area of the small intestine.
A
The major role of absorption in the ileum is to reclaim bile salts to be recycled back to the liver.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The law that applies to the amount of CO2 you could dissolve in a Pepsi is called ________ law.
Henry's
The parietal pleura lines the thoracic wall.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The respiratory membrane is a combination of ________.
alveolar and capillary walls and their fused basement membranes
atria and alveolar sacs
respiratory bronchioles and alveolar sacs
respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts
alveolar and capillary walls and their fused basement membranes
The partial pressure gradient for oxygen (in the body) is much steeper than that for carbon dioxide. Explain how equal amounts of these two gases can be exchanged (in a given time interval) in the lungs and at the tissues.
Having equal amounts of O2 and CO2 are exchanged in the lungs because CO2 is greater in the fluids like the plasma and alveolar fluid.
Which of the following incorrectly describes mechanisms of CO2 transport?
7-10% of CO2 is dissolved directly into the plasma
attached to the heme part of hemoglobin
as bicarbonate ion in plasma
20% of CO2 is carried in the form of carbaminohemoglobin
attached to the heme part of hemoglobin
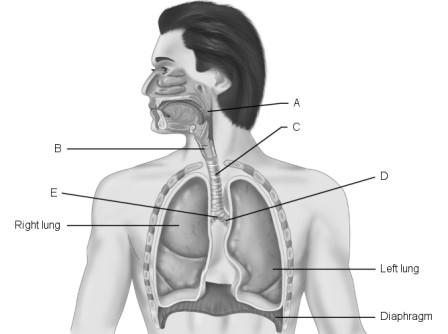
Main (primary) bronchus.
D
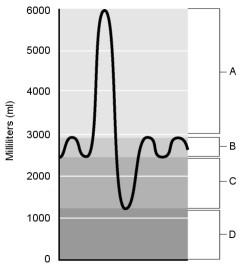
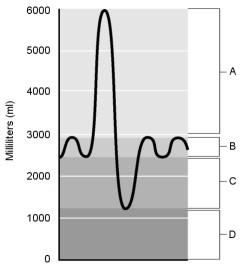
Residual volume.
D
Strong emotions and pain acting through the limbic system activate sympathetic centers in the hypothalamus, thus modulating respiratory rate and depth by sending signals to the respiratory centers.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The relationship between gas pressure and gas volume is described by ________.
Dalton's law
Boyle's law
Henry's law
Charles' law
Boyle's law
Labored breathing is termed dyspnea.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
Terminal bronchioles are lined with ________ epithelium.
cuboidal
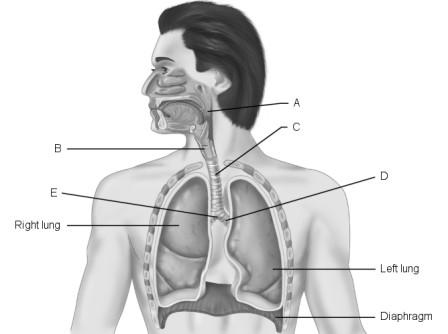
Larynx.
B
The main site of gas exchange is the ________.
alveoli
alveolar sacs
alveolar duct
respiratory bronchiole
alveoli
The alveolar ventilation rate is the best index of effective ventilation
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
If a baby is born at 28 weeks' gestation, what major problem will the doctors look for?
Aveolar cells are not developed, so there is a possibility that their lungs will collapse because they are not fully developed. They will have severe breathing problems.
What is the chloride shift and why does it occur?
Ionic exchange, Cl move from plasma to RBCs to balance the charges.
Air that does not participate in the exchange of gases.
D
Dalton's law states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the pressures exerted independently by each gas in the mixture.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
Increased temperature results in decreased O2 unloading from hemoglobin.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Which of the following is not a form of lung cancer?
Kaposi's sarcoma
adenocarcinoma
squamous cell carcinoma
small cell carcinoma
Kaposi's sarcoma
Unlike inspiration, expiration is a passive act because no muscular contractions are involved. Expiration, however, depends on two factors. Which of the choices below lists those two factors?
the negative feedback of expansion fibers used during inspiration and the outward pull of surface tension due to surfactant
the recoil of elastic fibers that were stretched during inspiration and the inward pull of surface tension due to the film of alveolar fluid
combined amount of CO2 in the blood and air in the alveoli
the expansion of respiratory muscles that were contracted during inspiration and the lack of surface tension on the alveolar wall
the recoil of elastic fibers that were stretched during inspiration and the inward pull of surface tension due to the film of alveolar fluid
Which center is located in the pons?
pacemaker neuron center
expiratory center
inspiratory center
pontine respirator group (PRG)
pontine respirator group (PRG)
Surfactant helps to prevent the alveoli from collapsing by ________.
protecting the surface of alveoli from dehydration and other environmental variations
warming the air before it enters
interfering with the cohesiveness of water molecules, thereby reducing the surface tension of alveolar fluid
humidifying the air before it enters
interfering with the cohesiveness of water molecules, thereby reducing the surface tension of alveolar fluid
Smoking diminishes ciliary action and eventually destroys the cilia.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the lungs and through all cell membranes by ________.
diffusion
filtration
osmosis
active transport
diffusion
The dartos and cremaster muscles are important to the integrity of the male reproductive system. Which of the following is true about the role they play?
A) They contract to push sperm along the ductus deferens.
B) They regulate the temperature of the testes.
C) They are responsible for penile erection.
D) They contract to allow ejaculation.
B) They regulate the temperature of the testes.
2) The ability of sperm cells to move along the ductus deferens is due to ________.
A) gravity
B) peristaltic contractions
C) enzymatic activity
D) hormonal action
B) peristaltic contractions
3) The ability of a male to ejaculate is due to the action of ________.
A) parasympathetic nerves
B) the dartos muscle
C) luteinizing hormone
D) the bulbospongiosus muscles
D) the bulbospongiosus muscles
4) The most important risk for testicular cancer in young males is ________.
A) smoking
B) a diet high in fat
C) nondescent of the testes
D) sexually transmitted infections
C) nondescent of the testes
5) Which of the following glands are responsible for 60% of the synthesis of semen?
A) the seminal vesicles
B) the bulbourethral glands
C) the prostate
D) the pituitary
A) the seminal vesicles
6) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins?
A) LH
B) FSH
C) GnRH
D) testosterone
C) GnRH
7) Development of male reproductive structures depends on which of the following events?
A) that the female hormones are suppressed during pregnancy
B) the suppression of inhibin
C) secretion of male hormones prenatally and lasting into the first few months after birth
D) that human gonadotropin be synthesized in the first week of the pregnancy
C) secretion of male hormones prenatally and lasting into the first few months after birth
8) The primary function of the uterus is to ________.
A) protect the ovaries
B) synthesize female hormones
C) regulate the ovarian and menstrual cycles
D) receive, retain, and nourish a fertilized ovum
D) receive, retain, and nourish a fertilized ovum
9) Why is the blood-testis barrier important?
A) because spermatozoa and developing cells produce surface antigens that are recognized as foreign by the immune system
B) because some blood contents are toxic to the spermatozoa
C) because immature sperm cells lose their motility when they encounter any blood component
D) Actually, the blood-testis barrier has no function.
A) because spermatozoa and developing cells produce surface antigens that are recognized as foreign by the immune system
10) The structures that receive the ovulated oocyte, providing a site for fertilization, are called the ________.
A) Graafian follicles
B) fallopian tubes
C) infundibula
D) fimbriae
B) fallopian tubes
11) If gametes were diploid like somatic cells, how many chromosomes would the zygote contain?
A) twice the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to double and normal development could not occur
B) triple the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to triple and normal development would not occur
C) half the diploid number with no change in development
D) There is no relationship between gametes and somatic cells.
A) twice the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to double and normal development could not occur
12) Human egg and sperm are similar in that ________.
A) about the same number of each is produced per month
B) they have the same degree of motility
C) they have the same number of chromosomes
D) they are about the same size
C) they have the same number of chromosomes
13) The constancy of the chromosome number from one cell generation to the next is maintained through ________.
A) mitosis
B) meiosis
C) cytokinesis
D) DNA synthesis
B) meiosis
14) Fertilization generally occurs in the ________.
A) ovary
B) uterus
C) vagina
D) fallopian tubes
D) fallopian tubes
15) Spermiogenesis involves the ________.
A) formation of four haploid cells from a spermatogonium
B) movement of sperm in the female genital tract
C) formation of a functional sperm by the stripping away of superfluous cytoplasm
D) sequence of events in the rete testis
C) formation of a functional sperm by the stripping away of superfluous cytoplasm
16) All of the following can be considered male secondary sex characteristics except the ________.
A) development of body hair
B) lowering of the voice
C) development of testes as opposed to ovaries
D) increasing mass of the skeleton
C) development of testes as opposed to ovaries
17) In humans, separation of the cells at the two-cell state following fertilization may lead to the production of twins, which in this case would be ________.
A) dizygotic
B) identical
C) fraternal
D) of different sexes
B) identical
18) Characteristics of the mature sperm include the ________.
A) presence of two X chromosomes in approximately half the sperm
B) presence of Y chromosomes in approximately half the sperm
C) absence of an acrosome
D) absence of coiled mitochondria
B) presence of Y chromosomes in approximately half the sperm
19) How do the testes respond to exposure to excessive body warmth?
A) They move close to the pelvic cavity.
B) They move away from the pelvic cavity.
C) Excessive warmth has no effect on the testicles because of their location in the scrotum.
D) Excessive warmth is actually beneficial in that it speeds up the maturation of sperm.
B) They move away from the pelvic cavity.
20) Effects of estrogen include ________.
A) increased oiliness of the skin
B) deepening of the voice
C) growth of the breasts at puberty
D) growth of the larynx
C) growth of the breasts at puberty
21) Secretion of progesterone stimulates ________.
A) contraction of uterine muscles
B) preparation of the mammary glands for lactation
C) secretory activity of the uterine myometrium
D) development of the female secondary sex characteristics
B) preparation of the mammary glands for lactation
22) Which of the following statements about sperm is not true?
A) They contain very little cytoplasm or stored nutrients.
B) They are sluggish in an alkaline environment.
C) The acrosome is produced by the Golgi apparatus and contains hydrolytic enzymes.
D) The sperm midpiece consists of mitochondria spiraled tightly around the contractile filaments of the tail.
B) They are sluggish in an alkaline environment.
23) The cells that produce testosterone in the testis are called ________.
A) spermatocytes
B) spermatogonia
C) sustentacular cells
D) interstitial cells
D) interstitial cells
24) The testicular cells that construct the blood-testis barrier are the ________.
A) spermatocytes
B) spermatogonia
C) sustentacular cells
D) interstitial cells
C) sustentacular cells
25) Which of the following occurs as a result of undescended testes?
A) Male sex hormones will not be circulated in the body.
B) Sperm will have no means of exit from the body.
C) Inadequate or nonviable sperm will be produced.
D) Inadequate blood supply will retard the development of the testes.
C) Inadequate or nonviable sperm will be produced.
26) Erection of the penis results from ________.
A) a sympathetic reflex
B) parasympathetic activation of the bulbourethral glands
C) dilation of the veins in the penis
D) a parasympathetic reflex
D) a parasympathetic reflex
27) Which is not a part of the proliferative phase of the female menstrual cycle?
A) late in this phase, cervical mucus becomes thin and crystalline
B) vesicular follicle growth
C) corpus luteum
D) development of endometrial cells
C) corpus luteum
28) Which of the choices below is not a function of the vagina?
A) serves as a passageway for the primary oocyte
B) serves as a passageway for menstrual flow
C) is the birth canal
D) receives semen from the penis during sexual intercourse
A) serves as a passageway for the primary oocyte
Select the correct statement about male sexual response.
A) Sympathetic impulses are responsible for causing penile arteriolar dilation, resulting in erection.
B) Erection is the result of vascular spaces in the erectile tissues filling with blood.
C) Expansion of the penile tissues results in dilation of the venous outflow.
D) Ejaculation is the result of parasympathetic stimulation.
B) Erection is the result of vascular spaces in the erectile tissues filling with blood.
Which of the choices below is not a function of testosterone?
A) stimulates the male pattern of development
B) contributes to male sexual behavior and spermatogenesis
C) stimulates protein synthesis
D) stimulates mammary gland development
D) stimulates mammary gland development
Which male hormone inhibits the secretion of FSH?
A) ACTH
B) inhibin
C) ICSH
D) testosterone
B) inhibin
During the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle ________.
A) LH reaches its highest levels
B) progesterone levels are at their highest
C) estrogen reaches its highest levels
D) the Graafian follicle forms
B) progesterone levels are at their highest
Select the correct statement about the uterine cycle.
A) The menstrual phase of the cycle is from day 1 to day 8.
B) During the secretory phase, estrogen levels are at their highest.
C) During the proliferative phase, levels of progesterone rise as the follicle begins to produce more hormone.
D) If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum is maintained by a hormone secreted by the developing embryo.
D) If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum is maintained by a hormone secreted by the developing embryo.
Which of the following statements is true concerning the mammary glands of both males and females?
A) Both sexes are equally prone to breast cancer.
B) All lumps identified in breast tissue are malignant.
C) The only time hormones target breast tissue is during pregnancy and lactation.
D) The mammary glands are modified sweat glands that are actually part of the integumentary system.
D) The mammary glands are modified sweat glands that are actually part of the integumentary system.
Which of the choices below is not a part of the brain-testicular axis?
A) hypothalamus
B) anterior pituitary gland
C) thalamus
D) testes
C) thalamus
Normally menstruation occurs when ________.
A) blood levels of FSH fall off
B) blood levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease
C) blood levels of estrogen and progesterone increase
D) the corpus luteum secretes estrogen
B) blood levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease
The basic difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis is that ________.
A) during spermatogenesis two more polar bodies are produced
B) the mature ovum is n, while the sperm is 2n
C) in oogenesis, one mature ovum is produced, and in spermatogenesis four mature sperm are produced from the parent cell
D) spermatogenesis involves mitosis and meiosis, but oogenesis involves meiosis only
C) in oogenesis, one mature ovum is produced, and in spermatogenesis four mature sperm are produced from the parent cell
Occasionally three polar bodies are found clinging to the mature ovum. One came from an unequal division of the ovum, but from where did the other two arise?
A) There were originally four polar bodies and one disappeared.
B) One is an undeveloped primary oocyte that failed to mature.
C) The first polar body has also divided to produce two polar bodies.
D) What you really see are two polar bodies and the sperm that will fertilize the egg.
C) The first polar body has also divided to produce two polar bodies.
Which of the following will occur after ovulation?
A) The corpus luteum secretes estrogen only.
B) The endometrium enters its secretory phase.
C) The secretion of anterior pituitary gonadotropins is enhanced.
D) The corpus luteum prepares to become a corpus albicans.
B) The endometrium enters its secretory phase.
Why doesn’t semen enter the urinary bladder during ejaculation?
A) There is no common duct between the reproductive system and the urinary system.
B) There is no urge to urinate during sexual intercourse because of the suppression of LH by testosterone buildup in the blood.
C) The smooth muscle sphincter at the base of the urinary bladder closes.
D) Ejaculation is a parasympathetic reflex resulting in no response by urinary contraction muscles.
C) The smooth muscle sphincter at the base of the urinary bladder closes
Spermatogenesis ________.
A) is the process of releasing mature sperm cells into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule
B) involves a kind of cell division limited to the gametes
C) results in the formation of diploid cells
D) uses mitosis to produce gamete cells
B) involves a kind of cell division limited to the gametes
Which hormone is absolutely necessary for ovulation to occur?
A) LH
B) FSH
C) progesterone
D) estrogen
A) LH
The brain-testicular axis ________.
A) is the tight relationship between the cortex and the control of testicular function
B) involves FSH and LH release
C) involves posterior pituitary release of regulating hormones
D) involves a positive feedback loop control of spermatogenesis
B) involves FSH and LH release
Select the correct statement about testosterone control.
A) GnRH from the hypothalamus causes FSH and LH release from the anterior pituitary.
B) FSH stimulates testicular production of testosterone.
C) Inhibin and testosterone exert positive feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary.
D) The pineal gland is believed to be the gland that exerts the most influence in testosterone control.
A) GnRH from the hypothalamus causes FSH and LH release from the anterior pituitary.
Which of the following is a correct statement about uterine tubes?
A) The ampulla is the narrow constricted region.
B) The infundibulum is the funnel-shaped region near the ovary.
C) The isthmus is the normal site of fertilization.
D) The mesometrium supports the uterine tubes along their entire length.
B) The infundibulum is the funnel-shaped region near the ovary.
Select the correct statement about the hormonal events of the ovarian cycle.
A) Rising levels of estrogen start follicle development.
B) High estrogen levels result in a surge of LH release.
C) The follicle begins to secrete progesterone in response to estrogen stimulation.
D) The LH surge stimulates further development of the secondary oocyte.
B) High estrogen levels result in a surge of LH release.
Which of these statements about sexually transmitted infections is false?
A) Chlamydia is caused by bacteria that can often be asymptomatic or bring on a wide variety of symptoms.
B) Gonorrhea is caused by a bacterium that can bring on painful discharges in males.
C) Syphilis is caused by a virus that may lead to death if untreated.
D) Genital herpes is caused by a virus that may cause intermittent lesions.
C) Syphilis is caused by a virus that may lead to death if untreated.
Which of the following statements about spermatogenesis is not true?
A) The spermatogonium forms the primary spermatocyte.
B) The primary spermatocyte forms two secondary spermatocytes.
C) The secondary spermatocytes each form two spermatids.
D) Each spermatid forms two sperm
D) Each spermatid forms two sperm
A boy who has not passed through puberty sustains an injury to his anterior pituitary such that FSH is no longer released, but LH is normal. After he grows to maturity, one would expect that he would ________.
A) be sterile
B) not develop secondary sex characteristics
C) be impotent (unable to have an erection)
D) have impaired function of interstitial cells
A) be sterile
Which of the following statements about the female reproductive process is not true?
A) Fertilization usually occurs in the fallopian tube.
B) Ovulation usually occurs 14 days after the beginning of menses.
C) Rebuilding the endometrium is under the control of prolactin.
D) The monthly discharge of the uterus (menses) is initiated by the decrease in secretion of female hormones.
C) Rebuilding the endometrium is under the control of prolactin.
A low secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the normal male adult would cause ________.
A) decreased testosterone secretion
B) excessive beard growth
C) increased spermatogenesis
D) shrinkage of the anterior pituitary gland
A) decreased testosterone secretion
All of the following statements referring to the uterine cycle are true except ________.
A) FSH and LH directly promote development of the uterine endometrium
B) estrogen is secreted by the developing follicle in the follicular phase of the cycle
C) the corpus luteum is formed from the ruptured follicle after ovulation
D) a decrease in the levels of ovarian hormones signals menstruation
A) FSH and LH directly promote development of the uterine endometrium
Which of the following phases or processes in the monthly reproductive cycle of the female occur simultaneously?
A) maximal LH secretion and menstruation
B) maximal steroid secretion by the corpus luteum and menstruation
C) early follicular development and the secretory phase in the uterus
D) regression of the corpus luteum and a decrease in ovarian progesterone secretion
D) regression of the corpus luteum and a decrease in ovarian progesterone secretion
The duct system of the male reproductive system does not include the ________.
A) epididymis
B) urethra
C) ductus deferens
D) corpus spongiosum
D) corpus spongiosum
An ovulating oocyte is actually activated by hormones about ________ days before ovulation.
A) 14
B) 28
C) 85
D) 110
D) 110
Prostate cancer is _______.
A) the number-one cause of death in men
B) sometimes a slow-growing cancer that may never represent a threat to the patient
C) most common in Asians
D) often the result of a distortion of the urethra
B) sometimes a slow-growing cancer that may never represent a threat to the patient
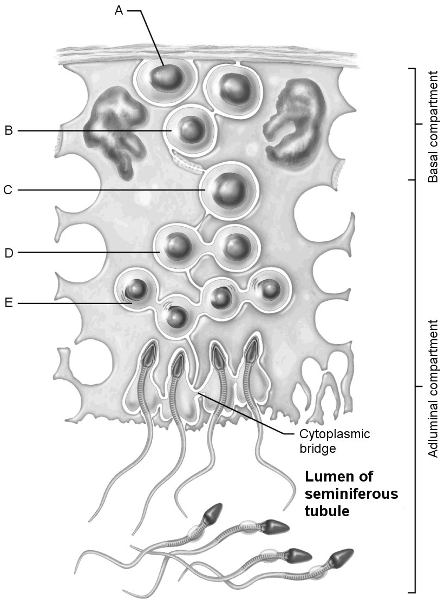
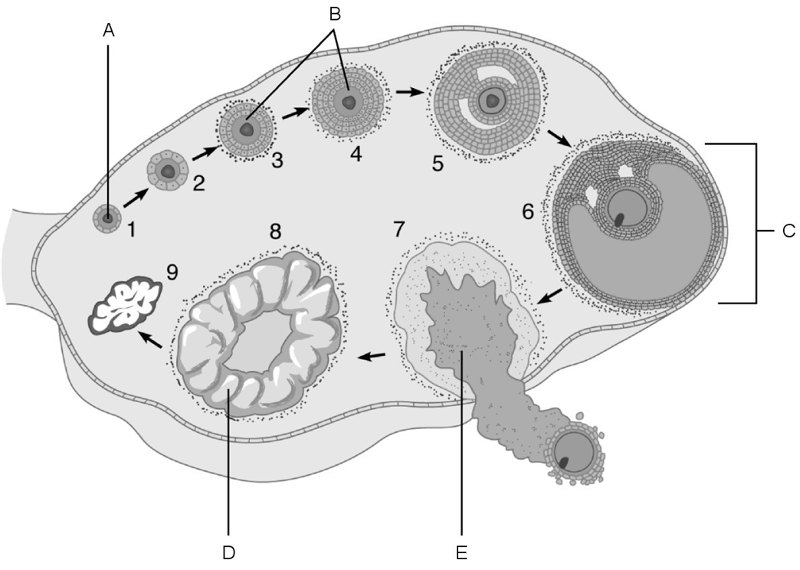
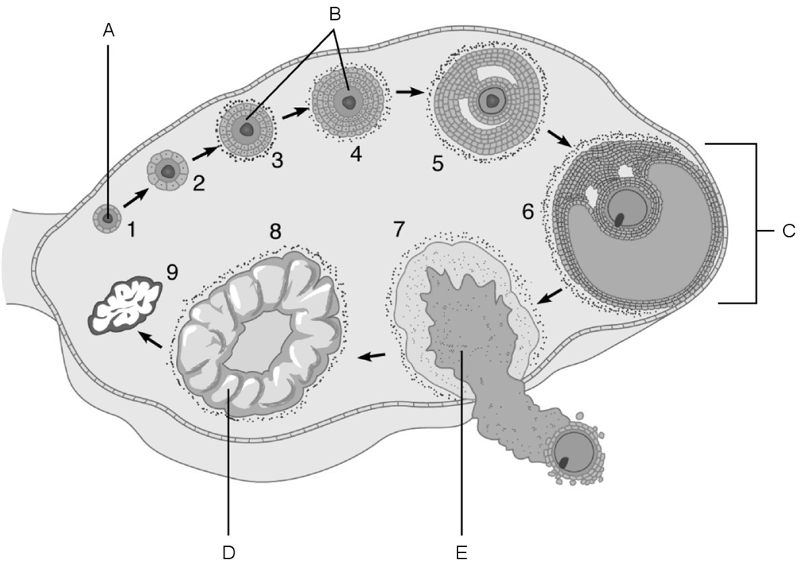
Stem cell.
A
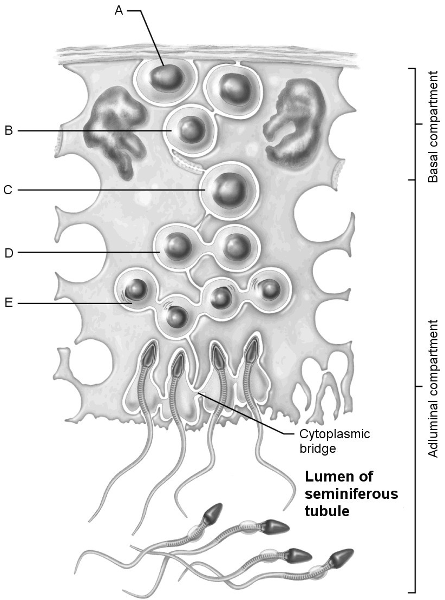
First cells with n number of chromosomes.
D
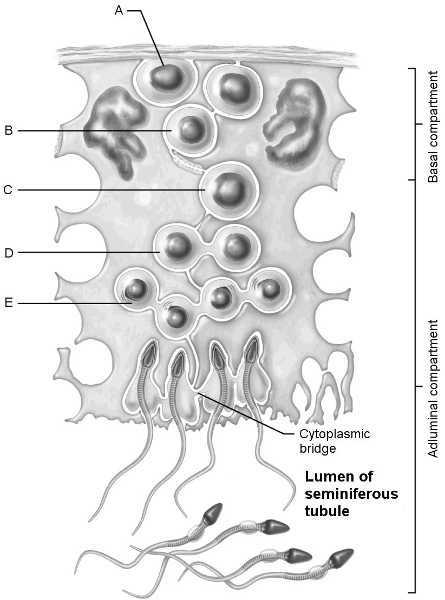
Type B spermatogonia.
B
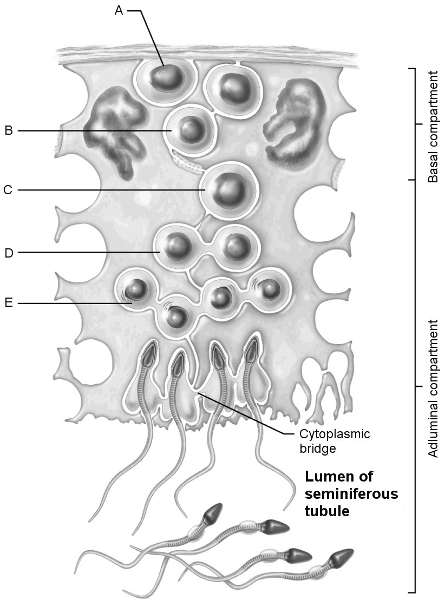
Early spermatids.
E
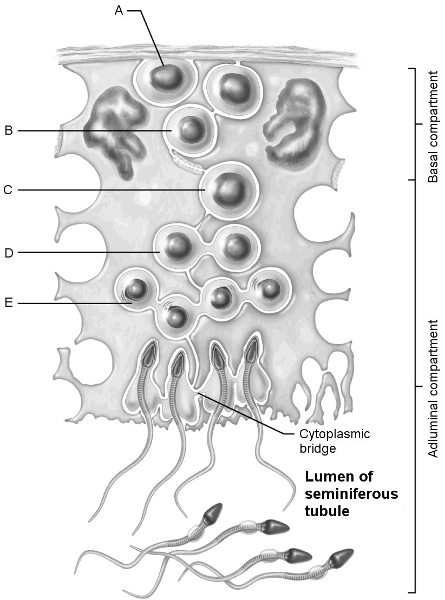
Primary spermatocyte.
C
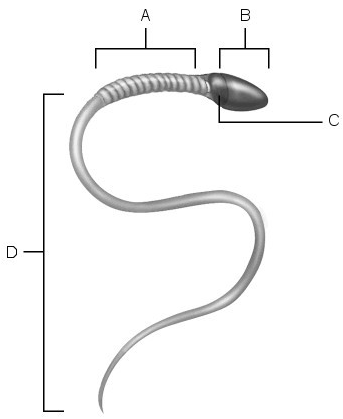
Acrosome.
B
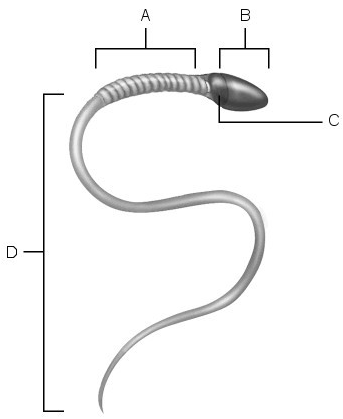
Location of mitochondria.
A
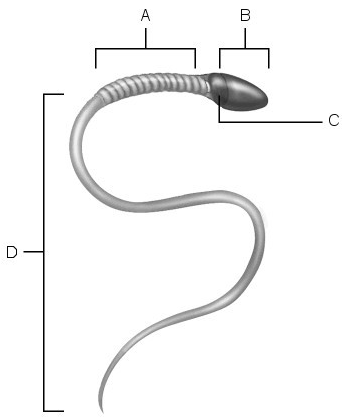
Midpiece.
A
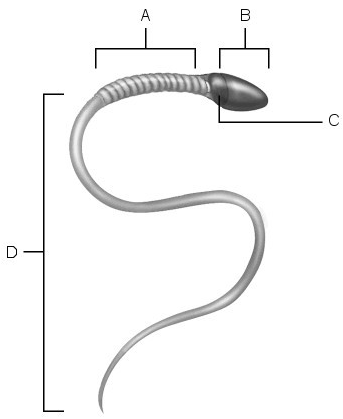
Location of nucleus.
C
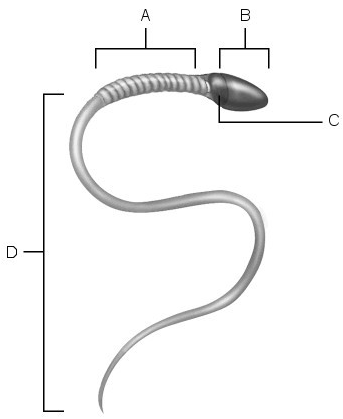
Area of compacted DNA.
C
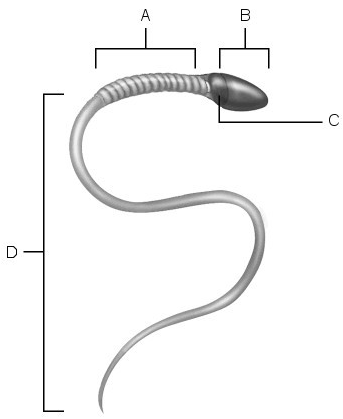
Flagellum.
D
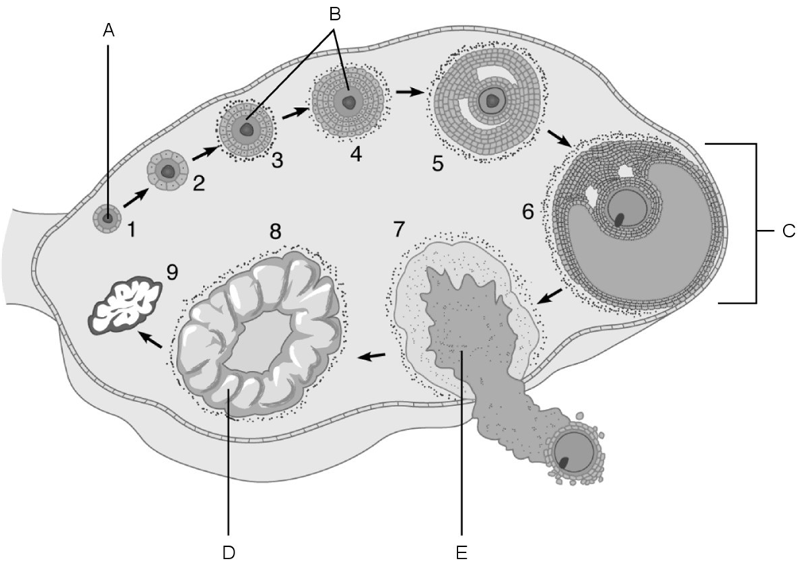
The stage called ovulation.
E
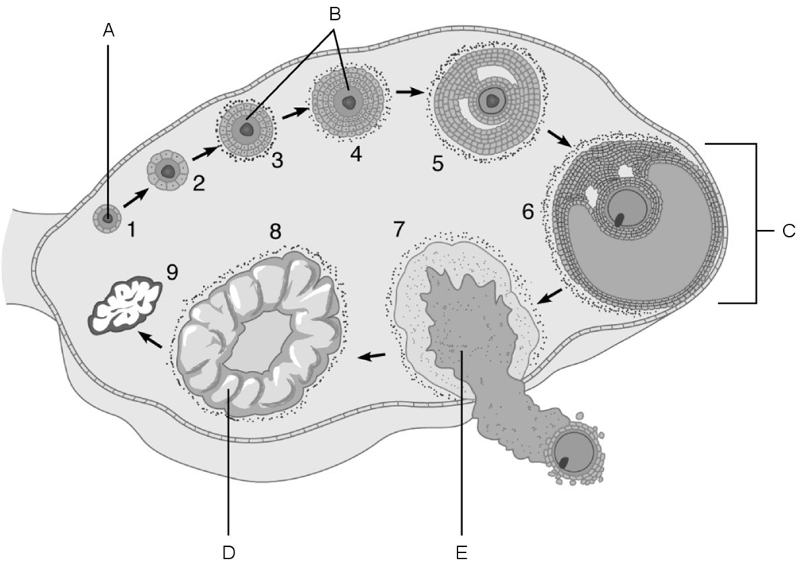
Vesicular (Graafian) follicle.
C
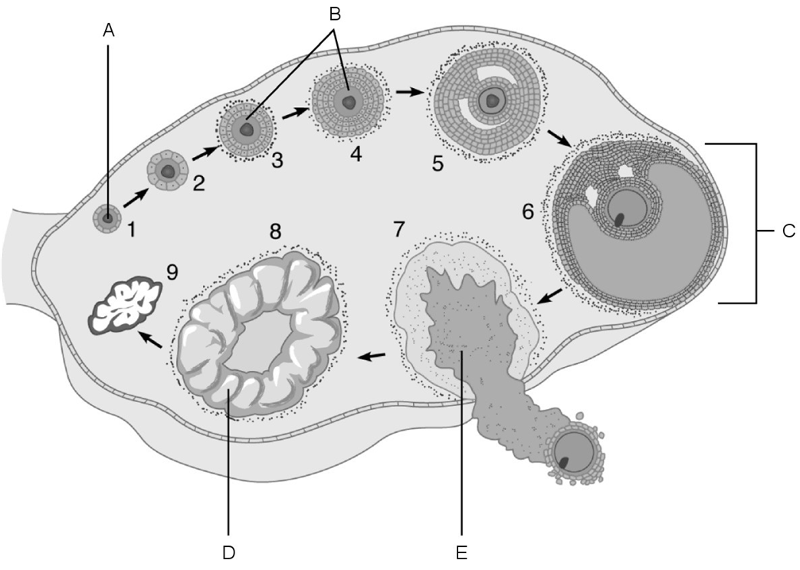
Primary follicles.
B
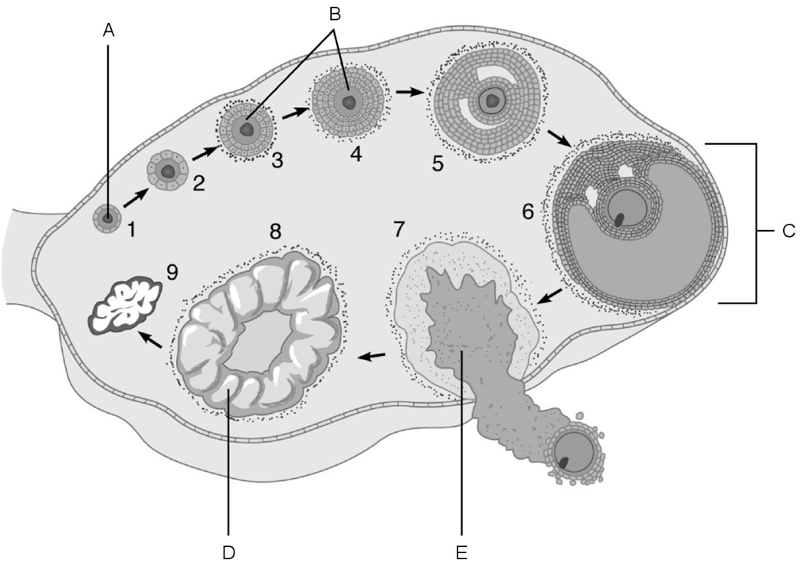
Primordial follicle.
A
Corpus luteum.
D
Mature follicle.
C
It is necessary for the testes to be kept below body temperature.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The prostate atrophies as a man ages, and it usually causes no health problems.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
The hormone oxytocin combines with enzymes in semen to enhance sperm motility.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
When a couple is having difficulty conceiving a child, it is necessary to investigate the sperm
of the male.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The amount of testosterone and sperm produced by the testes is dependent on the influence of
FSH alone.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Ovarian follicles contain mature eggs.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Sexually transmitted infections are the most important cause of reproductive disorders.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
Reproduction is not possible in males or females until one year after puberty has begun.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
he smaller cell produced by oogenesis meiosis I, called the first polar body, is essentially a
packet of discarded nuclear material.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
Pain during ovulation is called dysmenorrhea.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
A human egg or sperm contains 23 pairs of chromosomes.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The Pap smear is a test to detect cancerous changes in cells of the cervix.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The adenohypophyseal hormone that triggers ovulation is estrogen.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
The male urethra serves the urinary system only.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Both tetrads and crossovers are seen during meiosis.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
Failure to attain erection is called impotence.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
Ovulation occurs near the end of the ovarian cycle.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
The corpus luteum secretes progesterone only.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
Female orgasm is required for conception.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
The first sign of puberty in females is budding breasts.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The primary function of the testes is to produce testosterone.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
The stage in meiosis where chromosomal exchange takes place is telophase.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
The diamond-shaped area between the coccyx, pubic arch, and ischial tuberosities in the
female is the vulva.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE
The soft mucosal lining of the uterus is the endometrium.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
A scrotal muscle that contracts in response to cold environmental temperature is the
cremaster.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The secretions of the bulbourethral glands neutralize traces of acidic urine in the urethra and
serve as a lubricant during sexual intercourse.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The zona pellucida is formed as the follicle becomes a secondary follicle.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The molecule that enhances the ability of testosterone to promote spermatogenesis is inhibin.
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
The ________ plexus of testicular veins assists in cooling the testis.
pampiniform
Surgical cutting of the ductus deferens as a form of birth control is called a(n) ________.
vasectomy
The erectile tissue around the urethra is the corpus ________.
spongiosum
The midpiece of the sperm tail contains mostly ________.
mitochondria
The ________ cells of the testis nourish the newly formed sperm cells.
sustentacular
The suspensory ligament and mesovarium are part of the ________ ligament.
broad
A follicle with only a small antrum in it would be classified as a(n) ________ follicle.
secondary
The small opening of the uterus that sperm would first enter is called the ________.
external os
The portion of the uterine endometrium that is not sloughed off every month is called the ________.
stratum basalis
________ is caused by Treponema pallidum.
Syphilis
What are some risk factors for developing breast cancer?
Some of the risk factors for developing breast cancer are: (1) early onset of menses and late menopause; (2) first pregnancy late in life or no pregnancies at all; (3) familial history of breast cancer; (4) postmenopausal hormone replacement.
What is the name given to the female homologue to the penis?
The female clitoris is homologous to the glans penis of the male. It is homologous in that it contains dorsal erectile columns and can become swollen with blood during tactile stimulation.
Describe the composition and functional roles of semen.
Semen is a fluid mixture of sperm and accessory gland secretions (prostate, seminal vesicles, and bulbourethral glands). The liquid provides a transport medium for nutrients and contains chemicals that protect the sperm and facilitate their movements.
Explain the function of the myometrium and endometrium.
he myometrium plays an active role during childbirth when it contracts rhythmically to force the baby out of the mother's body. The endometrium is the innermost lining of the uterus where the embryo implants and stays for the rest of its development.
What is the purpose of the male bulbourethral gland?
Because it releases its contents prior to ejaculation, its function is probably to neutralize the acids in the urethra.
What is the physiological importance of the fact that the male testes descend to reside in the scrotal sac?
The male testes descend into the scrotal sac so that a fairly constant intrascrotal temperature is maintained. Failure of the testes to descend results in sterility, because production of viable spermatozoa requires a temperature several degrees lower than normal body temperature.
Ovulation occurs when the oocyte is released into the peritoneal cavity. By what means does it usually enter the uterine tube?
Fimbriae, which drape over the ovary, become very active close to the time of ovulation and undulate to create currents in the peritoneal fluid. These currents usually carry the oocyte to the uterine tube, where it begins its journey toward the uterus.
At what point is the sex of the embryo determined, and what determines it?
Genetic sex is determined at the instant the genes of a sperm combine with those of an ovum. The determining factor is the sex chromosomes each gamete contains.
What are the three layers of the Uterine Wall?
Perimetrium, Myometrium, and Endometrium.