The action potential is a transient change in the resting membrane potential from -70 mV to +30 mV, then back to -70 mV. This change is caused by the opening of first _____ then _____ voltage-gated channels.
Na+ then K+
What area(s) of the neuron generate signals that open the voltage-gated channels in the first part of the axon, thus causing an action potential?
Dendrites and cell body
As the axon hillock depolarizes, Voltage-gated Na+ channels open and Na+ moves (into or out of) __________ the cell causing further (depolarization or repolarization) __________.
into; depolarization
If depolarization reaches -55 mV, an action potential will be generated. What is this -55 mV trigger point called?
Threshold
At the end of the depolarization phase, what voltage-gated channels open to help restore the resting membrane potential?
Voltage-gated K+ channels
Repolarization is caused by the movement of what ion (sodium or potassium), in what direction (into or out of the cell)?
potassium; out of the cell
After an action potential, the membrane becomes more negative than -70 mV. This period is called:
hyperpolarization.
After a neuron has generated an action potential, it cannot generate another one for a while. This period is called:
the absolute refractory period.
The fastest conduction of an action potential would occur in an axon with which of the following characteristics?
Large diameter and myelinated
What is the name of the disease in which the myelin sheaths of central nervous system axons are destroyed?
Multiple sclerosis
Which anatomical division of the nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord?
central nervous system
Which functional division of the nervous system controls skeletal muscle contractions?
somatic nervous system
What part of the neuron is a long cytoplasmic process capable of propagating an action potential?
axon
What part of the neuron consists of the cytoplasm that surrounds the nucleus?
perikaryon
Which structural class of neurons consists of neurons with one axon and one dendrite?
bipolar neurons
Which functional class of neurons carries electrical signals to control the contraction of smooth muscle and cardiac muscle?
visceral motor neurons
What type of neuroglial cell participates in the production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid?
ependymal cells
What type of neuroglial cell myelinates axons in the peripheral nervous system?
Schwann Cells
Which type of neuroglial cell functions in the central nervous system to engulf cellular debris, waste products, and pathogens?
microglia
Which type of active channels in the plasma membrane open or close when they bind certain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters?
chemically gated channels
A movement of ions that increases the negativity of the resting membrane potential is _____.
hyperpolarization
What is the term for the period when the voltage-gated sodium channels are opened and the membrane cannot respond to a new stimulus, even a strong one?
absolute refractory period
An action potential increases the membrane potential to ___ mV.
+30mV
Which type of axon would propagate action potentials at the highest speed?
large diameter, myelinated
What type of synapse has the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes locked together at gap junctions?
Electrical synapses have presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes locked together at gap junctions.
What causes the release of acetylcholine (ACh) into the synaptic cleft in a cholinergic synapse?
calcium ions entering the cytoplasm of the synaptic terminal
Which neurotransmitter is associated with a person's emotional states and moods and is linked to depression?
Serotonin
Which of the following has/have effects similar to morphine and function(s) to relieve pain?
Dopamine, Endorphin, Serotonin
Endorphin
A graded depolarization caused by the arrival of a neurotransmitter at the postsynaptic membrane is a(n) __________.
excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
The addition of stimuli occurring in rapid succession at a single synapse is called __________.
temporal summation
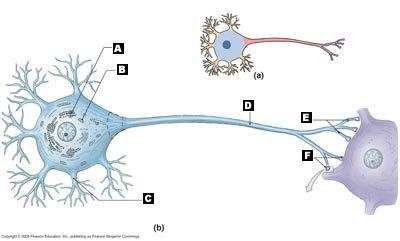
Label the following structural components of a neuron.
A. Nissl bodies (RER and free ribosomes)
B. Mitochondrion
C. Dendrite
D. Axon
E. Telodendria
F. Synaptic Terminals
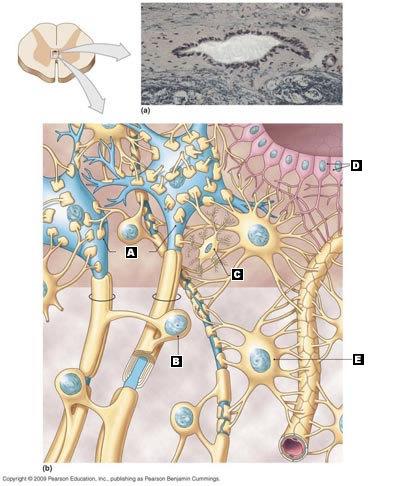
Correctly label the cells of the central nervous system on the diagram.
A. Neuron
B. Oligodendrocyte
C. Microglial Cell
D. Ependymal Cell
E. Astrocyte
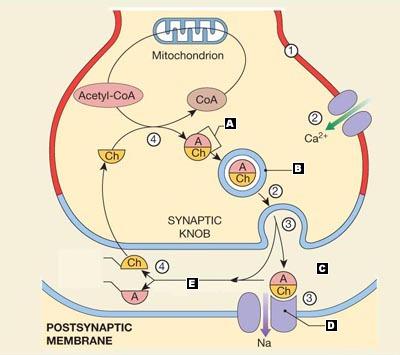
Correctly match the labels to the following parts of a cholinergic synapse.
A. Acetylcholine
B. Synaptic Vesicle
C. Synaptic Cleft
D. ACh Receptor
E. Acetylcholinesterase
What is the implication of a mature neuron having no centrioles?
The cell is not able to divide.
The axon emerges from the soma at a thickened region called the __________.
Axon Hillock
The movement of materials from the soma to the synaptic terminal is called __________.
axoplasmic transport
The movement of substances from the synaptic terminal to the soma is called __________.
retrograde flow
Motor neurons form the __________ division of the __________.
efferent; PNS
What type of sensory neurons would Amy, a gymnast, use to inform her brain of the position of her skeletal muscles and joints?
proprioceptors
The ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord are filled with __________.
cerebrospinal fluid
Which of the following glial cells surrounds cell bodies in the PNS and regulates levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide around ganglionic neurons?
satellite cells
Which of the following glial cells can form a myelin sheath around axon fibers in the central nervous system?
oligodendrocyte
The transmembrane potential found in all living cells is maintained by __________.
the sodium–potassium pump
There are two major categories of ion channels: leak channels and __________.
Active Channels
Which one of the following statements about the transmembrane potential is correct?
The resting negative charge on the interior of the plasma membrane is due mainly to charges on proteins.
The refractory period occurs __________.
from the time an action potential begins until the normal resting potential has stabilized
The speed at which an action potential is transmitted depends on __________.
the myelination and diameter of the axon
Compared with type C fibers, type A fibers have a larger diameter and can increase propagation ________ times faster.
120
Presynaptic facilitation __________.
is activity at an axoaxonal synapse that increases the amount of neurotransmitter released when an action potential arrives at the synaptic terminal
Name some of the functions of the astrocytes.
-Guiding neuron development.
-Repairing damaged nerve tissue.
-Controlling the interstitial environment.
A stimulus causes a neuron's membrane potential to rise to −60 mV. What occurs?
Depolarization, action potential, opening of sodium channels
Give some characteristics of saltatory transmission.
-Occurs in myelinated neurons.
-Occurs at the nodes of Ranvier.
-Is faster than continuous propagation.
-One node of Ranvier to another.
During the initiation of an action potential in an area of excitable membrane, what happens?
A graded potential raises the transmembrane potential toward threshold.
Voltage-regulated sodium ion channels open as threshold is reached.
Name the three classes of mechanisms by which neurotransmitters function.
-lipid-soluble gases that can diffuse into the cell and bind to enzymes inside the cell.
-compounds that have an indirect effect on membrane potential by means of second messengers.
-compounds that have a direct effect on membrane potential by affecting chemically regulated channels.
Extracellular chemicals other than neurotransmitters and neuromodulators can cause ___________________?
facilitation or inhibition of function in neurons.
If the axon hillock remains depolarized for an extended time, what will happen?
A new action potential will be generated as soon as the absolute refractory period of the previous one has ended.
True/False. The ependymal cells line the blood vessels that supply the neural tissues of the brain, thereby forming the blood-brain barrier.
False. Ependymal cells line the central canal and brain ventricles and may monitor or produce some of the CSF that fills these open spaces.
True/False. Neurotransmitters that depress the resting potential are called excitatory.
False. Depressing the resting potential causes hyperpolarization of the membrane and inhibits action potential.
True/False. The all-or-none principle applies to excitable membranes, such as neuron membranes. This principle states that either a stimulus is great enough to depolarize a membrane to threshold and thus trigger an action potential, or the stimulus is not able to depolarize to threshold and thus an action potential does not occur.
True. Once the action potential has been triggered, all impulses are identical in strength and speed. However, the stimulus must be great enough to cause the triggering of the action potential.
True/False. Unipolar neurons have only one cell process, the axon.
False. Unipolar neurons have both dendrites and an axon.
True/False. Acetylcholine is broken down in the mitochondrion by acetylcholinesterase.
False. Acetylcholine is broken down in the synaptic cleft by acetylcholinesterase.
Which part of the nervous system performs the higher-order thinking required to complete these set of note cards?
Central Nervous System
Neurons are responsible for __________.
information transfer and processing in the nervous system
The region of a neuron with voltage-gated sodium channels is the __________.
axon hillock
Neurons are classified on the basis of their structure as __________.
anaxonic, unipolar, bipolar, multipolar
Neurons are classified on the basis of their function as __________.
motor, sensory, association
What are the two major cell populations of neural tissue?
neurons and neuroglia
Which of the following CNS glial cells removes debris, wastes, and pathogens by phagocytosis?
microglia
The white matter of the CNS represents a region dominated by the presence of __________.
oligodendrocytes
Depolarization of the membrane will shift the membrane potential toward __________.
0mV
What is the term given to describe a shift in transmembrane potential from −70 mV to −90 mV?
hyperpolarization
If resting membrane potential is −70 mV and the threshold is −60 mV, a membrane potential of −62 mV will __________.
not produce an action potential
At the site of an action potential, the membrane contains __________.
an excess of positive ions inside and an excess of negative ions outside
A node along the axon represents an area where __________.
there is an absence of myelin
Nerve cell bodies in the PNS are clustered together in masses called __________.
ganglia
What are the most important factors that determine the rate of action potential conduction?
the presence or absence of a myelin sheath and the diameter of the axon
At an electrical synapse, the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes are locked together at __________.
gap junctions
Exocytosis and the release of acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft are triggered by __________.
calcium ions flooding into the synaptic terminal
An important neurotransmitter in emotional states and moods is __________.
serotonin
An excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is __________.
a graded depolarization produced by the arrival of a neurotransmitter
An inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) is a __________.
graded hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane
Rabies is a viral disease contracted from the bite of an infected animal. Rabies bypasses many immune system defenses by traveling in peripheral neurons to reach the CNS. Which method of transport is NOT used by the rabies virus to reach the CNS?
anterograde flow
Sensory neurons are responsible for carrying impulses __________.
Efferent pathways consist of axons that carry impulses __________.
to the CNS
away from CNS
Interneurons, or association neurons, differ from sensory and motor neurons in their __________.
exclusive location in the brain and spinal cord
Graded potentials that develop on the postsynaptic membrane in response to a neurotransmitter are __________.
postsynaptic potentials
The addition of stimuli occurring in rapid succession at a single synapse is __________.
temporal summation
What type of gated channel opens or closes in response to distortion of the membrane?
mechanically gated channel
Interneurons are responsible for __________.
analysis of sensory inputs and coordination of motor outputs
Sensory (ascending) pathways distribute information __________.
from peripheral receptors to processing centers in the brain
Tyson decides to travel overseas but does not have all the required vaccines needed before he goes. While on his trip, he contracts diphtheria. Which type of glial cell is particularly at risk from this disease?
Schwann cells
Schwann cells are glial cells responsible for __________.
producing a neurilemma around peripheral axons
What happens when a barrier prevents the movement of opposite charges toward one another?
A potential difference exists.
Which of the following statements about the sodium–potassium pump is correct?
The activity of the sodium–potassium pump is needed after every action potential to restore resting potential.
Which of the following is a correct statement of the all-or-nothing principle?
A given stimulus either triggers a typical action potential or does not produce one at all.
During the relative refractory period, a larger-than-normal depolarizing stimulus can __________.
bring the membrane to threshold and initiate a second action potential
Saltatory conduction conducts impulses along an axon __________.
five to seven times faster than continuous conduction
In type C fibers, action potentials are conducted at speeds of approximately __________.
2 mph
The larger the diameter of the axon, the __________.
faster the rate of transmission
Rachel decides to go swimming, but when she sticks her big toe into the water, she changes her mind because the water is too cold. The sensory neurons responsible for sending the message about the temperature of the cold water are __________.
exteroceptors
The main functional difference between the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system is that the activities of the ANS are __________.
primarily involuntary, or under "automatic" control
Lulu, who is 50 years old, decides she wants to receive Botox treatments. If Botox, short for botulism toxin, prevents the release of ACh from synaptic terminals, what effect should Lulu expect from having Botox injected into her facial muscles?
temporary paralysis in the injected facial muscles
What happens when depolarization to threshold occurs?
Voltage-gated sodium channels are opened.
Emma is very excited because after taking up running several months ago, she has begun to experience the phenomenon called "runner's high." This is caused by the production of endorphins. What is the effect of the endorphins on Emma when she runs?
Endorphins are blocking the transmission of substance P, a neurotransmitter that sends information about pain to the CNS.
Which of the following is the most excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and functions in learning and memory?
glutamate
Ann and Elise are two college students on an overseas vacation. Because they both love seafood, they stop at a restaurant in a coastal town for lunch. After dining on shellfish, they become very sick and have trouble breathing. What may have happened to Ann and Elise?
-They may have consumed some tetrodotoxin (TTX), which can cause abnormal sensations.
-They may have consumed saxitoxin (STX), which blocks sodium ion channels.
-They may have consumed ciguatoxin (CTX), which can interfere with muscle control.
-Any of the responses could be correct. TTX, STX, and CTX all block sodium ion channels, cause abnormal sensations, and interfere with muscle control.
Facilitation in the neuron's transmembrane potential toward threshold results from __________.
-any shift that makes the cell more sensitive to further stimulation
-summation of EPSPs
-exposure to certain drugs, such as nicotine.
The reason that active neurons need ATP is to support_______.
-the synthesis, release, and recycling of neurotransmitter molecules.
-the recovery from action potentials.
-the movement of materials to and from the soma via axoplasmic flow.
The primary functions of the nervous system include ______.
-providing sensation of the internal and external environments
-integrating sensory information
-regulating and controlling peripheral structures and systems
Name some structure parts of the PNS.
-a ganglion
-an interneuron within an autonomic ganglion
-a sensory receptor
The CNS has _ types of neuroglia. Name them.
4 types, ependymal cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and microglia.
Ependymal Cells. Where are they located, name their functions.
CNS. They line ventricles (brain) and central canal (spinal cord); assist in producing, circulating, and monitoring CSF.
Astrocytes. Where are they located, name their functions.
CNS. Maintain blood-brain barrier; provide structural support; regulate ion, nutrient, and dissolved gas concentrations; absorb and recycle neurotransmitters; form scar tissue after injury.
Oligodendrocytes. Where are they located, name their functions.
CNS. Myelinate CNS axons; provide structural framework.
Microglia. Where are they located, name their functions.
CNS. Remove cell debris, wastes, and pathogens by phagocytosis.
The PNS has _ types of neuroglia. Name them and their functions.
2 types. Satallite cells- surround neuron cell bodies in ganglia; regulate O2, CO2, nutrient, and neurotransmitter levels around neurons in ganglia.
Schwann Cells- Surround all axons in PNS; responsible for myelination of peripheral axons; participate in repair process after injury.
Describe Wallerian degeneration.
The axon distal to the injury site degenerates, and macrophages migrate into the area to clean up the debris.
The sequence of events at a typical cholinergic synapse
Step 1: An arriving ap depolarizes the synaptic terminal.
Step 2: Calcium ions enter the cytoplasm of the synaptic termina. ACh is released through exocytosis of synaptic vesicles. ACh release ceases because calcium ions are removed from the cytoplasm of the synaptic terminal.
Step 3: ACh diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptoros of the postsyn. mem. Chemically gated Na+ channels on the postsyn mem open, producing a graded depolarization.
Step 4: The depolarization ends as ACh is broken down into acetate and choline by AChE. The synaptic terminal reabsorbs choline from the synaptic cleft and uses it to resynthesize ACh.