what is the CNS defined as
brain and spinal cord
what are the cells of the CNS
neurons
glia: astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, microglia)
what is the added dimension of disease in CNS
traumatic
where is there nissl substance
dendrites but not axons
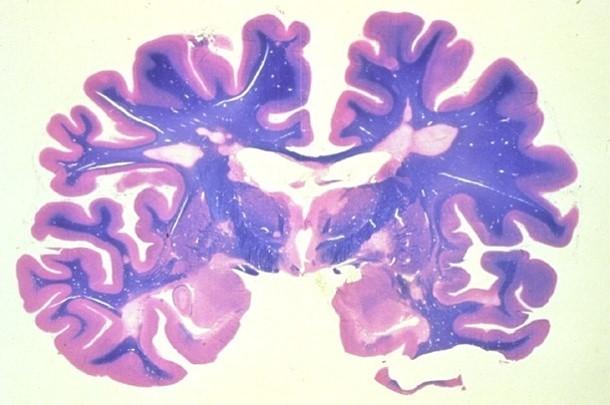
what is this section from
spinal cord
are neurons or glial cells more common in the CNS
nerons
what are the glial cells associated with the CNS
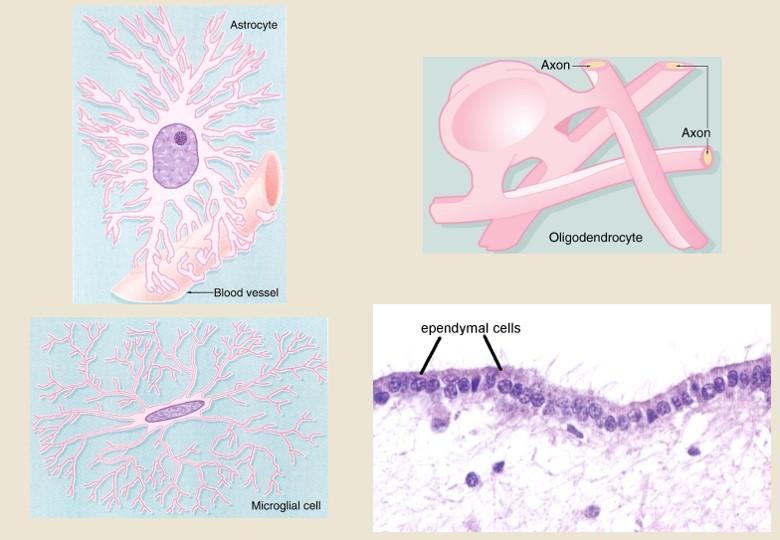
astrocyte
microglial cell
oligodendrocyte
ependymal cell
what do ependymal cells line
all ventricles and choroid plexus
what are the most common glial cells
astrocyte
what are the haloed cells in the CNS
oligodendrocytes
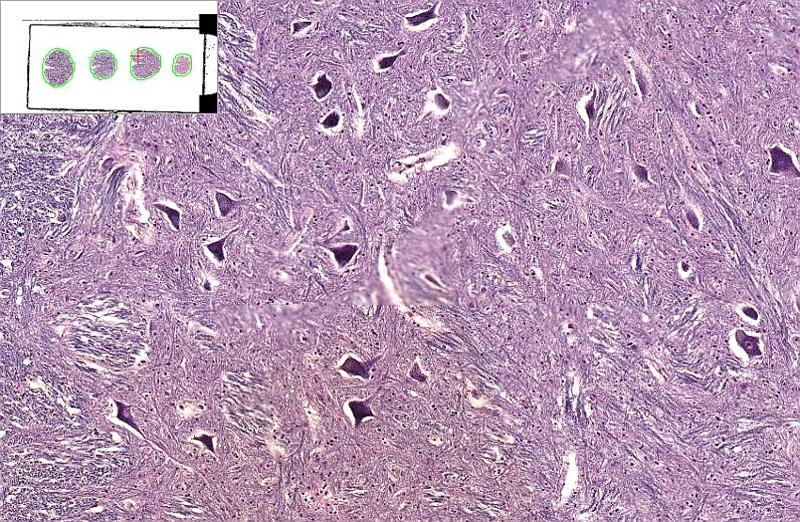
what are the cells that populate this screen
oligodendrocytes
why would there be clear spaces around these oligodendrocytes
just like fat (myelin) washes out from Schwann glial cells
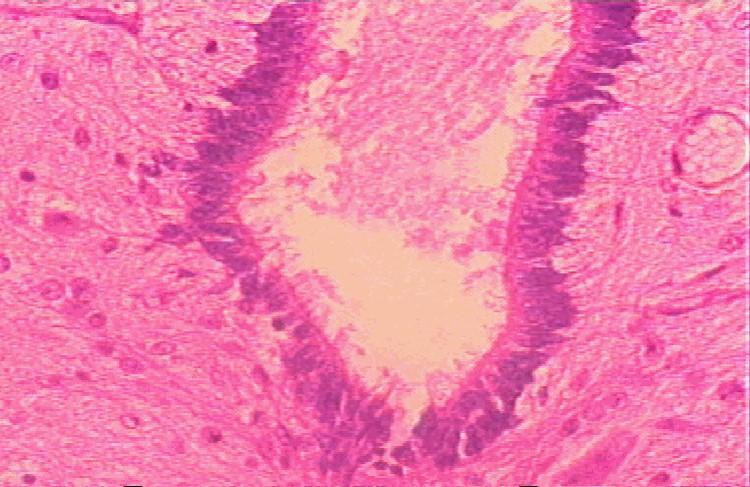
hat cells are lining this space in this frame
ependymal cells
what cells do ependymal cells look like
ciliated columnar cells
what is the only glial cell that looks epithelial
ependymal cells (simple columnar like in glands)
what is the configureation of the choroid plexus
papillary in configuration
what is the role of the choroid plexus
pump out CSF
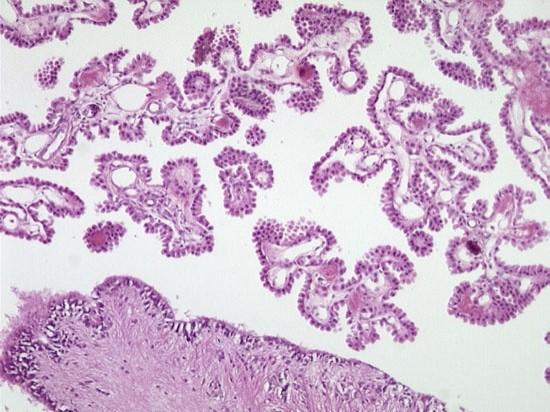
what is this
choroid plexus
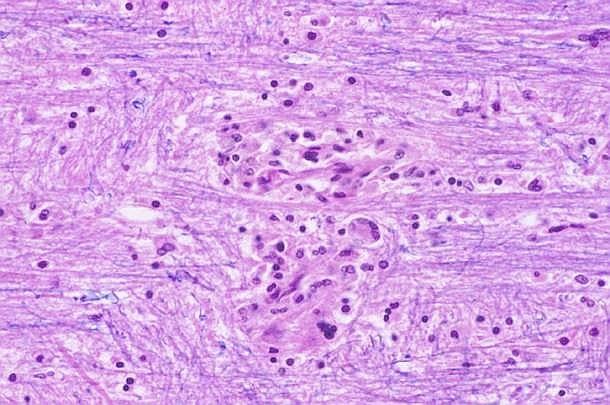
what type of cells is this a cluster of
microglia (MP of CNS)
what are the cellular reactions of neurons
acute: red neuron=karyolysis
subacute, chronic, cell loss, gliosis
axonal
inclusions
what are the cellular reactions of glia
gliosis
(swelling, fibers, inclusions)
what all go hand in hand with gliosis in terms of nonspecific reaction to injury
GLIOSIS
EDEMA
DEMYELINIZATION
nonspecific reactions to almost any type of injury
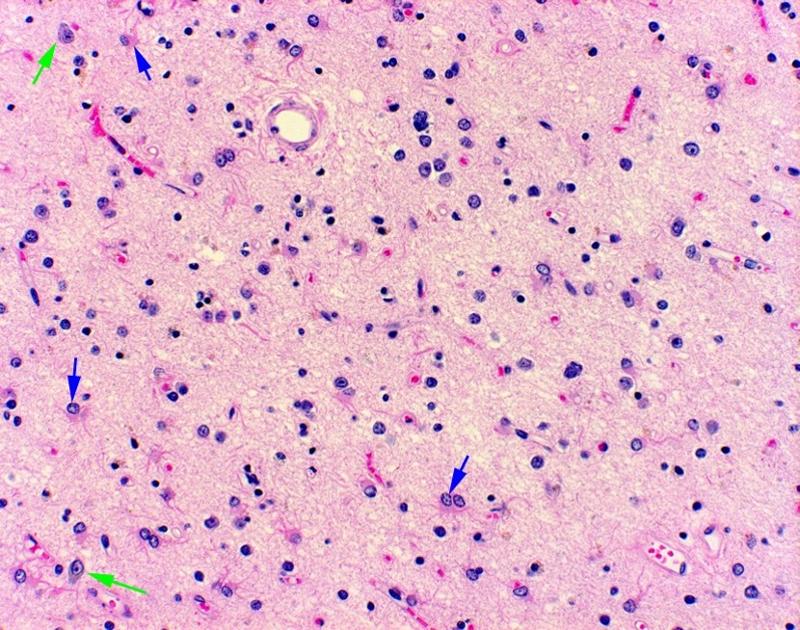
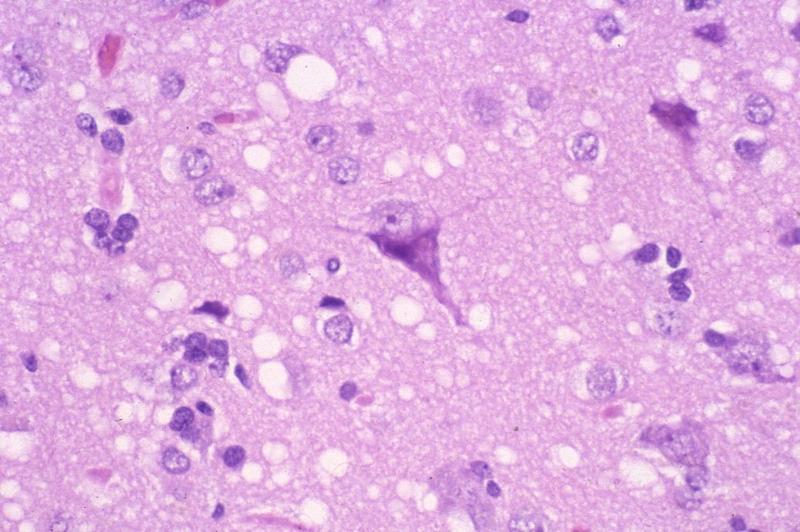
what kind of neuronal injury took place here
acute neuronal injury (red nucleus)
look for gliosis, neuronal loss in this picture
...
what types of cerebral edema can take place
vasogenic
cytotoxic
what is the normal weight of the CNS
1200-1300 gms
what happens in vasogenic cerebral edema
BBB is disturbed; intravascular to intercellular
what type of cerebral edema is cytotoxic
intracellular
where can cerebral edema go
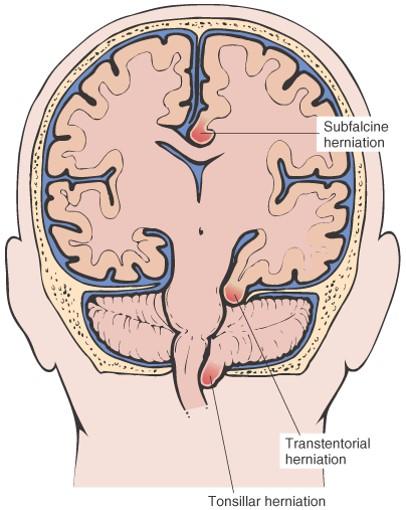
subfalcine (supratentorial)
cingulate (tentorial)
cerebellar tonsillar (subtentorial or infratentorial)
what is the fourth obvious sign of cerebral edema
flattening of gyri and small sulci
why do flattened gyri signify edema
compression against calvarium
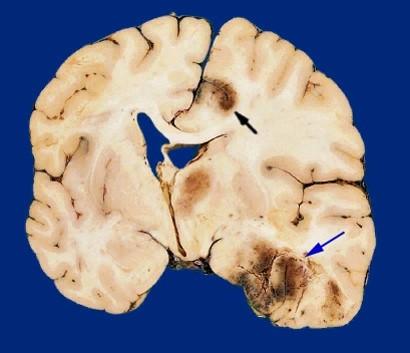
what was likely going on here
hemorrhage and edema
what does notching of the cingulate gyrus indicate
cerebral edema
what does cerebellar tonsil herniation indicate
cerebral edema
what are the symptoms of cerebral edema
headache
hallucinations
coma
death
what can cause hydrocephalus
impaired resorption
increased production (rare)
obstruction
what is communicating vs noncommunicating hydrocephalus
entire head vs part of the head
what types of pressures will someone have in hydrocephalus
high pressure and normal pressure
what is the key factor in whether hydrocephalus will result in any cranial enlargment
fontanelle closure
which fontanelle stays open for a while
anterior
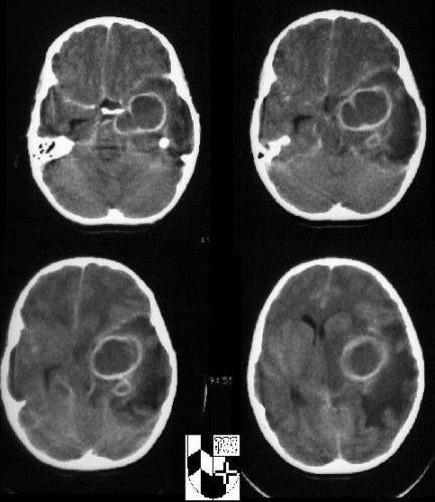
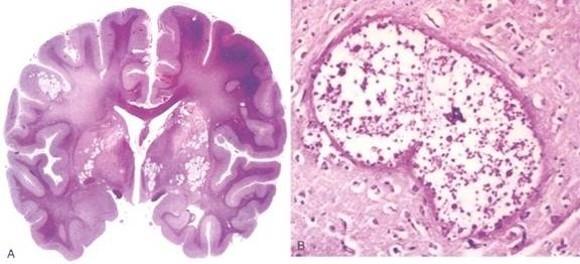
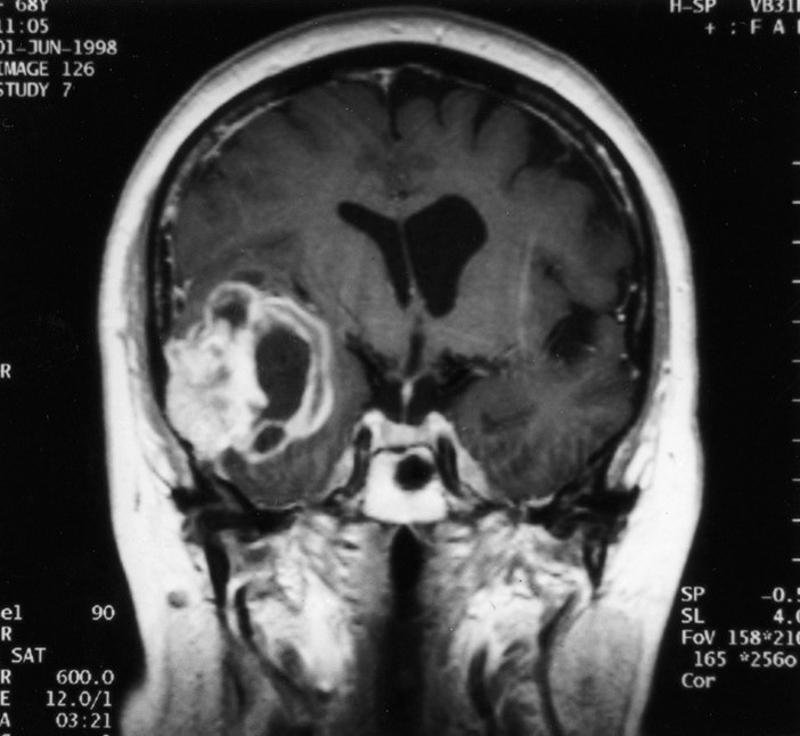
what can hydrocephalus on the CT look like
dilated ventricles
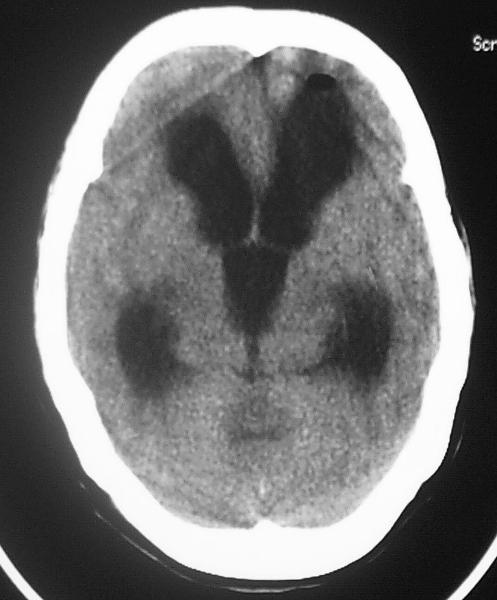
what is going on here
hydrocephalus
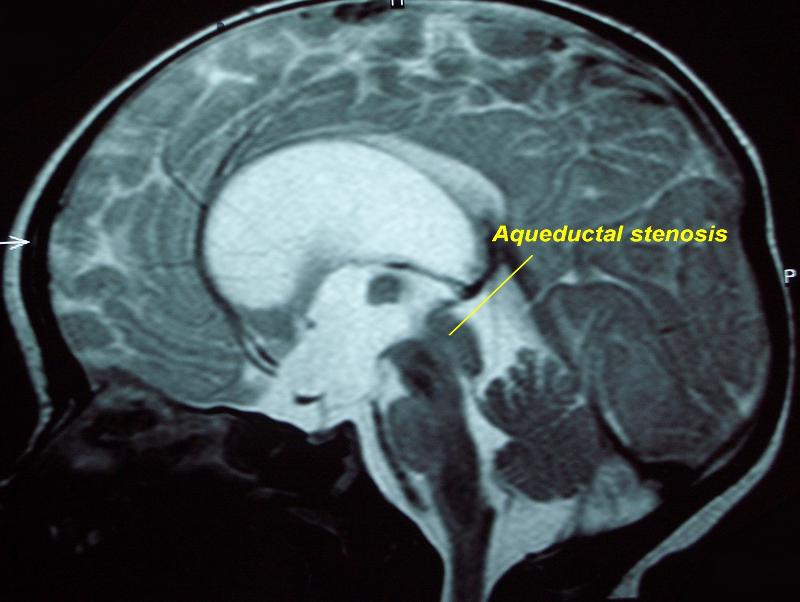
what is this aqueductal stenosis causing
hydrocephalus on MRI
what space would be more dilated: space after aqueductal stenosis or before it
before
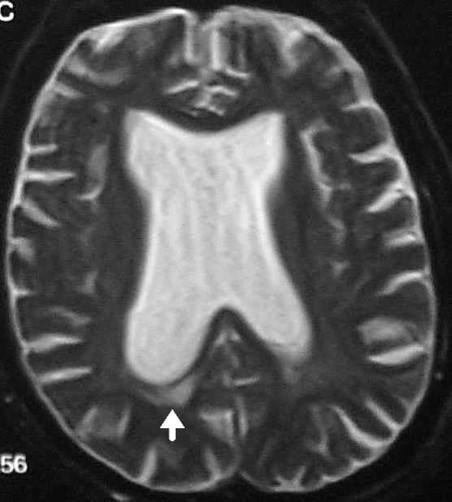
what type of imaging is this and what is being shown
MRI: water dense in MRI
arrow poniting to periventricular damage, which is more likely with high pressure hydrocephalus
would dilated ventricles at autopsy signal hydrocephalus
YEP
where are some places where the CNS is malformed
neural tube
forebrain
posterior fossa (infratentorial)
syringomyelia/hydromyelia
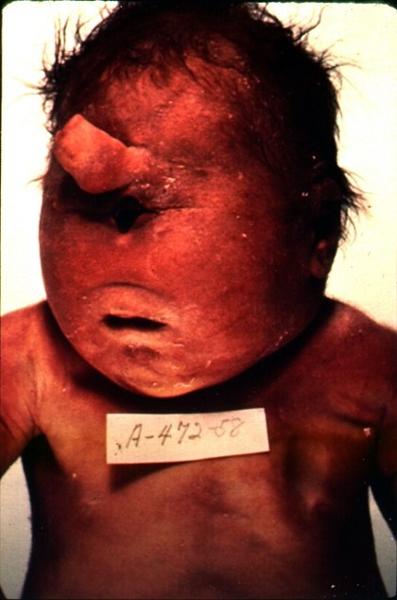
what are some neural tube malformations
anencephaly
encephalocele
spinal bifida
what are some forebrain malformations
polymicrogyria
holoprosencephaly
agaensis of CC
what are some posterior fossa malformations
arnold chiari (infratentorial herniation)
dancy walker (cerebellar cyst)
what is this
anencephaly
what antigen is found when spina bifidas are present
AFP
what type of cancer also has a penchant for AFP presence in the bloodstream
hepatoma
where is spina bifida usually
bottom of the zipper
what is polymicrogyria
small gyri
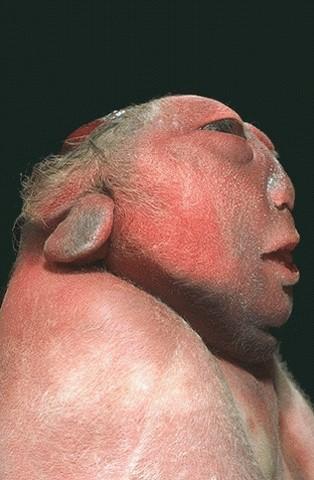
what is holoprosencephaly
failure of the prosencephalon to develop and separate
what is the prosencephalon
anterior/superior portion of the neural tube
what is wrong with this baby
holoprosencephaly
what is the limiting factor of the falx
corpus callosum
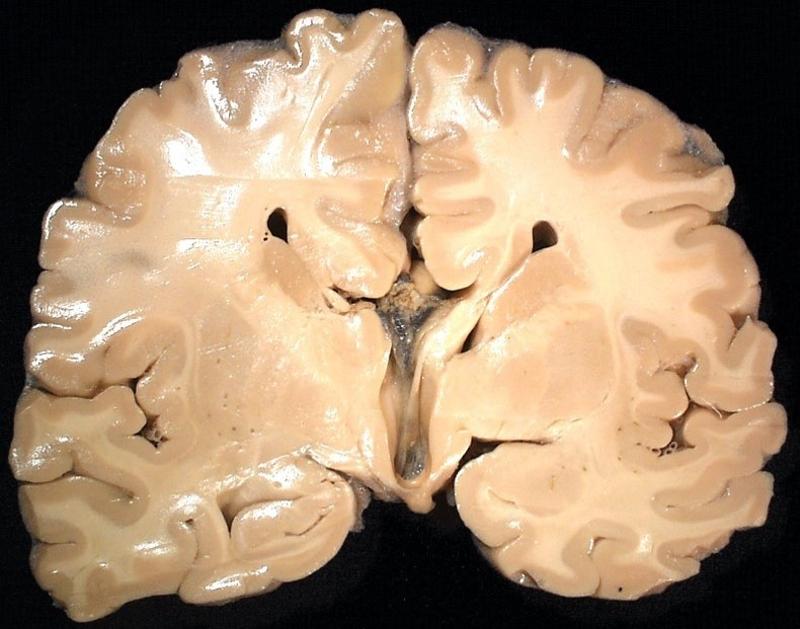
what is wrong with this brain
absent corpus callosum
what is the range of symptoms with an absent corpus callosum
mild or partial cases are asymptomatic, severe cases result in severe retardation or fatality
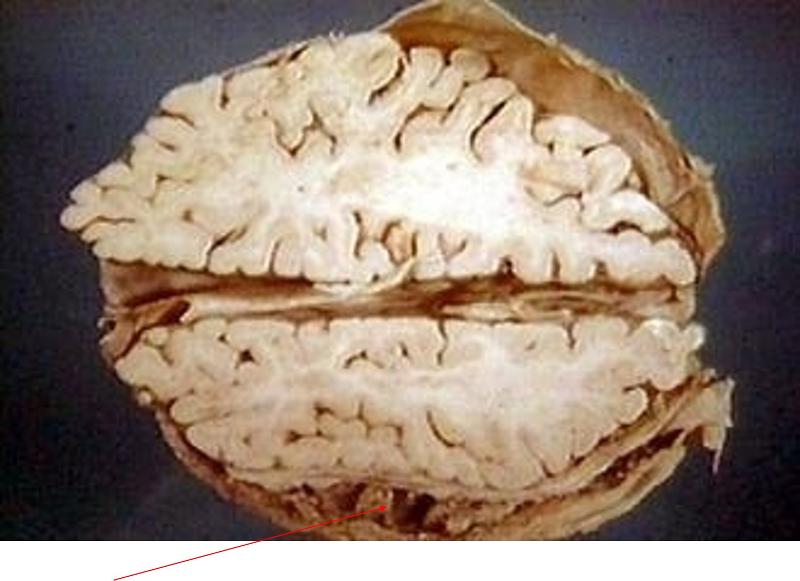
what is syrinx
dilation of the central canal of the spinal cord
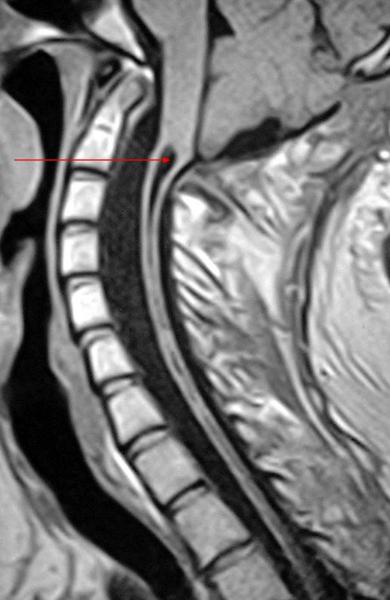
what is being pointed out
syrinx
what are some perinatal brain injuries
intraparenchymal hemorrhage
intraventricular hemorrhage
periventricular leukomalacia
cerebral palsy refers to nonprogressive diffuse cerebral pathology apparent at childbirth
can intracerebral hemorrhage extend intraparenchymally and vice versa
yep
what types of things can CNS trauma cause
skull fractures
parenchymal injuries
traumatic vascular injury
sequelae
spinal cord trauma
what are the brain traumas
contusion (bruise)
laceration (tear)
coup/contre coup
concussion
is a concussion clinical or pathological
clinical
what is the hallmark of contusion
hemorrhage
what are the types of skull fractures
hairline
depressed/displaced
what are skull fractures associated with
epidural hematoma
if there is contact but no skull fracture what is next on the list of thoughts
subdural hematoma
what do subarachnoid hematomas result from
some sort of arterial leak, no trauma
how does an intraparenchymal hemorrhage go
any way
how does an intraventricular hematoma transpire
no trauma, rare in adults, common in premies
what does the most superficial layer of the dura blend with
periosteum
what can subdural hematomas be related to
congenital aneurysms
where does a subarachnoid hemorrhage occur
big intracranial arteries
what 2 things commonly cause subarachnoid hemorrhage
hemorrhagic CVAs due to arterial wall rupture
ruptured aneursym
could HTN be a risk factor for subarachnoid hemorhage
yep
could intraparenchymal hemorrhage extend/dissect both ways if it is big enough
yes ventricular and subarachnoid
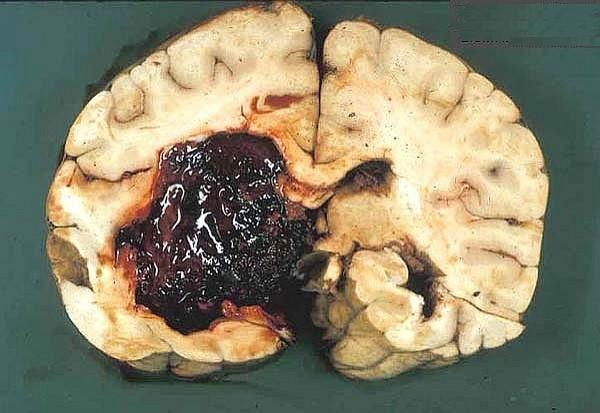
which way is this intraparenchymal hemorrhage dissecting
intraventricularly
could an intraventricular hemorrhage diseaect intraparenchymally
yes
what are the 3 main CNS trauma sequelae
hydrocephalus
dementia (punch drunk syndrome)
diffuse axonal injury
what is the most common CNS trauma sequelae
hydrocephalus
what is the more often sequelae of CNS trauma and what is it from
hydrocephalus from impaired reabsorption (hemorrhage that affected reabosrption parasagittally
is dementia a specific syndrome
no
what is difffuse axonal injury from
repeated trauma damaging white matter
what does spinal cord trauma parallel
brain patterns of injury (cellularly)
what is spinal cord trauma secondary to
spinal column displacement
what does the level of injury of the spinal cord mirror
motor loss (death, quadriplegia, paraplegia
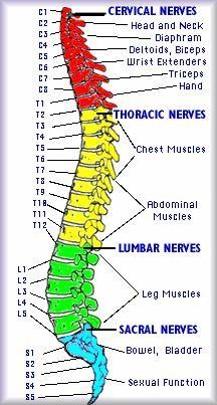
know this fucking chart
...
what are the cereebrovascular diseases usualyl called
stroke
what are the types of stroke
ischemic and hemorrhagic
what is another name for ischemic stroke
thrombotic
what is decreased in ischemic stroke
blood and O2
what happens in acute ischemic stroke
edema to neuronal microvacuolization to pyknosis to karyorrhexis to neutrophils
what happens in chronic ischemic stroke
MP to gliosis
what is hemorrhagic stroke due to usually
rupture of artery/aneurysm
what does the middle cerebral artery supply
lateral brain
what does the posterior cerebral artery supply
medial, some posterior and anterior
what does the anterior cerebral artery supply
medial, some posteiror and anterior
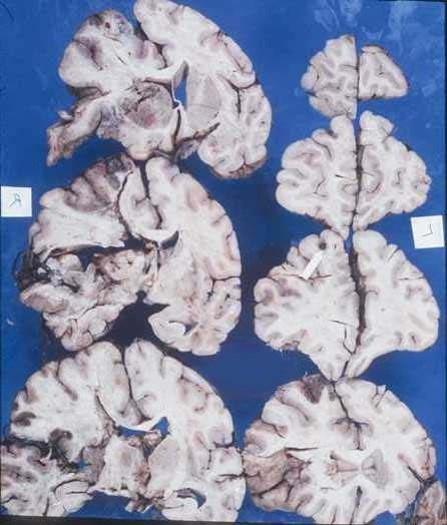
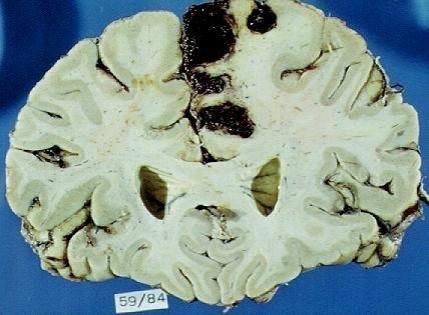
what has happened here
thrombotic MCA
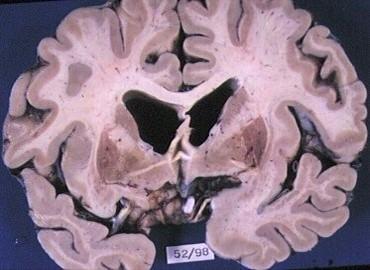
what has happened here
hemorrhagic ACA
what is the only exception in the brain to normal progression of inflammatory response
usually no fibrosis in the brain, gliosis
where would the CNS be sensitive to HTN

intracerebral area
basal ganglia region (lenticulostriate arteries of internal capsule and putamen)
what type of stroks would be more likely in a hypertensive issue
hemorrhagic
can edema be felt better than seen on gross brain
yep
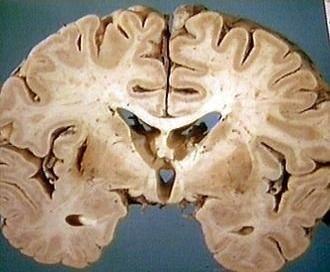
what type of infarct is this
lacunar infarct
are lacunar infarcts asymptomatic? why?
yes because of very small pinpoint size
what type of hemorrhage is this
slit hemorrhage
what usually ruptures in a subarachnoid hemorrhage
large intracerebral arteries which are the primary branches of the circle of willis
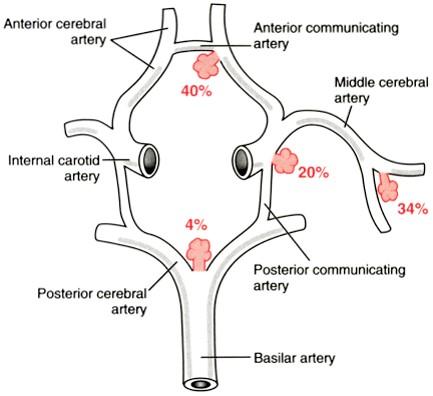
what are some causes of subarachnoid hemorrhage
congenital (berry aneurysm)
atherosclerotic (direct wall rupture)
what is young woman dropping dead instantly for not reason
berry aneurysm
are berry aneurysms or atherosclerotic aneurysms more common
athero by a LOT
where are the most common places for berry aneurysms
what are the types of hypertensive encephalopathy
acute
chronic
what are the symptoms of acute hypertensive encephalopathy
headaches
confusion
anxiety
convulsions
what are the symptoms of chronic hypertensive encephalopathy
dementia
gait disturbances
basal ganglia symptoms
what are some basal ganglia symptoms of hypertensive encephalopathy
tremors
athetosis
chorea
ballism
dystonia
what are some various CNS infections
acute meningitis
acute focal suppurative infections
chronic bacterial
viral fungal
what are the main infections of the CNS
meningitis
encephalitis
meningoencephilits
what causes meningitis (generally)
bacterial
what causes encephalitis (generally)
viral
what are the specific causes of meningitis
e. coli, strep b
HIB
n. meningitis
s. pneumo
what is sign of meningitis infection
PMNs in CSF, increased protein, reduced glucose
what particular viruses cause encephalitis
arboviruses
HSV
CMV
VZV
polio
rabies
HIV
what will be present in the virchow robbins spaces in encephalitis
lymphs and MPs
what is the big CNS invader when someone has HIV
toxoplasma
how will leptomeninges look for in CNS infection
cloudiness
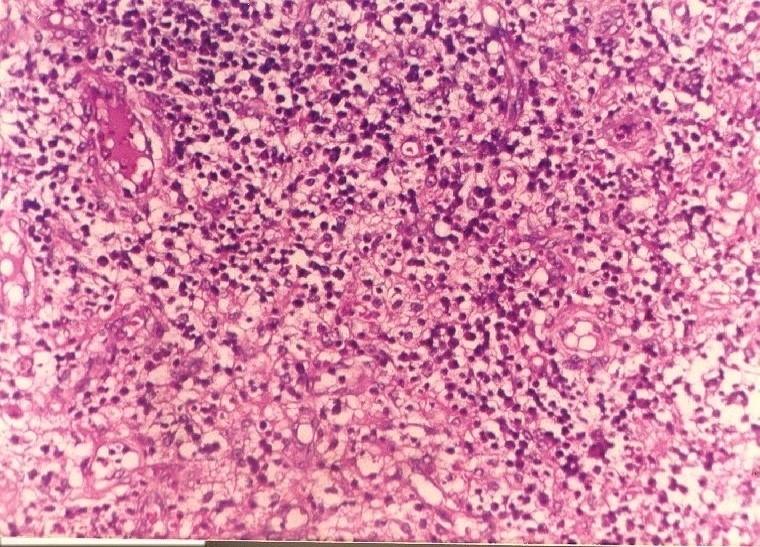
what are some acute focal suppurative CNS infections
cerebral abscesses
subdural empyema
extradural abscess
where can cerebral abscesses take effect
local (mastoiditis, sinusitis)
hematogenous (tooth extraction, sepsis)
staph, strep
fibrous capsule
what do subdural empyemas take placce in
sinusitis
where do extradural abscesses take place i n
osteomyelitis
what is shown here
abscesses with satellits
RIM SIGN
what is the difference between capsules or pseudocapsules
true capsules are lined with epithelium
whats all over this abscess
neutrophils
what is being pointed out here
subdural empyema
why are many epidural abscesses in the spinal cord secondary to surgery
bone trauma
what are the chronic bacterial meningoencephalitises
TB, brain and meninges
syphilis: gummas in brain
lyme disaes: neuro borrielosis
what is a gumma
large granuloma from syphillis
can large granulomas look like tumors?
yep: tuberculoma
what is going on here
NeuroBorreliosis: encephalitis BACTERIAL THIS TIM
why would encephlo-meningitis be a better term than meningo-encephalitis
viruses usually involve CNS parenchyma rather than meninges
what is th hallmark of viral encephalitis
perivascular lymphocytic cuffing
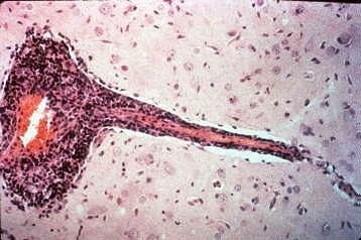
wahts going on here
viral encephaitis
what is bitemporal encephalitis until proven otherwise
HSV
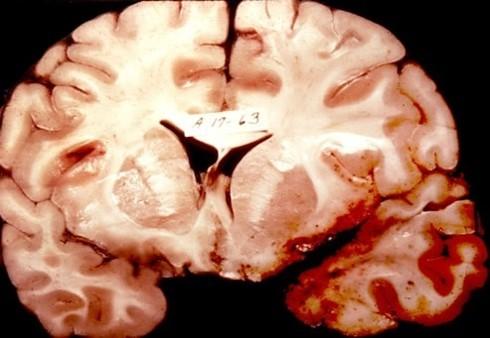
what is going on here
bitemporal encephalitis
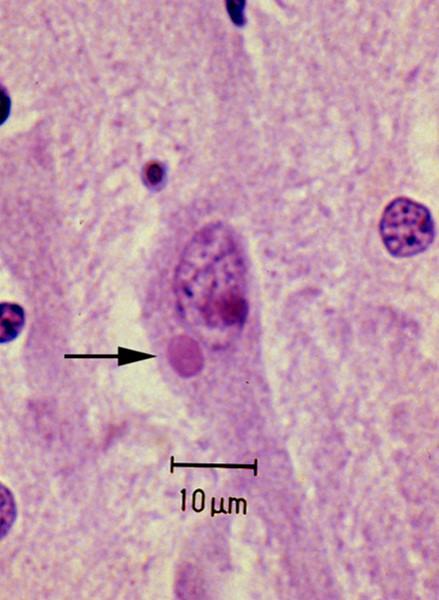
what is labeled by the arrow
eosinophilic negri body of rabies
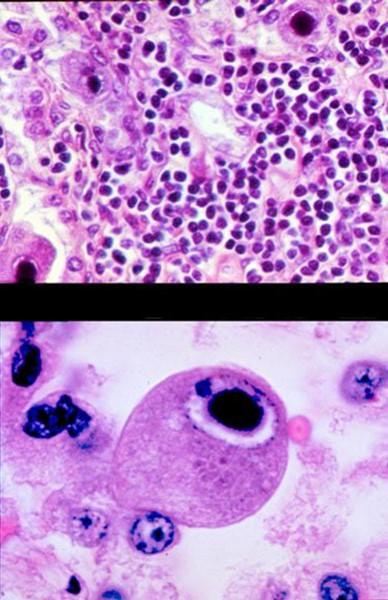
what is this shit
CMV basophilic inclusins
what if you see perivascular giant cells in white matter
HIV ENCEPHALITIS
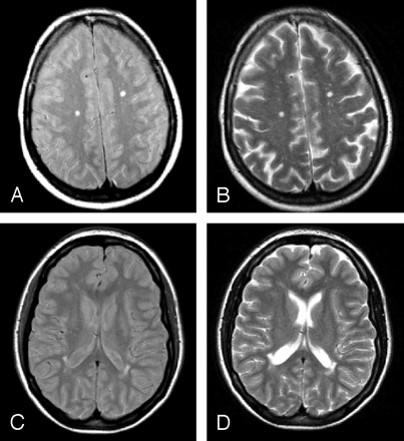
what is the cause of PML (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy)
JC polyoma virus
what does PML primarily affect
oligodendrocytes
what is the main feature of PML
demyelination
what is demyelination associated with
gliosis and edema
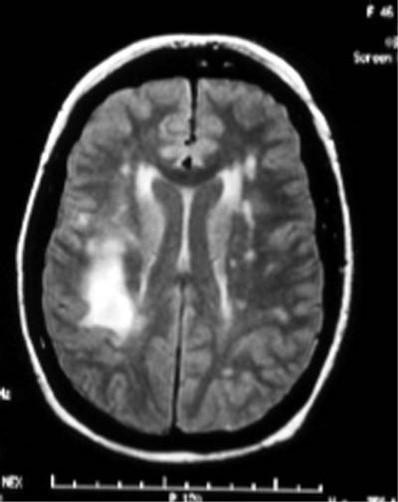
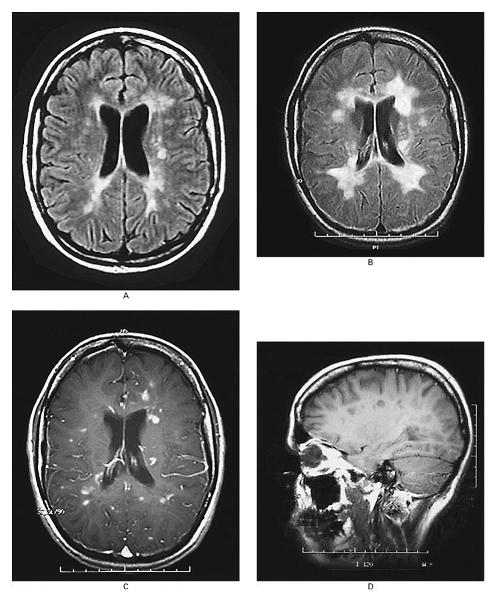
what is this on the MRI
demyelinization
what is gliosis associated with
demyelinazation and edema
what is edema associated with
demyelininzation and gliosis
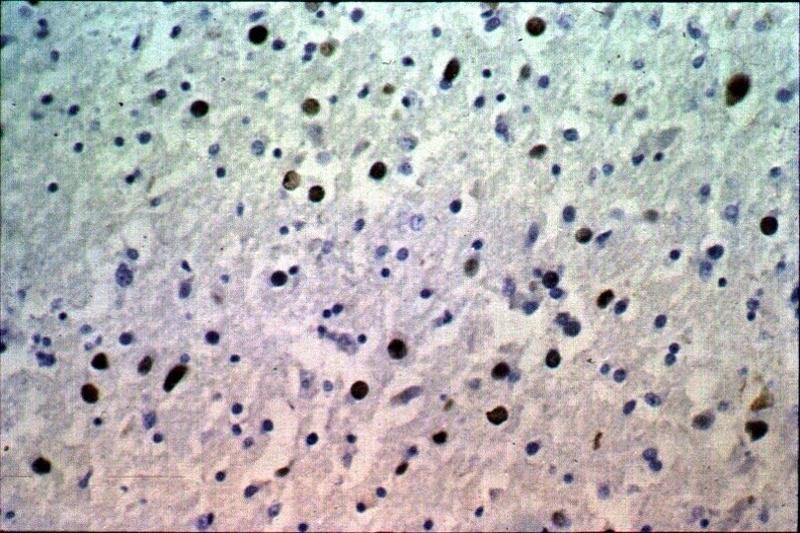
what is shown here
gliosis
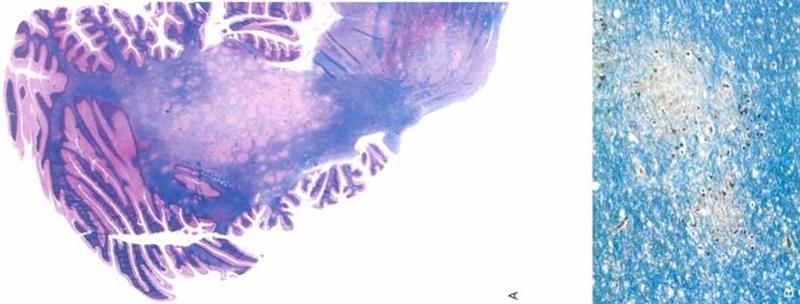
what is this
myelin/fat stain of PML: large area in middle with no myelin
what is subacute sclerosing panencephalitis associated with
measles virus
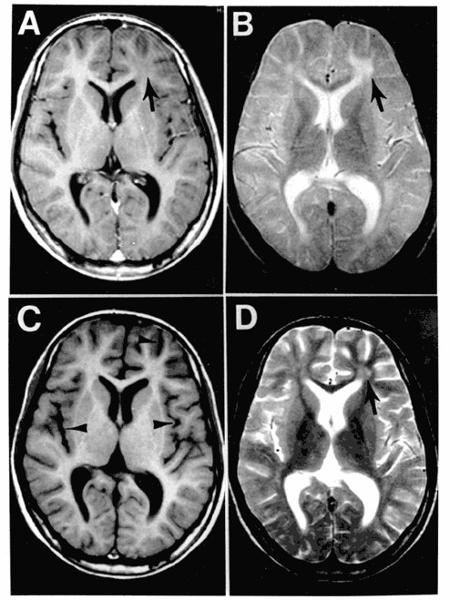
what happened here
subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
what are the fungal meningo-encephalities
cryptococcus
candida
aspergillus
mucor
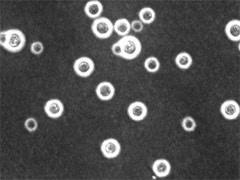
what type of stain is this
India ink
what are these microabscesses caused by
cryptococus
what simple fungal stain could you use for abnormal areas in the brain
PAS
what are the "other" things that can infect the CNS
malaria
toxoplasmosis
amebiasis
trypanosomes
rickettsiae
echinococcus
what are the prion diseases
creutzfeldt-jakob diseasee
gerstmann-straussler-schneinker syndrome
fatal familial insomnia
kuru
scrapie
mink transmissible encephalopathy
chronic wasting disease
BSE
what are some common features of prion diseases
infectious agents with no DNA
lead to dementia
prion protein accumulation
spongiform changes in neurons and glia
transmissble, fatal no treatment
why are prion diseases called spongiform
due to spaces between the cells caused by conformational changes
what is prion replication due to
protein undergoes conformational change to induce neighboring proteins to become like it
are prion proteins normally found in humans
yes
what chromosome are prion proteins on
20
what is this a dead giveaway of
spongiform (prion disease)
is CJD epidemic
no
what happens in CJD
rapidly progressive dementia
cerebelar ataxia
what is affected in CJD
grey matter
what are some of the demyelinating disaess
MS
MS variants: Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, acute necrotizing hemorrhagic encephalomyelitis
if not for edema associated with demyelination, would the plaques be seen on MRI
no
what is the cause of MS
nobody knows
does MS affect females or males more
females
when does MS usually take course
30-40
what is MS a disease against
white matter: plaquing of the nerves
what is increased in the CSF with MS
CSF gamma globulin/oligoclonal bands
what does MS often present with
visual probelms
what is happeneing here
demyelination: MS
what is stained blue here
myelinated white matter
grossly, what would plaques look like in contrast to better myelinated areas
less white
what would plaques look like microscopicallly
demyelination, edema, gliosis, preseravtion of nerve fibers, inflammtory cells
what are some degenerative disaeses of the CNS
cortex
basal ganglia and brain stem
spinocerebellar
motor neurons
what are CNS degenerative disaess of the cortex
dementias
what are CNS degenerative diseass of the BG and brainstem
parkinsonian diseass
what are CNS degenerative diseass of the spinocerebellar tract
ataxias
what are CNS degenerative diseass of the motor neurons
muscle atrophy
what are some cortical degenerative diseas
alzheimer's diseas
frontotemporal dimentia
pick disease
progressive supranuclear palsy
corticobasal degen
vascular dimentias
what is the most common CNS cortical degenerative diseass
alzheimer's
what are most of the dementias
tauopathies
what happens to the cortex (grey matter) in alzhemiers
atropphy
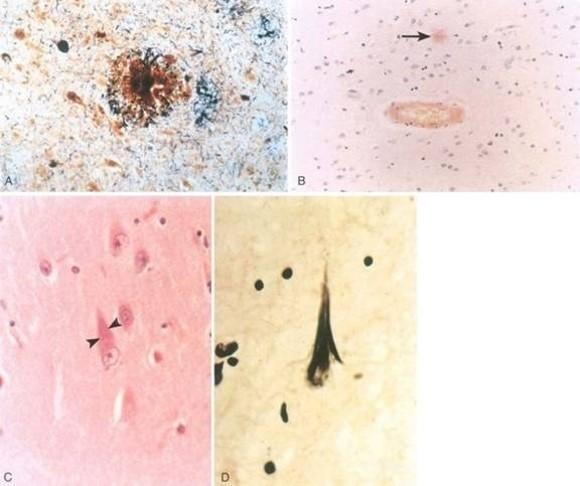
what is present in alzheimers
neuritic plaques
neurofibrillary tangles
amyloids
are neuritic plaques just like MS's plaques
NO
are the sulci or gyri prominent in cortical atrophy
cortical loss
what is being shown here
plaques and tangles and beta amyloid of alzhemier's sieas
what is aneuritic plaque
cluster of nerve fibers surrounding a substance that ends up being beta amyloid
what is a tangle
phosphorylated MTs around indivdiual neurons
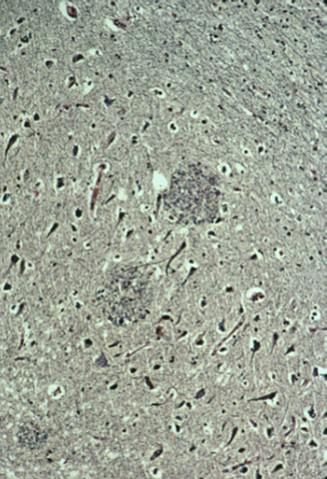
what is this
neuritic plaque
what type of stain can be used to find beta amyloid
immunohistochemical stain
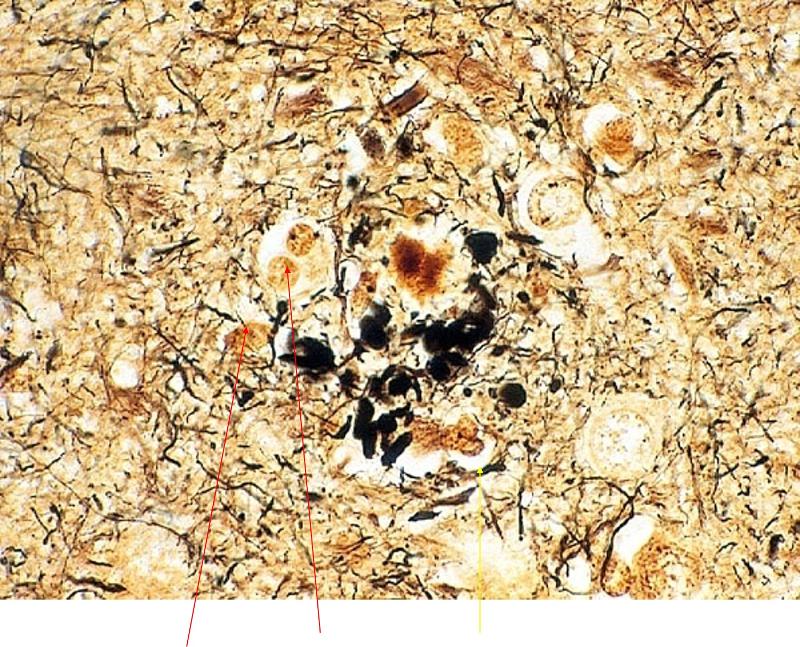
what is ponted out in red and yelow here
red: plaques
yellow: tangles
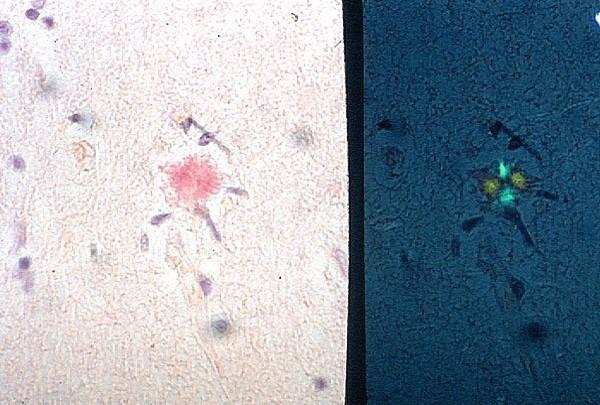
what stains are used here
congo red on left
congo red with polarized light on right
is there alpha amyloid
yes with Igproliferative disaess like myelomas

what is being ponited out here
neurons with tangles displacing nucleus
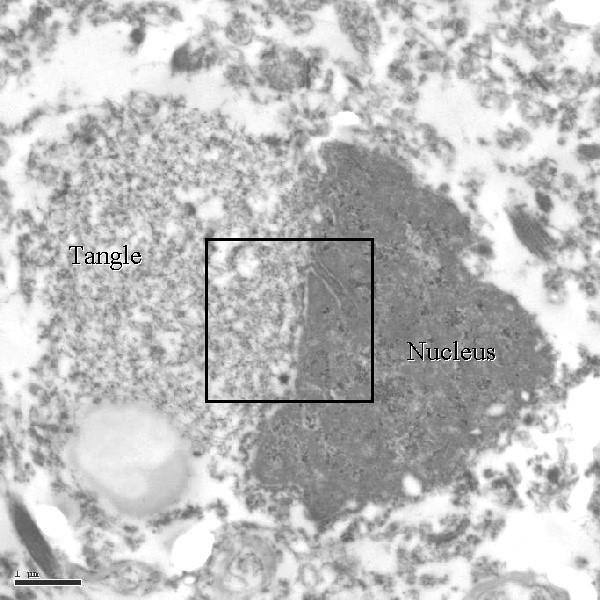
...
what is a tangle
hyperphosphorylation of a neuron microtubule, causing it to precipitate
what are the "other" cortical dementias
tau gene proteins/tauopathies
frontotmeporal
pick disaese (lobar atrophy)
progressive supranuclear palsy
corticobasal degeneration
vascular dementia
what are most cortical dementias known as
tauopathies
what is vascular dementia associated with
multiple infarcts: lacunar, cortical, embolic
what is the second commonest form of dimentia after alzheimer
vascular dimentia
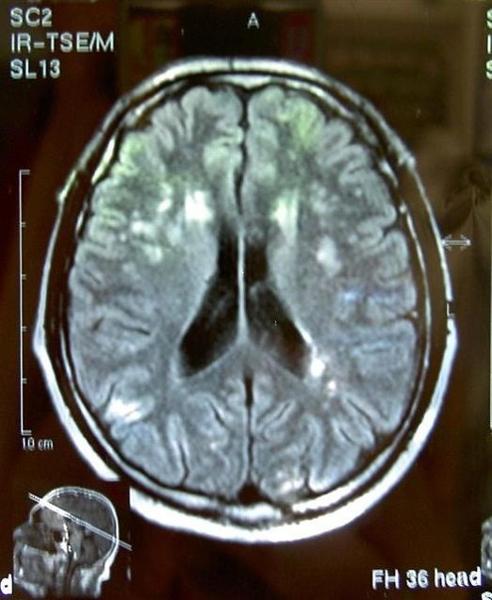
what is this and how do we know
MID because MS is purely white matter loss
what are the CNS degenerative diseases in the basal ganglia and brainstem
parkinsonism
parkinson diseas
multiple system atrophy
huntington disaes
is parkinsonism a clinical syndrome or a diseas
clinical syndrome
what are the featurs of parkinson syndrome
diminished facial expression
stooped posture
slowness of voluntary movement
festinating gait (short, fast)
rigidity
pillrolling tremor
what is the clinical finding of parkinsonism
substantia nigra pathologic state
what are some other substantia nigra diseass
parkinson diseas
multiple system atrophy
postencephalic parkinsonism
progressive supranuclear palsy, cortical basilar degeneration
what is the key idea in parkinsonsim
not enough dopamine
where is there pallor in parkinson's disease
substantia nigra and locus ceruleus
LEWY BODIES ALSO present
what are lewy bodies
alpha-synuclien protein
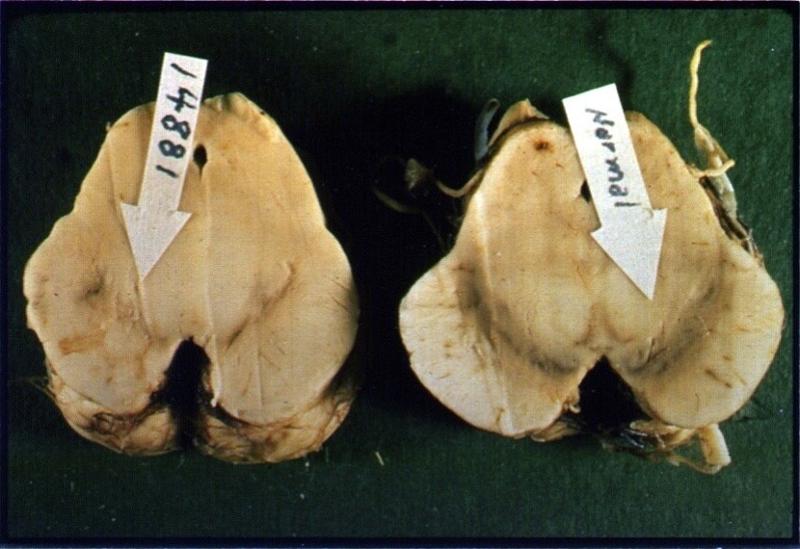
what happened here
parkinson's diseas as seen in SN
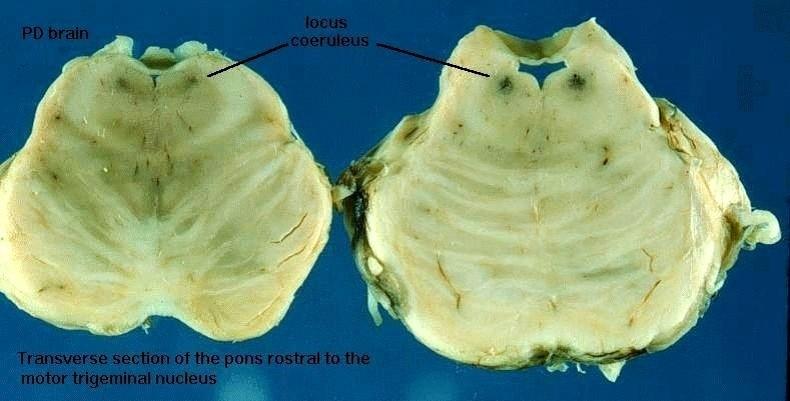
what happened here
parkinsons diseas as seen in LC

which patient has parkinson's
right becuase of decreased dopamine
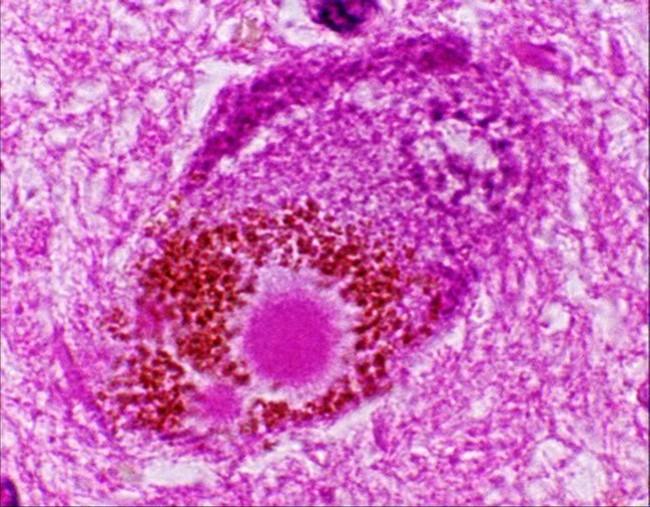
what is this and what is it from (disease)
lewy body
parkinson's
along iwth the parkinson symptoms, what does parkinsons disaese involve
progressive symptoms
hallucinations
dementia
symptomatic response to Ldopa
what happens in multiple system atrophy
wide spectrum of diseasses
glial cytoplasmic inclusions in oligodendrocytes (alpha synuclein)
what are the clinical symptoms of multiple system atrophy
parkinsonism
autonomic dysfunction

what is this
alpha synuclein stains
what type of disease is Huntingon's
genetic
what happens in Huntingon's
progressive motor loss and dementia
chorea and jerky movements
fatal
atrophy of basal ganglia (corpus striatum
ventricular enlargment
what types of disesases are spinocerebellar degenerations
ataxias
what are some spinocerebellar degenerations
spinocerebellar ataxias
Friedrich ataxia
ataxia telangiectasia
what are some motor neuron diseass
ALS
bulbospinal atrophy (kennedy syndrome)
spinal muscular atrophy
what is the etiology of ALS
unknown
what is ALS
progressive muscle atrophy due to motor neuron loss
what does ALS progress from
hand weaknes to diaphragm
where does ALS take place
anteiror horn cells reduece and gliotic
demyelination in corticospinal tracts
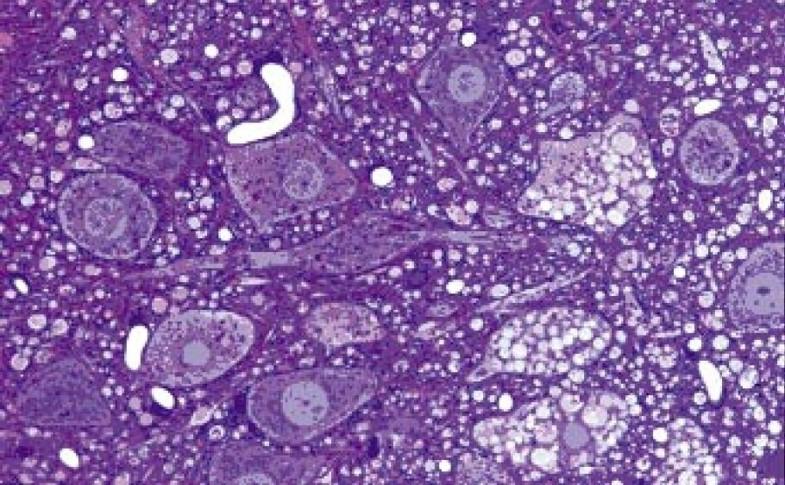
what is this a pic of
ALS
what are the categories of genetic metabolic diseass
neuronal storage diseases
leukodystrophies
mitochondrial encephalitis
what trait do the neuronal storage diseases have
classical autosomal recessive enzyme deficiencies
whta do the leukodystrophies present
abnormal myelin synthesis
what happens with mitochondrial encephalopathies
mitochondrial gene mutations
what are the major leukodystrophies
Krabbe
metachromatic
adreno
pelizaeus-merzbacher
canavan
what are leukodystorphies
a group of disorders characterized by progressive degeneration of the myelinated white matter of the brain
what are leukodystrophies caused by
imperfect growth/development of myelin due to genetic defects in the enzymes required for proper myelin production and maintenance
what are the acquired toxic/metabolic CNS diseases
vitamin B1 def (Wernicke-Korsakoff)
vitamin B12 def (vibratory sense)
diabetes (increase/decreased glucose)
hepatic failure (NH4)
CO (cortex, hippocampus, purkinje cells)
CH3-OH (retinal ganglion cells)
CH3-CH2-OH (acute/chronic, direct/nutritional)
radiation (brain most resistant to radiation therapy)
chemo (methtrexate+radiation)
what is the showing of wernicke korsakoff syndrome
hemorrhagic mamillary bodies
what column will demyelinate in B12 deficiency
posterior column (subacute combined degeneration)
what is earliest clinical symptom of Wernicke Korsakoff
loss of vibratory sense
what are some CNS tumors
gliomas of astrocytes, oligodendrogliomas, ependymomas
neuroblastomas
medulloblastomas
meningiomas
lymphomas
metastatic
what do ependymal cells look like
glandular
what do oligodendrocytes have around them
halos
what do meningiomas have the constistency of
super ball
are primary lymphomas of the brain rare? when are they common
yes
AIDS most common
if there is just one lesion in the brain, what is the probablity it is primary
50/50
if there is a nonprimary tumor in the brain, where did it pprobably come from
lung
what are the symptoms of CNS tumors
headache
vomiting
mental changes
motor problems
seizures
increased IC pressure
any localizting CNS abnormality
do CNS tumors present abruptly
no very subtle, only appear after tumor is sizeable
what is the routine workup of CNS tumors
history
physcial
neurologic exam
LP (cytology)
CT
MRI
brain angiography
biopsy
what are the questions to be asked of a CNS tuomor
benign or malignant
primary or met
location
age
x ray density and MRI signals
calcifications
vascularity
necrosis
liquefaction
edema
compression of neighbors
how old are people that normally get CNS tumors
younger
what do certain CNS tumors have an abundant amount of
Ca
what do you do an angiogram for in CNS tumors
vascularity determinatino (how much this thing has grown)
gliosis vs. glioma, how to tell
age
white vs grey matter
gross texture
vascularity
mitoses
N/C, pleomorhpism, hyperchromasia
calcifications
cysts
satellitosis
delineation
what is a good indication of malignancy
vascularity and necrosis in high amounts usually indicate malignancy
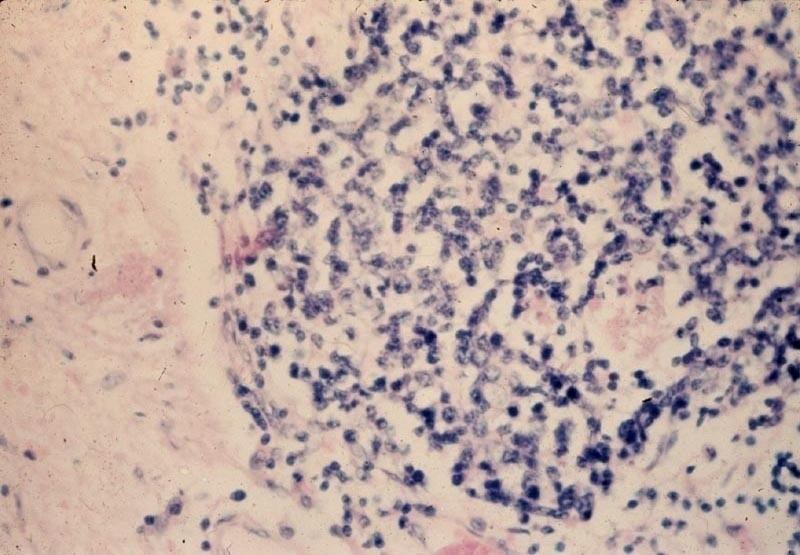
gliiosis or glioma
could be either one
what is this
glioma, intermediate grade
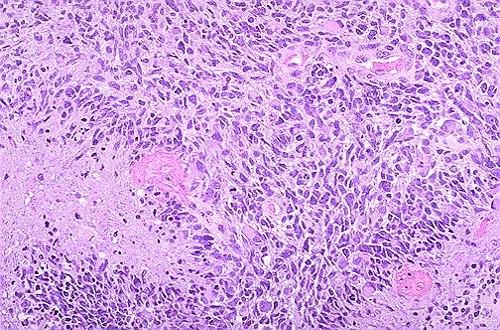
what is this
glioma high grade
what is needed for the diagnosis of a high grade glioma
necrosis
what are the higher grade gliomas called
gliobastome multiforme
what is often seen in GBM
perivascular growth pattern
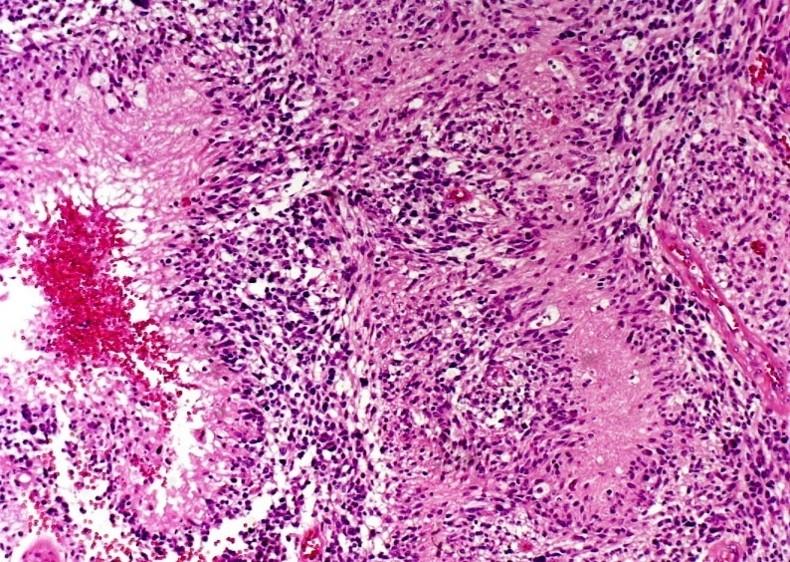
what is this
GBM
palisading and necrosis
what is the sign of rapid growth in a tumor
central necrosis
why would there be central necrosis in a tumor
outgrows blood supply and liquiefies centrally, like abscess
what is this
central necrosis
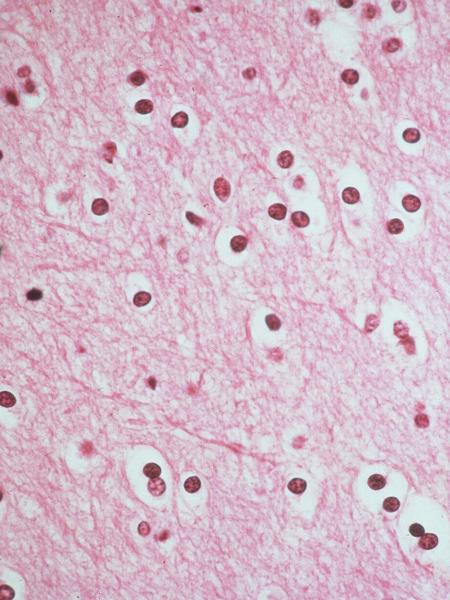
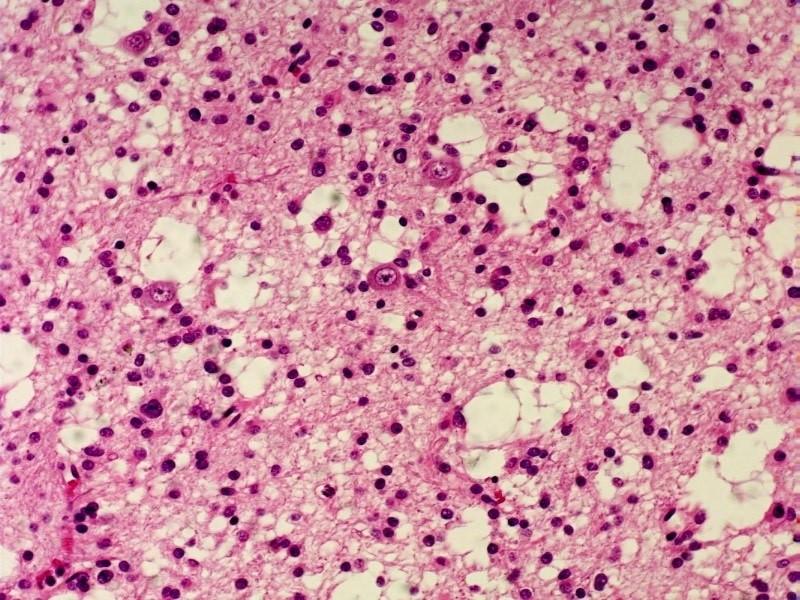
what kinds of glial cells are these
oligodendrocytes
what is this
oligodendroglioma
where do oligodendroglomas frequently occur
frontal or temporal lobes
what are oligodendroglioma classifications
low or high grade
who are oligodendrogliomas commmon in
men and women 20-40, but also children
are oligodendrogliomas more common in men or wome
men
how many of brain tumors are oligodendrogliomas
2%
what chromosome losses are associated with oligodendrogliomas
1p or 19q
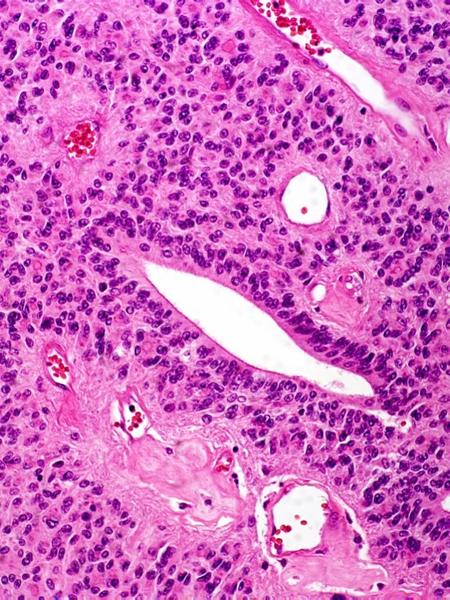
what is this
ependymomas
would a choroid plexus tumor be a type of ependymoma
yep
would an ependymoma result in an overproduction of CSF
yep
are ependymomas diffuse in the brain
no, localized
where do ependymomas develop from
cells that line the hollow cavities at bottom of brian and canal containing the spinal cord
do ependymomas grow slow or fast
either
where are ependymomas located
ventricles
where do ependymomas extend
spinal cord
what can ependymomas do
block ventricles causing hydrocephalus
what does occurrence peak in ependymomas
5 and 34
how many brain cancer are ependymomas
2%
what do ependymomas look most like
adenocarcinoma

what type of cancer is this
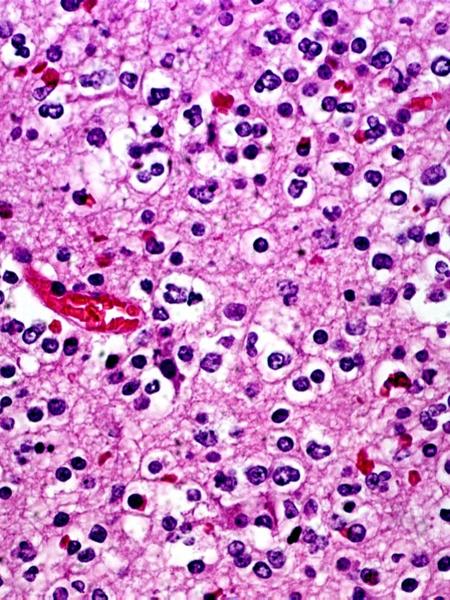
neuroblastoma (rosettes)
what is any midline cerebellum tumor in a child until proven otherwise
medulloblastoma
are medulloblastomas PNET tumors
yes
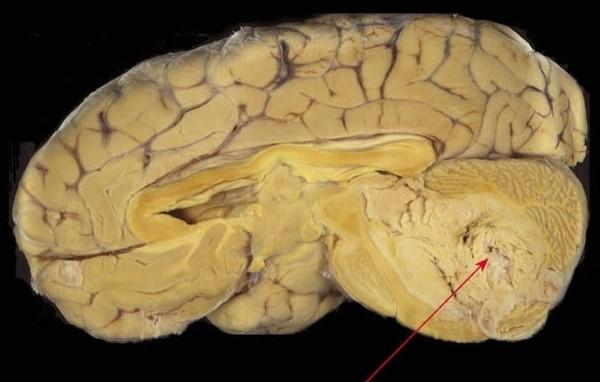
what is this
medulloblastoma
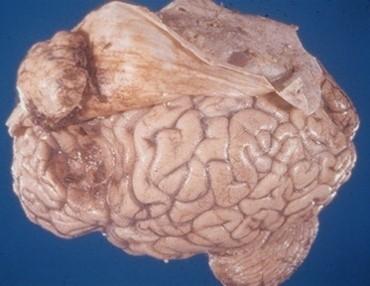
where do meningiomas occur
where dura is
are meningiomas vascular
yes
are meningtiomas benign
yes but can be invasive
what do meningiomas invade
areas adjacent to dura, parasagittal, falx, tentorium, venous sinuses
what are meningiomas like
well defined like a superball
what are often meningiomas have
psammoma bodies
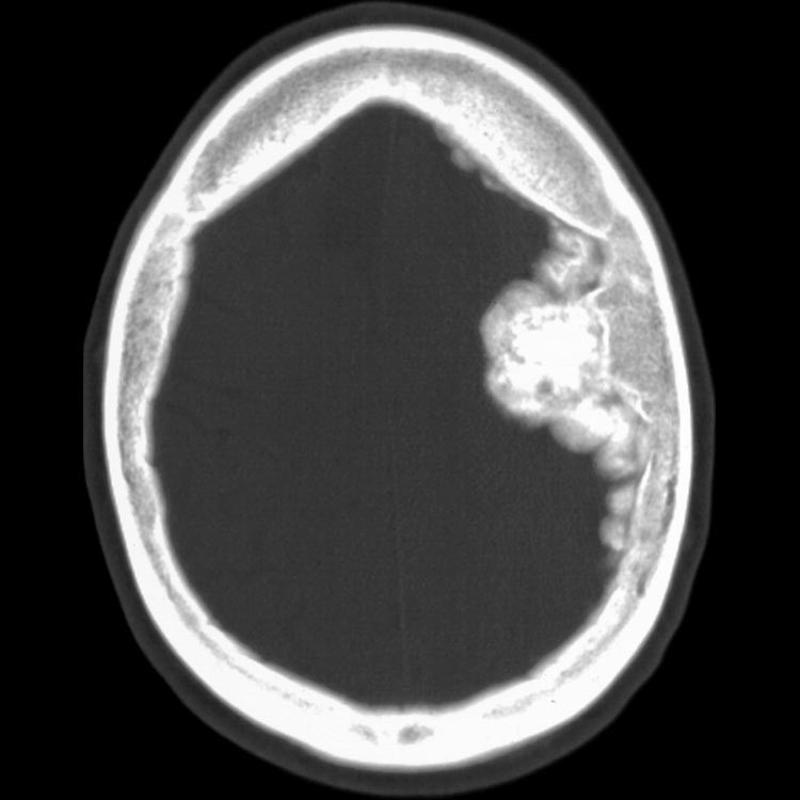
what is part of this meningioma denser than
bone
what is this
meningioma
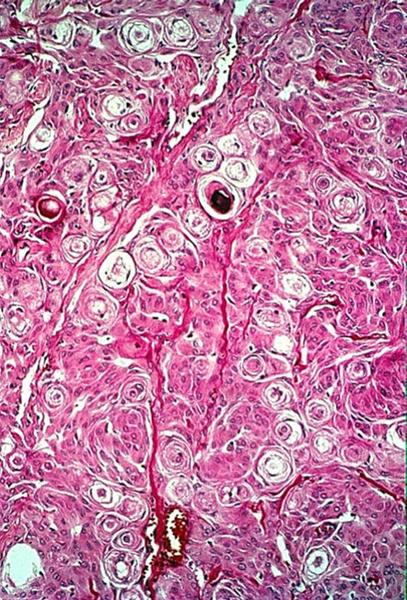
other than meningiomas what are psammoma bodies diagnostic of
papillary carcinomas
what CNS diseases are common in AIDS
toxoplasmosis
lymphomas
encephalitis
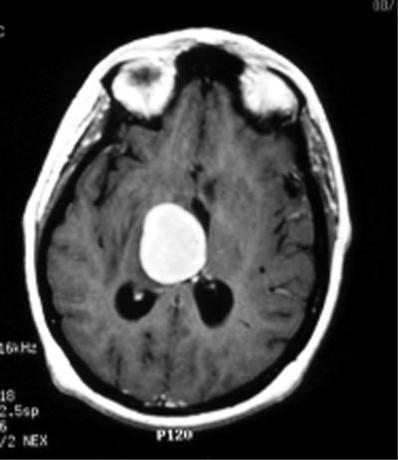
what is this
toxoplasmoma
what are the metastatic CNS tumors that go to the brain
lung
breast
melanoma
kidney
GI
is a solitary brain mass more likely to be metastatic or primary
same odds
what are the paraneoplastic syndromes
small cell, lung
lymphomas
breast cancer
purkinje cell degen
encephalitis, limbic system
sensory neurodegen (DRG)
eye movement disorders
what are the familial CNS tumor syndromes
NF1 (neurofibromas and gliomas)
NF2 (schwannomas and meningiomas)
tuberous sclerosis (CNS and somatic hamartomas)
Von hippel lindau (CNS hemangioblastomas, chiefly cerebellar)