EN1H-Biological systems use free energy based on empirical data that all organisms require a constant energy input. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can be neither created nor destroyed. For living organisms, which of the following statements is an important consequence of this first law?
The organism must ultimately obtain all the necessary energy for life from its environment.
EN1H-The synthesis of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation, using the energy released by movement of protons across the membrane down their electrochemical gradient, is an example of ____.
an endergonic reaction coupled to an exergonic reaction
EN1H-Why is ATP an important molecule in metabolism?
It provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
EN1H-Which of the following statements is representative of the second law of thermodynamics?
Cells require a constant input of energy to maintain their high level of organization.
EN1I-The process of photosynthesis probably originated ____.
in prokaryotes
EN1I-Which of the following sequences correctly represents the flow of electrons during photosynthesis?
H2O to NADPH to Calvin-Benson cycle
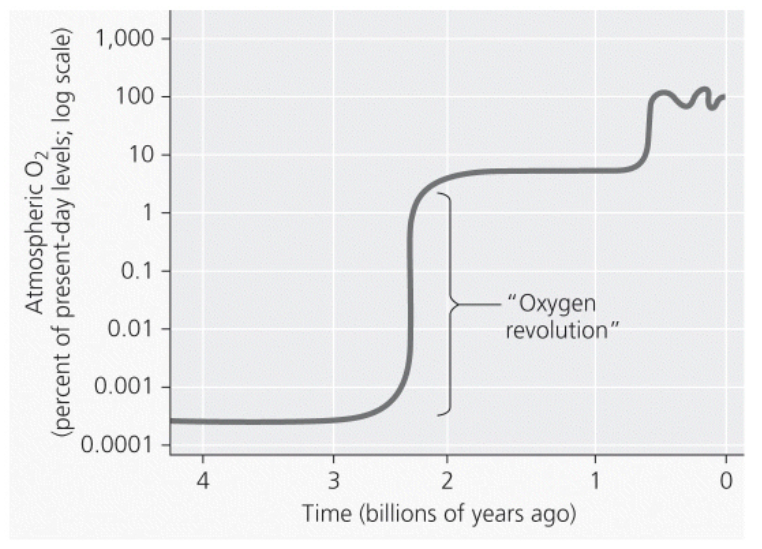
EN1I-The gradual rise in global oxygen concentrations is believed to have occurred as a result of early photosynthetic bacteria and then an “oxygen revolution” arose as photosynthetic eukaryotes evolved. Which type of data could be used to justify the graph shown here?
Measurement of bands of iron in sedimentary rock from dissolved iron precipitating as rust due to increased oxygen.
EN1I-Which of the following are products of the light reactions of photosynthesis that are utilized in the Calvin-Benson cycle?
ATP and NADPH
EN1J-If photosynthesizing green algae are provided with CO2 containing heavy oxygen (18O), later analysis will show that all of the following molecules produced by the algae contain 18O EXCEPT ____.
O2
EN1J-As electrons are passed through the system of electron carriers associated with photosystem II, they lose energy. What happens to this energy?
It is used to establish and maintain a proton gradient.
EN1J-Which process is most directly driven by light energy?
removal of electrons from chlorophyll pigment molecules
EN1J-Some photosynthetic organisms contain chloroplasts that lack photosystem II, yet are able to survive. The best way to detect the lack of photosystem II in these organisms would be to ____.
test for the release of O2 in the presence of light
Use the following information to answer the question below.
In the presence of oxygen, the three-carbon compound
pyruvate can be catabolized in the citric acid cycle. First, however,
the pyruvate (1) loses a carbon, which is given off as a molecule of
CO2, (2) is oxidized to form a two-carbon compound called
acetate, and (3) is bonded to coenzyme A.
EN1K-Which of the following events takes place in the electron
transport chain?
the extraction of energy from high-energy electrons remaining from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
EN1K-When hydrogen ions are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space, the result is the ____.
creation of a proton-motive force
EN1K-Why is glycolysis considered to be one of the first metabolic pathways to have evolved?
It does not involve organelles or specialized structures, does not require oxygen, and is present in most organisms.
EN1K-In mitochondria, chemiosmosis moves protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space, whereas in chloroplasts, chemiosmosis moves protons from the ____.
stroma to the thylakoid space
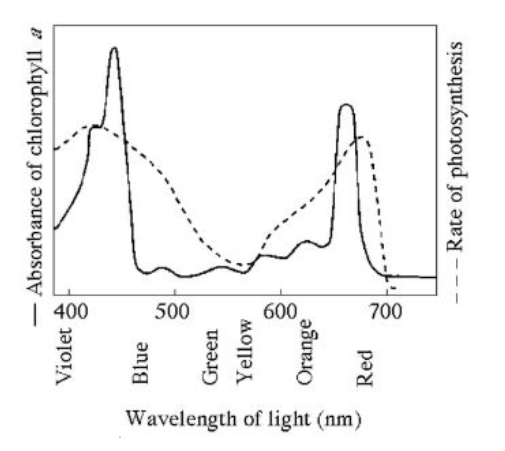
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
S3A-The figure shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll
a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis (dashed line).
Why are they different (meaning the peaks and valleys are not a
perfect match)?
Other pigments absorb light in addition to chlorophyll a.
S3A-Why are there several structurally different pigments in the reaction centers of photosystems?
This arrangement enables the plant to absorb light energy of a variety of wavelengths.
S3A-Why are C4 plants able to photosynthesize with no apparent photorespiration?
They use PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO2.
S3A-Compared to C3 plants, C4 plants ____.
can continue to fix CO2 even at lower CO2 concentrations and higher oxygen concentrations
S1F-In a plant cell, where are the ATP synthase complexes located?
thylakoid membrane and inner mitochondrial membrane
S1F-In mitochondria, chemiosmosis moves protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space, whereas in chloroplasts, chemiosmosis moves protons from the ____.
stroma to the thylakoid space
S1F-Which of the following are directly associated with photosystem I?
receiving electrons from the thylakoid membrane electron transport chain
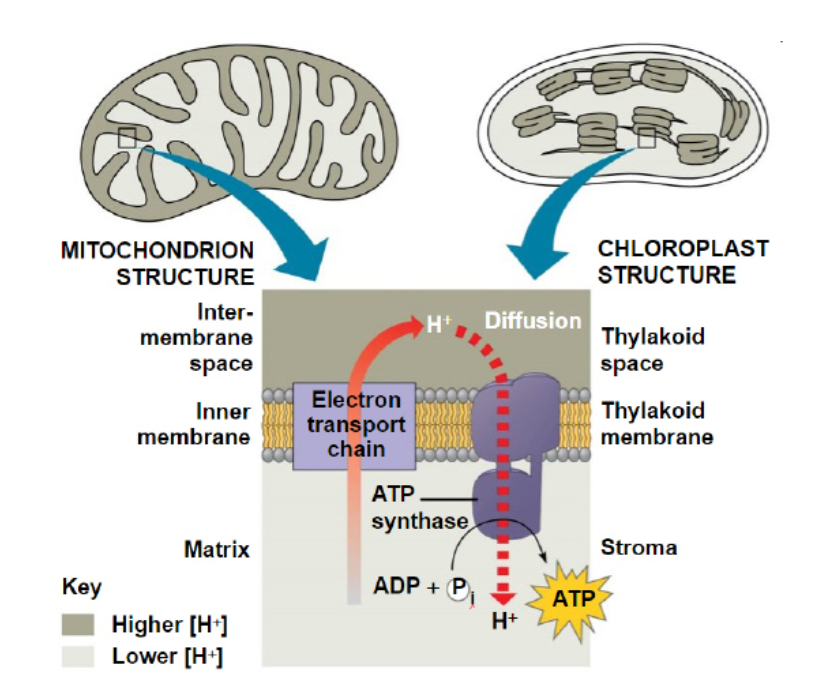
S1F - Identify a structural feature of the mitochondrion that allow organisms to capture, store, and use energy.
Electron transport and ATP synthesis occur on the inner mitochondrial membrane.
EV1B - Which of the following is the strongest evidence supporting the endosymbiont hypothesis?
Mitochondria have their own DNA and divide independently of the cell.
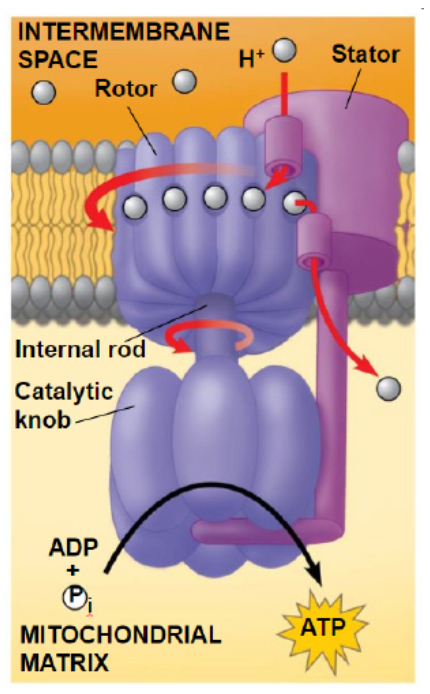
EV1B-Prokaryotes produce ATP by generating proton gradients across their plasma membrane. A similar process is observed in mitochondria. This would suggest
Membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria evolved from previous free-living prokaryotic cells via endosymbiosis.

EV1B-Identify evidence from the figure above that support the claim endosymbiosis of previously free-living prokaryotic cells resulted in membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondrion and chloroplast.
Both organelles possess an inner and outer membrane.
EV1B - Which of the following best supports the statement that mitochondria are descendants of endosymbiotic bacteria-like cells?
Mitochondria and bacteria possess similar ribosomes and DNA.
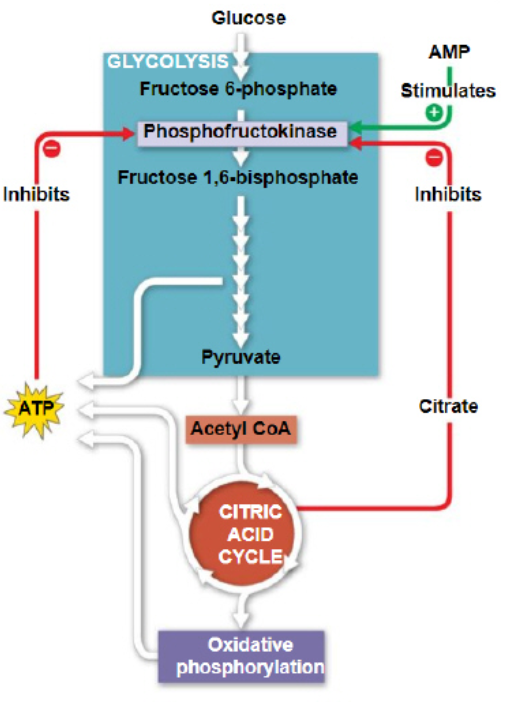
EN3B-Negative feedback mechanisms maintain homeostasis for a particular condition by regulating physiological processes. These processes operate at the molecular and cellular levels. Based on the model of cellular respiration depicted above,
High levels of ATP and citrate promote the allosteric inhibition of phosphofructokinase.
EN3B-Glycolysis is active when cellular energy levels are ____; the regulatory enzyme, phosphofructokinase, is ____ by ATP.
low; inhibited

EN3B-Explain the consequence of high levels of ATP on the production of pyruvate.
Negative feedback mechanisms will decrease the production of pyruvate.
EN3B-High levels of citric acid inhibit the enzyme phosphofructokinase, a key enzyme in glycolysis. Citric acid binds to the enzyme at a different location from the active site. This is an example of ____.
allosteric regulation
EN2K-Besides turning enzymes on or off, what other means does a cell use to control enzymatic activity?
localization of enzymes into specific organelles or membranes

EN2L-Explain how the inner membrane of the mitochondrion and thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast contribute to the proper functioning of the cell.
Both membranes are involved in the formation of proton gradients used to power ATP synthesis by ATP synthase.
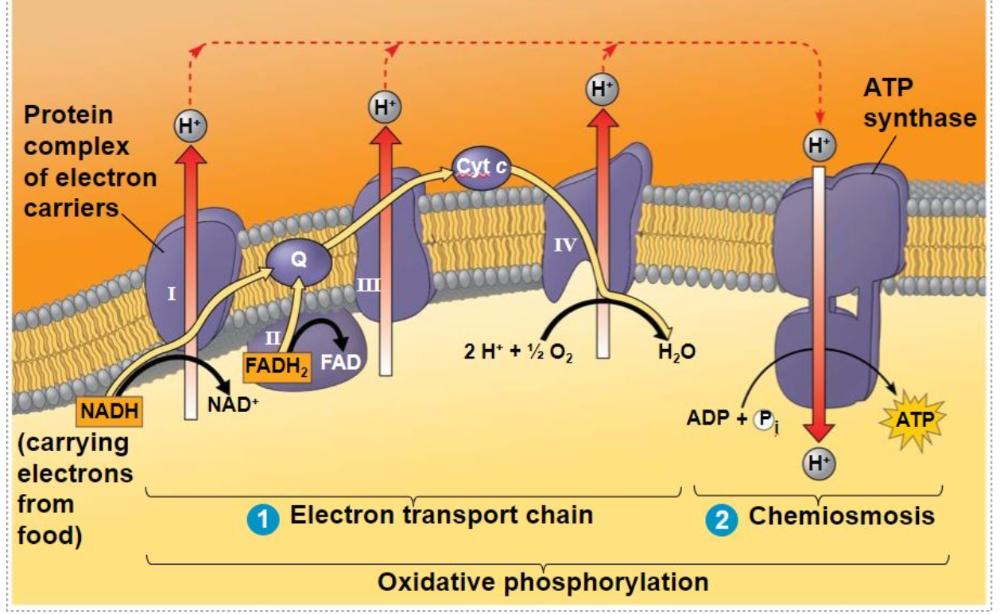
EN2L - Researchers working on metabolic disorders discover natural compounds that alter the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Explain how changing concentrations of these natural compounds inside muscle cells might affect the metabolic rate of an organism.
If the compouds increase the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membrane, the metabolic rate will increase.
EN2L-In liver cells, the inner mitochondrial membranes are about five times the area of the outer mitochondrial membranes. What purpose must this serve?
It increases the surface for oxidative phosphorylation.
EN1L-Even though plants cells photosynthesize, they still use their mitochondria for oxidation of pyruvate. This will occur in ____.
all cells all the time
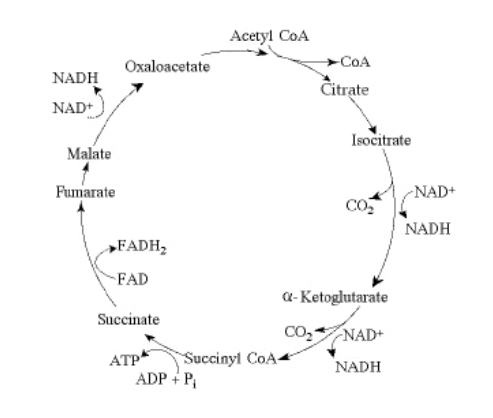
The citric acid cycle.
EN1L-If pyruvate oxidation is blocked, what will happen to the
levels of oxaloacetate and citrate in the citric acid cycle shown in
the accompanying figure?
Oxaloacetate will accumulate and citrate will decrease.
EN1L-Fatty acids usually have an even number of carbons in their structures. They are catabolized by a process called beta-oxidation. The end products of the metabolic pathway are acetyl groups of acetyl CoA molecules. These acetyl groups ____.
directly enter the citric acid cycle
EN1L-A young dog has never had much energy. He is brought to a veterinarian for help and she decides to conduct several diagnostic tests. She discovers that the dog's mitochondria can use only fatty acids and amino acids for respiration, and his cells produce more lactate than normal. Of the following, which is the best explanation of the dog's condition?
His mitochondria lack the transport protein that moves pyruvate across the outer mitochondrial membrane.