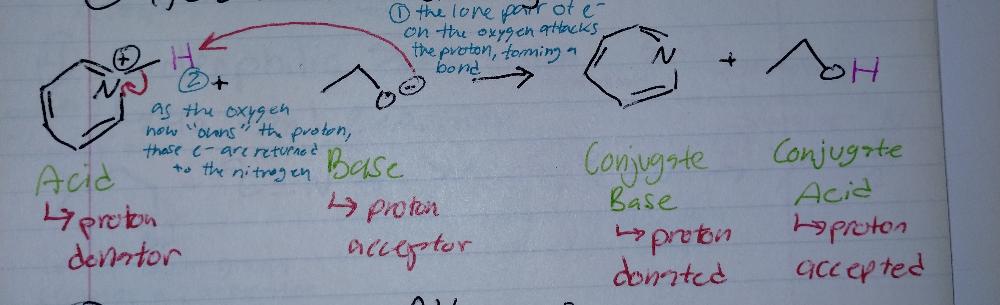
Acid-Base Reaction
ELECTROPHILIC Addition to Alkenes
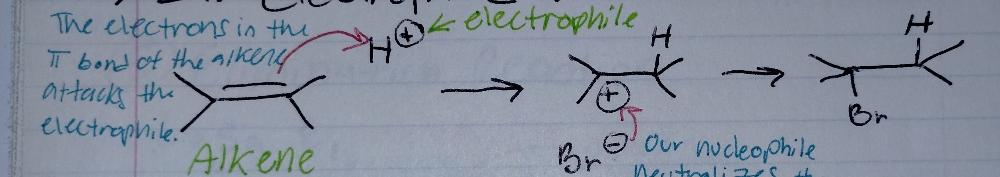
what is an alkene? H2C = CH2
- a double bond between carbons
what is an electrophile?
- an electron DEFICIENT species/molecule
NUCLEOPHILIC Addition to Alkenes
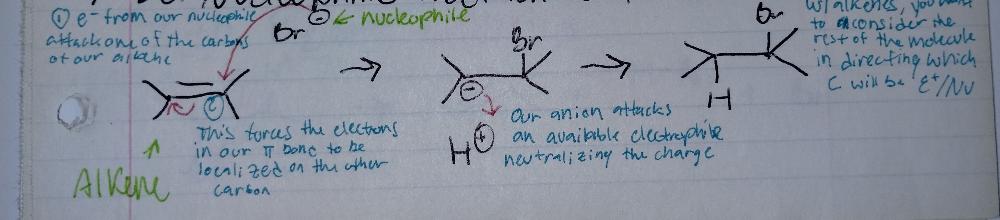
what is a nucleophile? ex) halides (I, Br, Cl)
- an electron RICH species/molecule
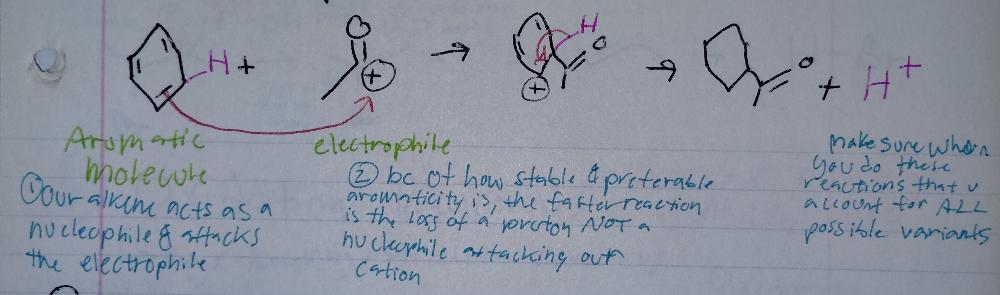
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
Sn1, stepwise
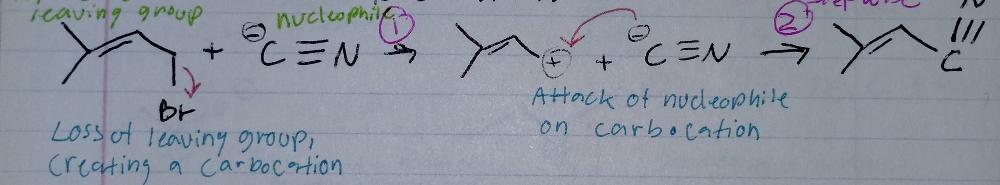
Nucleophilic Substitution
Sn2, concerted

nucleophilic substitution
E1, stepwise
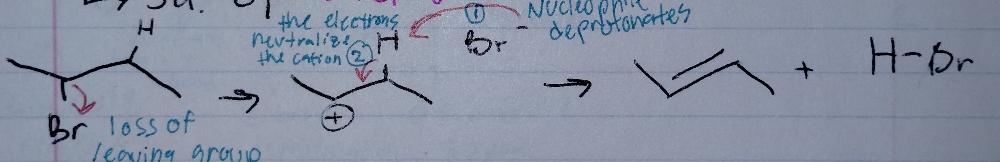
Elimination
E2, concerted
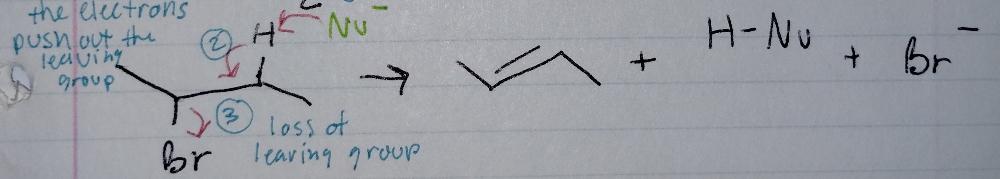
Elimination
E1cb, catalyzed by base
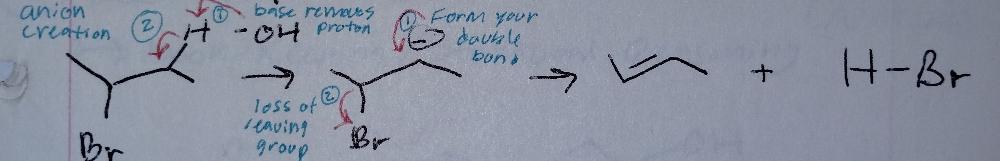
Elimination
Book-keeping/ Structural Reasoning
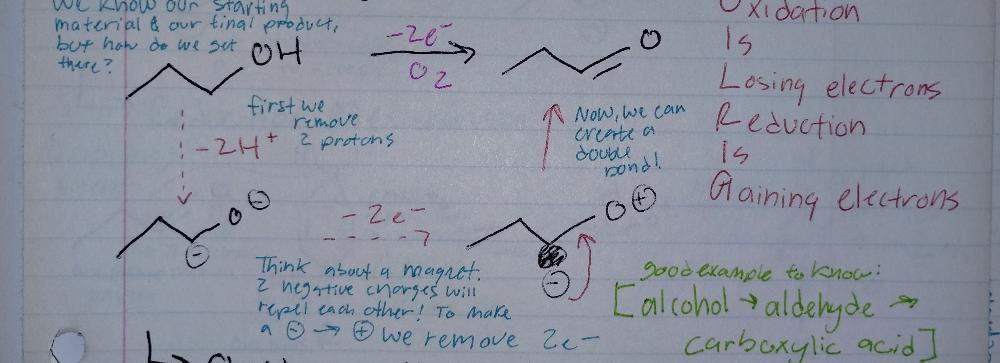
Oxidixing Reactions
- recquires an oxidizing agent (O2, NAD)
Oxidation Mechanism
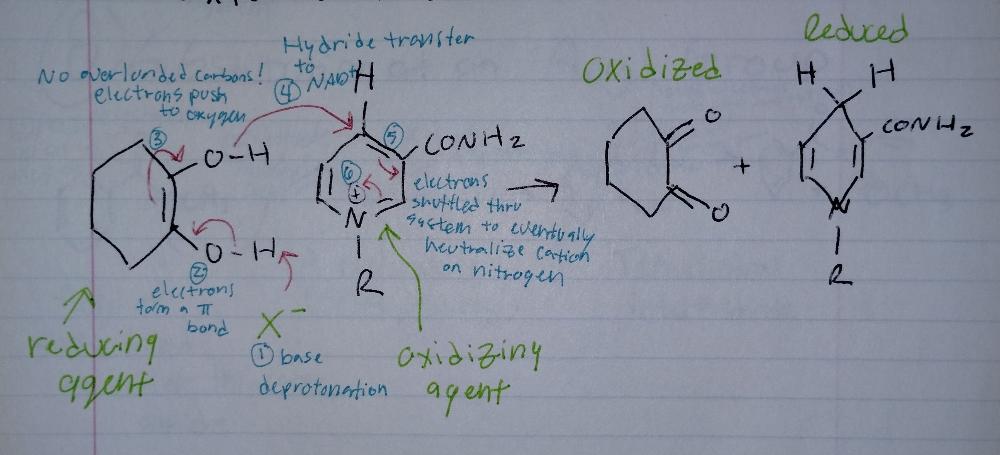
Oxidizing Reactions
- requires an oxidizing agent (O2, NAD)
Book-keeping/Structural Reasoning
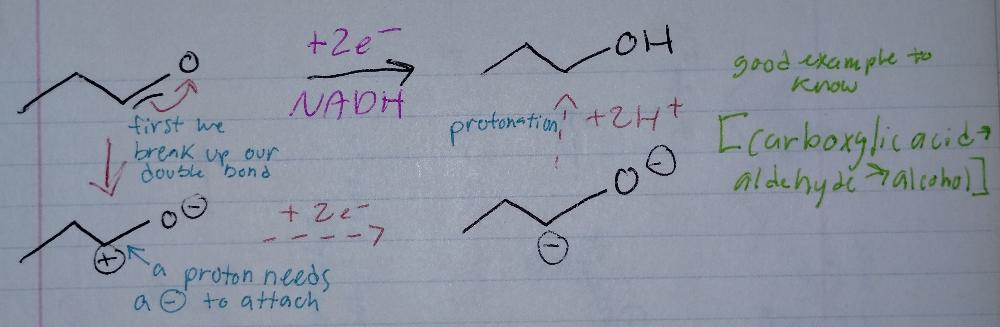
Reduction Reactions
- requires a reducing agent (NADH)
Reduction Mechanism
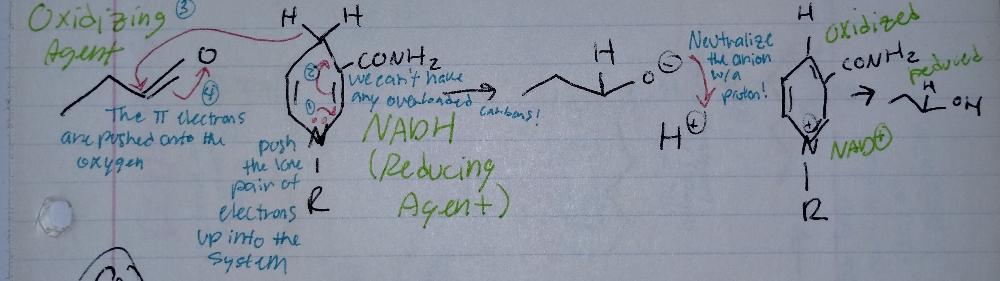
Reduction Reactions
- requires a reducing agent (NADH)
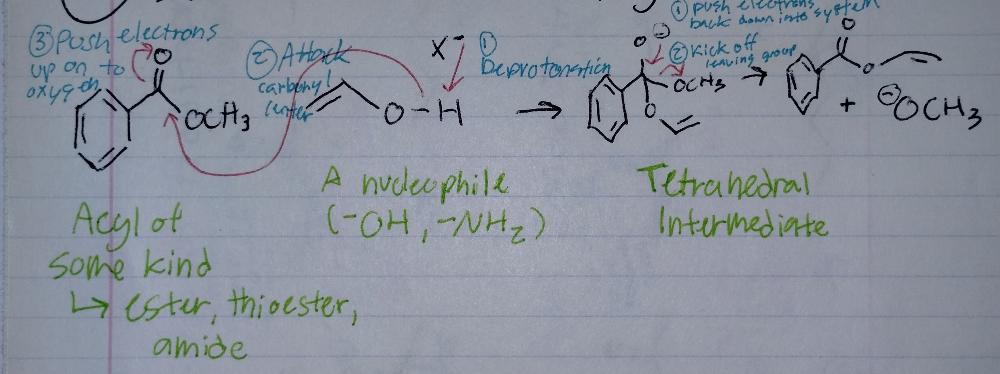
Substitution at an Acyl Group
Aldol Addition
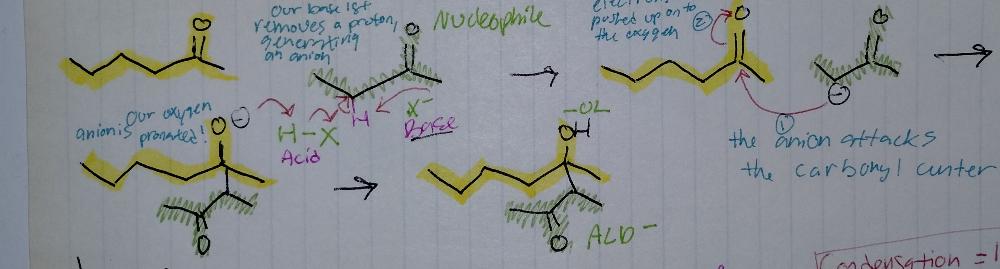
Aldol Reactions
- requires base
Aldol Condensation
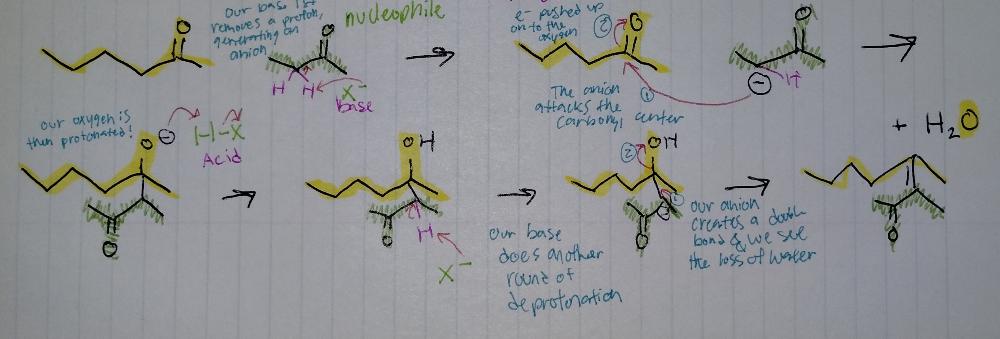
Aldol Reactions
- requires base
condensation = loss of H2O
Reverse Aldol Reaction
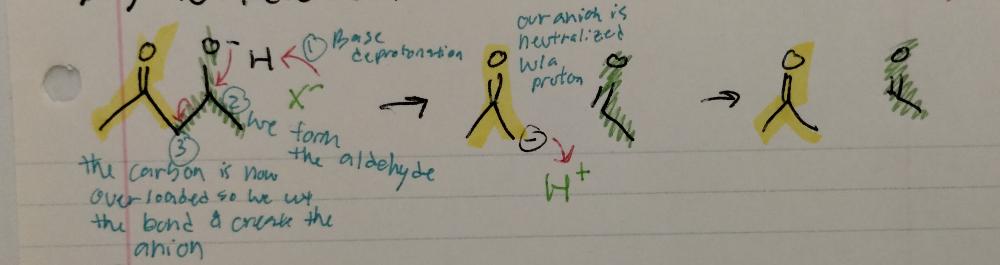
Aldol Reactions
- requires base
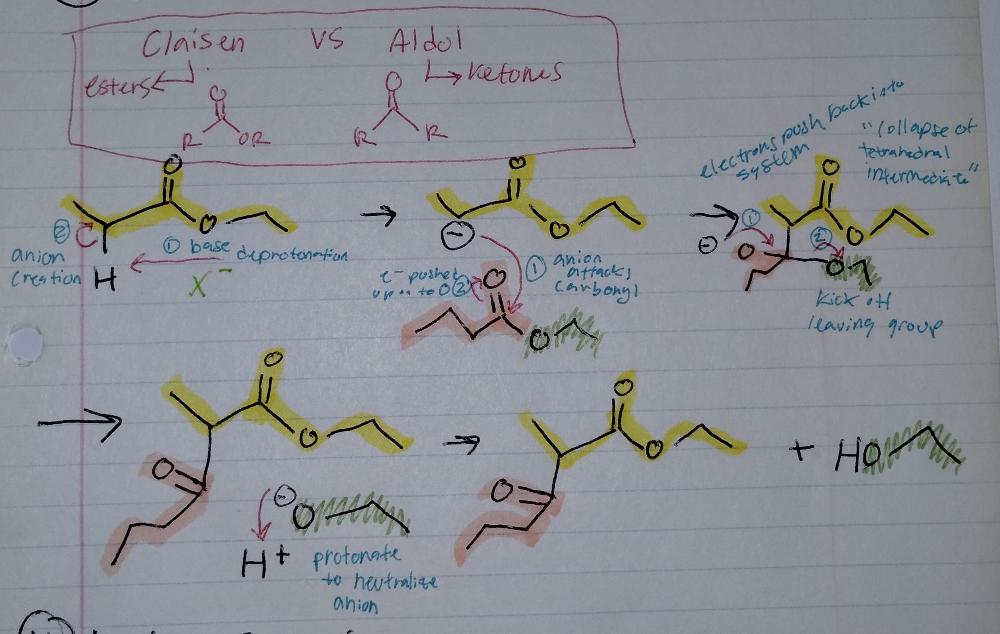
Claisen Reaction
- requires base
- --> esters (double bond O to an R and an OR) NOT ketones (O double bond to 2 R's)
Imine Formation
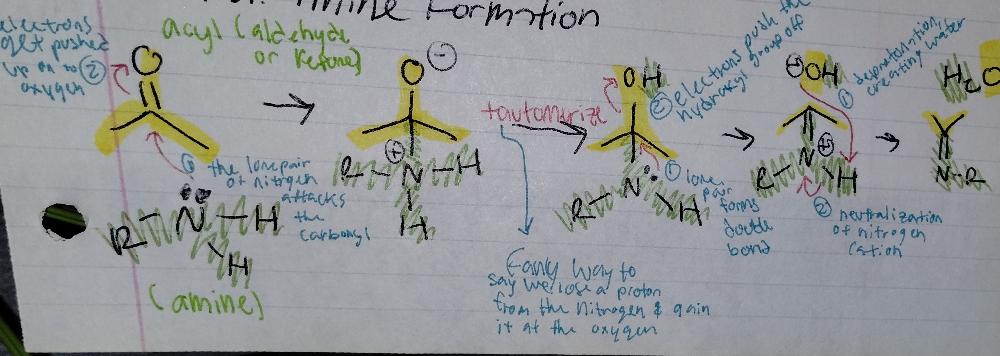
Imine Creation
Transimination
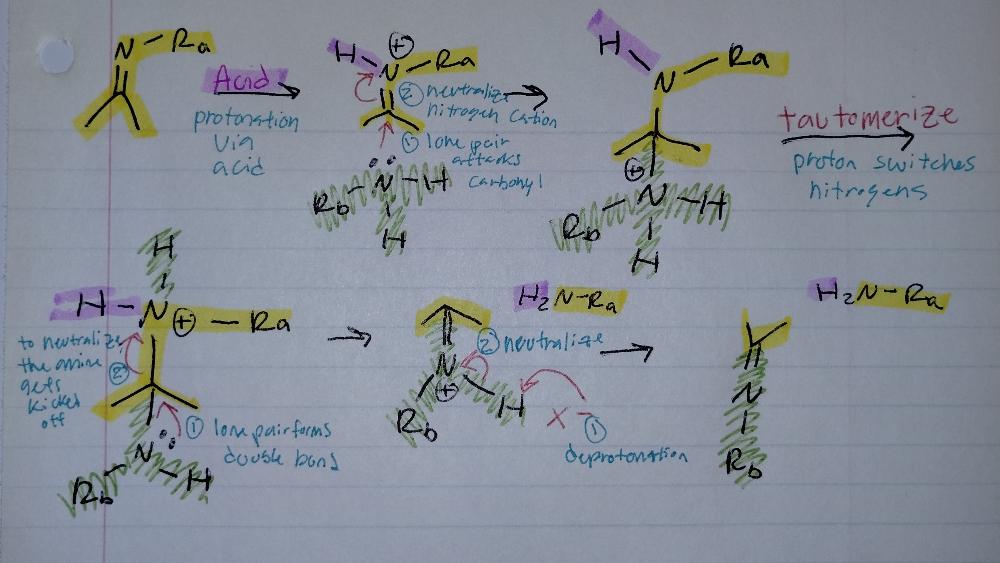
Imine Creation
- requires acid
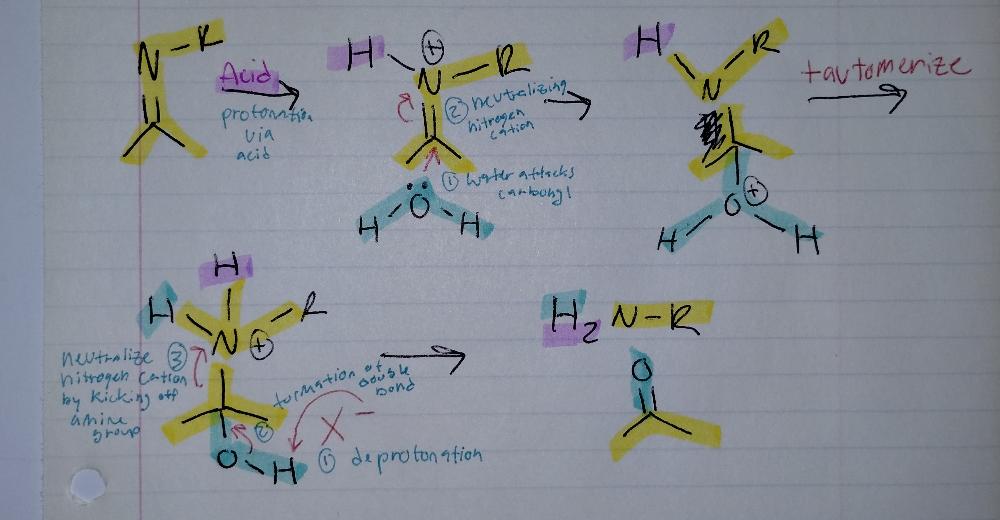
Imine Hydrolysis
- requires acid
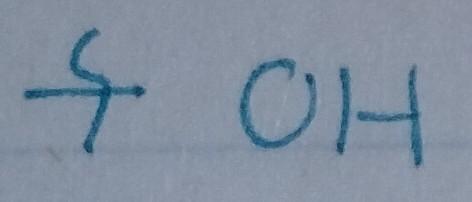
Alcohol
- Nu
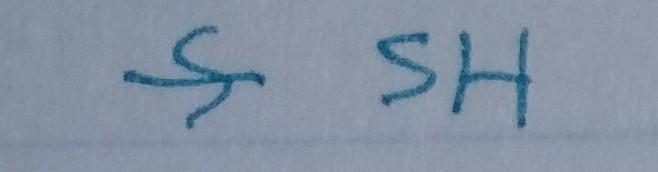
Thiol
- Nu
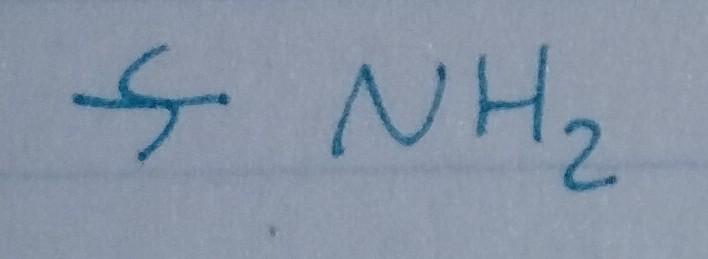
Amine
- Nu
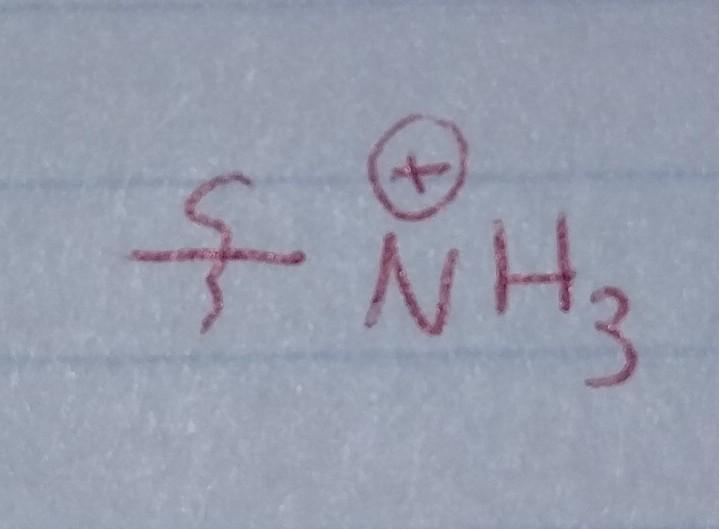
Protonated Amine
- Nu
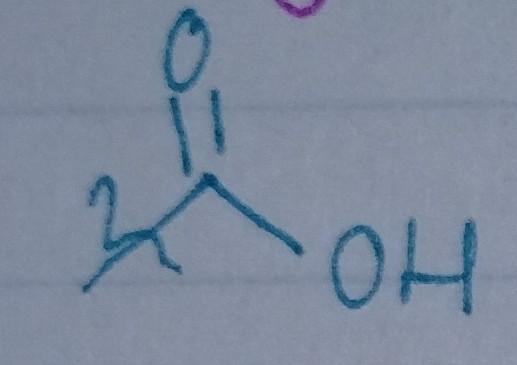
Carboxylic Acid
- acyl group
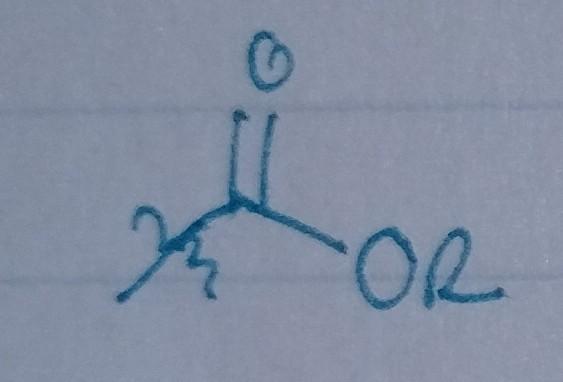
Ester
- Acyl group
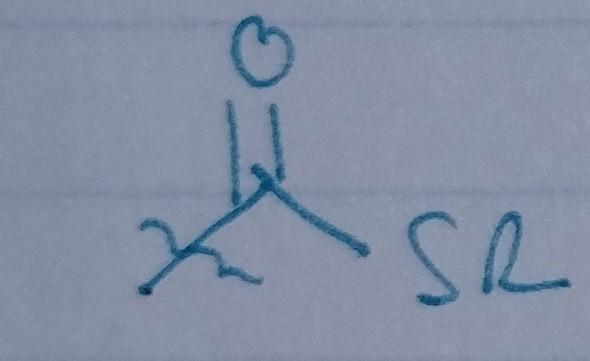
Thioester
- acyl group
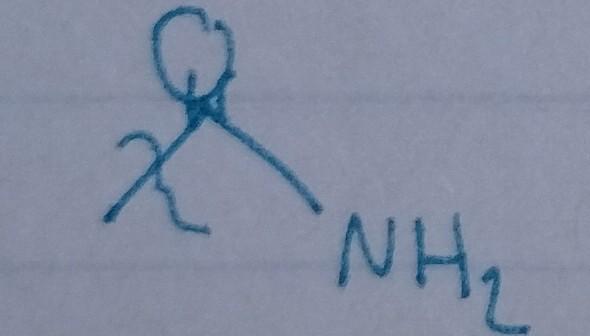
Amide
- acyl group
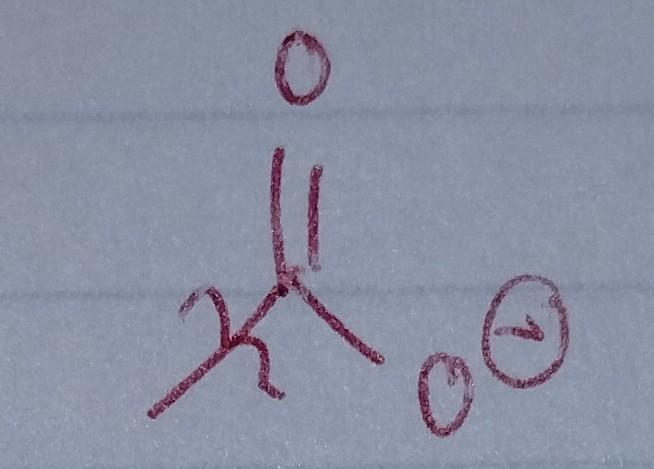
Carbonate
- acyl group
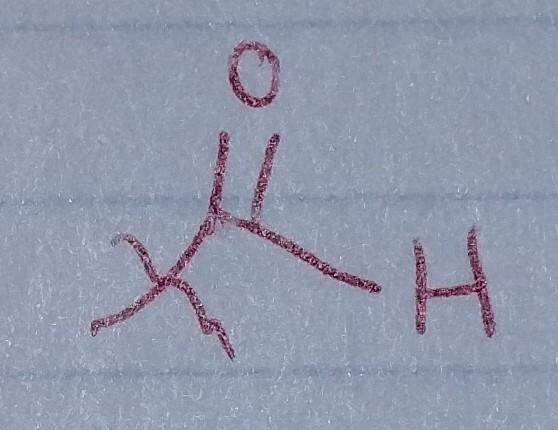
Aldehyde
- acyl group
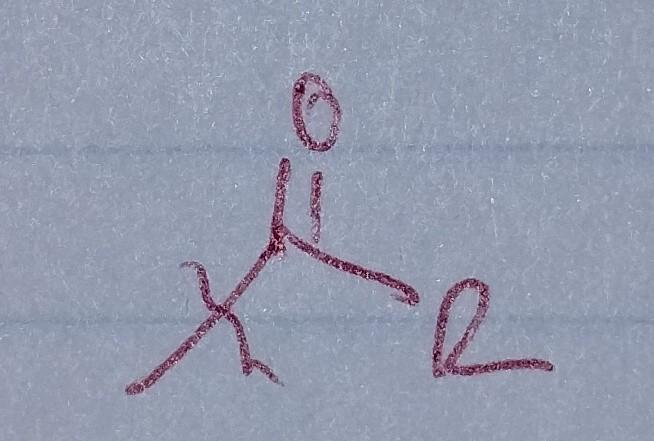
Ketone
- acyl group
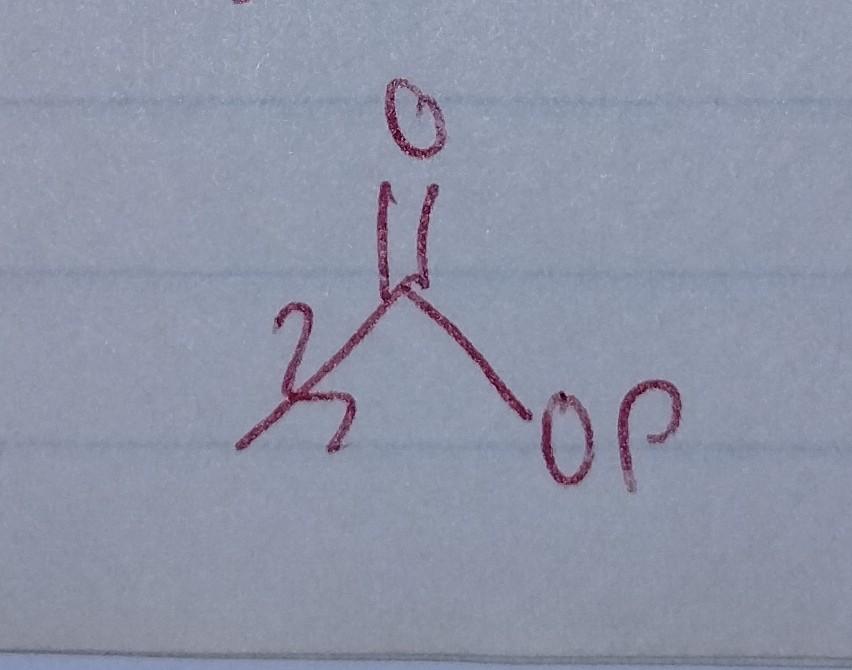
Acyl Phosphate
- acyl group
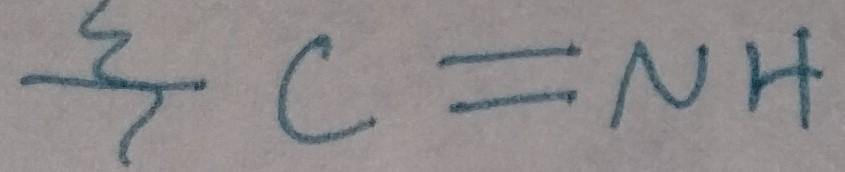
Imine
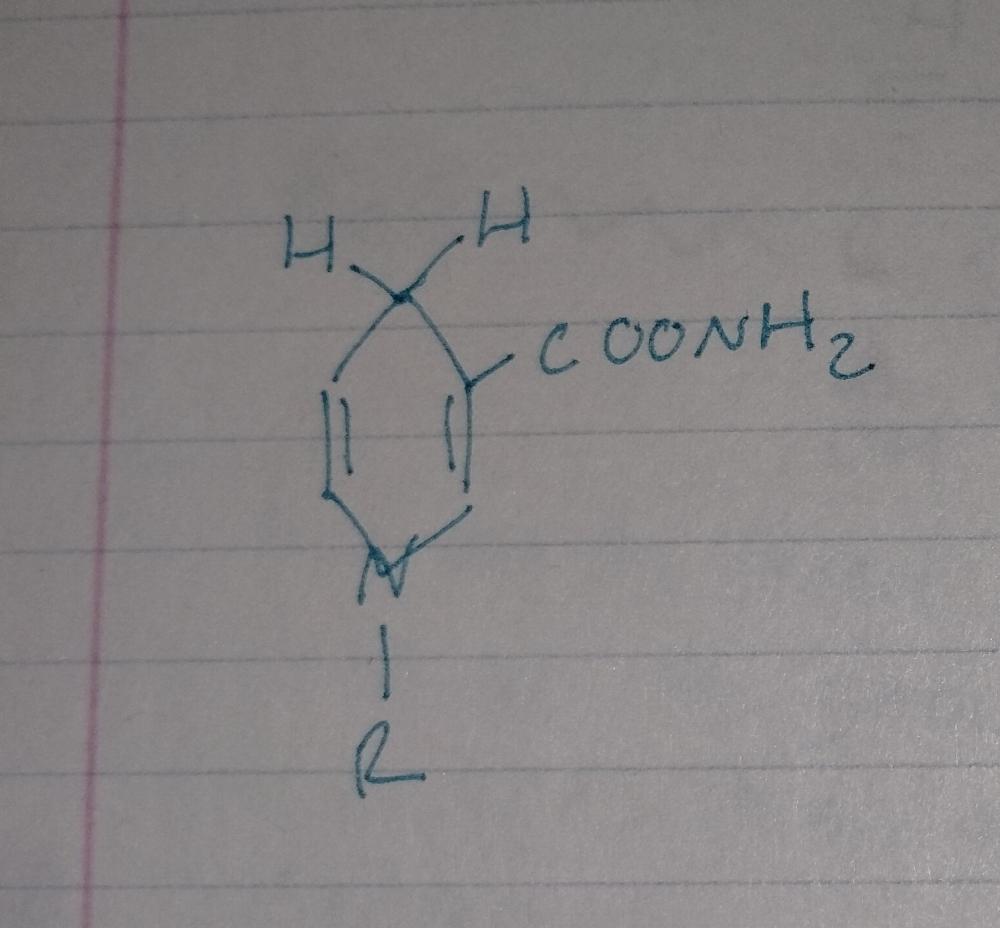
NADH

Benzene
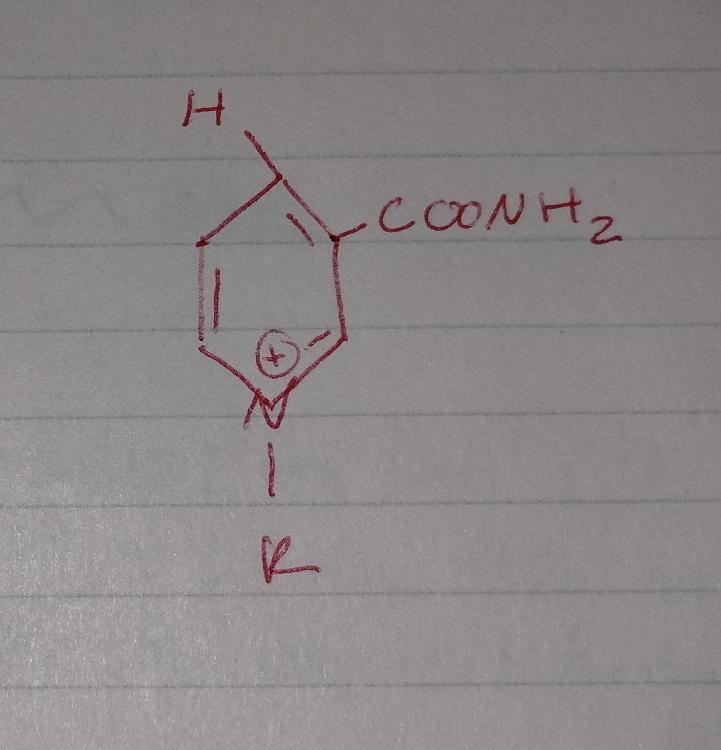
NAD