Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
crash course chem 222
front 1 Acid-Base Reaction | back 1 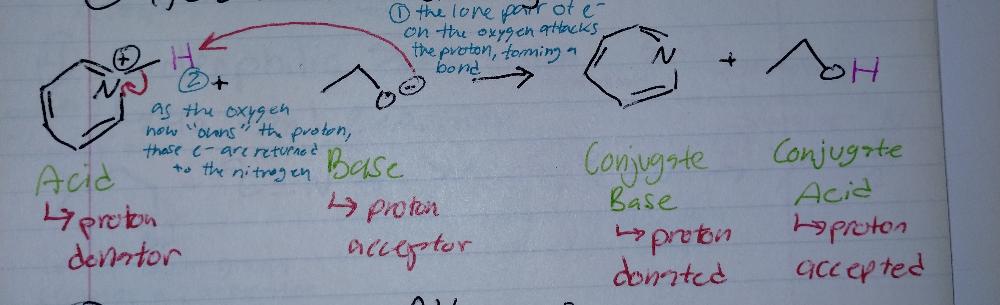 |
front 2 ELECTROPHILIC Addition to Alkenes | back 2 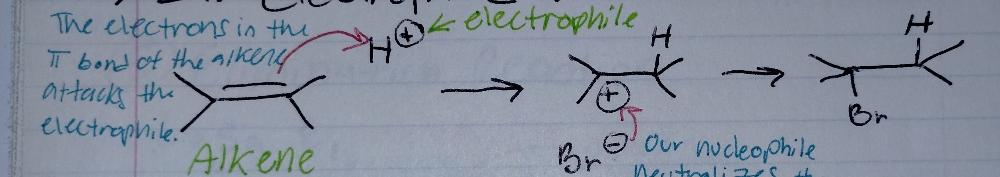 what is an alkene? H2C = CH2
what is an electrophile?
|
front 3 NUCLEOPHILIC Addition to Alkenes | back 3 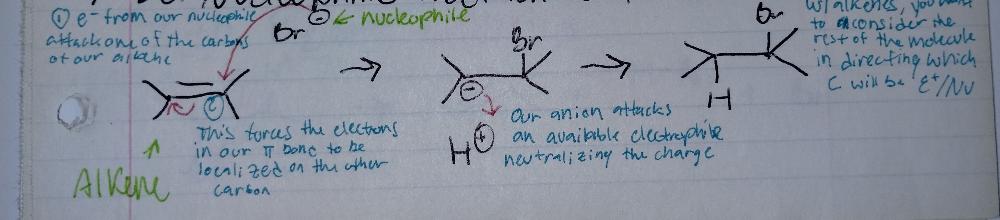 what is a nucleophile? ex) halides (I, Br, Cl)
|
front 4 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution | back 4 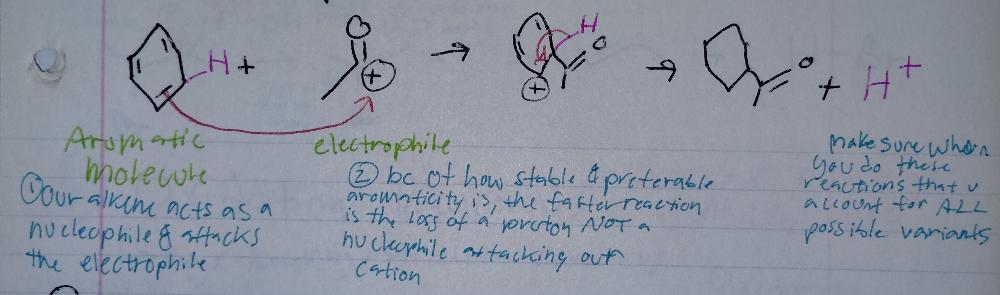 |
front 5 Sn1, stepwise | back 5 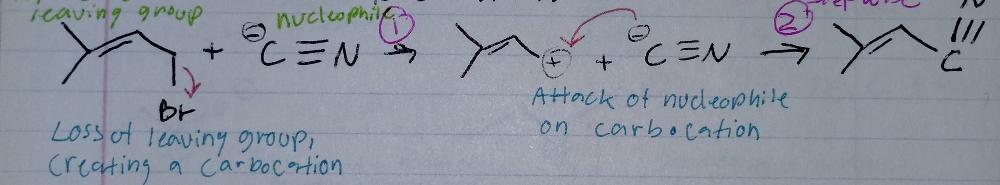 Nucleophilic Substitution |
front 6 Sn2, concerted | back 6  nucleophilic substitution |
front 7 E1, stepwise | back 7 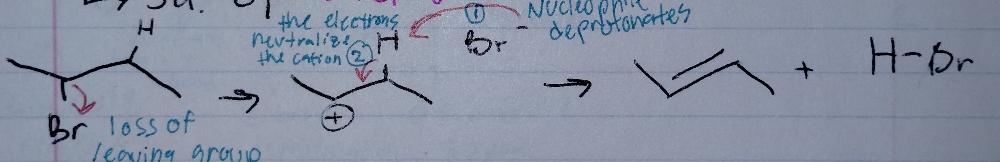 Elimination |
front 8 E2, concerted | back 8 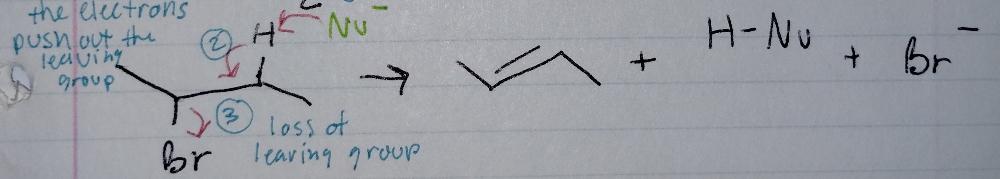 Elimination |
front 9 E1cb, catalyzed by base | back 9 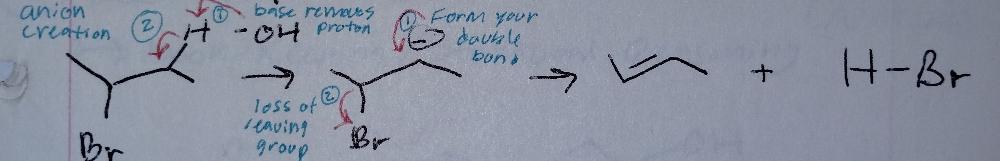 Elimination |
front 10 Book-keeping/ Structural Reasoning | back 10 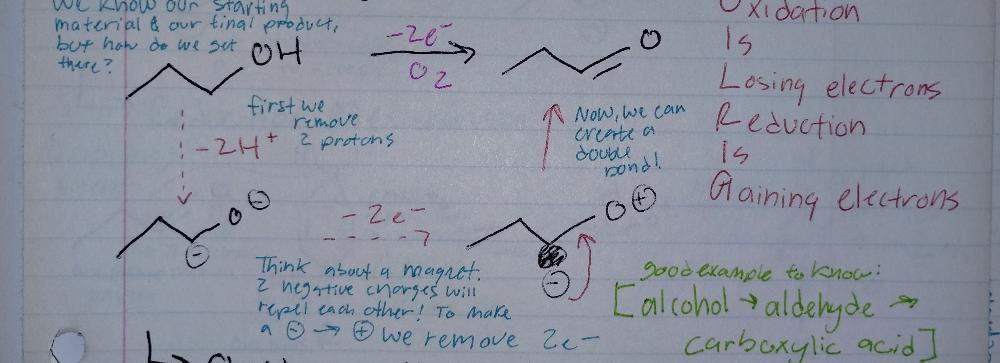 Oxidixing Reactions
|
front 11 Oxidation Mechanism | back 11 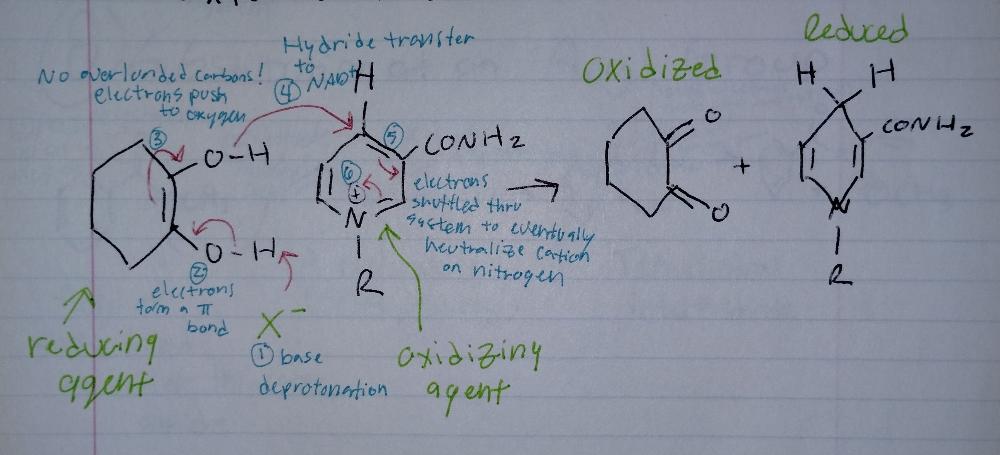 Oxidizing Reactions
|
front 12 Book-keeping/Structural Reasoning | back 12 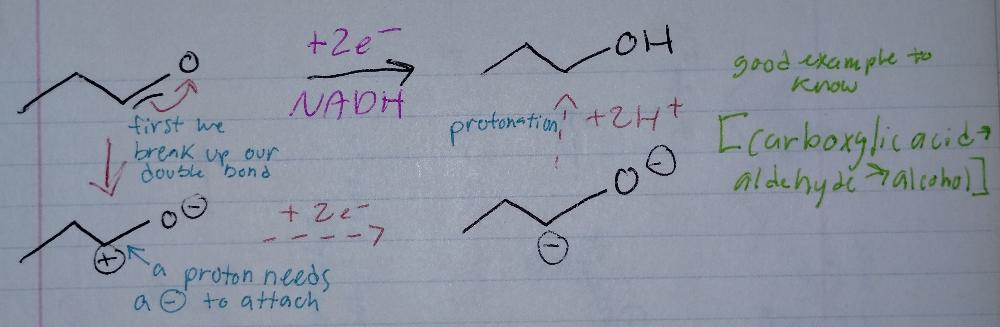 Reduction Reactions
|
front 13 Reduction Mechanism | back 13 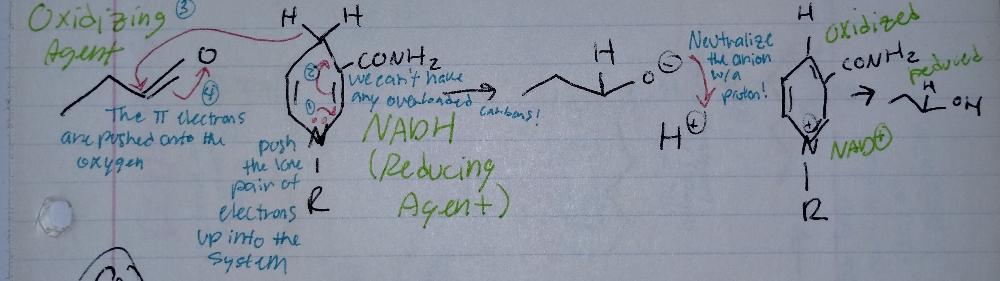 Reduction Reactions
|
front 14 Substitution at an Acyl Group | back 14 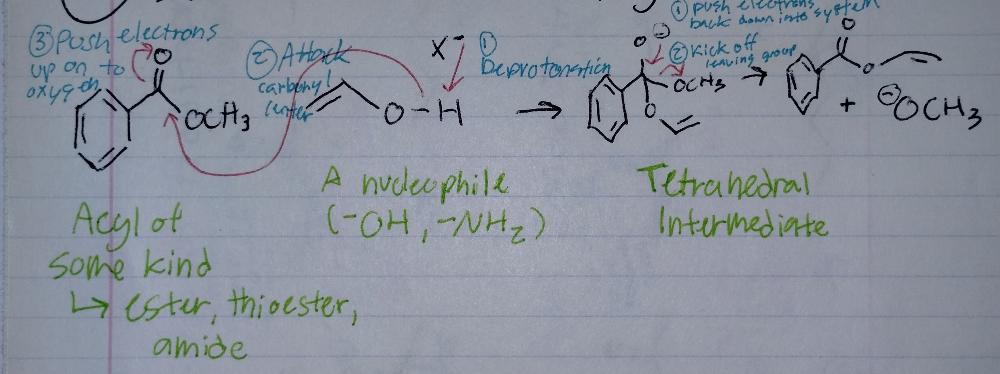 |
front 15 Aldol Addition | back 15 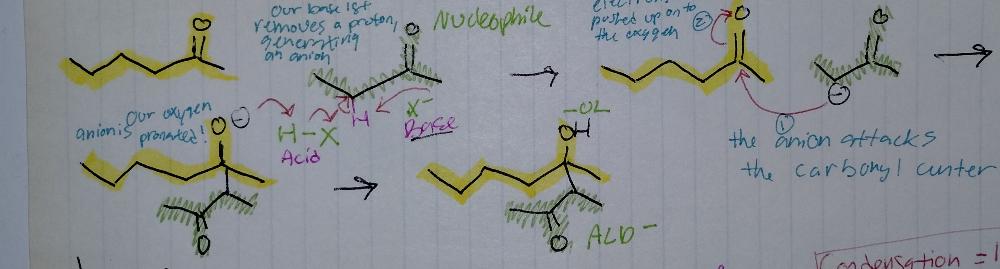 Aldol Reactions
|
front 16 Aldol Condensation | back 16 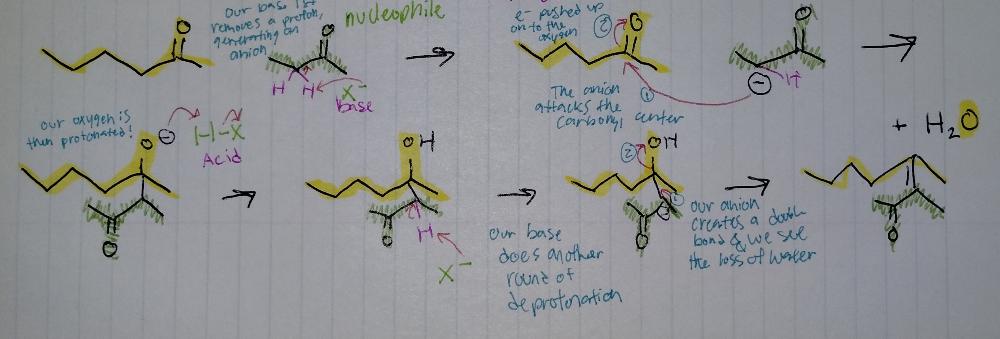 Aldol Reactions
condensation = loss of H2O |
front 17 Reverse Aldol Reaction | back 17 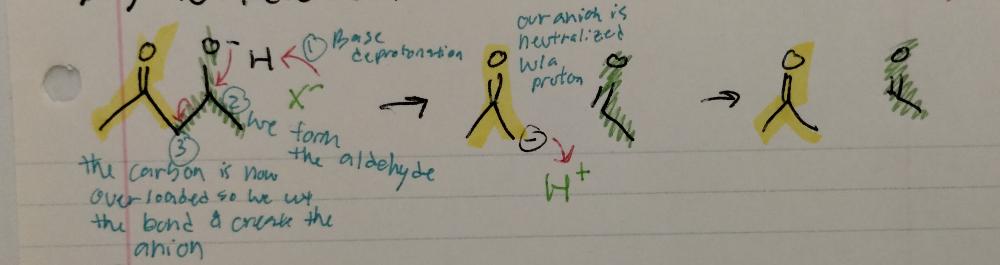 Aldol Reactions
|
front 18 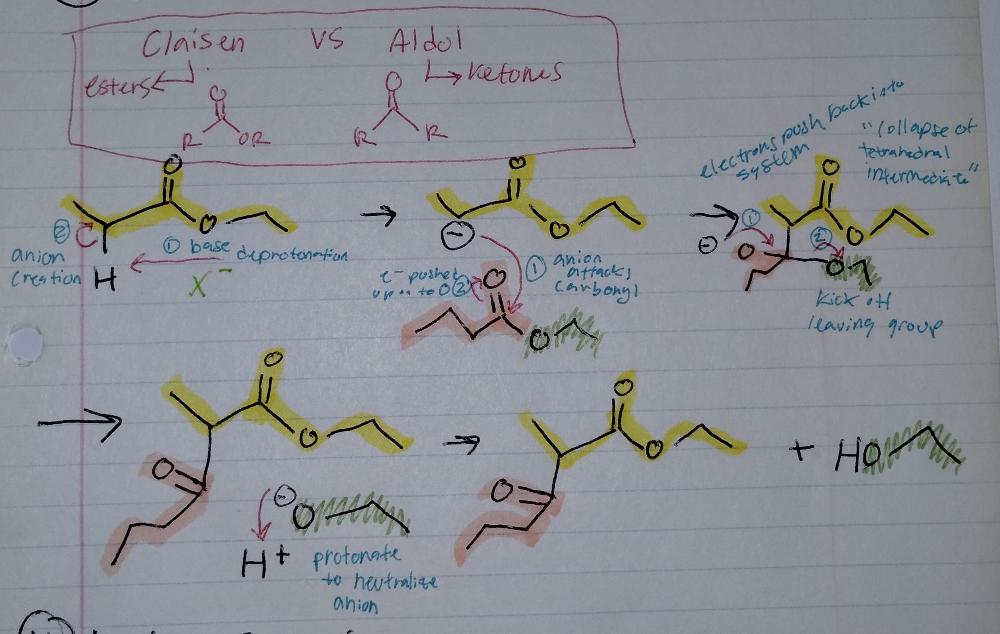 | back 18 Claisen Reaction
|
front 19 Imine Formation | back 19 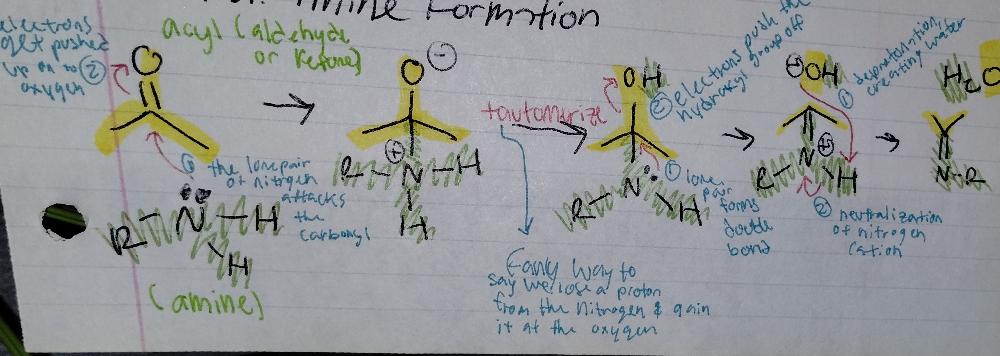 Imine Creation |
front 20 Transimination | back 20 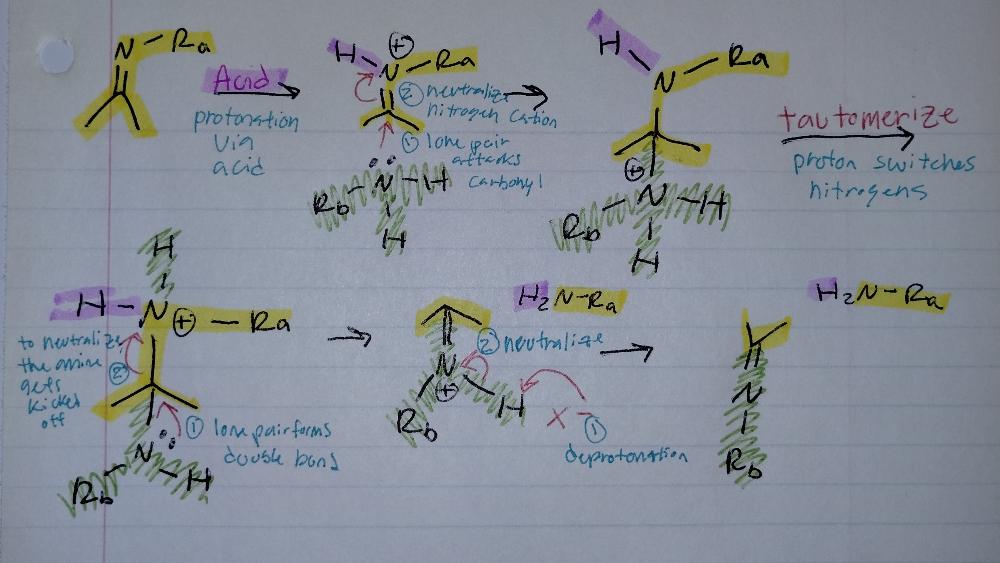 Imine Creation
|
front 21 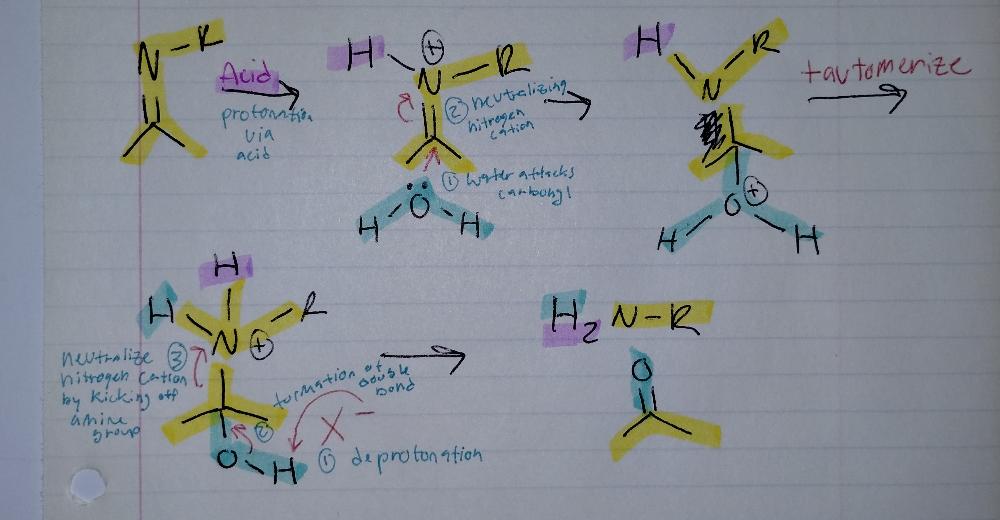 | back 21 Imine Hydrolysis
|
front 22 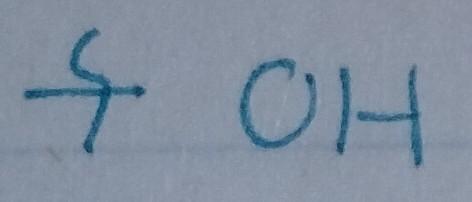 | back 22 Alcohol
|
front 23 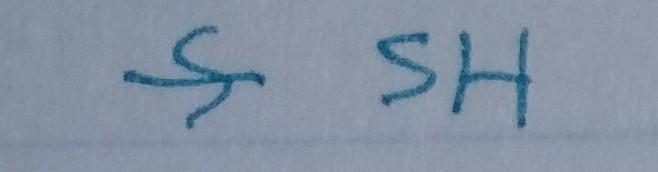 | back 23 Thiol
|
front 24 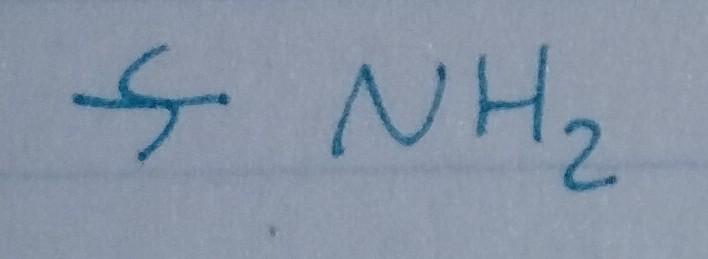 | back 24 Amine
|
front 25 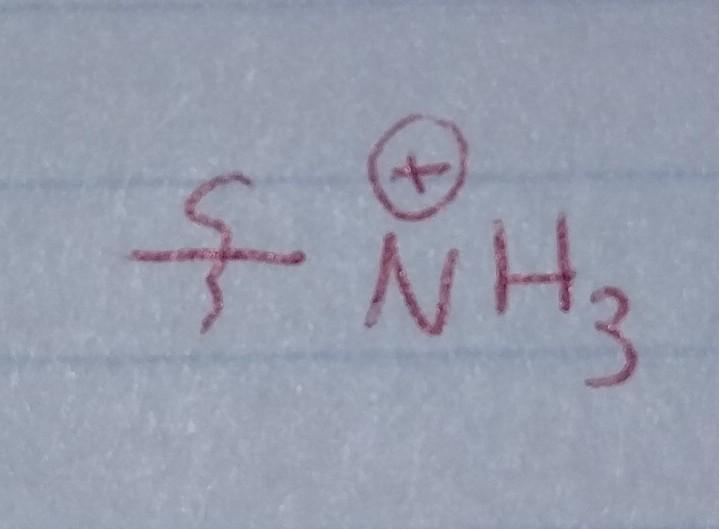 | back 25 Protonated Amine
|
front 26 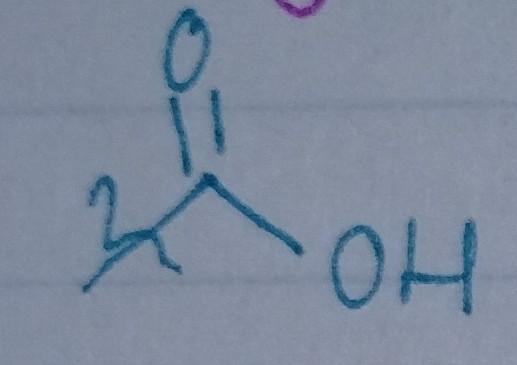 | back 26 Carboxylic Acid
|
front 27 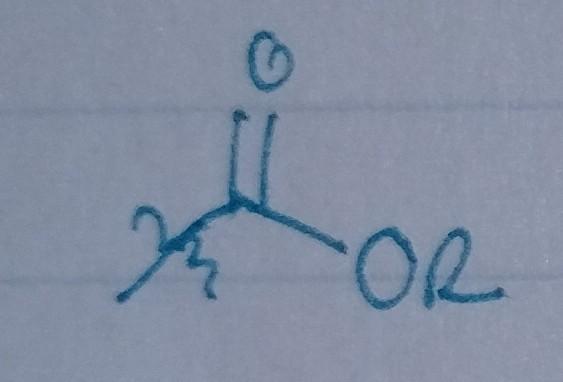 | back 27 Ester
|
front 28 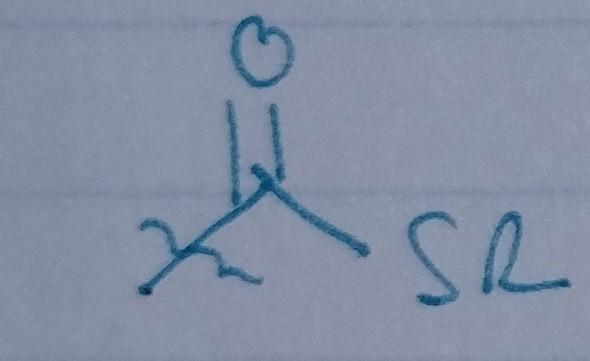 | back 28 Thioester
|
front 29 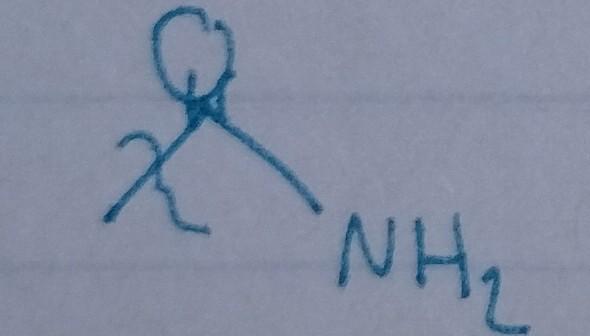 | back 29 Amide
|
front 30 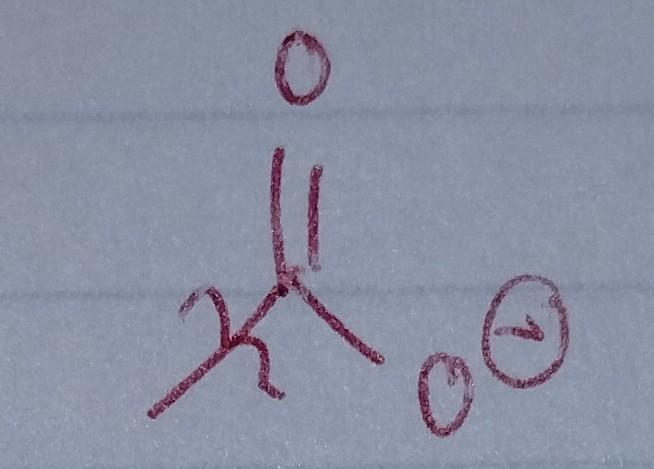 | back 30 Carbonate
|
front 31 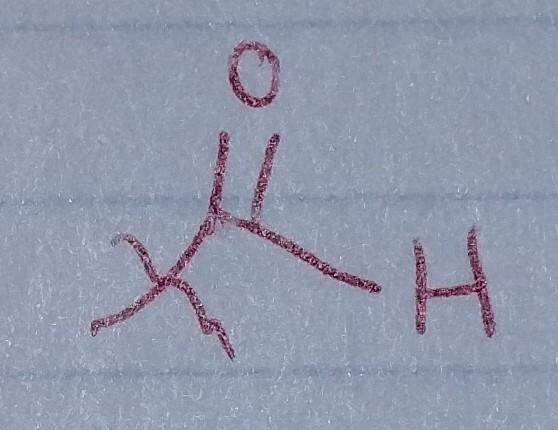 | back 31 Aldehyde
|
front 32 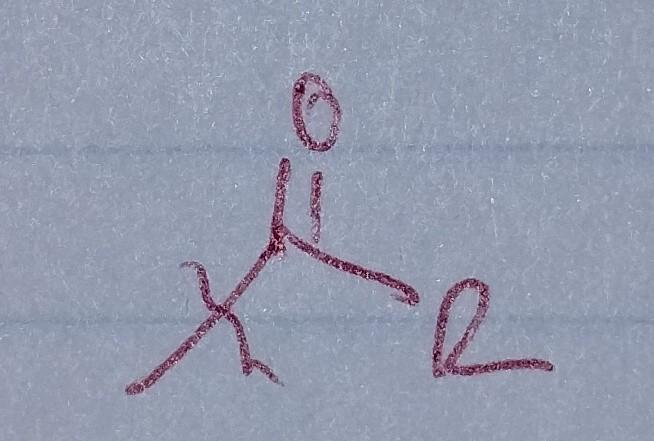 | back 32 Ketone
|
front 33 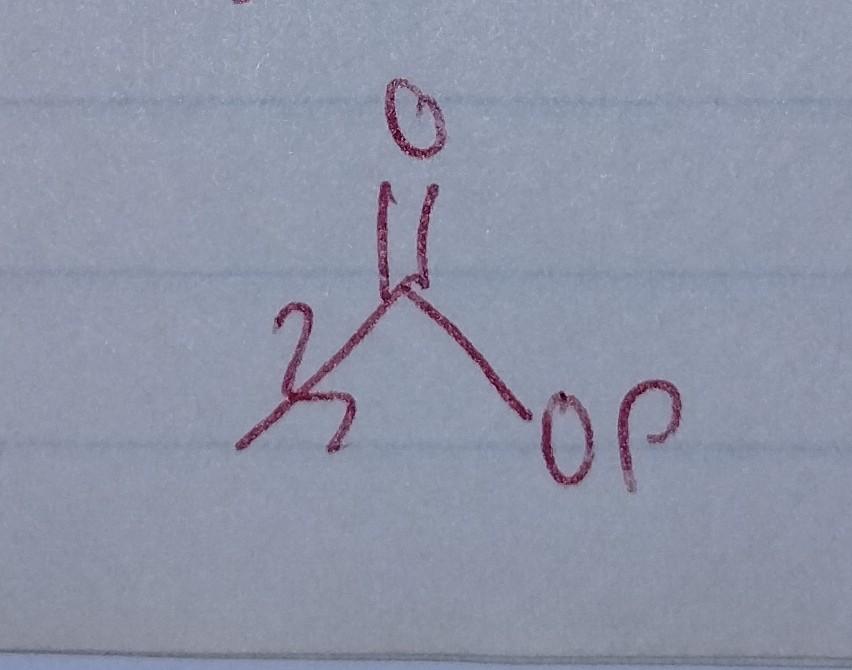 | back 33 Acyl Phosphate
|
front 34 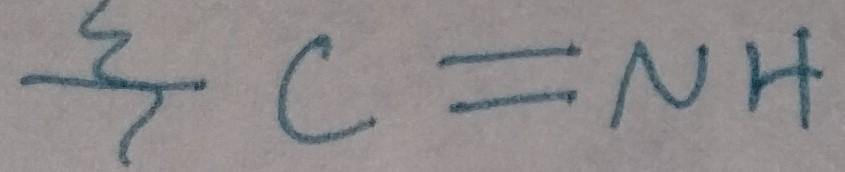 | back 34 Imine |
front 35 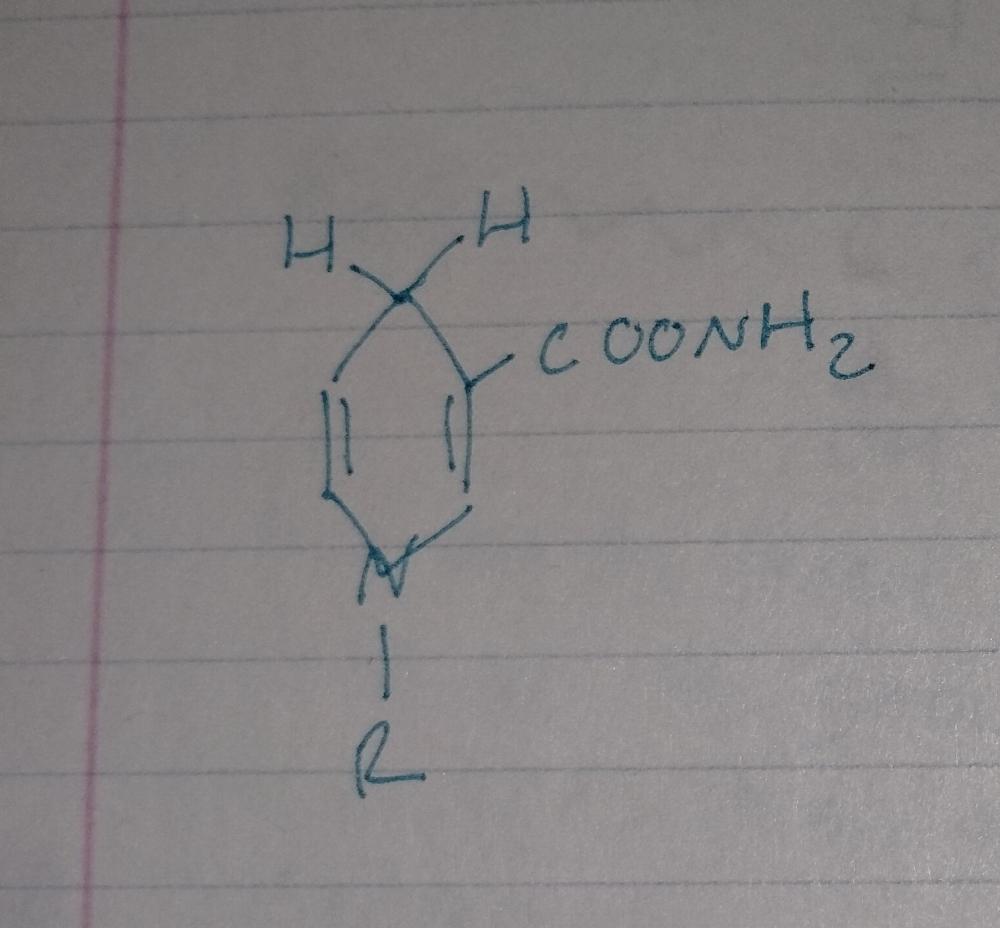 | back 35 NADH |
front 36  | back 36 Benzene |
front 37 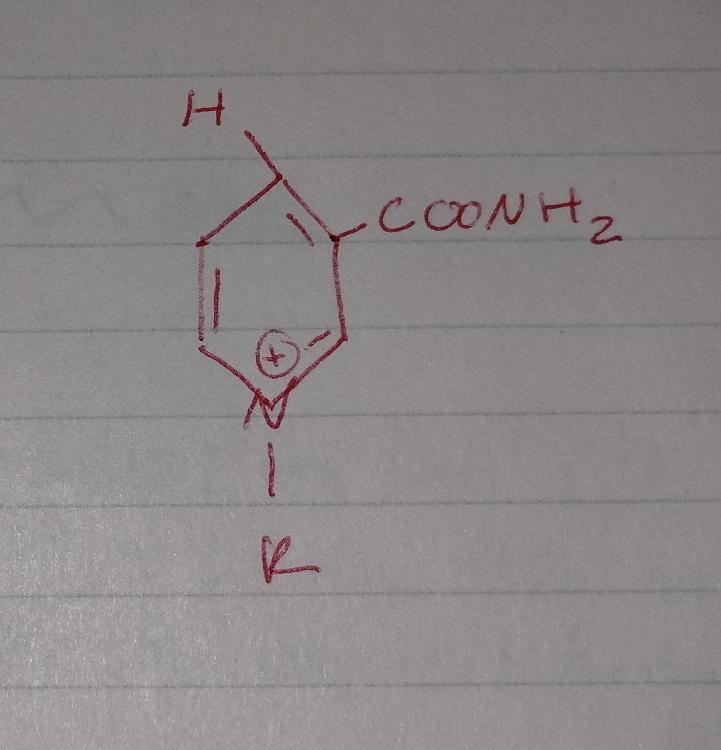 | back 37 NAD |