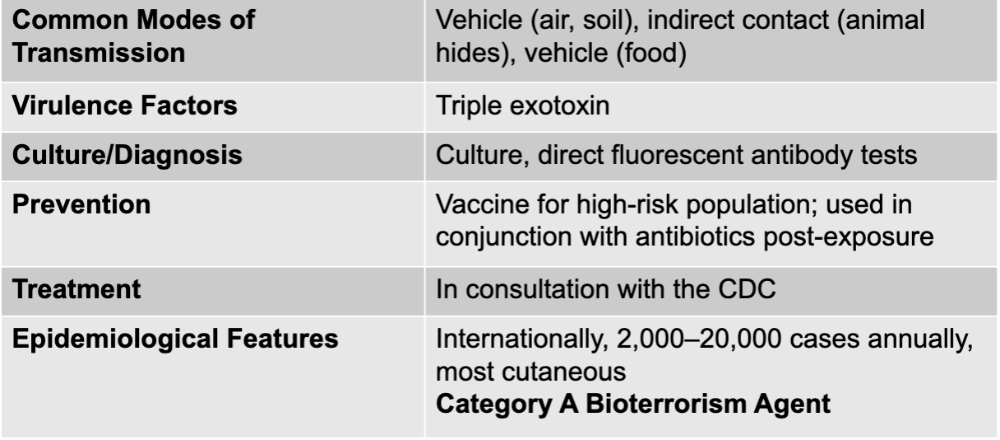
bacillus anthracis causing anthrax
bacillus anthracis
gram-positive endospore-forming rod
aerobic and catalase positive
forms a tripartite toxin (edema factor, protective antigen, lethal factor)
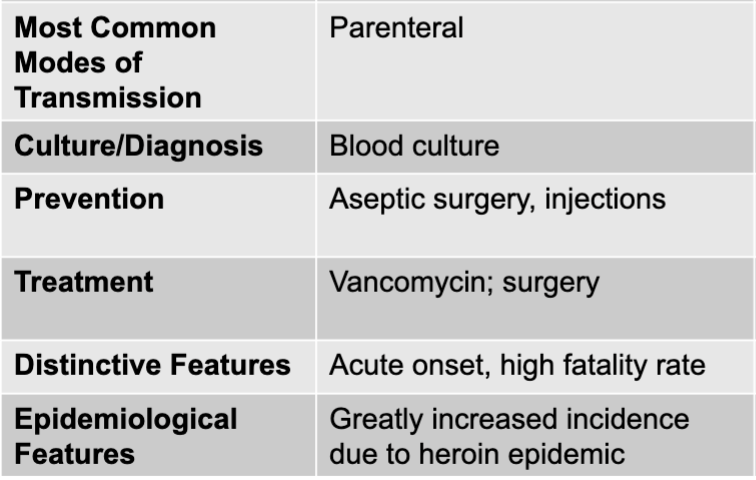
staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus pneumoniae causing acute endocarditis
staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus
gram positive bacteria
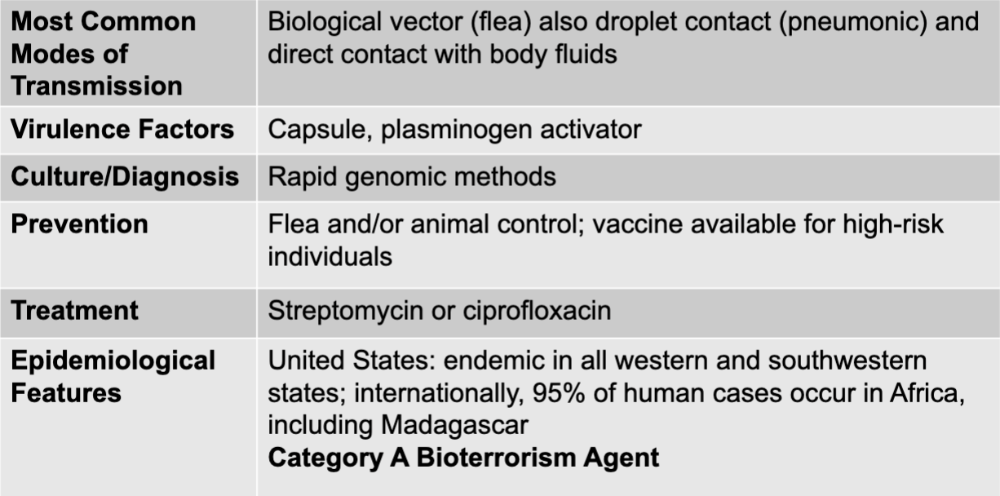
yersinia pestis causing plague
yersinia pestis
gram-negative bacteria
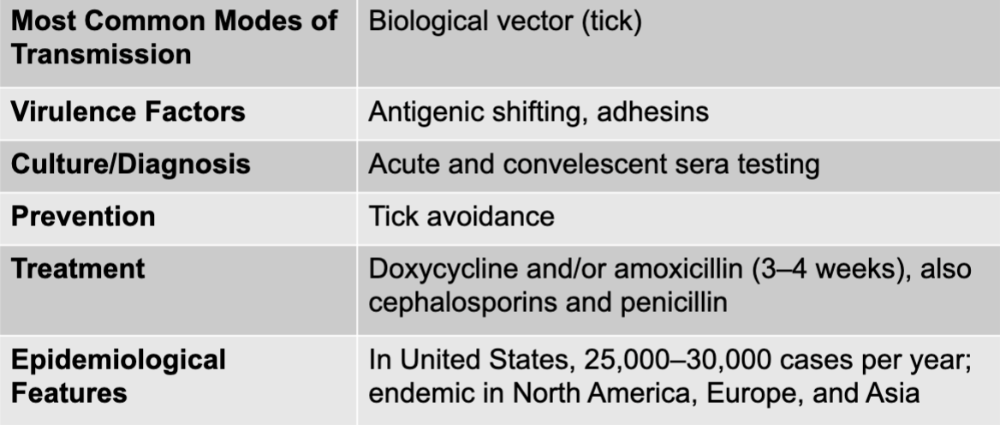
borrelia burgdoferi causing lyme disease
borrelia burgdoferi
large spirochete with 3 to 10 irregularly spaced coils
evades the immune system by changing antigens
has multiple proteins for attachment to host cells
possible that immune response contributes to the pathology of the disease
bartonella henslae causing cat-scratch disease

bartonella henslae
small gram-negative rod, fastidious, will grow on blood agar
rickettsia species causing spotted fever rickettsiosis
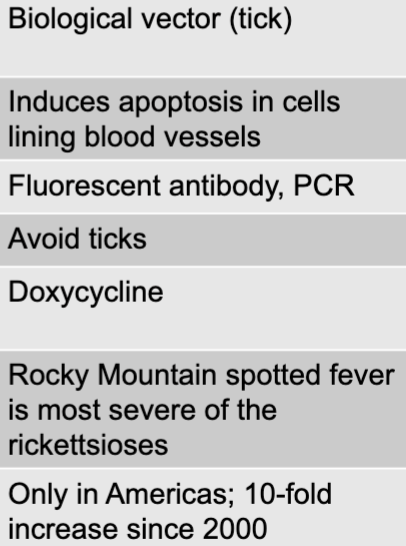
rickettsia species
gram-negative bacteria
epstein-barr virus causing mono
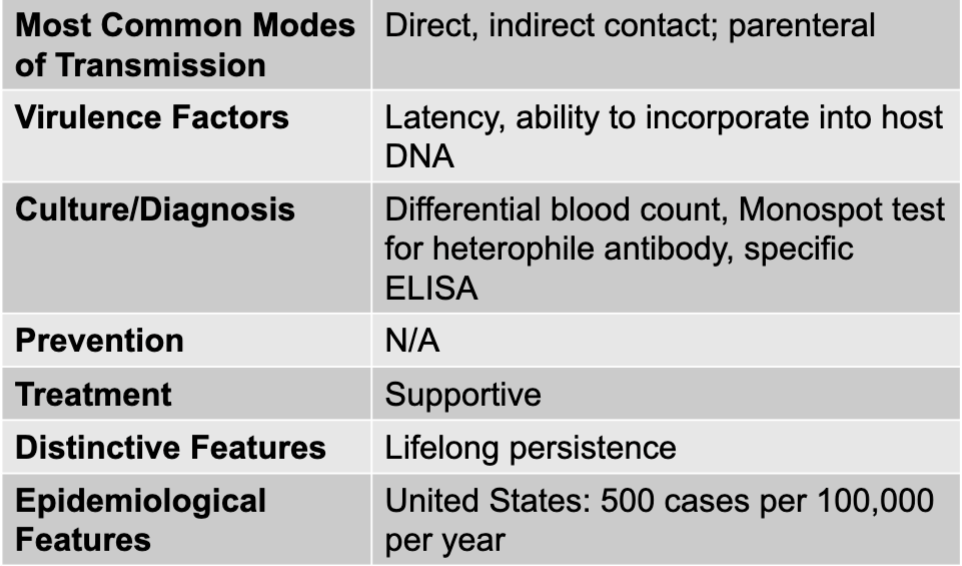
epstein-barr virus
circular form of DNA
herpesviruses
latency
SARS-CoV-2 causing COVID
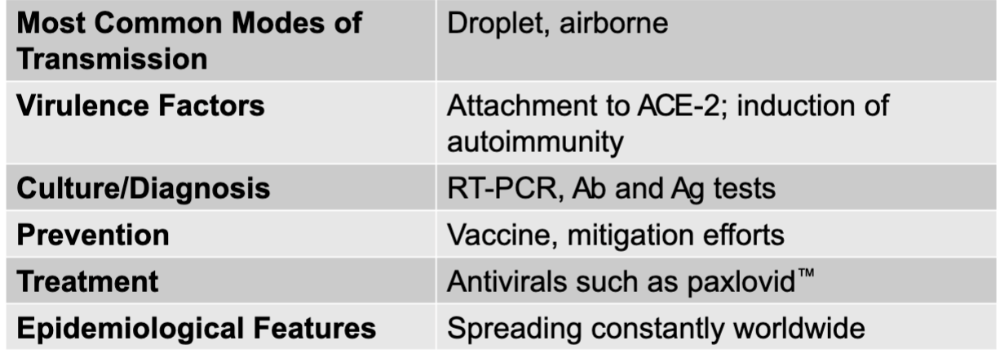
SARS-CoV-2
RNA virus
enveloped, positive-sense RNA viruses with spike proteins
yellow fever disease
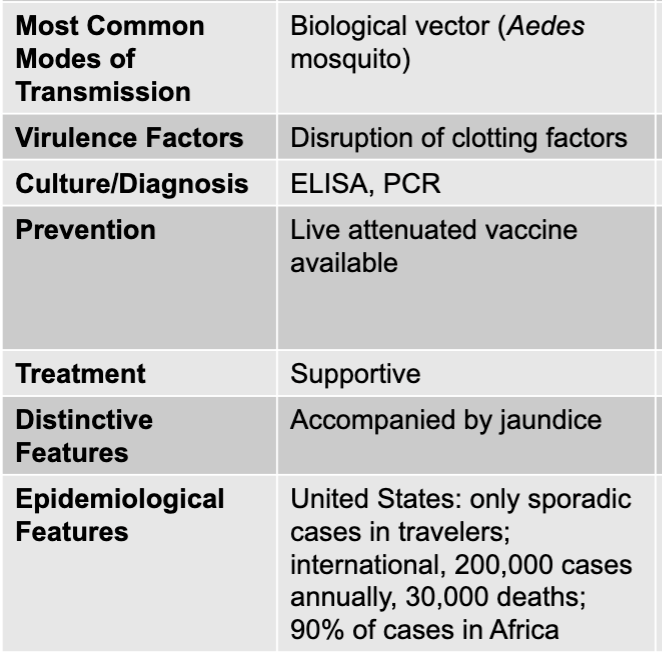
yellow fever virus
RNA virus
HIV disease
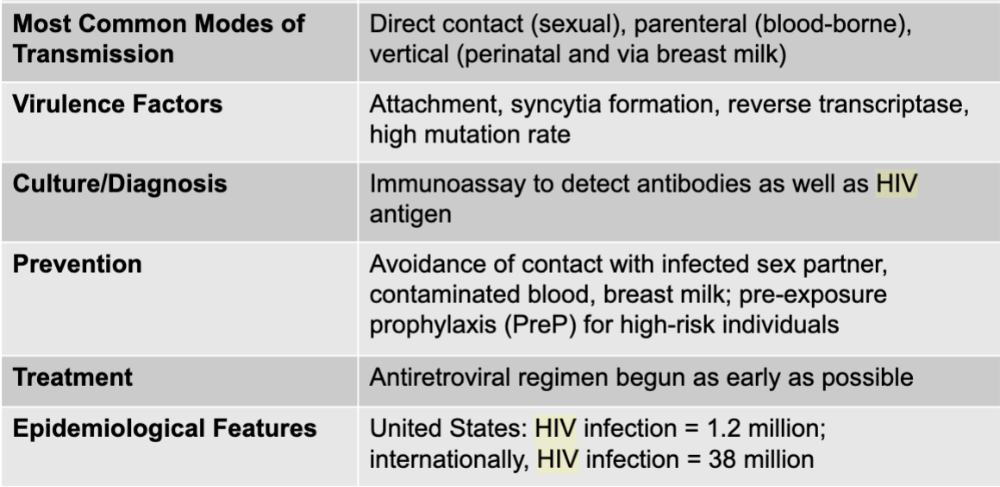
HIV
retrovirus
streptococcus mutans causing dental caries
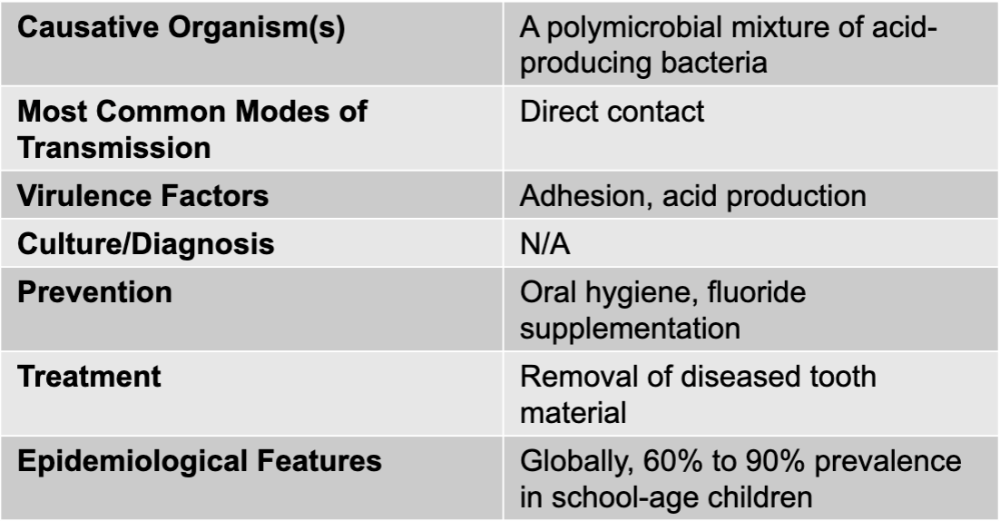
streptococcus mutans
gram-positive bacteria
helicobacter pylori causing gastric ulcers
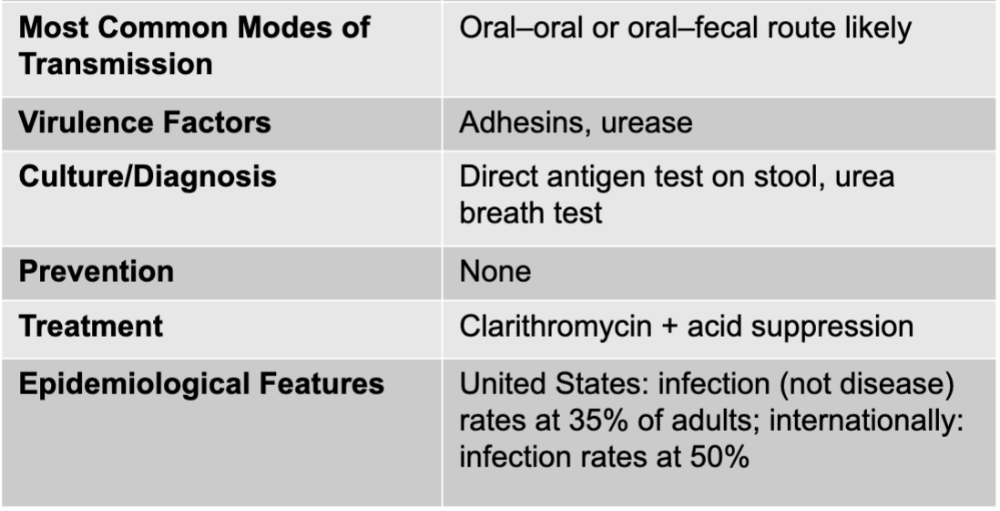
helicobacter pylori
gram-negative bacteria
acute diarrhea and food poisoning causative agents
salmonella, shigella, shiga toxin-producing E. coli, other E. coli, campylobacter, clostridioides difficile, vibrio cholerae, and non-cholera vibrio species
salmonella causing acute diarrhea
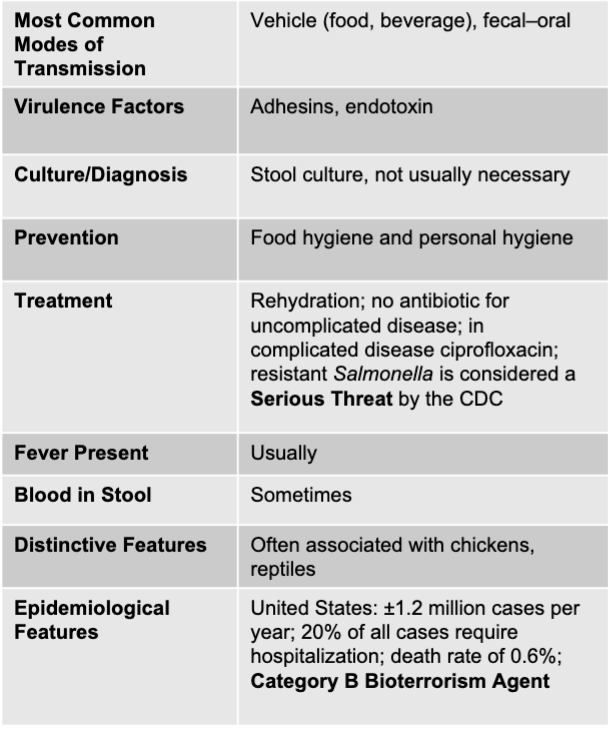
shigella causing acute diarrhea

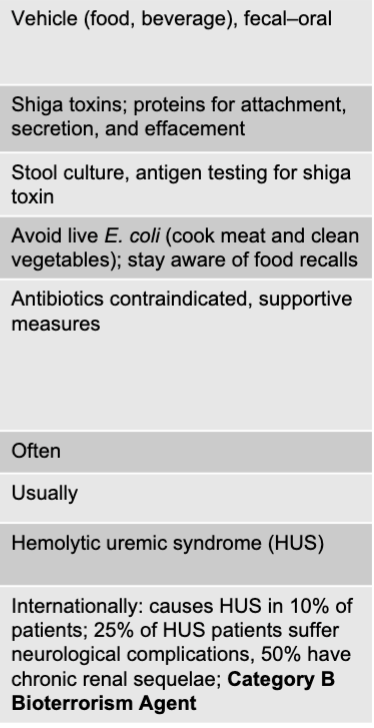
shiga toxin-producing E. coli causing acute diarrhea
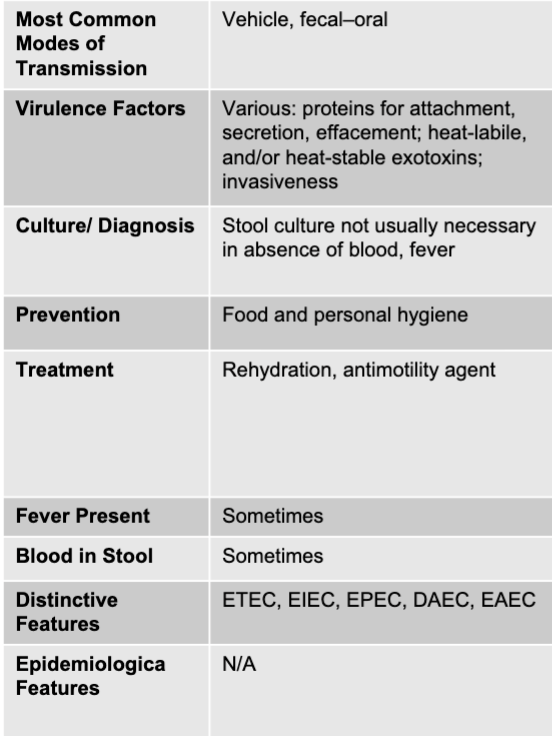
other E. coli causing acute diarrhea
campylobacter causing acute diarrhea

clostridioides difficiles causing acute diarrhea

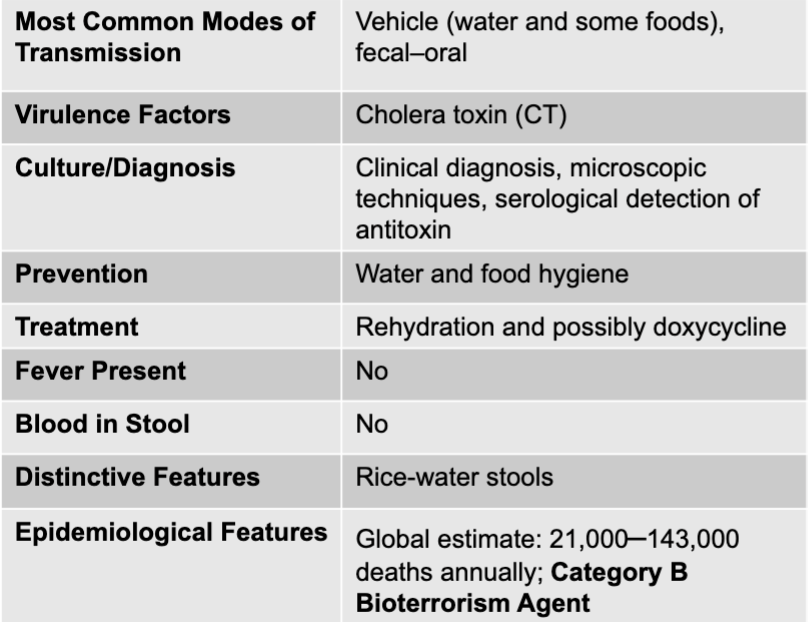
vibrio cholerae causing acute diarrhea
non-cholera vibrio species causing acute diarrhea

non-bacterial causes of acute diarrhea
cryptosporidium, rotavirus, norovirus
clostridium perfringen causing acute diarrhea with vomiting

clostridium perfringen
gram-positive endospore-forming bacteria
hepatitis A disease table
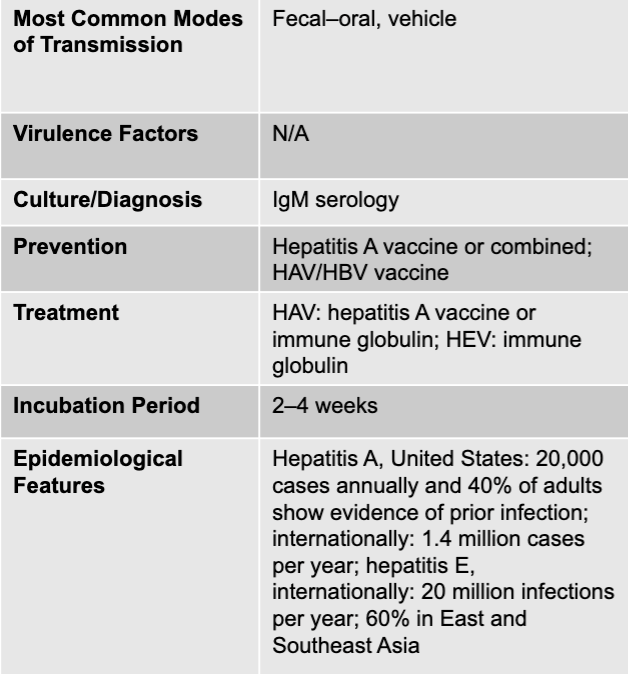
hepatitis A
non-enveloped, single stranded RNA enterovirus
hepatitis B disease table

hepatitis B
enveloped DNA virus
transmitted by minute amounts of blood
hepatitis C disease table
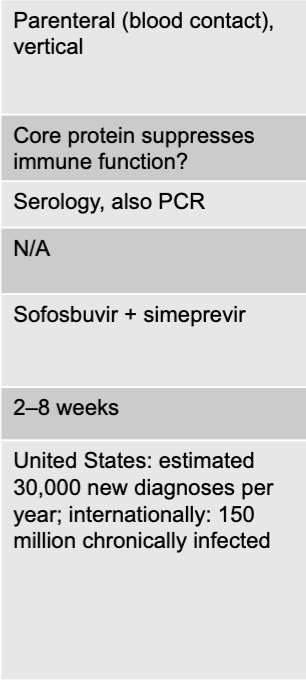
hepatitis C
silent epidemic
RNA virus
schistosomas causing liver disease
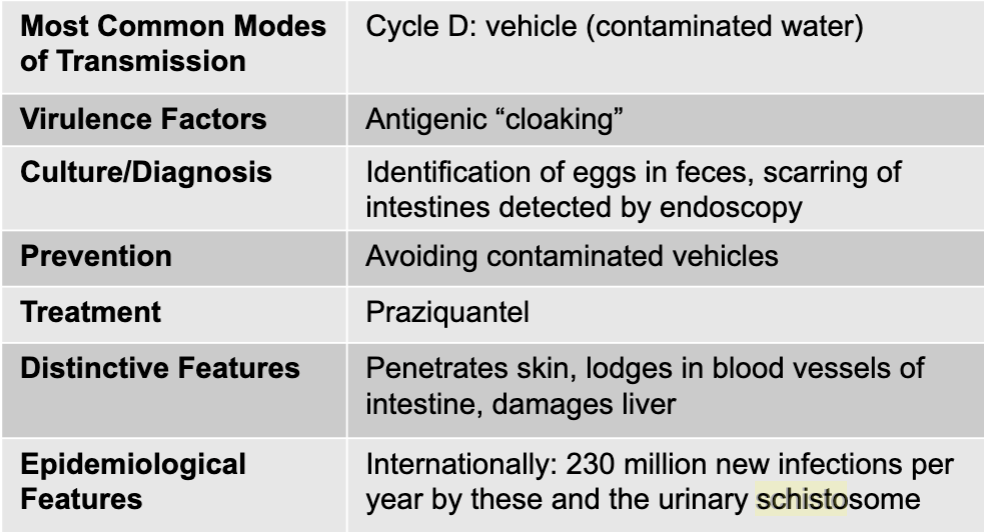
schistosoma
helminths - trematodes
rotavirus

mumps disease table
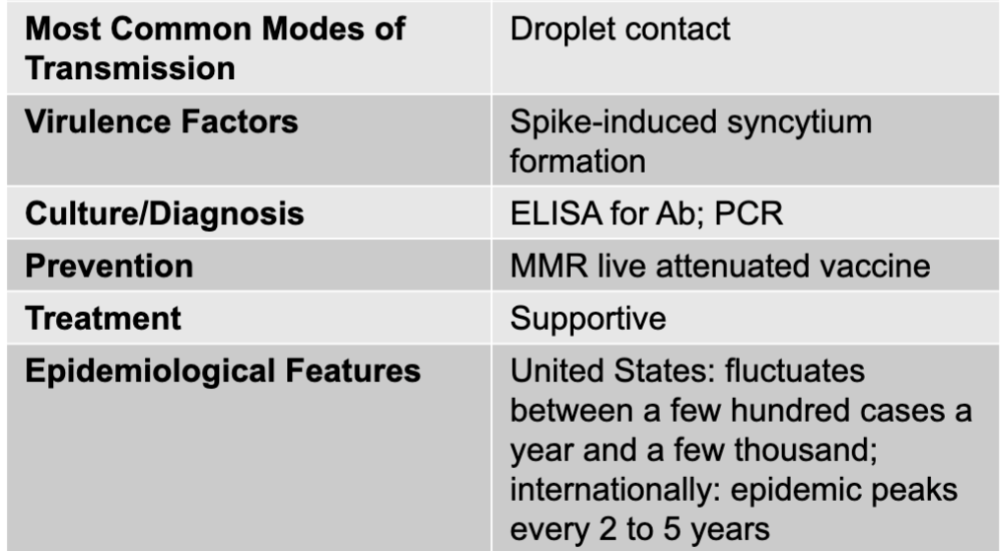
mumps virus
single-stranded RNA virus from the paramyxovirus genus
giardia duodenalis causing chronic diarrhea
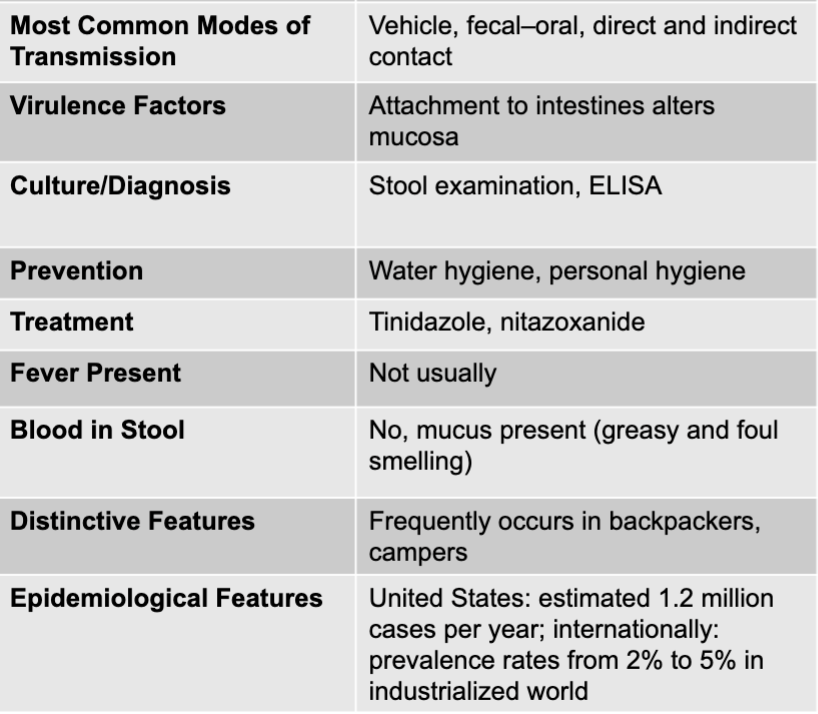
giardia duodenalis
flagellated protozoan
enterobius vermicularis disease table
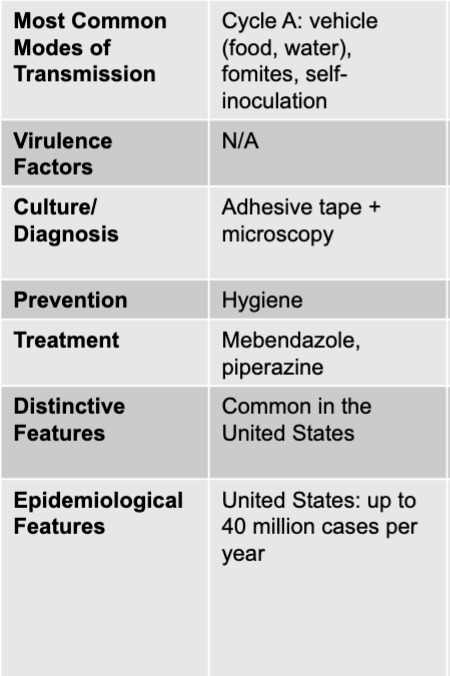
enterobius vermicularis
pinworm
most common worm disease in children of temperate zones
taenia solium disease table
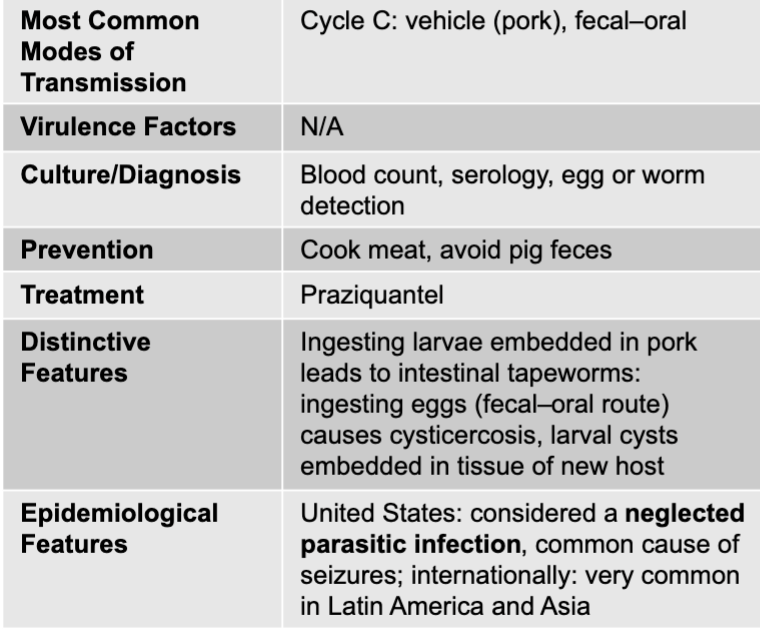
taenia solium
tapeworm
adults worms are up to 5 m long
fasciola hepatica causing liver and intestinal disease

fasciola hepatica
liver fluke common in sheep, cattle, goats, and other mammals
E. coli causing UTIs
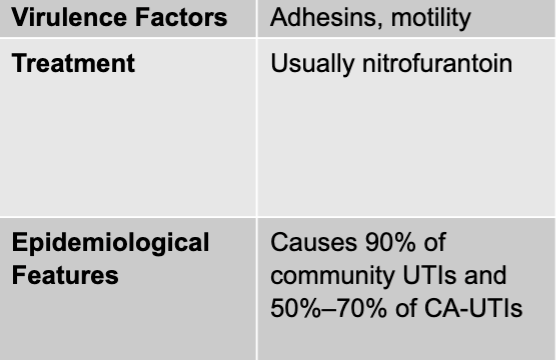
mode of transmission - opportunism, transfer from GI tract (community-acquired) or environment (catheter)
culture/diagnosis - usually culture-based; antimicrobial susceptibilities always checked
prevention - hygiene practices; in case of CA-UTIs, limit catheter usage
chlamydia disease table

chlamydia trachomatis
gram-negative bacteria
obligate intracellular parasite
cell wall prevents phagosome - lysosome fusion
treponema pollidum causing syphilis
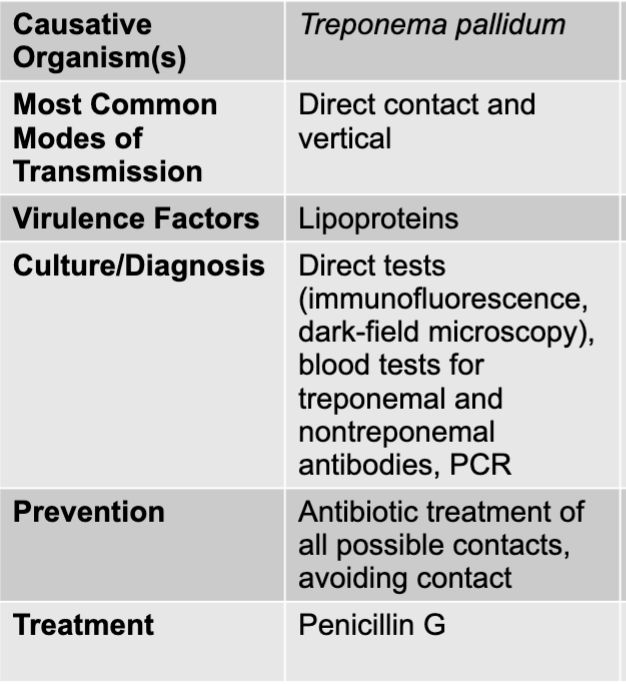
treponema pollidum
thin, regularly coiled cell with a gram-negative cell wall
hooked tip
neisseria gonorrhoaea disease table
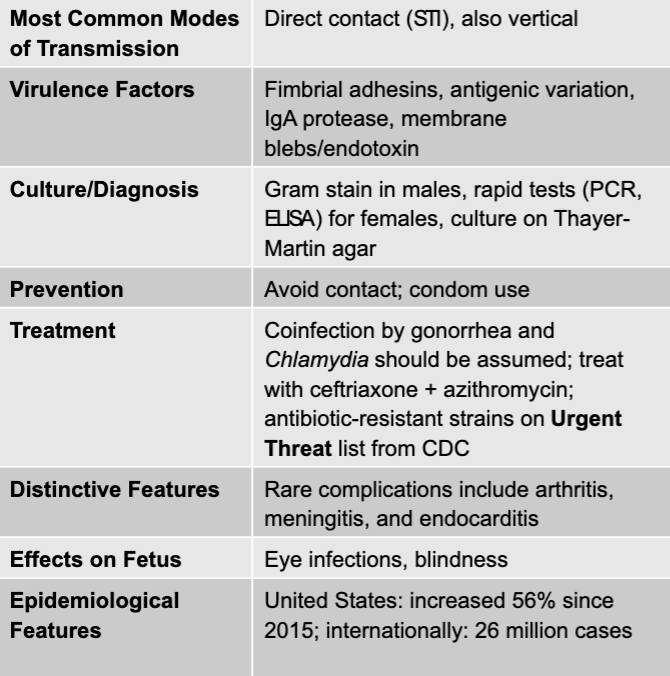
neisseria gonorrhoeae
pyogenic, gram-negative diplococcus
use fimbriae to attach to mucosal epithelial cells
haemophilus ducreyi causing chancroid

haemophilus ducreyi
pleomorphic gram-negative rod
forms a soft chancre
herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2 disease table

herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2
DNA viruses with icosahedral capsids and envelopes with glycoprotein spikes
becomes latent in ganglion
human papilomaviruses causing genital warts
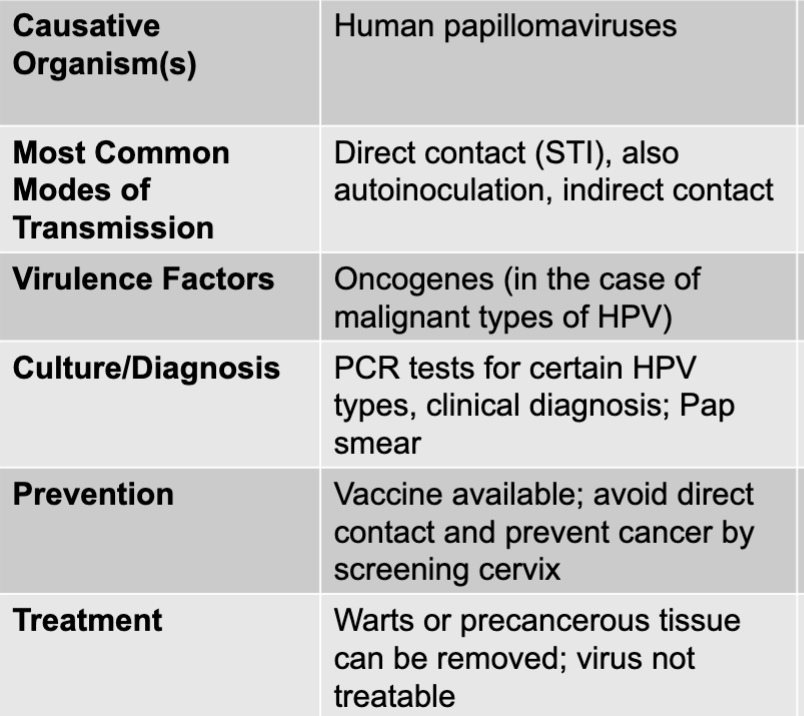
infection may or may not result in warts; infection may result in malignancy
may cause laryngeal warts on fetus
candida albicans causing vaginitis
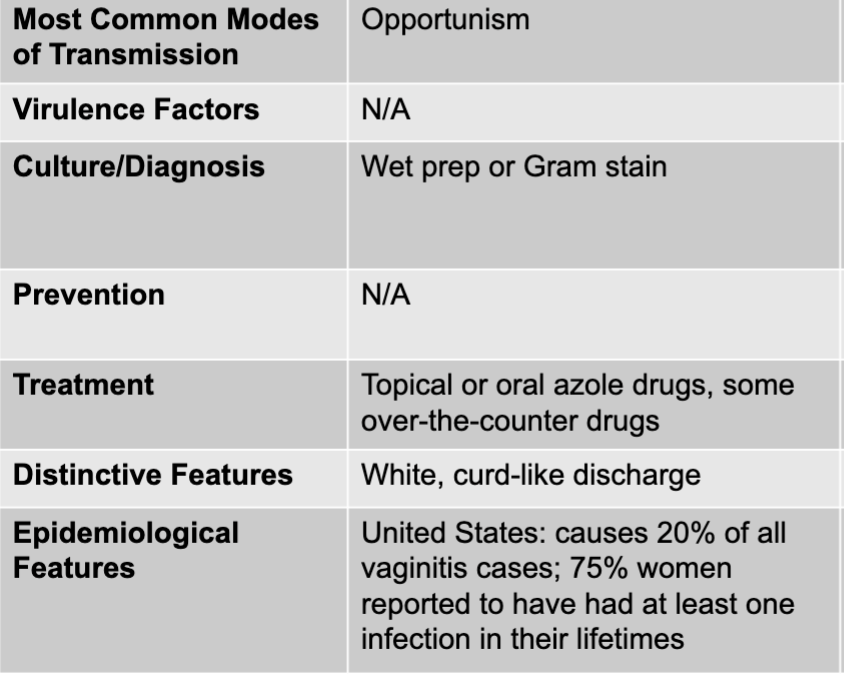
candida albicans
dimorphic fungus
normal biota of human mouth, GI tract, and vagina
trichomonas vaginalis causing vaginitis

trichomonas vaginalis
small, pear shaped protozoa
many cases are asymptomatic
schistosoma haematobium disease table

schistosoma haematobium
helminth - trematode