Priyanka is highly restrictive of her calorie intake and exercises vigorously each day. Despite having a severely low body weight, Priyanka believes she is overweight and needs to continue losing weight. When Priyanka goes to a doctor, she is MOST likely to be diagnosed with
Anorexia nervosa
Mel has been diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. His body weight is
15
percent below its ideal weight. Mel will often tell his
parents that he
isn’t hungry because he ate at school or work.
Mel claims to have
stopped on the way home at a fast-food place.
He can even produce a
receipt and the wrapping paper of the food
he ate. When Mel does eat
at home he just moves food around on
the plate. Based on this
description, Mel was most likely
diagnosed with _____ type of anorexia
nervosa.
Restricting
Research indicates that approximately _____ percent of individuals
who struggle
with anorexia nervosa are male.
25%
Which of the following symptoms is NOT characteristic of anorexia nervosa?
lack of interest in food
(symptoms: distorted body image, amenorrhea, fear of gaining weight)
Research indicates that approximately _____ percent of individuals
who struggle
with bulimia nervosa are female.
75%
Which of the following symptoms is characteristic of bulimia nervosa
but is NOT
characteristic of anorexia nervosa?
concern about pleasing others
(distorted body perception, disturbed eating attitudes, feelings of anxiety, depression, obsessiveness, and perfectionism)
Which of the following is true about the prevalence rates of anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and binge-eating disorder (BED)?
BED>BN>AN
Which of these is NOT true about anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder?
The age of onset is typically over the age of 20
Relatives of people with eating disorders are up to _____ times more likely to develop one of these disorders themselves.
6
While many individuals with anorexia nervosa benefit from treatment, studies indicate that this disorder continues to be a chronic, serious problem for at least _____ percent of these people, even after treatment.
20%
The drugs receiving the most attention recently for reducing binge
eating and
purging behaviors are:
antidepressants
Treatment is shown to provide immediate, significant improvement in about _____ of cases of bulimia nervosa.
40%
What are some key features of an Anorexia Nervosa diagnosis?
The individual purposely takes in too little food, resulting in a low BMI, fear of gaining weight, and seeks to prevent it, distorted body perception, and places inappropriate emphasis on weight or shape in self-judgements or does not consider the implications of their low weight
What are the two main subtypes of Anorexia Nervosa?
Restricting type and Binge-eating/purging type
What are the traits of the restricting type
Lose weight by cutting out sweets and fattening snacks, and eventually eliminating all food.
What are the traits of the binge-eating/purging type?
Lose weight by forcing themselves to vomit after meals or by abusing laxatives or diuretics.
What are some key features of Bulimia Nervosa
Repeated binge-eating episodes, repeated performance of ill-advised compensatory behaviors to prevent weight gain (vomiting), symptoms take place at least weekly for 3 months, and inappropriate influence of weight and shape on appraisal of oneself.
What are some key features of Binge-eating disorder to obtain a diagnosis?
Recurrent binge-eating episodes, binge eating episodes can contain at least three of these features ( really fast eating, absence of hunger, uncomfortably full, secret eating cause of shame, feelings of disgust, guilt, depressed, significant distress, binge eating episodes take place at least weekly over the course of 3 months, absence of excessive compensatory behaviors.
What are the specifiers and their criteria for Anorexia Nervosa?

Severe and Extreme usually treated in hospital settings
Escalation toward anorexia nervosa ______________________________________
may follow a stressful event
What are some key points about the clinical picture of anorexia nervosa?
- fear driving motivation
- Thinking is distorted
-potential psychological problems
-substance misuse
What are some medical problems that can occur as a result of anorexia nervosa?
Amenorrhea and Lanugo (thin hairs)
In bulimia nervosa, weight is _____________________________________________
Typically in the normal range, but can fluctuate.
What are some similarities between anorexia and bulimia nervosa?
- DISTURBED EATING ATTITUDES
- distorted body perception
- fear of becoming obese
-preoccupied with food, weight, and appearance
What are some differences between anorexia and bulimia nervosa?
AMENORRHEA is LESS likely, different medical complications, dental problems more likely
What are some key points about the Dx checklist for Binge-eating disorder.
- recurrent binge-eating episodes
- episodes consist of at least three of these features (usually fast eating, absence of hunger, uncomfortably full, secret eating due to shame, feelings of disgust, depression, or guilt
- significant distress
-take place weekly over the course of 3 months
- absence of excessive compensatory behaviors
What are the specifiers for binge eating disorder?
Mild: 1-3 episodes per week
Moderate: 4-7 episodes per week
Severe: 8-13 episodes per week
Extreme: 14 or more binge eating episodes per week
What is the main cause of eating disorders?
Multidimensional risk perspective
- more factors = greater likelihood of developing a disorder
(psychodynamic, CB, biological, societal pressures, family environment, multicultural)
Psychodynamic factors of eating disorders:
Ego deficiencies
*Bruch: psychodynamic theory of eating disorders
- disturbed mother-child interactions
- People with eating disorders inaccurately perceive internal cues, including emotional cues, and are more likely to worry about how they are viewed by others.
Cognitive-behavioral factors of ED's
- improper labeling of internal sensations and needs
-Little control over life may result in excess control of body size.
How does depression contribute to eating disorders?
Helps set the stage for eating disorders
- Similar brain circuit abnormalities are involved in those with eating disorders and depression
- Antidepressant drugs
Biological factors of ED's
Genetics, brain circuit dysfunction, WEIGHT SET POINT
- Larger and more active insula, orbitofrontal cortex, and striatum; smaller prefrontal cortex.
How do societal pressures contribute to eating disorders?
- Western standards for female attractiveness
- socially accepted prejudice against overweight people
- social networking, internet activity, TV
How does family environment contribute to eating disorders?
- History of emphasis on thinness, appearances, or dieting
- Dieting and perfectionistic mothers
What multicultural factors cause ED's ?
Racial and ethnic differences, Gender differences
- Eating behaviors, values, and goals of women in minority groups in the United States were considerably healthier than those of non-Hispanic white American women
What are the specifiers for bulimia nervosa?

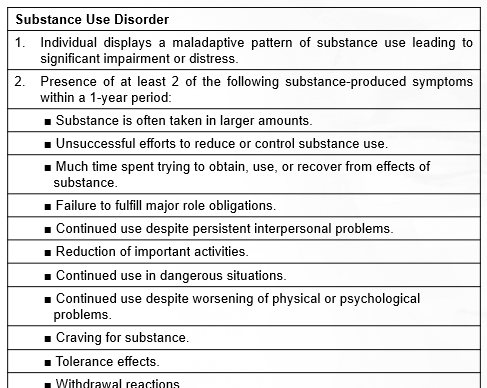
What is the Dx checklist for substance use disorders?
In any given year, ____ percent of all teens and adults in the United States, more than 20 million people, have a substance use disorder.
7.4
Only ____ percent of all those with substance use disorders receive treatment from a mental health professional.
18.4
What are some drugs that fall under depressants?
- alcohol
- sedative/hypnotics anxiolytics (benzos, barbs)
- opioids
What are some examples of stimulants?
-caffeine
- amphetamines (legals, meths)
- cocaine
What are some examples of hallucinogens?
MDMA, Ectasy, Molly, LSD
What is the main example of cannabis?
THC, used recreationally typically, relaxing and stimulates.
What is an important symptom of withdrawal, especially from prolonged use?
DTs, deliurium tremens
What are the personal and social impacts of alcoholism?
- it destroys families, social relationships, and careers
What are examples of opioids?
opium, heroin, morphine, codeine, methadone
Medical opioids are:
morphine, codeine, oxycodone
Why are opioids dangerous?
overdose, ignorance of tolerance, mixing with other substances
What are the physical dangers of cocaine?
Overdose, death
Hallucinogens produce-
powerful changes primarily in sensory perception, natural hallucinogens
Effects of polysubstance use
Synergistic effects ( they add )
Antagonistic effects ( they counteract each other)
What are the causes for substance-related disorders?
- sociocultural views
- psychodynamic views
- CB views
- Bio views
COMBINATION
What is the sociocultural view of SUD
- people who live in socioeconomic conditions
- families that value or tolerate drug use
- other stress
Psychodynamic views of SUD
-powerful early years dependency needs
- display substance abuse personality
CB views of SUD?
Operant conditioning by tension reduction, the rewarding effects of drugs
all related to conditioning
Bio views of SUD?
genetics, NTs, Pleasure Pathway
* Incentive-sensitization theory
* reward deficiency syndrome
What are the types of treatments for SUD
Detox, antagonist drugs, and drug maintenance therapy.
Antabuse is used for (antagonist)
Alcoholism
Narcan is used for (antagonist)
Opioids
Methadone is used for (drug maintenence therapy)
pain killers and heroin
Cramps, anxiety attacks, sweating, and
nausea as a result of
stopping or cutting
back alcohol use are examples of:
Withdrawal
Epidemiological studies indicate that ____
percent of the
population has a substance
use disorder in any given year.
7.4
Studies indicate that no more than _____
percent of individuals
with substance use
disorders receive treatment from a
mental
health professional.
20
Which racial or ethnic group has the lowest rates of substance use disorders
Asian americans
What percentage of the American
population, over the age of 11,
binge-drink each month?
25%
Long-term excessive alcohol use can lead to____, a disease involving
memory loss,
confusion, and other neurological
symptoms.
Korsakoff's syndrome
Despite long established links between
alcohol use during
pregnancy and fetal
alcohol spectrum disorders, about
_____
percent of pregnant women have consumed
alcohol in the
past month.
10%
The sedative-hypnotic drugs Xanax, Ativan, and Valium are all classified as:
benzodiazepines
Unlike the withdrawal symptoms that are
associated with alcohol
use disorder,
withdrawal from opioid use does NOT run
the
risk of
death
Cocaine increases the available supplies of
all of the following neurotransmitters
EXCEPT:
acetylcholine
Studies indicate that approximately 1 in
_____ college students
misuse stimulants,
such as Adderall or Ritalin, for weight
loss,
to enhance academic performance, or
simply to get high.
10
Opioids are an example of a
depressant
Tolerance to stimulant drugs is in part
caused by cutbacks in
the brain’s
production of certain
neurotransmitters,
specifically lower _____ production.
dopamine
People are MOST likely to obtain
prescription pain killers for
nonmedical
drug use from:
a friend or relative
_________ is known as an increase of effects
when multiple
substances are acting on the
body at the same time.
A synergistic effect
Teaching clients to identify high-risk
situations, learn from
mistakes and lapses,
and modify their lifestyle is MOST likely
to
happen in:
relapse-prevention training