dental caries disease table
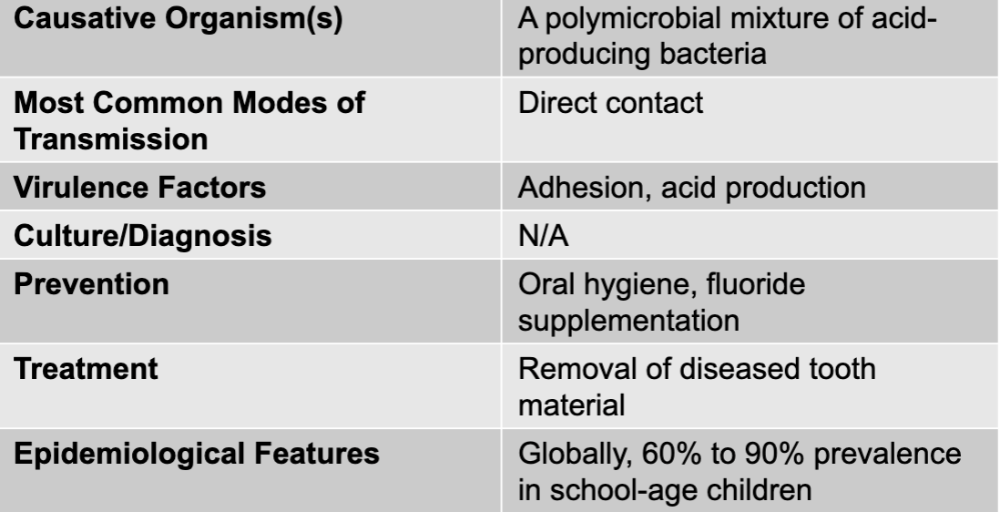
dental caries causative agent
a polymicrobial mixture of acid-producing bacteria
dental caries mode of transmission
direct contact
dental caries virulence factors
adhesion, acid production
dental caries culture/diagnosis
N/A
dental caries prevention
oral hygiene, fluoride supplementation
dental caries treatment
removal of diseased tooth material
dental caries epidemiological features
globally, 60% to 90% prevalence in school-age children
periodontitis disease table
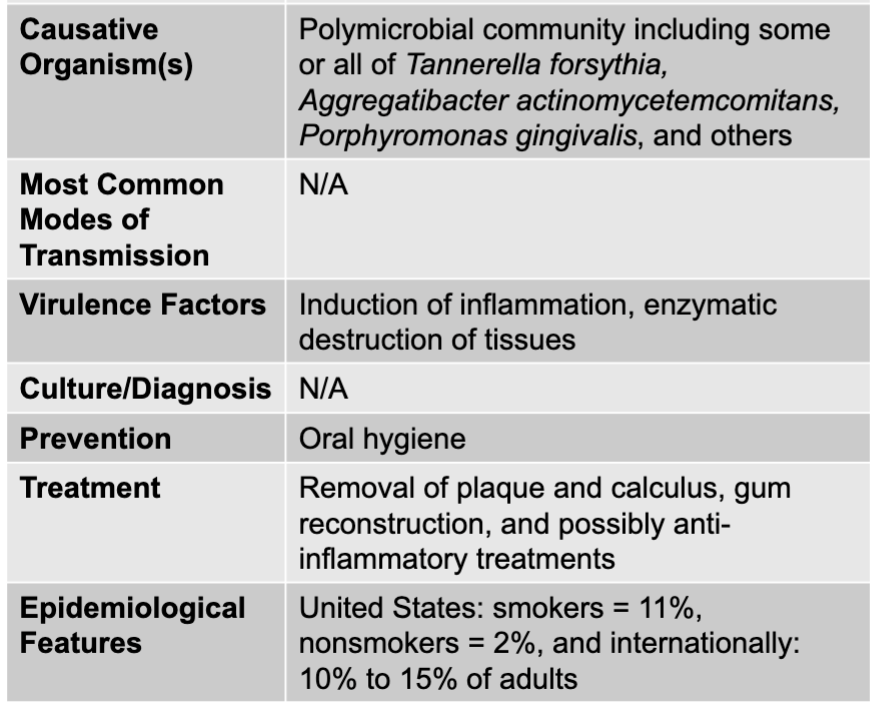
necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis and periodontitis disease table
periodontitis causative agents
polymicrobial community including some or all of Tannerella forsythia, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, and others
periodontitis virulence factors
induction of inflammation, enzymatic destruction of tissues
periodontitis prevention
oral hygiene
periodontitis treatment
removal of plaque and calculus, gum reconstruction, and possibly anti-inflammatory treatments
periodontitis epidemiological features
US: smokers = 11%, nonsmokers = 2%, and internationally: 10% to 15% of adults
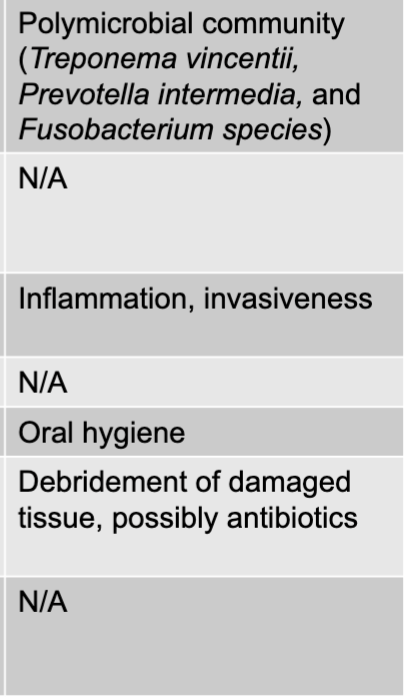
NUG or NUP causative agents
polymicrobial community (treponema vincentii, prevotella intermedia, and fuso bacterium species)
NUG or NUP virulence factors
inflammation, invasiveness
NUG or NUP prevention
oral hygiene
NUG or NUP treatment
debridement of damaged tissue, possibly antibiotics
NUG or NUP epidemiological features
N/A
mumps disease table
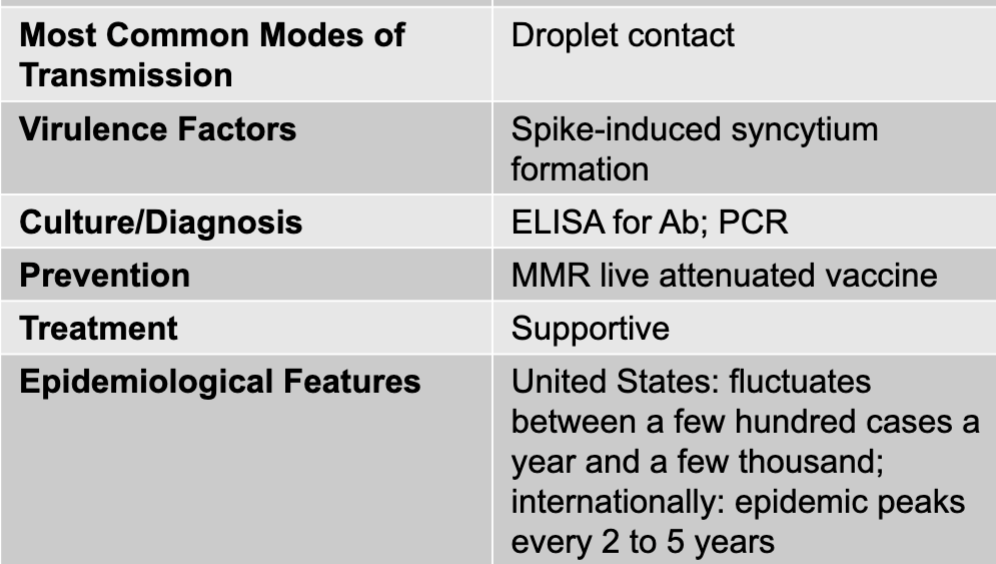
mumps causative agent
mumps virus (genus paramyxovirus)
mumps mode of transmission
droplet contact
mumps virulence factors
spike-induced syncytium formation
mumps culture/diagnosis
ELISA for Ab; PCR
mumps prevention
MMR live attenuated vaccine
mumps treatment
supportive
mumps epidemiological features
US: fluctuates between a few hundred cases a year and a few thousand; internationally; epidemic peaks every 2 to 5 years
gastritis and gastric ulcers disease table
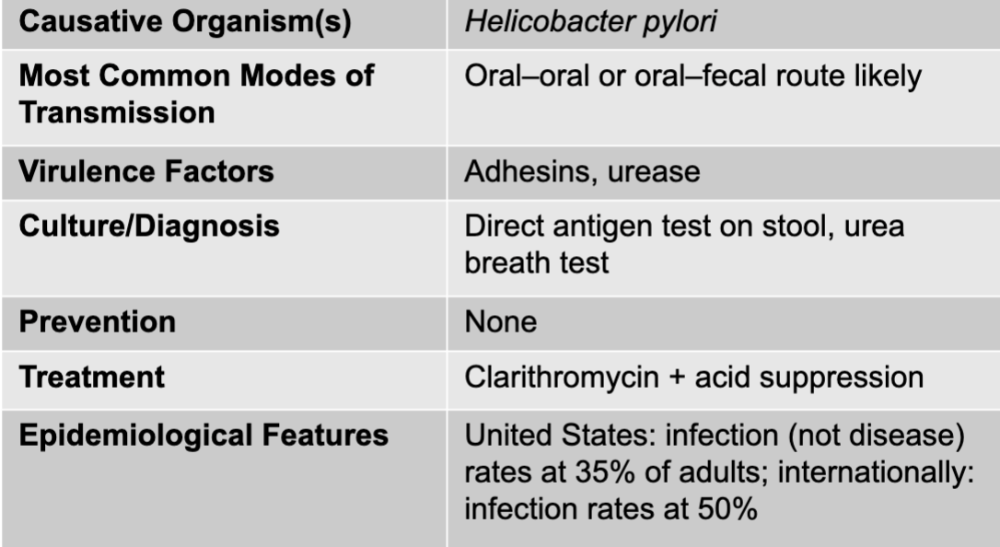
gastritis causative agents
helicobacter pylori
gastritis mode of transmission
oral-oral or oral-fecal route likely
gastritis virulence factors
adhesins, urease
gastritis culture/diagnosis
direct antigen test on stool, urea breath test
gastritis prevention
none
gastritis treatment
clarithromycin + acid suppression
gastritis epidemiological features
US: infection (not disease) rates at 35% of adults; internationally: infection rates at 50%
acute diarrhea causative agents
salmonella, shigella, shiga toxin-producing E. coli, other E. colie, campylobacter, clostridioides difficile, vibrio cholerae, and non-cholera vibrio species
salmonella disease table
shigella disease table
shiga toxin-producing E. coli disease table

other E. coli disease table
campylobacter disease table

clostridioides difficile disease table

vibrio cholerae disease table
non-cholera vibrio species
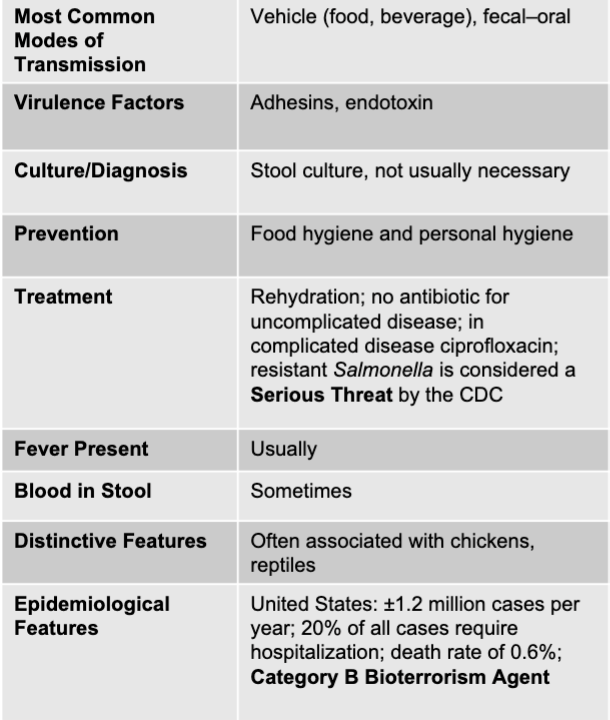
salmonella mode of transmission
vehicle (food, beverage), fecal-oral
salmonella virulence factors
adhesions, endotoxin
salmonella culture/diagnosis
stool culture, not usually necessary
salmonella prevention
food hygiene and personal hygiene
salmonella treatment
rehydration; no antibiotic for uncomplicated disease; in complicated disease ciprofloxacin; resistant salmonella is considered a serious threat by the CDC
is fever present with salmonella?
usually
is blood present in the stool with salmonella?
sometimes
salmonella distinctive features
often associated with chickens, reptiles
salmonella epidemiological features
US: +/- 1.2 million cases per year; 20% of all cases require hospitalization; death rate of 0.6%; category b bioterrorism agent
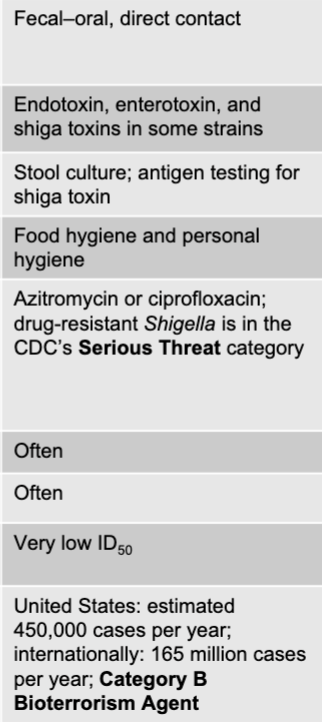
shigella mode of transmission
fecal-oral, direct contact
shigella virulence factors
endotoxin, enterotoxinm and shiga toxins in some strains
shigella culture/diagnosis
stool culture; antigen testing for shiga toxin
shigella prevention
food hygiene and personal hygiene
shigella treatment
azitromycin or ciprofloxacin; drug-resistant shigella is in the CDC's serious threat category
is fever present with shigella?
often
is blood in the stool with shigella?
often
shigella distinctive features
very low in ID50
shigella epidemiological features
US: estimated 450,000 cases per year; internationally: 165 million cases per year; category b bioterrorism agent
shiga toxin-producing E. coli mode of transmission
vehicle (food, beverage), fecal-oral
shiga toxin-producing E.coli virulence factors
shiga toxins; proteins for attachment, secretion, and effacement
shiga toxin-producing culture/diagnosis
stool culture, antigen testing for shiga toxin
shiga-toxin producing E.coli prevention
avoid live E. coli (cook meat and clean vegetables); stay aware of food recalls
shiga-toxin producing E.coli treatment
antibiotics contraindicated, supportive measures
is fever present when shiga-toxin producing E.coli?
often
is blood in the stool with shiga-toxin producing E.coli?
usually
shiga toxin-producing distinctive features
hemolytic uremic syndrome
shiga toxin-producing epidemiological features
internationally: causes HUS in 10% of patients; 25% of HUS patients suffer neurological complications, 50% have chronic renal sequelae; category b bioterrorism agent
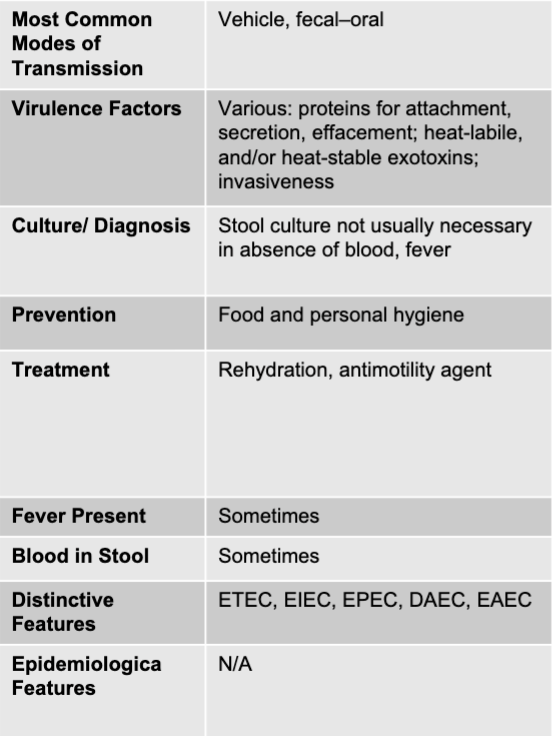
other E.coli mode of transmission
vehicle, fecal-oral
other E.coli virulence factors
various: proteins for attachment, secretion, effacement; heat-liable, and/or heat-stable exotoxins; invasiveness
other E.coli culture/diagnosis
stool culture not usually necessary in absence of blood, fever
other E.coli prevention
food and personal hygiene
other E.coli treatment
rehydration, anti-motility agent
other E.coli fever present
sometimes
other E.coli blood in stool
sometimes
other E.coli distinctive features
ETEC, EIEC, EPEC, DAEC, EAEC
campylobacter mode of transmission
vehicle (food, water), fecal-oral
campylobacter virulence factors
adhesins, exotoxin, and induction of autoimmunity
campylobacter culture/diagnosis
stool culture not usually necessary; dark-field microscopy
campylobacter prevention
food and personal hygiene
campylobacter treatment
rehydration; azithromycin in severe cases
campylobacter fever present
usually
campylobacter blood in stool
no
campylobacter distinctive features
guillain-barre syndrome
campylobacter epidemiolgica features
US: 1.3 million cases per year; internationally: 400 million cases per year
clostridioides difficle mode of transmission
endogenous (normal biota)
clostridioides difficle virulence factors
enterotoxins A and B
clostridioides difficle culture/diagnosis
stool culture, PCR, ELISA demonstration of toxins in stool
clostridioides difficle prevention
N/A
clostridioides difficle treatment
metronidazole in mild cases, vancomycin for severe, fecal transplants, resistant strains are in the CDC's urgent threat category
clostridioides difficle fever present
sometimes
clostridioides difficle blood in stool
not usually; mucus prominent
clostridioides difficle distinctive features
associated with disruption of normal biota
clostridioides difficle epidemiologic features
US: 500,000 cases per year
vibrio cholerae mode of transmission
vehicle (water and some foods), fecal-oral
vibrio cholerae virulence factors
cholera toxin
vibrio cholerae culture/diagnosis
clinical diagnosis, microscopic techniques, serological detection of antitoxin
vibrio cholerae prevention
water and food hygiene
vibrio cholerae treatment
rehydration and possibly doxycycline
vibrio cholerae fever present
no
vibrio cholerae blood in stool
no
vibrio cholerae distinctive features
rice-water stools
vibrio cholerae epidemiological features
global estimate: 21,000-143,000 deaths annually; category b bioterrorism agent
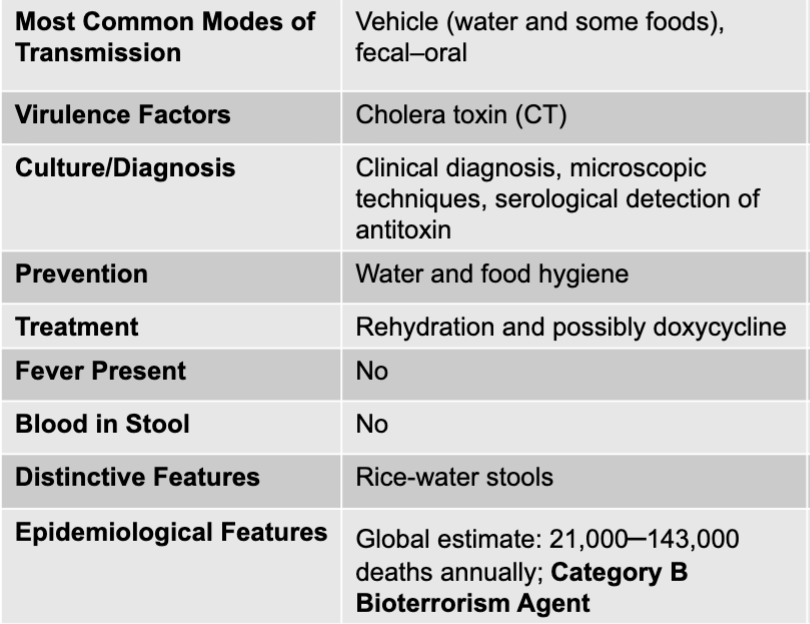
non-cholera vibrio species mode of transmission
vehicle (food or natural bodies of water)
non-cholera vibrio species virulence factors
N/A
non-cholera vibrio species culture diagnosis
culture of stool or blood
non-cholera vibrio species prevention
avoiding raw shellfish
non-cholera vibrio species treatment
doxycycline
non-cholera vibrio species fever present
yes
non-cholera vibrio species blood in stoool
no
non-cholera vibrio species distinctive features
sepsis can follow
non-cholera vibrio species epidemiological features
cause: 90% of seafood-related deaths in the US
nonbacterial causes of acute diarrhea
cryptosporidium, rotavirus, norovirus
cryptosporidium mode of transmission
vehicle (water, food), fecal-oral
cryptosporidium virulence factors
intracellular growth
cryptosporidium culture/diagnosis
acid-fast staining, ruling out bacteria
cryptosporidium prevention
water treatment, proper food handling
cryptosporidium treatment
none of nitazoxanide
cryptosporidium fever present
often
cryptosporidium blood in stool
not usually
cryptosporidium distinctive features
resistant to chlorine disinfection
cryptosporidium epidemiological features
US: estimated 748,000 cases per year; 30% seropositive; category b bioterrorism agent
rotavirus mode of transmission
fecal-oral, vehicle, formite
rotavirus virulence factors
N/A
rotavirus culture/diagnosis
rapid antigen test
rotavirus prevention
oral live-virus vaccine
rotavirus treatment
rehydration
rotavirus fever present
often
rotavirus blood in stool
no
rotavirus distinctive features
severe in infants
rotavirus epidemiological features
US: 2-3 million cases per year internationally; 125 million cases of infantile diarrhea annually
norovirus mode of transmission
indirect, vehicle (food), direct contact
norovirus virulence factors
limited immunity to reinfection
norovirus culture/diagnosis
rapid antigen test
norovirus prevention
hygiene
norovirus treatment
rehydration
norovirus fever present
sometimes
norovirus blood in stool
no
norovirus distinctive features
resistant to disinfection
norovirus epidemiological features
US: second most common cause of foodborne illness hospitalizations
are fevers present in acute diarrhea with vomitting?
not usually
is blood in stool present in acute diarrhea with vomitting?
no
acute diarrhea with vomiting causative agents
staphylococcus aureus exotoxin, bacillus cereus exotoxin, clostridium perfringens exotoxin
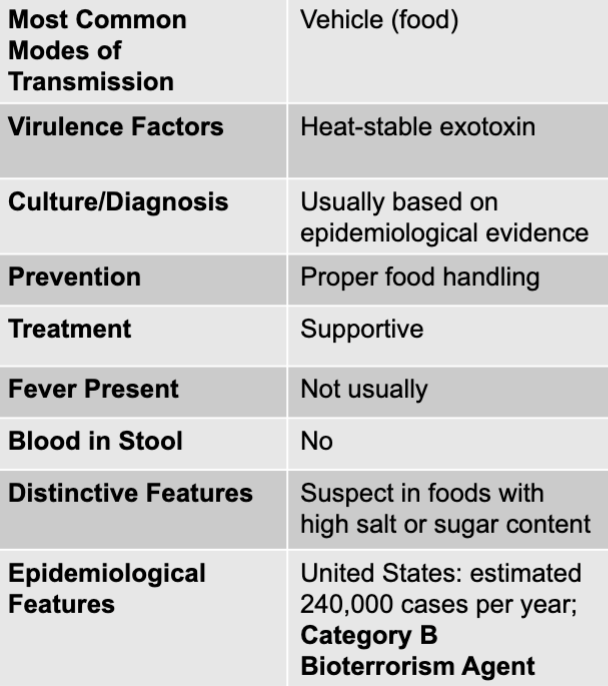
staphylococcus aureus exotoxin mode of transmission
vehicle (food)
staphylococcus aureus exotoxin virulence factors
heat-stable exotoxin
staphylococcus aureus exotoxin culture/diagnosis
usually based on epidemiological evidence
staphylococcus aureus exotoxin prevention
proper food handling
staphylococcus aureus exotoxin treatment
supportive
staphylococcus aureus exotoxin distinctive features
suspect in foods with high salt or sugar content
staphylococcus aureus exotoxin epidemiological features
US: estimated 240,000 cases per year; category b bioterrorism agent
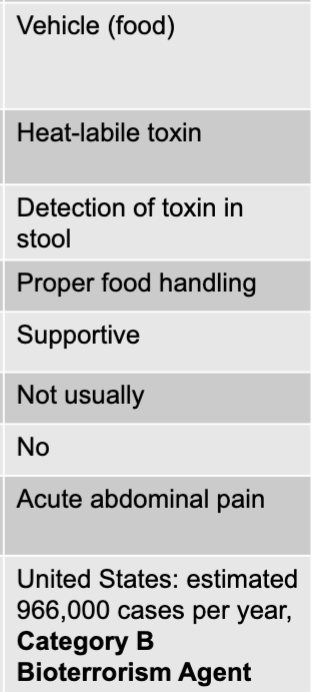
bacillus cereus exotoxin mode of transmission
vehicle (food)
bacillus cereus exotoxin virulence factors
heat-stable toxin, heat-liable toxin
bacillus cereus exotoxin culture/diagnosis
microscopic analysis of food or stool
bacillus cereus exotoxin prevention
proper food handling
bacillus cereus exotoxin treatment
supportive
bacillus cereus exotoxin distinctive features
two forms: emetic and diarrheal
bacillus cereus exotoxin epidemiological features
US: estimated 63,000 cases per year
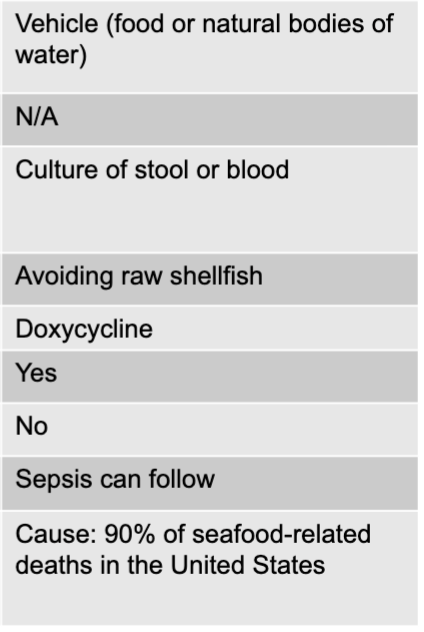
clostridium perfringens exotoxin mode of transmission
vehicle (food)
clostridium perfringens exotoxin virulence factors
heat-liable toxin
clostridium perfringens exotoxin culture/diagnosis
detection of toxin in stool
clostridium perfringens exotoxin prevention
proper food handling
clostridium perfringens exotoxin treatment
supportive
clostridium perfringens exotoxin distinctive features
acute abdominal pain
clostridium perfringens exotoxin epidemiological features
US: estimated 966,000 cases per year, category b bioterrorism agent
clostridium perfringens exotoxin disease table
bacillus cereus exotoxin disease table

staphylococcus aureus exotoxin disease table
chronic disease causative agents
enteroaggregative E.coli (EAEC), cyclospora cayetanensis, giardia lamblia, entamoeba histolytica
enteroaggregative E.coli (EAEC) mode of transmission
vehicle (food, water), fecal-oral
enteroaggregative E.coli (EAEC) virulence factors
?
enteroaggregative E.coli (EAEC)
difficult to distinguish from other E. coli
enteroaggregative E.coli (EAEC) treatment
rehydration of ciprofioxacin
enteroaggregative E.coli (EAEC) blood in stool
sometimes, mucus also
enteroaggregative E.coli (EAEC) fever present
no
enteroaggregative E.coli (EAEC) distinctive features
chronic in the malnourished
enteroaggregative E.coli (EAEC) epidemiological features
developing countries: 87% of chronic diarrhea in children >2 years old
cyclospora cayetanensis mode of transmission
fecal-oral, vehicle
cyclospora cayetanensis virulence factors
invasiveness
cyclospora cayetanensis culture/diagnosis
stool examination, PCR
cyclospora cayetanensis prevention
washing, cooking food, and personal hygiene
cyclospora cayetanensis treatment
TMP-SMZ
cyclospora cayetanensis fever present
usually
cyclospora cayetanensis blood in stool
no
cyclospora cayetanensis distinctive features
N/A
cyclospora cayetanensis epidemiological features
US: estimated 16,000 cases per year; internationally: endemic 27 countries, mostly tropical
giardia lamblia mode of transmission
vehicle, fecal-oral, direct and indirect contact
giardia lamblia virulence factors
attachment to intestines alters mucosa
giardia lamblia culture/diagnosis
stool examination, ELISA
giardia lamblia prevention
water hygiene, personal hygiene
giardia lamblia treatment
tinidazole, nitazoxanide
giardia lamblia fever present
not usually
giardia lamblia blood in stool
no, mucus present (greasy and foul smelling)
giardia lamblia distinctive features
frequently occurs in backpackers, campers
giardia lamblia epidemiological features
US: estimated 1.2 million cases per year; internationally: prevalence rates from 2% to 5% in industrialized world
entamoeba histolytica mode of transmission
vehicle, fecal-oral
entamoeba histolytica virulence factors
lytic enzymes, induction of apoptosis, invasiveness
entamoeba histolytica culture/diagnosis
PCR, stool examination, ELISA, serology
entamoeba histolytica prevention
water hygiene, personal hygiene
entamoeba histolytica treatment
metronidazole or paromomycin
entamoeba histolytica fever present
yes
entamoeba histolytica blood in stool
yes
entamoeba histolytica distinctive features
N/A
entamoeba histolytica epidemiological features
internationally: 40,000-100,000 deaths annually
hepatitis A or E virus mode of transmission
fecal-oral, vehicle
hepatitis A or E virus culture/diagnosis
IgM serology
hepatitis A or E virus prevention
hepatitis a vaccine or combined; HAV/HBV vaccine
hepatitis A or E virus treatment
HAV: hepatitis A vaccine or immune globulin; HEV: immune globulin
hepatitis A or E virus incubation period
2-4 weeks
hepatitis A or E virus epidemiological features
hepatitis A, US: 20,000 cases annually and 40% of adults show evidence of prior infection; internationally: 1.4 million cases per year; hepatitis E, internationally: 20 million infections per year; 60% in east and southeast asia
hepatitis B virus mode of transmission
parenteral (blood contact), direct contact (especially sexual), vertical
hepatitis B virus virulence factors
latency
hepatitis B virus prevention
HMV recombinant vaccine
hepatitis B virus culture/diagnosis
ELISA
hepatitis B virus treatment
interferon, tenofovir, or entecavir
hepatitis B virus incubation period
1-6 months
hepatitis B virus epidemiological features
US: 19,000 new cases per year; 800,000 to 2.2 million have chronic infection internationally: 240 million
hepatitis C virus mode of transmission
parenteral (blood contact), vertical
hepatitis C virus virulence factors
core protein suppresses immune function
hepatitis C virus culture/diagnosis
serology, also PCR
hepatitis C virus prevention
N/A
hepatitis C virus treatment
sofosbuvir + simeprevir
hepatitis C virus incubation period
2-8 weeks
hepatitis C virus epidemiological features
US: estimated 30,000 new diagnoses per year; internationally: 150 million chronically infected
intestinal distress causative agents
enterobius vermicularis (pinworm), trichuris trichiura (whipworm), diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm), hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta
enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) disease table
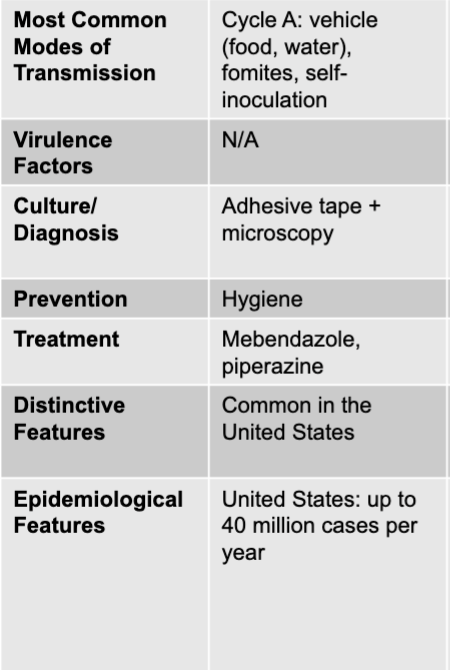
enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) modes of transmission
cycle A: vehicle (food, water), formites, self-inoculation
enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) culture/diagnosis
adhesive tape + microscopy
enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) prevention
hygiene
enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) treatment
mebendazole, piperazine
enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) distinctive features
common in the US
enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) epidemiological features
US: up to 40 million cases per year
trichuris trichiura (whipworm) disease table
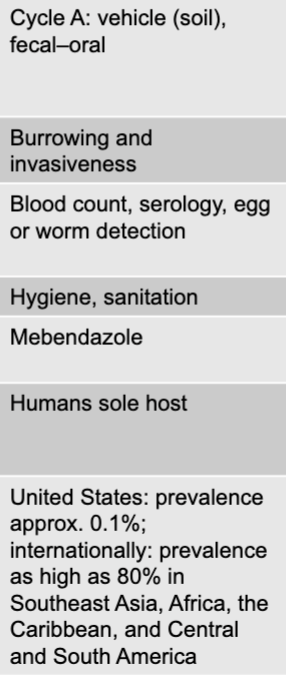
trichuris trichiura (whipworm) mode of transmission
cycle A: vehicle (soil), fecal-oral
trichuris trichiura (whipworm) virulence factors
burrowing and invasiveness
trichuris trichiura (whipworm) culture/diagnosis
blood count, serology, egg or worm detection
trichuris trichiura (whipworm) prevention
hygiene, sanitation
trichuris trichiura (whipworm) treatment
mebendazole
trichuris trichiura (whipworm) distinctive features
humans sole host
trichuris trichiura (whipworm) epidemiological features
US: prevalence approx 0.1% internationally: prevalence as high as 80% in southeast asia, africa, the caribbeam, and central and south america
diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm) disease table
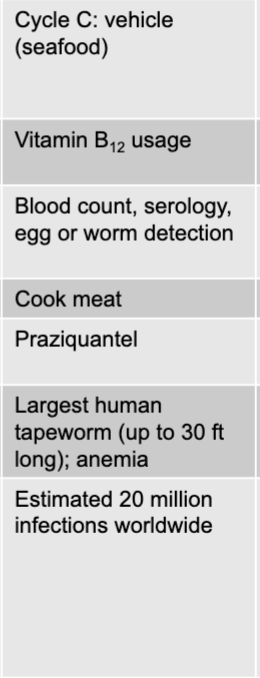
diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm) mode of transmission
cycle C; vehicle (seafood)
diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm) virulence factors
vitamin B12 usage
diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm) culture/diagnosis
blood count, serology, egg or worm detection
diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm) prevention
cook meat
diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm) treatment
praziquantel
diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm) distinctive features
largest human tapeworm (up to 30ft long); anemia
diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm) epidemiological features
estimated 20 million infections worldwide
hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta disease table

hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta mode of transmission
cycle C; vehicle (ingesting insects), fecal-oral
hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta virulence factors
N/A
hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta culture/diagnosis
blood count, serology, egg or worm detection
hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta prevention
hygienic environment
hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta treatment
praziquantel
hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta distinctive features
most common tapeworm infection
hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta epidemiological features
US: prevalence approximately 0.4%; internationally: the single most prevalent tapeworm infection
intestinal distress plus migratory symptoms causative agents
toxocara species, ascaris lumbricoides (intestinal roundworm), necator americanus and ancylostoma duodenale (hookworms)
toxocara species disease table
cycle A; dog or cat feces
toxocara species culture/diagnosis
blood count, serology, egg or worm detection
toxocara species prevention
hygiene
toxocara species treatment
albendazole
toxocara species distinctive features
can cause migration symptoms or blindness
toxocara species epidemiological features
nearly 100% of newborn puppies in the US are infected; 14% of people in the US have been infected; considered a neglected parasitic infection
ascaris lumbricoides (intestinal roundworm)
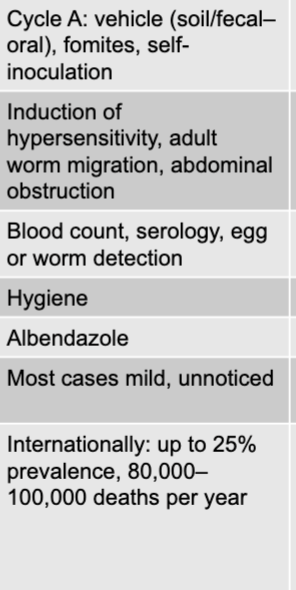
ascaris lumbricoides (intestinal roundworm) mode of transmission
cycle A: vehicle (soil/fecal-oral), formites, self-inoculation
ascaris lumbricoides (intestinal roundworm) virulence factors
induction of hypersensitivity, adult worm migration, abdominal obstruction
ascaris lumbricoides (intestinal roundworm) culture/diagnosis
blood count, serology, egg or worm detection
ascaris lumbricoides (intestinal roundworm) prevention
hygiene
ascaris lumbricoides (intestinal roundworm) treatment
albendazole
ascaris lumbricoides (intestinal roundworm) distinctive features
most cases mild, unnoticed
ascaris lumbricoides (intestinal roundworm) epidemiological features
internationally: up to 25% prevalence, 80,000-100,000 deaths per year
necator americanus and ancylostoma duodenale (hookworms) disease table

necator americanus and ancylostoma duodenale (hookworms) mode of transmission
cycle B: vehicle (soil), formite
necator americanus and ancylostoma duodenale (hookworms) virulence factors
induction of hypersensitivity, adult worm migration, abdominal obstruction
necator americanus and ancylostoma duodenale (hookworms) culture/diagnosis
blood count, serology, egg or worm detection
necator americanus and ancylostoma duodenale (hookworms) prevention
sanitation
necator americanus and ancylostoma duodenale (hookworms) treatment
albendazole
necator americanus and ancylostoma duodenale (hookworms) distinctive features
penetrates skin, serious intestinal symptoms
necator americanus and ancylostoma duodenale (hookworms) epidemiological features
US: widespread in southeast until early 1900s; internationally: 800 million infected
cysticercosis disease table
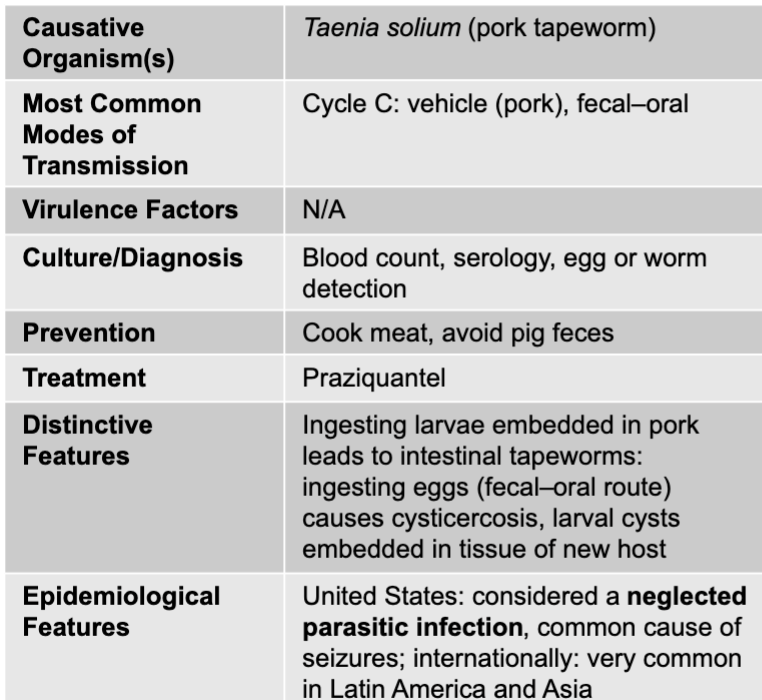
cysticercosis mode of transmission
cycle C: vehicle (pork), fecal-oral
cysticercosis culture/diagnosis
blood count, serology, egg or worm detection
cysticercosis prevention
cook meat, avoid pig feces
cysticercosis treatment
praziquantel
cysticercosis distinctive features
ingesting larvae embedded in pork leads to intestinal tapeworms: ingesting eggs (fecal-oral route) causes cysticercosis, larval cysts embedded in tissue of new host
cysticercosis epidemiological features
US: considered a neglected parasitic infection, common cause of seizures; internationally: very common in latin america and asia
liver and intestinal disease table
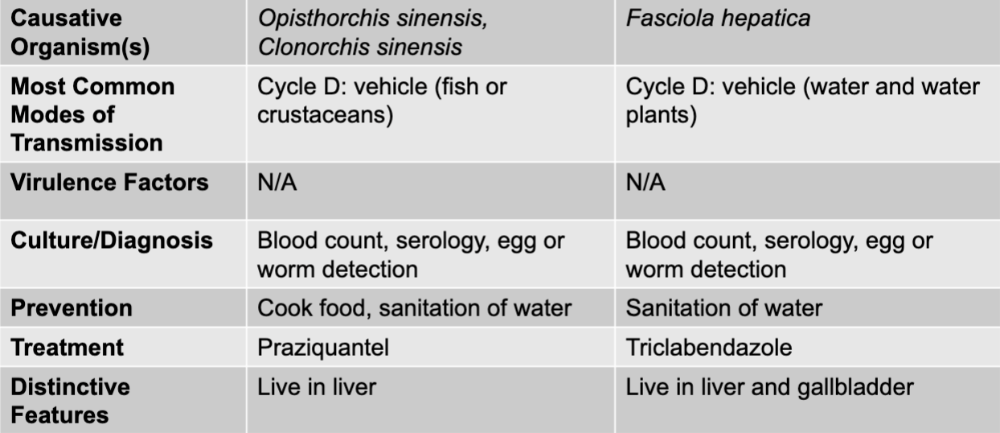
liver and intestinal causative agents
opisthorchis sinesis, clonorchis sinesis, and fasciola hepatica
opisthorchis sinesis, clonorchis sinesis mode of transmission
cycle D: vehicle (fish or crustaceans)
opisthorchis sinesis, clonorchis sinesis culture/diagnosis
blood count, serology, egg or worm detection
opisthorchis sinesis, clonorchis sinesis prevention
cook food, sanitation of water
opisthorchis sinesis, clonorchis sinesis treatment
praziquantel
opisthorchis sinesis, clonorchis sinesis distinctive features
live in liver
fasciola hepatica mode of transmission
cycle D: vehicle (water and water plants)
fasciola hepatica culture/diagnosis
blood count, serology, egg or worm detection
fasciola hepatica prevention
sanitation of water
fasciola hepatica treatment
triclabendcazole
fasciola hepatica distinctive features
live in liver and gallbladder
muscle and neurological symptoms disease table
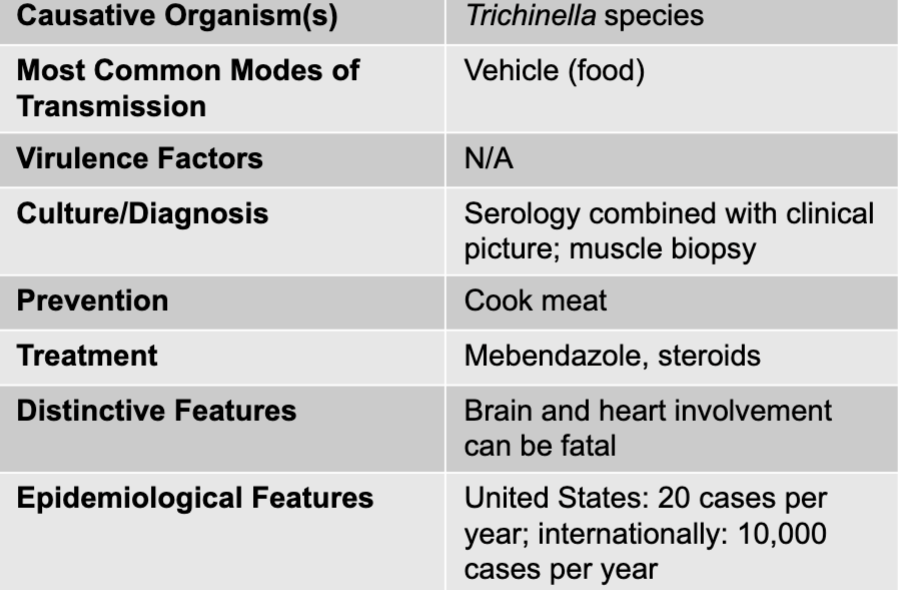
muscle and neurological symptoms causative agents
trichinella species
muscle and neurological symptoms culture/diagnosis
serology combined with clinical picture; muscle biopsy
muscle and neurological symptoms prevention
cook meat
muscle and neurological symptoms treatment
mebendazole, steroids
muscle and neurological symptoms distinctive features
brain and heart involvement can be fatal
muscle and neurological symptoms epidemiological features
US: 20 cases per year; internationally: 10,000 cases per year
schistosomiasis liver disease table
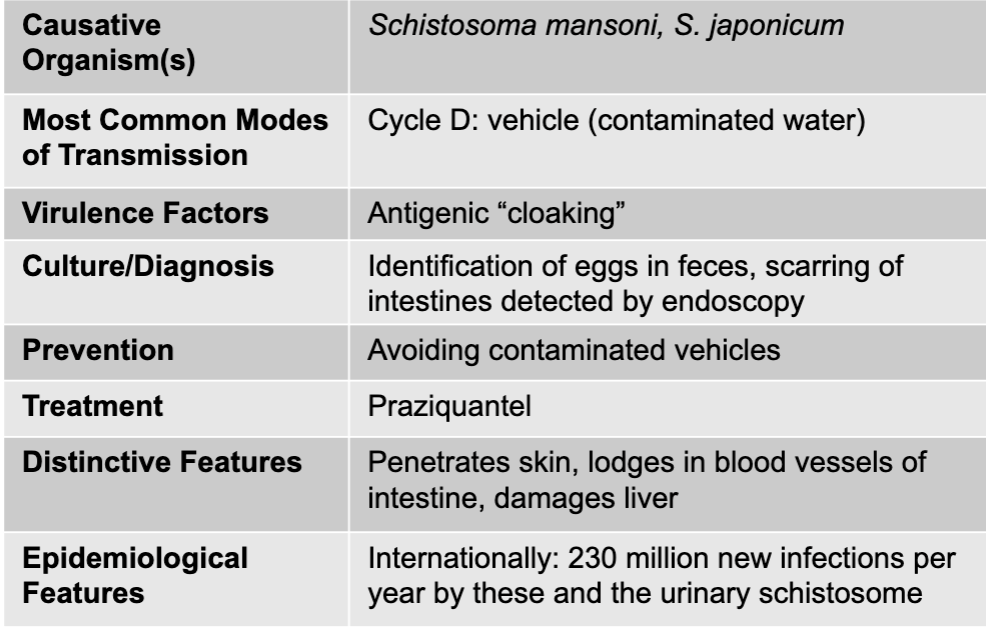
schistosomiasis causative agent
schistosoma mansoni, S. japonicum
schistosomiasis mode of transmission
cycle D: vehicle (contaminated water)
schistosomiasis virulence factors
antigenic "cloaking"
schistosomiasis culture/diagnosis
identification of eggs in feces, scarring of intestines detected by endoscopy
schistosomiasis prevention
avoiding contaminated vehicles
schistosomiasis treatment
praziquantel
schistosomiasis distinctive features
penetrates skin, lodges in blood vessels of intestine, damages liver
schistosomiasis epidemiological features
internationally: 230 million new infections per year by these and the urinary schistosome
gram-positive, endospore-forming bacteria
clostridioides difficile (antibiotic-associated diarrhea), bacillus cereus (food poisoning), clostridium perfringens (food poisoning)
gram-positive bacteria
streptococcus mutans (dental caries), streptococcus sobrinus (dental caries), staphylococcus aureus (food poisoning)
gram-negative bacteria
periodontal disease, helicobacter pylori, salmonella, shigella, escherichia coli STEC, other E.coli, campylobacter jejuni, vibrio cholera, non-cholera vibrio species
DNA viruses
hepatitus B virus
RNA viruses
mumps, rotavirus, norovirus, hepatitis A, E, and C
protozoa
cryptosporidium, cyclospora cayetanesis, giardia duodenalis, enatmoeba histolytica
helminths-nematodes
enterobius vermicularis, trichuris trichiura, toxocara species, ascaris lumbricoides, necator americanus, ancylostoma duodenale, trichinella species
helminths-cestodes
diphyllobothrium latum, hymenolepis nana, H. diminuta, taenia solium, opisthorchis sinensis, clonorchis sinensis
helminths-trematodes
fasciola hepatica, schistosoma mansoni, S. japonicum