What's the differences between mesopredators and top predators?
Only consume herbivores vs consuming herbivores and other predators.
Explain how removal of top predators can cause an increase in the distribution and abundance of mesopredators.
- Less predation of mesopredators
- Less competition for food and territory
Explain how grazing can lead to higher diversity of the plant community that is being grazed.
By reducing the biomass of certain species others have more space to grow.
Describe one factor that allows predators and prey to coexist and explain how it allows coexistence.
- The presence of suitable refuges for prey
- Dispersal advantages for prey
What is the purpose of the Lotka-Volterra model?
to explain mathematically why and how
predator and prey
populations cycle in relation to each other
Link corresponding regions on the Lotka-Volterra population trajectory graph and a graph showing prey and predator population cycles over time.
...
What is a functional response? Give an example.
The relationship between the density of prey and an individual predator’s rate of food consumption.
Ex. [enter ex. here]
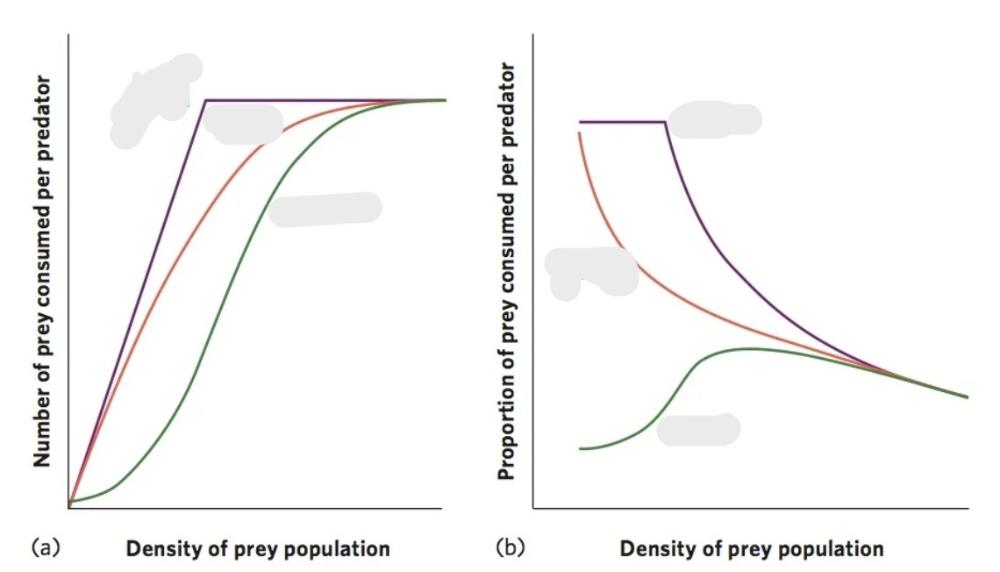
Which colour of line is which type of functional response? What causes the shapes?
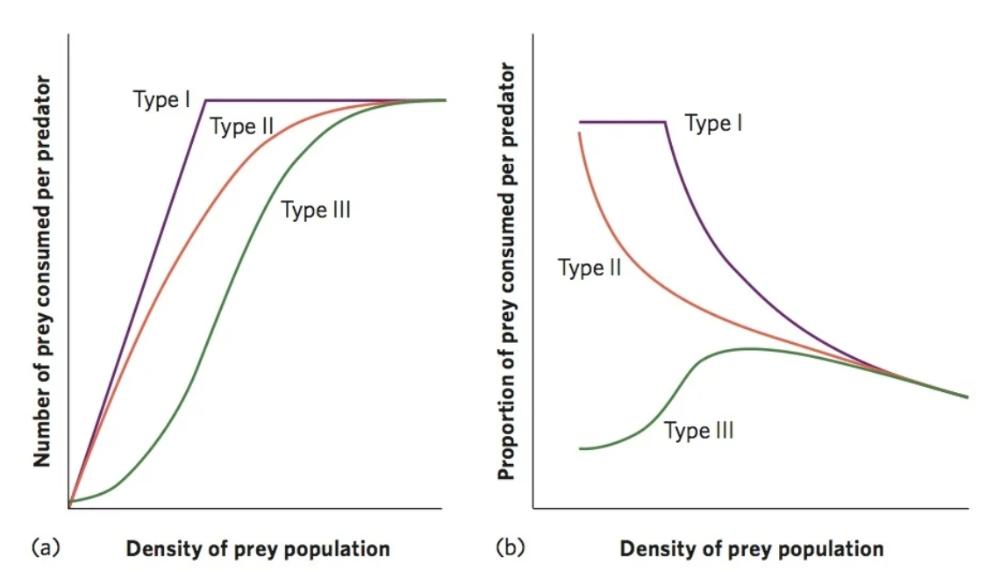
Purple= type 1, increases in prey density result in an ever-increasing number of prey consumed by a predator until the predator becomes satiated and can consume no additional prey.
Orange = type 2, the number of prey consumed slows because as predators consume more prey, they must spend more time handling the prey.
Green = type 3, as prey density increases there is an initial increase in the proportion of prey consumed. However, as the predators spend more time handling prey and become satiated, this proportion subsequently declines.
Differentiate between functional response and numerical response
Prey density and an individual predator's rate of consumption vs the change in predator population through population growth or population movement.
Give a structural example of defense against predation or herbivory.
- Porcupine quills
- Camouflage
- Change in shape of body (not camouflage)
Give a chemical example of defense against predation or herbivory.
- Foul scents (skunks)
- Bad tastes (monarchs, toads)
- Bombardier beetles (inflicting pain with hot chemical liquids)
Give a behavioural example of defense against predation or herbivory.
- Alarm calling (warn relatives)
- Spatial avoidance (move away from predator)
- Reduced activity (minimize movements, stop moving when predator is detected)