Is the surface energy balance the same everywhere on the earth's surface?
No
In addition to radiation fluxes there are also fluxes of __________ and _________ heat.
sensible and latent
All energy coming to earth enters and leaves through what?
the top of the atmosphere
Describe where shortwave radiation is absorbed, reflected or transmitted as it goes from space to Earth's surface. (think of unit amounts in the energy balance)
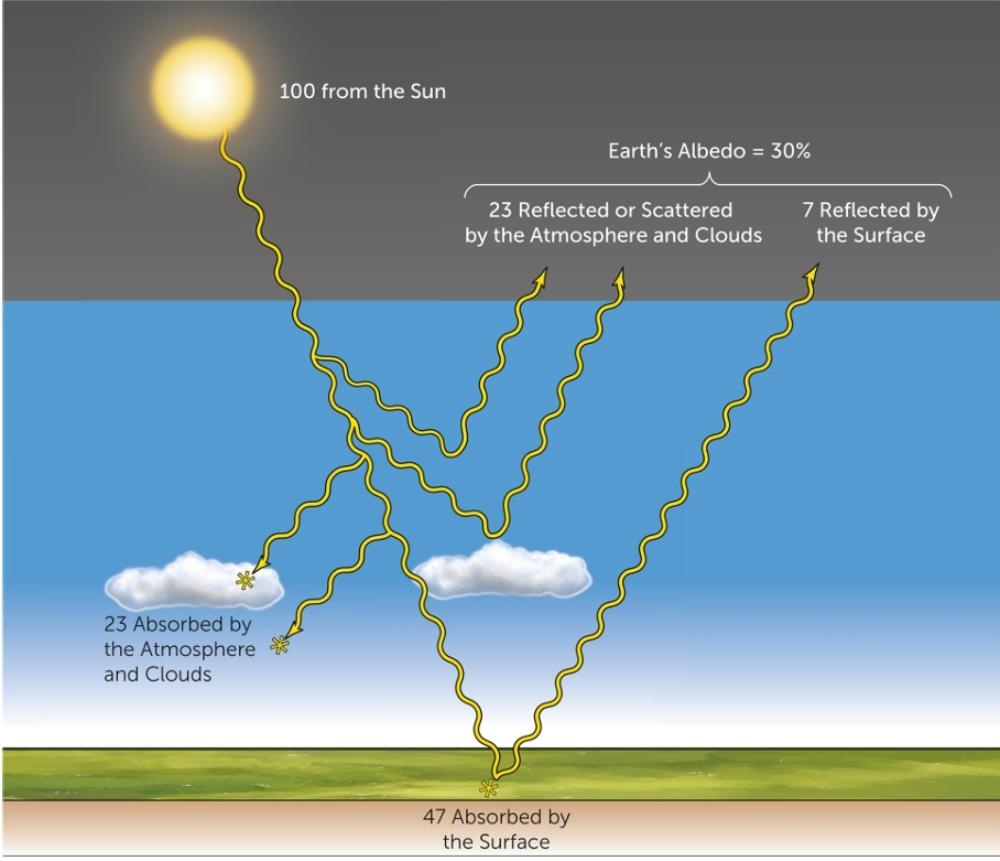
Most shortwave radiation is transmitted through the atmosphere where 23 units are absorbed and another 23 are reflected by clouds. Most of what reaches the surface is absorbed but 7 units are reflected.
Most longwave radiation emitted by the surface is ______________ by the atmosphere. What in the atmosphere is doing this?
absorbed, Greenhouse gases and clouds
Radiation emitted by the atmosphere is split between what?
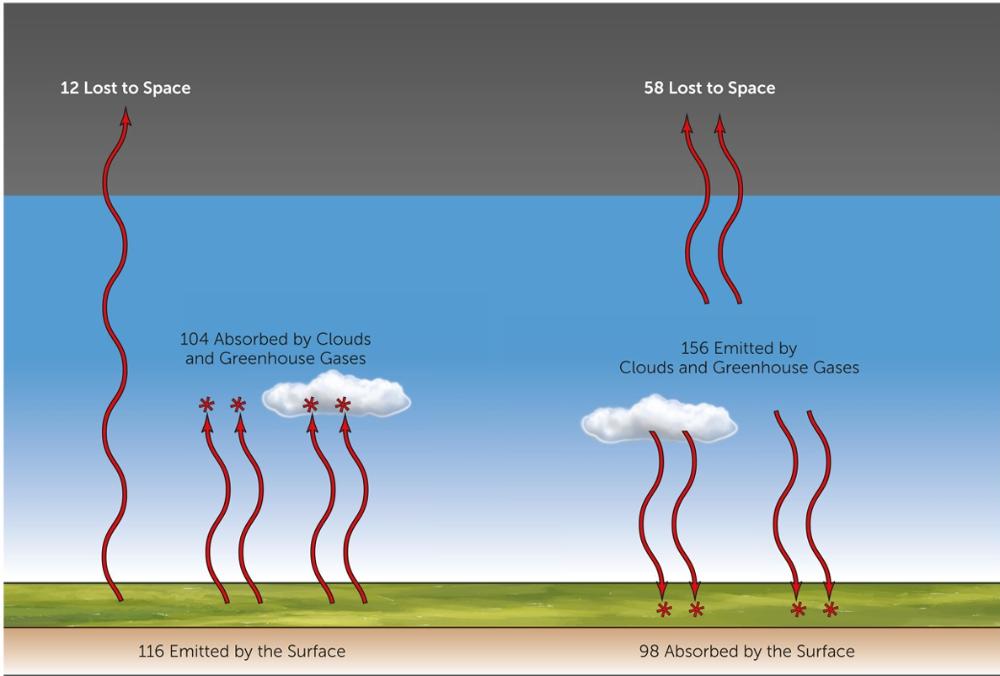
emission to space and return to the surface
Ongoing heating of the atmosphere can be seen as what in the energy balance?
an imbalance at the top of the atmosphere where 0.9 W/m2 of additional energy is being absorbed per year.
A change in the energy balance is called what?
A radiative forcing (RF value)
Give an example of a local and global radiative forcing.
• Urbanization drastically alters surface characteristics and
produces a local radiative forcing (urban
heat island)
• Greenhouse gas
emissions alter the composition of the atmosphere and produce
a global radiative forcing
What are the three fundamental types of forcings in nature?
• Tectonic
• Earth-orbital changes
• Changes in solar outputs
Give three examples of tectonic forcings.
• Land/Ocean Distribution
• Mountain Building (Rain
Shadows)
• Volcanoes
• Changes in Ocean Currents
Earth-orbital changes in the context of RFs refers to Milankovitch Cycles. What are the three orbital cycles?
• Eccentricity (wobble)
• Tilt
• Precession (path)
What is the Solar Radiation Forcing?
Sunspots
How have anthropogenic forcings influenced the atmosphere?
Changed it's composition
Which forcing source has the shortest response time?
Anthropogenic sources
What do we describe as response time?
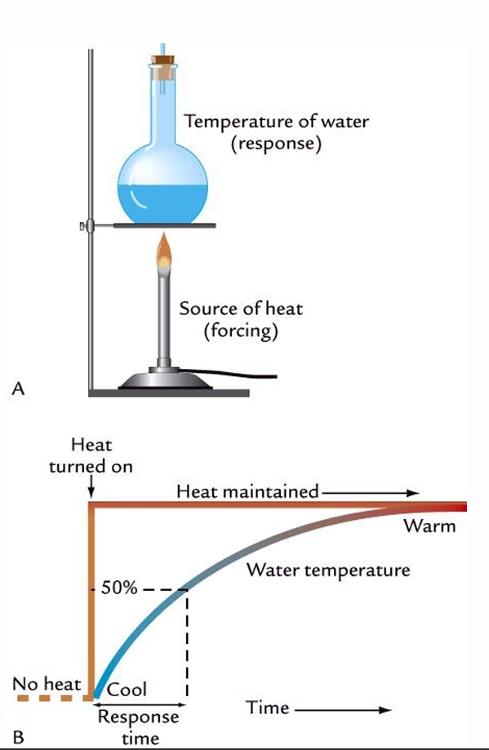
how long it takes to reach 50% of the equilibrium value
"Fast" response times in nature means changes over what spans of time? Give two examples.

Hours to centuries
"Slow" response times in nature means changes over what spans of time? Give two examples.
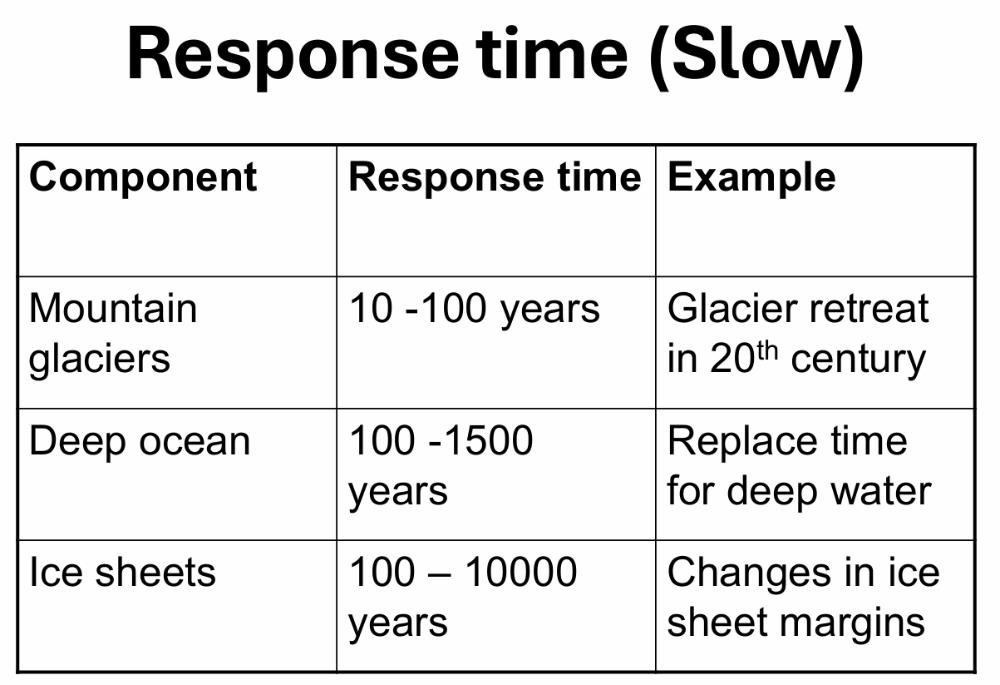
Climate responses depend on the relative rate of changes in climate ___________ verses the response time of the climate __________.
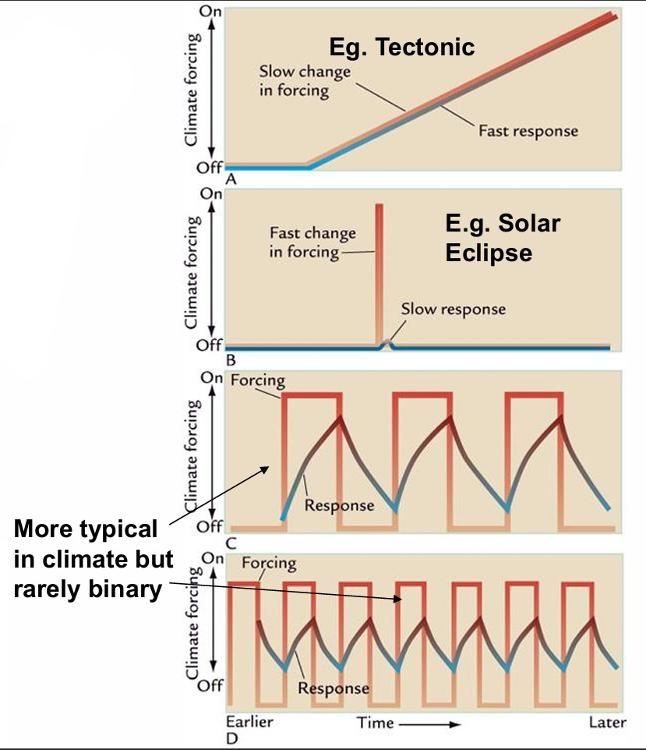
forcing vs system
What is Effective Radiating Temperature? (In words and equation)
The temperature at which a system radiates away as much energy as it receives
radiation absorbed = radiation emitted
What prevents Earth’s temperature from continuously rising or falling?
Negative feedback loops
What are the two radiative properties of clouds?
- reflect solar radiation
- absorb and emit longwave radiation
(Different cloud types may have different effects)
During the day Low ______ clouds tend to ________ the surface while High ______ clouds tend to _________ it.
thick clouds cool, thin clouds warm
At night all clouds tend to (cool/warm) the surface
warm
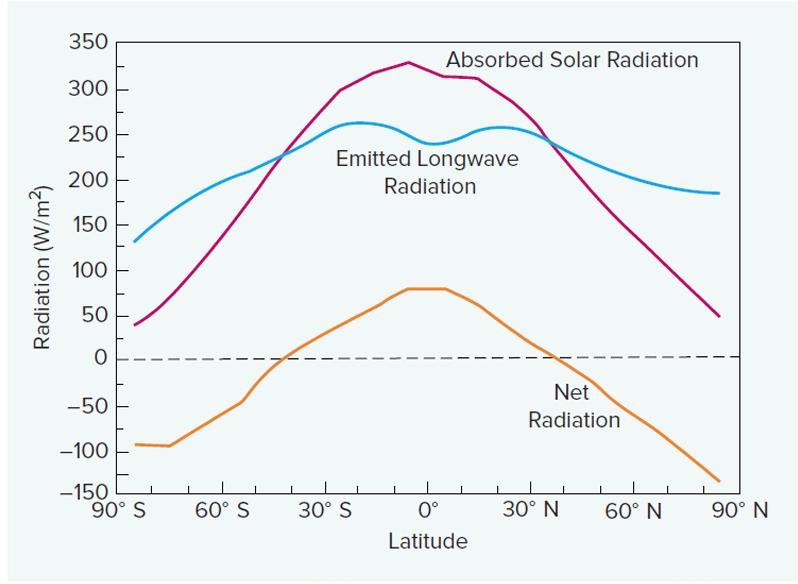
Where is does this graph tell you absorbs the most solar radiation? (The common term for this area, not the latitude)
The equator
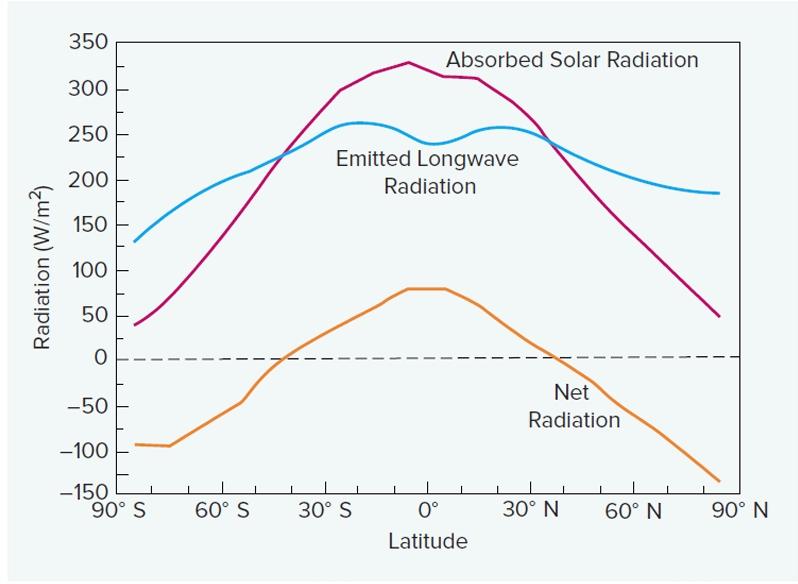
This graph has a dip in the emitted longwave radiation near the equator due to the ______________ effect, which transports energy from the ___________ to the _____________.
meridional, tropic, poles
_____________ is the transport of heat by the movement of a fluid
Advection
Name three surface conditions that greatly affect microclimates.
• Albedo
• Emissivity
• Roughness
• Moisture
content
• Heat conductivity
• Specific heat
What is the equation for net shortwave radiation? (think of the letter(s))
K* = K⇩ - K⇧
Net shortwave radiation is the difference between the incoming radiation and the amount reflected
What is the equation for net longwave radiation? (think of the letter(s))
During the day
...