Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Climate and weather, E balance
front 1 Is the surface energy balance the same everywhere on the earth's surface? | back 1 No |
front 2 In addition to radiation fluxes there are also fluxes of __________ and _________ heat. | back 2 sensible and latent |
front 3 All energy coming to earth enters and leaves through what? | back 3 the top of the atmosphere |
front 4 Describe where shortwave radiation is absorbed, reflected or transmitted as it goes from space to Earth's surface. (think of unit amounts in the energy balance) | back 4 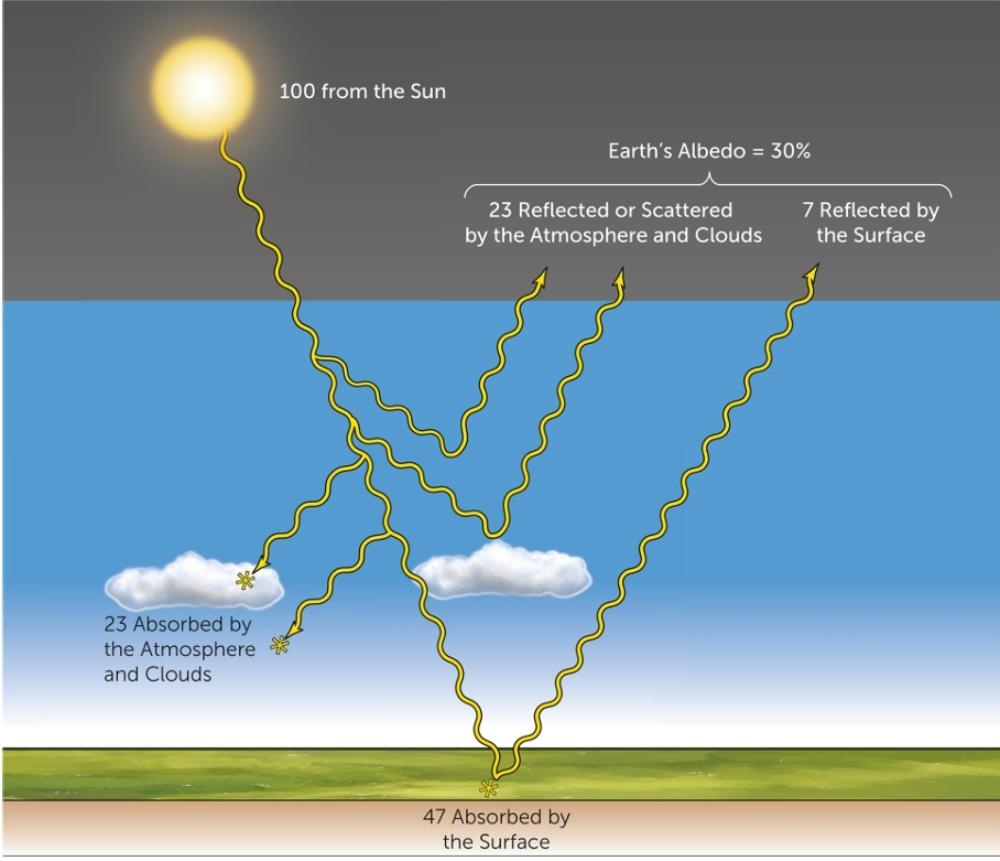 Most shortwave radiation is transmitted through the atmosphere where 23 units are absorbed and another 23 are reflected by clouds. Most of what reaches the surface is absorbed but 7 units are reflected. |
front 5 Most longwave radiation emitted by the surface is ______________ by the atmosphere. What in the atmosphere is doing this? | back 5 absorbed, Greenhouse gases and clouds |
front 6 Radiation emitted by the atmosphere is split between what? | back 6 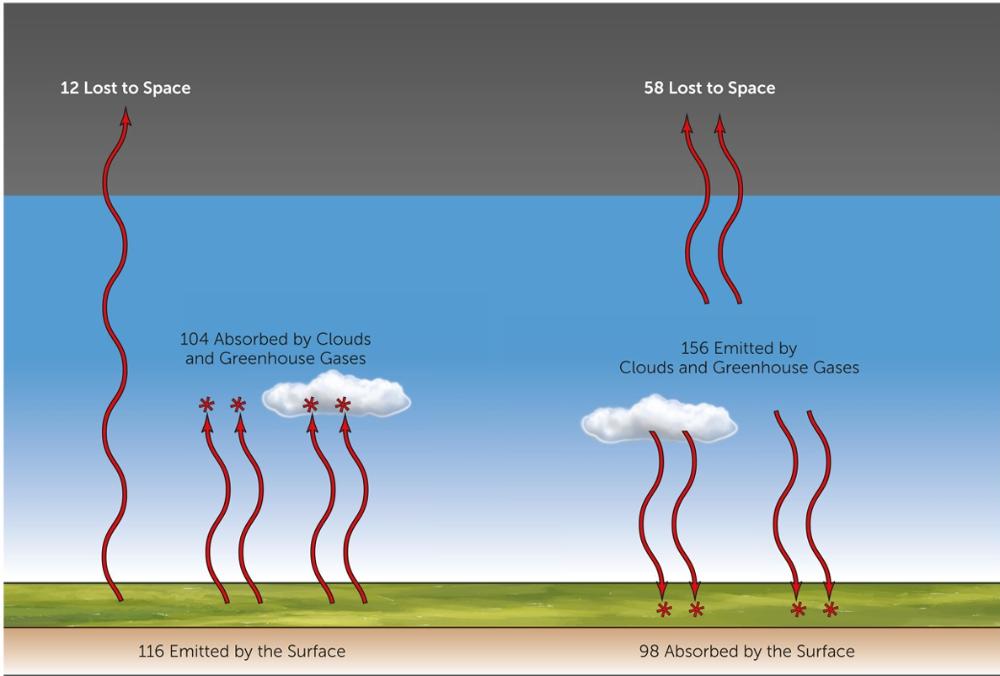 emission to space and return to the surface |
front 7 Ongoing heating of the atmosphere can be seen as what in the energy balance? | back 7 an imbalance at the top of the atmosphere where 0.9 W/m2 of additional energy is being absorbed per year. |
front 8 A change in the energy balance is called what? | back 8 A radiative forcing (RF value) |
front 9 Give an example of a local and global radiative forcing. | back 9 • Urbanization drastically alters surface characteristics and
produces a local radiative forcing (urban
heat island) |
front 10 What are the three fundamental types of forcings in nature? | back 10 • Tectonic |
front 11 Give three examples of tectonic forcings. | back 11 • Land/Ocean Distribution |
front 12 Earth-orbital changes in the context of RFs refers to Milankovitch Cycles. What are the three orbital cycles? | back 12 • Eccentricity (wobble) |
front 13 What is the Solar Radiation Forcing? | back 13 Sunspots |
front 14 How have anthropogenic forcings influenced the atmosphere? | back 14 Changed it's composition |
front 15 Which forcing source has the shortest response time? | back 15 Anthropogenic sources |
front 16 What do we describe as response time? | back 16 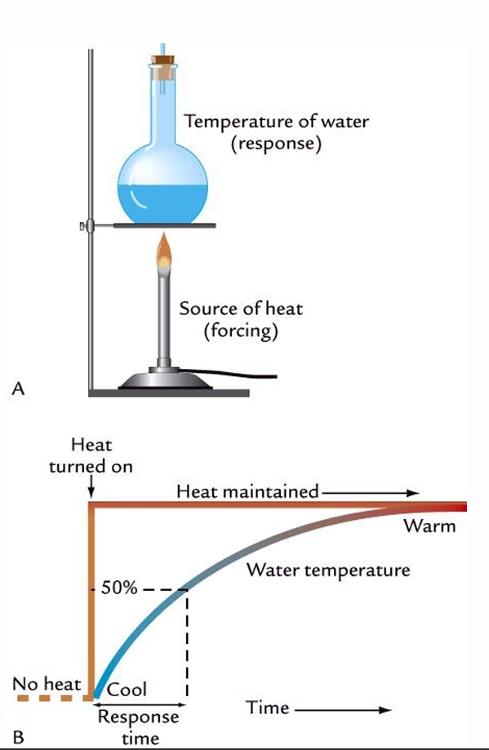 how long it takes to reach 50% of the equilibrium value |
front 17 "Fast" response times in nature means changes over what spans of time? Give two examples. | back 17  Hours to centuries |
front 18 "Slow" response times in nature means changes over what spans of time? Give two examples. | back 18 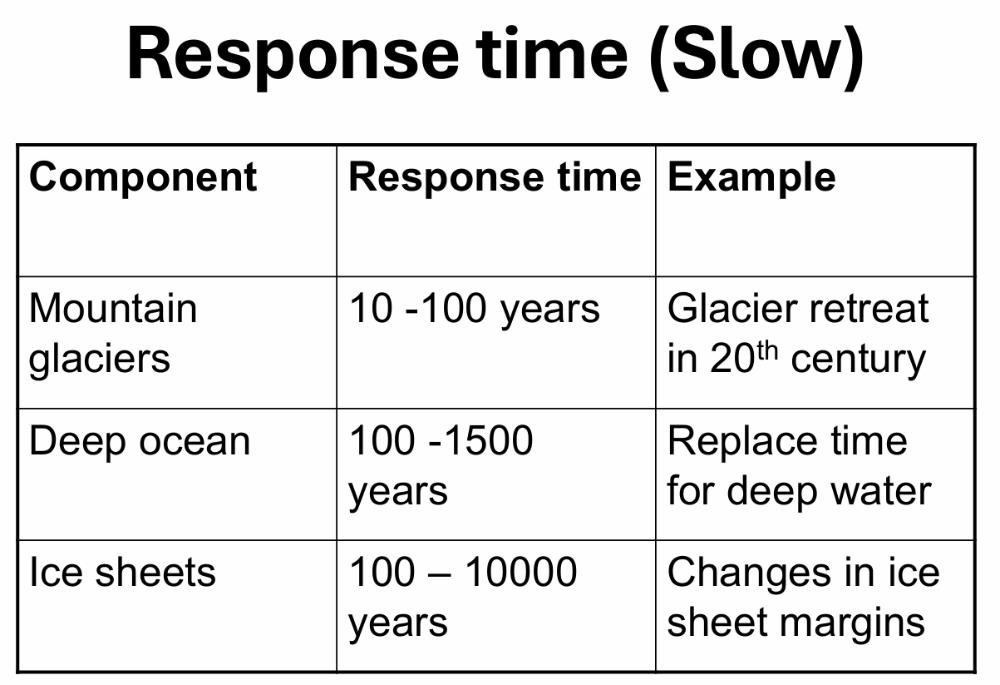 |
front 19 Climate responses depend on the relative rate of changes in climate ___________ verses the response time of the climate __________. | back 19 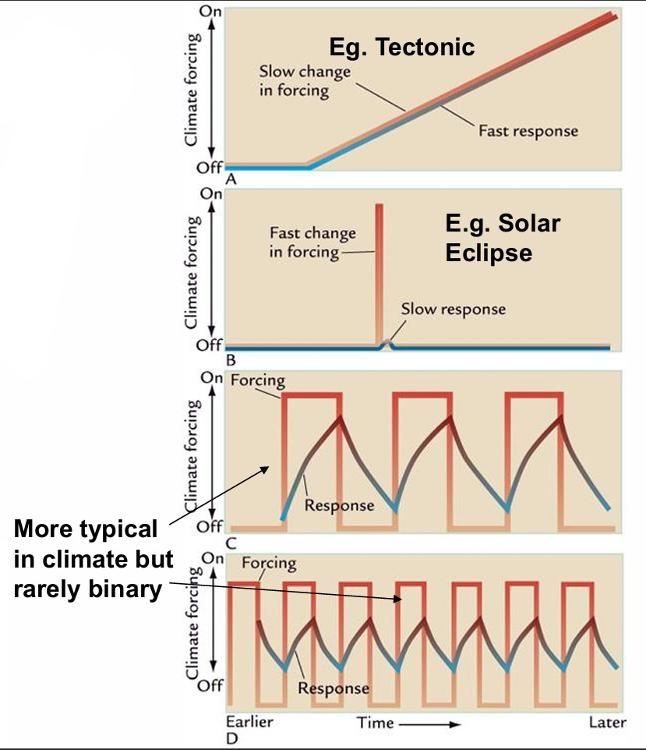 forcing vs system |
front 20 What is Effective Radiating Temperature? (In words and equation) | back 20 The temperature at which a system radiates away as much energy as it receives radiation absorbed = radiation emitted |
front 21 What prevents Earth’s temperature from continuously rising or falling? | back 21 Negative feedback loops |
front 22 What are the two radiative properties of clouds? | back 22
(Different cloud types may have different effects) |
front 23 During the day Low ______ clouds tend to ________ the surface while High ______ clouds tend to _________ it. | back 23 thick clouds cool, thin clouds warm |
front 24 At night all clouds tend to (cool/warm) the surface | back 24 warm |
front 25 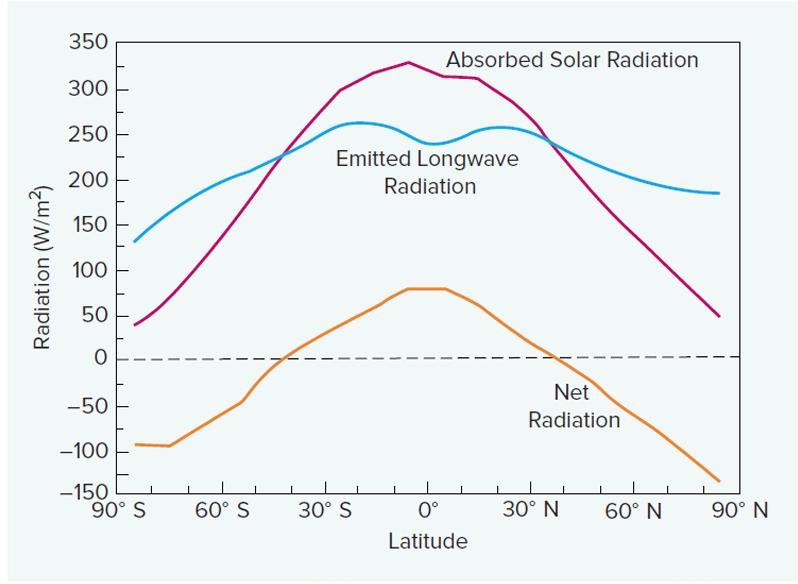 Where is does this graph tell you absorbs the most solar radiation? (The common term for this area, not the latitude) | back 25 The equator |
front 26 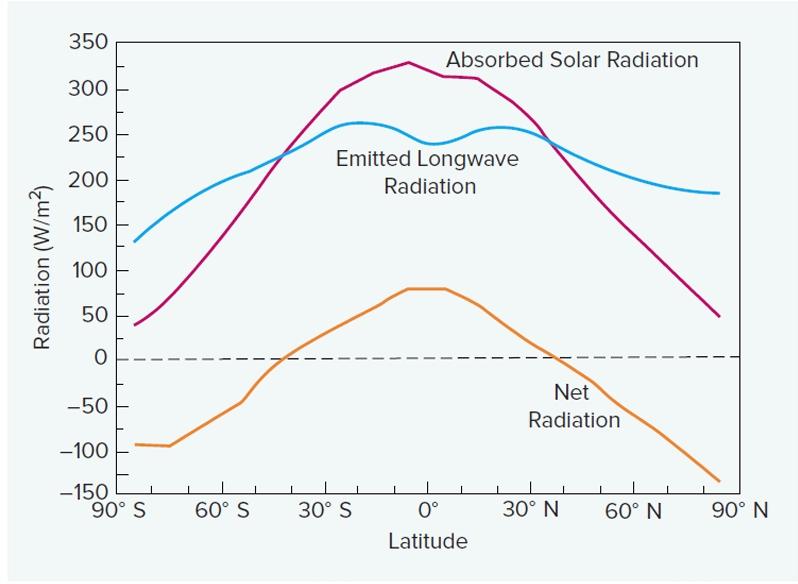 This graph has a dip in the emitted longwave radiation near the equator due to the ______________ effect, which transports energy from the ___________ to the _____________. | back 26 meridional, tropic, poles |
front 27 _____________ is the transport of heat by the movement of a fluid | back 27 Advection |
front 28 Name three surface conditions that greatly affect microclimates. | back 28 • Albedo |
front 29 What is the equation for net shortwave radiation? (think of the letter(s)) | back 29 K* = K⇩ - K⇧ Net shortwave radiation is the difference between the incoming radiation and the amount reflected |
front 30 What is the equation for net longwave radiation? (think of the letter(s)) | back 30 |
front 31 During the day | back 31 no data |