1
Cuticle
- Cuticle: A waxy, waterproof layer on the leaf surface that reduces water loss.
2
Guard Cells
- Guard Cells: Specialized cells that surround stomata and control their opening and closing, regulating gas exchange and water loss.
3
Stomata:
- Stomata: Pores on the leaf surface that allow for gas exchange.
4
Upper and Lower Epidermis:
- Upper and Lower Epidermis: Protective layers on the top and bottom of the leaf. Upper is a transparent layer that allows light to reach the palisade mesophyll. The lower epidermis is a single layer of cells on the underside of a leaf, containing stomata and guard cells. It plays a crucial role in regulating gas exchange and water loss through transpiration.
5
Palisade Mesophyll
- Palisade Mesophyll: A layer of tightly packed, elongated cells rich in chloroplasts, located near the top of the leaf to maximise light absorption.
6
Spongy Mesophyll
- Spongy Mesophyll: A layer of loosely arranged cells with air spaces that facilitate gas exchange.
7
Air Spaces
- Air Spaces: Gaps between spongy mesophyll cells that allow for the diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen.
8
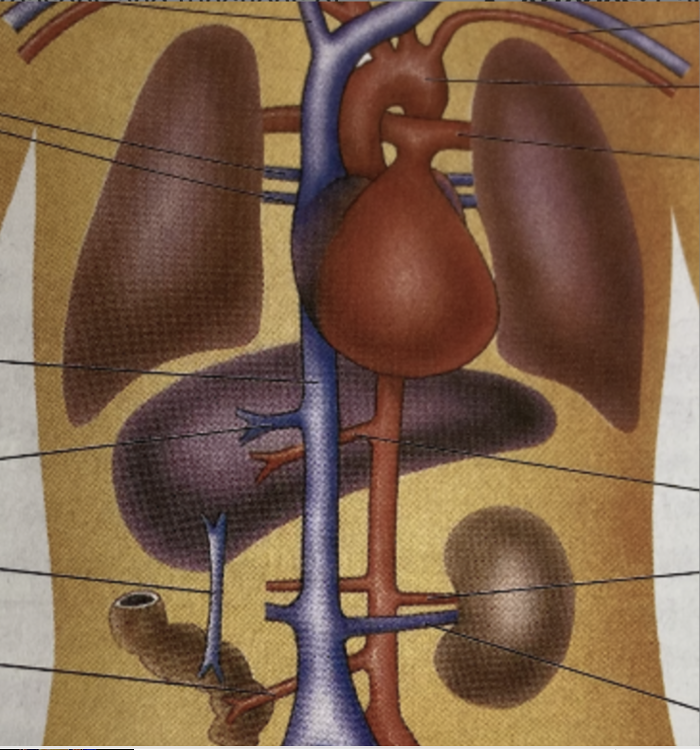
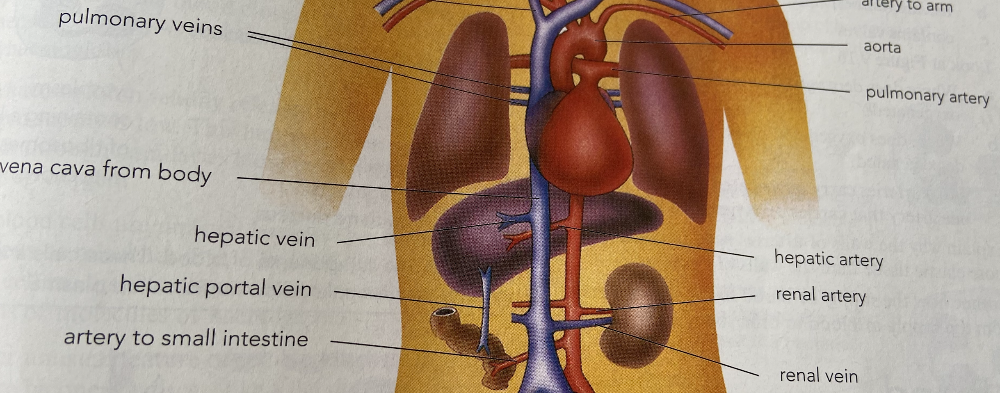
(a) heart, limited to: vena cava, aorta, pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein
(b) lungs, limited to: pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein
(c) kidney, limited to: renal artery and renal vein
(d) liver : hepatic artery, hepatic veins and hepatic portal vein