What larva feasts off of infections but cannot harm human bodies?
Maggots.
What bone can regenerate faster than any bone in the body?
Rib.
What soap forms when fat is exposed to bacteria or alkaline soil.
Adipocere.
Anatomy def.
the structure of body parts.
Physiology def.
the function of body parts
Gross Anatomy
the structures of organs and systems apparent to the naked eye
How do you study Gross Anatomy?
- dissection
- endoscopy
- MAI, x-ray, ultrasound.
Levels of Organization
cell - tissue - organ - organ system - organism
What are the 7 functions/characteristics of Human Life
- Organization
- Metabolism
- Responsiveness
- Movement
- Growth
- Reproduction
- Development
Organization
cells, tissues, organs
Metabolism
reactions in the body, requires energy
Responsiveness
senses changes and react to them
Movement
change in position, motion of internal parts
Growth
increase in body size
Reproduction
passing DNA to new individuals
Development
changes in the body
DNA
Genetic material, half from mother and half from father.
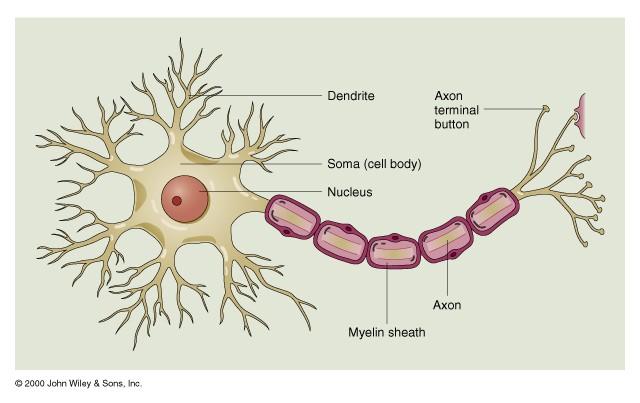
Nerve cell
Karyotype
used to determine genetic defects
23 pairs of chromosomes
chromosomes reside in nucleus of the cell
Sickle cell anemia occurs most with who?
African Americans
Chemical Changes that occur in the body to maintain life:
Obesity
Causes: Slow metabolism, overeating, lack of exercise, genetics
Results: Diabetes, heart failure, kidney disease.
Requirements for human life
- Oxygen; makes ATP
- Nutrients; water, food, vitamins
- Temperature; body responds to changes in temperature
- Atmospheric Pressure; pressure necessary for breathing
Homeostasis is the
Tendency of the body to maintain a stable, balanced, internal environment.
Thermoregulation
sweating, blood circulation, insulation (fat cells), muscle contraction
Negative Feedback loops
When some variable triggers a counter acting response
Examples: shivering when cold, sweating when hot.
Horeshoe crab blood.
used to detect bacteria in vaccines
Blood contains copper, which turns it blue.
Positive Feeback loops
intensifying the variable.
Example: The pituitary gland produces more and more oxytocin to cause contractions to give birth to a baby
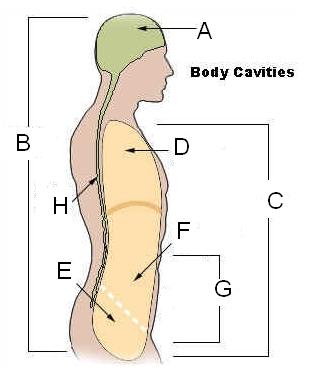
Body Cavities listed
- Cranial (A)
- Dorsal (B)
- Spinal (H)
- Ventral (C)
- thoracic (D)
- abdominal (F)
- diaphragm (G)
- pelvic (E)
Body cavities location
Integumentary system
Skin and sweat glands
functions to protect tissues and regulate temperature
Skeletal system
Bones and ligaments
functions to support.
Muscular system
Muscles
Functions to give movement
Respitory system
uses the lungs to bring oxygen into the blood
Circulatory system
uses the heart to pump blood
functions to transport.
Endocrine system
pituitary glands
controls hormones
Nervous system
spinal cord and brain
Urinary system
filters waste from blood and is removed through urine
Digestive system
Esophagus and stomach
breaks down food to be absorbed
Lymphatic system
Lymph nodes, draining fluids.
Reproductive system
ovaries and testes
sagital plane
left to right
_____
Frontal plane
from side to side
|
Transverse plane
Top and bottom, cut in half at midsection
Anatomical position
standing erect, facing forward, arms to the side, palms facing forward.
Supine
lying on his/her back
Prone
lying on his/her stomach