Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy Chap. 1
front 1 What larva feasts off of infections but cannot harm human bodies? | back 1 Maggots. |
front 2 What bone can regenerate faster than any bone in the body? | back 2 Rib. |
front 3 What soap forms when fat is exposed to bacteria or alkaline soil. | back 3 Adipocere. |
front 4 Anatomy def. | back 4 the structure of body parts. |
front 5 Physiology def. | back 5 the function of body parts |
front 6 Gross Anatomy | back 6 the structures of organs and systems apparent to the naked eye |
front 7 How do you study Gross Anatomy? | back 7
|
front 8 Levels of Organization | back 8 cell - tissue - organ - organ system - organism |
front 9 What are the 7 functions/characteristics of Human Life | back 9
|
front 10 Organization | back 10 cells, tissues, organs |
front 11 Metabolism | back 11 reactions in the body, requires energy |
front 12 Responsiveness | back 12 senses changes and react to them |
front 13 Movement | back 13 change in position, motion of internal parts |
front 14 Growth | back 14 increase in body size |
front 15 Reproduction | back 15 passing DNA to new individuals |
front 16 Development | back 16 changes in the body |
front 17 DNA | back 17 Genetic material, half from mother and half from father. |
front 18 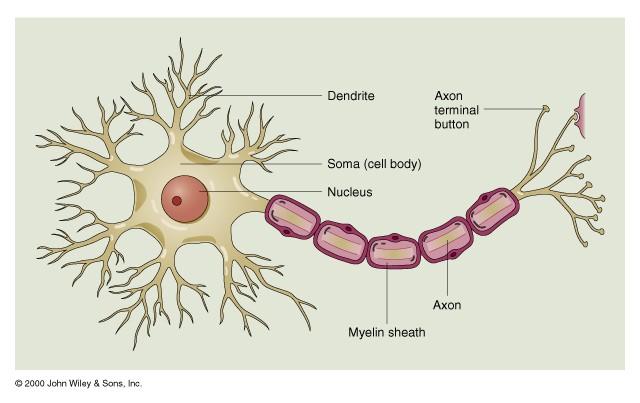 | back 18 Nerve cell |
front 19 Karyotype | back 19 used to determine genetic defects 23 pairs of chromosomes chromosomes reside in nucleus of the cell |
front 20 Sickle cell anemia occurs most with who? | back 20 African Americans |
front 21 Chemical Changes that occur in the body to maintain life: | back 21 |
front 22 Obesity | back 22 Causes: Slow metabolism, overeating, lack of exercise, genetics Results: Diabetes, heart failure, kidney disease. |
front 23 Requirements for human life | back 23
|
front 24 Homeostasis is the | back 24 Tendency of the body to maintain a stable, balanced, internal environment. |
front 25 Thermoregulation | back 25 sweating, blood circulation, insulation (fat cells), muscle contraction |
front 26 Negative Feedback loops | back 26 When some variable triggers a counter acting response Examples: shivering when cold, sweating when hot. |
front 27 Horeshoe crab blood. | back 27 used to detect bacteria in vaccines Blood contains copper, which turns it blue. |
front 28 Positive Feeback loops | back 28 intensifying the variable. Example: The pituitary gland produces more and more oxytocin to cause contractions to give birth to a baby |
front 29 Body Cavities listed | back 29
|
front 30 Body cavities location | back 30 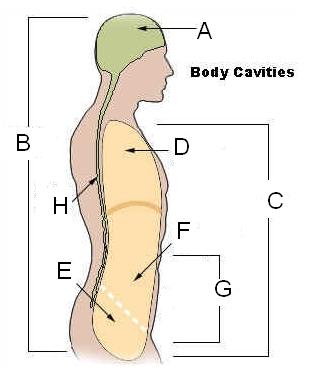 |
front 31 Integumentary system | back 31 Skin and sweat glands functions to protect tissues and regulate temperature |
front 32 Skeletal system | back 32 Bones and ligaments functions to support. |
front 33 Muscular system | back 33 Muscles Functions to give movement |
front 34 Respitory system | back 34 uses the lungs to bring oxygen into the blood |
front 35 Circulatory system | back 35 uses the heart to pump blood functions to transport. |
front 36 Endocrine system | back 36 pituitary glands controls hormones |
front 37 Nervous system | back 37 spinal cord and brain |
front 38 Urinary system | back 38 filters waste from blood and is removed through urine |
front 39 Digestive system | back 39 Esophagus and stomach breaks down food to be absorbed |
front 40 Lymphatic system | back 40 Lymph nodes, draining fluids. |
front 41 Reproductive system | back 41 ovaries and testes |
front 42 sagital plane | back 42 left to right _____ |
front 43 Frontal plane | back 43 from side to side | |
front 44 Transverse plane | back 44 Top and bottom, cut in half at midsection |
front 45 Anatomical position | back 45 standing erect, facing forward, arms to the side, palms facing forward. |
front 46 Supine | back 46 lying on his/her back |
front 47 Prone | back 47 lying on his/her stomach |