Find the HCF
Use tree diagram to find the product of prime numbers, (do factors and when prime number circle it) multiply the common ones from each number.
Find the LCM
Use tree diagram to do prime factorisation then multiply all the ones together without repeating from both numbers.
Recurring decimal to fraction
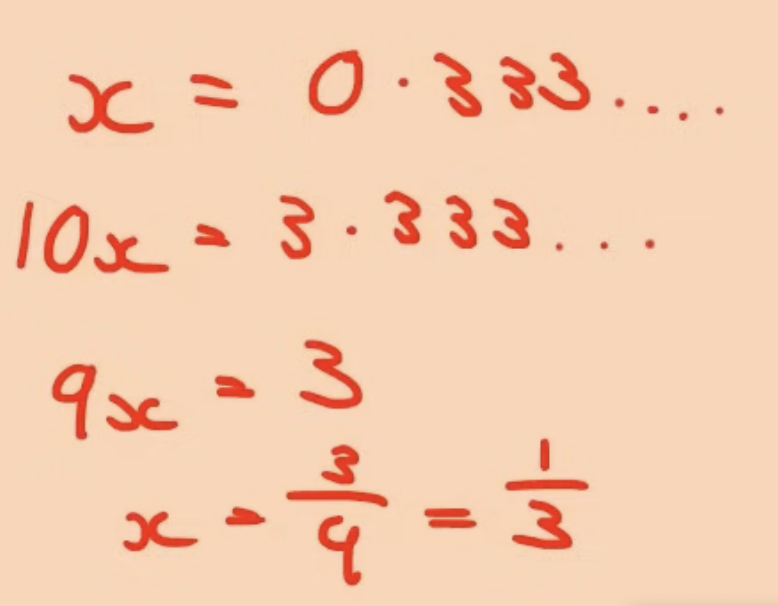
write x = recurring decimal, times both sides by ten. then take away 1x to remove the recurring decimal numbers and be left with the whole number. then simplify.
natural numbers
positive whole numbers, starting from 1.
integers
whole numbers (positive, zero and negative)
rational and irrational numbers
Rational numbers can be expressed as a fraction where both sides are integers, but irrational numbers can't.
reciprocal
a number that is found by dividing 1 by that number
∈
element is in set
∉
element isn't in set
∅
The empty set
A ⊆ B
A is a subset of B
A ⊈ B
A is not a subset of B
A ∪ B
all elements that are in either set A, or set B, or both
A ∩ B
The elements in both sets, intersection of Venn diagram
recall of squares and their corresponding roots from 1 to 15
1 = 12
4 = 22
9 = 32
16 = 42
25 = 52
36 = 62
49 = 72
64 = 82
81 = 92
100 = 102
121 = 112
144 = 122
169 = 132
196 = 142
225 = 152
recall cubes from 1 to 15
1 = 13
8 = 23
27 = 33
64 = 43
125 = 53
216 = 63
343 = 73
512 = 83
729 = 93
1000 = 103
What are the 6 laws of indices? 7
- When multiplying indices with the same base, add the powers.
- When dividing indices with the same base, subtract the powers.
- When there is a power outside the bracket multiply the powers.
- x to the power of 0 = 1
- When the index is negative, put it over 1 and flip (write its reciprocal) to make it positive x-m = 1/xm
- When the index is a fraction, the denominator is the root of the number or letter, then raise the answer to the power of the numerator. xa/b =( b√x)a
- A value raised to the power of ½ means take the square root and a value raised to the power of ⅓ means take the cube root and so on.
Simple interest
PRT/ 100
principal (original amount) x interest rate x time / 100
Compound interest
P(1 + r/100)n
Principal( 1 + rate/100)number of years
Exponential growth and decay
P(1+r)n and. P(1-r)n
principal (original amount) (1+rate)number of years etc.
Frequency density
Frequency / class width
Acceleration
Speed difference / time
Area of sector of a circle and sector length
area = (percentage of circumference x area of circle) xo /360 x π x r2
Sector length = (percentage of circumference x circumference ) x0 / 360 x 2π x r
Circle theorems
How to do differentiation and the notation that stands for it

The original formula only tells you the amount
(height, profit, distance, etc.) at a point.
The rate of change
tells you how fast that amount is increasing or
decreasing at that point, it is the gradient and if you know x and
want to find the gradient you sub this into the equation.
dy/dx
Different types of curves based off equations

Calculate percentage increase or decrease.

Value change / initial value x 100
Calculate using reverse percentages
- Identify the known value and the percentage it represents: For example, if a sale price is $81, and it represents a 10% discount, then $81 is 90% of the original price.
- Convert the percentage to a decimal or fraction: In the example above, 90% is 0.90 or 9/10.
- Divide the known value by the decimal or fraction: $81 / 0.90 = $90, or $81 / (9/10) = $90.
- The result is the original amount: The original price of the item was $90.
Rationalise the denominator.
You remove any square roots (surds) from the denominator by multiplying the entire fraction (numerator and denominator) by the surd in the denominator.
For denominators with a sum or difference of surds (e.g., a + b√c), you multiply by the same expression with the opposite sign (the conjugate) to use the difference of squares formula (a² - b²) and eliminate the surd.
Example with a rational number and a surd e.g., 1 / (√5 + √2)
- Identify the conjugate: The conjugate of √5 + √2 is √5 - √2.
- Multiply by the conjugate: (1 * (√5 - √2)) / (√5 + √2) * (√5 - √2)).
-
Expand and simplify:
- Numerator: √5 - √2.
- Denominator: (√5)² - (√2)² = 5 - 2 = 3.
- Final answer: (√5 - √2) / 3.
how to solve quadratic simultaneous equations
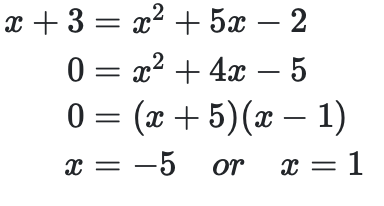
When don't know value of y:
For y = x + 3
and y = x2 + 5x -2
Then once have x sub and find y. 2 answers for quadratic equation.
When know: multiply equation to make coefficients the same. then take them away for each other to find one value. sub this value into the original to find the other. 2x + 2y = 6 from 2x + 3y = 7 would result in (2x - 2x) + (3y - 2y) = 7 - 6, or y = 1
how to solve regular simultaneous equations
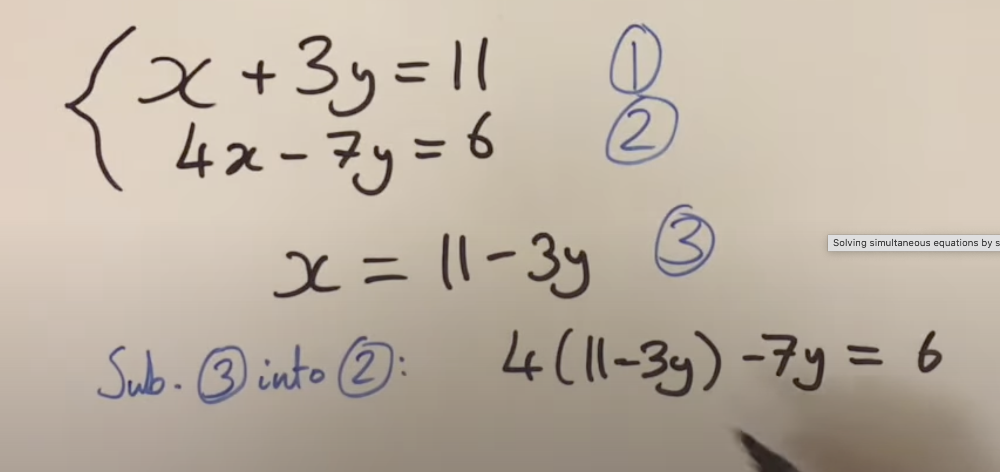
1. Find x or y
2. sub into other equation
3. solve
rules for linear equality graphs.
Broken lines are used to represent greater or lesser than but not equal (<, >) and straight lines for greater or lesser and equal (⩽, ⩾).
shading is used to represent unwanted regions
How to identify and solve linear, quadratic, cubic and exponential sequences.
Exponential sequences increase by a common ratio from term to term, with the nth term being defined as
a × r(n−1) where a is the first term and r is the value that you multiply by each time.
Patterns in linear sequences are recognizsd by identifying a constant difference between consecutive terms. First part is difference x n and then figure out what you have to add or minus to make it correct.
For quadratic (nth term = an2 + bn + c ) equal second difference) The coefficient of the n2 term of a quadratic sequence is half of the second difference. Then subtract this from the original sequence and you will have a regular linear equation to solve and make up the rest of the equation.
For cubic (equal third difference) nth term = an3 + bn2 + cn + d first find the third difference. The coefficient for the n3 term is the third difference divided by 6. Take this away and you will be left with a quadratic equation and second difference, solve this for the n2 coefficient and subtract. Then solve the linear and put it together.
graphs for sin, cos and tan and finding other solutions

Express direct and inverse proportion in algebraic terms
∝ is symbol for proportion. k is used for the constant.
Direct proportion = a∝ kb
Inverse proportion = The statement a is inversely proportional to b is written:
a ∝ 1/b then to solve replace 1 with the constant.
how to calculate Gradient
Gradient = rise ÷ run (or change in y ÷ change in x)
For a quadratic function how to sketch a graph and find turning point.
If coefficient of x2 is positive, the graph will be a positive U-shaped curve and vice versa.
Find y and x intercepts by making x and y 0 in the equation.
Find the turning point by either: using the equation x = -b/2a from the equation. This gives x and to find y sub value of x in original equation. If a is positive it is a min point, and if negative then max point. The original equation is y = ax2 + bx + c.
or complete the square to form a(x+p)2 + q where the coordinate are (-p, q)
How to complete the square
y = ax2 + bx + c style equation. say for y = x2 - 8x + 13.
Half the b quantity (-8) and make a bracket (x - 4)2 this makes everything match the above equation but the -42 = 16 which needs 3 take off it to become 13. so the final equation is (x - 4)2 - 3
For a recipricoral function how to sketch a graph and find the asymptotes
standard form equation is y = a/x + q
when a is negative the graph will be top left and bottom right and vice versa.
The graph will intercept x if q is not equal to 0. To find the x intercept make y = 0 and find for x in the above equation.
One asymptote is the y axis and the other is equal to y = q
maxima and minima and stationary points on a cubic graph

at stationary point dy / dx = 0 so differentiate the equation to find its new version and sub y for zero to find the values for x.
how to find stationary points on a cubic graph

at stationary point dy / dx = 0 so differentiate the equation to find its new version and sub y for zero to find the values for x. then sub x into original equation to find y.
second differential when finding max and min points on a cubic graph

first differentiate once, then do it a second time to find the new equation. Into the new equation sub the stationary point value for x and if it is positive it is the minimum point.
The function for differentiating twice is d2y / (dx)2 .
order of composite functions
if gf(x) then find for f first then g.
for a function the domain is anything that can become x and the range is what the answer range can be.
how to find difference of a line segment and the midpoint of a line segment

the midpoint is found by finding the mean of x and y. add the x coordinates together and divide by 2 to find the new x coordinate and same for y.
how to find the equation of a perpendicular bisector of a line
First find the midpoint of the line the (midpoint is found by finding the mean of x and y).
Then find the slope of the line with the formula y2 - y1 / x2 - x1 .
To find the gradient of the bisecting line calculate the negative reciprocal (when you swap numerator and denominator) so 3/2 becomes -2/3.
Sub all this into the y = mx + c formula. we have the gradient and the x and y coordinates of the point it goes through. and solve to find c. then you have the entire equation.
Find the gradient and equation of a straight line parallel
The gradient is the same as they are parallel and you are given the x and y coordinates it passes through.
Sub all this into the y = mx + c formula. (the gradient and the x and y coordinates) and solve to find c. then you have the entire equation.
acute, obtuse and reflex angles
Acute - below 90
Obtuse - between 90 and 180
Reflex - between 180 and 360
similar vs congruent
Congruent shapes are identical in both shape and size, meaning one can be perfectly superimposed on the other, while similar shapes have the same shape but can differ in size.
rhombus • parallelogram • trapezium.

Rhombus All four sides are of equal length, Both pairs of opposite sides are parallel, Opposite angles are equal, and It is a type of parallelogram.
Parallelogram
- Opposite sides are parallel.
- Opposite sides are equal in length.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- Examples of parallelograms include rhombuses, squares, and rectangles.
Trapezium (Trapezoid) Has four sides, Has exactly one pair of parallel sides, and The non-parallel sides are called legs.
prism and cuboid

a 3D shape with two identical, parallel ends (the bases) and a constant cross-section throughout its length
a cubbies is any 3d shape with 6 faces like a cube but it can be a rectangle etc.
frustum

the shape created when the top part of a cone or pyramid is cut off by a plane parallel to its base, leaving a solid with two parallel bases
parts of circle
• chord
• major and minor arc
• sector
• segment.

Draw nets.
cubes, cuboids, prisms and
pyramids

For a cylinder : The length of the rectangle is equal to the circumference of the circles. The width of the rectangle is equal to the height of the cylinder.
For a pyramid : The perpendicular height of each triangle is equal to the slant height of the pyramid.
The relationship of similar shapes lengths, surface areas and volumes of similar solids.
k is used to depict scale scale factor.
Lengths are related by the scale factor (k), areas by k², and volumes by k³.
k = length A / length B
k2 = area A / area B
k3 = volume A / Volume B
and when converting between them.
how to calculate the sum of interior angles on a polygon and therefore each individual angle
For any polygon with n sides, the sum of its interior angles is calculated with the formula (n - 2) × 180°. For a regular polygon, you can then find each interior angle by dividing the sum by n.
m3 to L
1m3 = 1000L
same as ml
find the surface area and volume of a frustum.
V = (πh/3)(R² + Rr + r²), where h is the height, R is the radius of the larger base, and r is the radius of the smaller base.
The total surface area is the sum of the areas of the two circular bases and the curved lateral surface: A = πL(R + r) + πR² + πr², where L is the slant height.
The ambiguous case
The ambiguous case is identified when the side opposite the known angle is shorter than the other known side. This means it can swing like a pendulum and form 2 triangles so there are 2 possible answers for the angle you are finding.
The ambiguous case, which can arise when using the sine rule with two sides and a non-included angle, requires checking for two possible solutions for an angle, one acute and one obtuse, by considering their sum with the given angle.
Calculate the magnitude of a vector

For a vector if given A and B find AB

To find PQ P subtract the values of the coordinates of from the coordinates of Q because you start at P and want to get to Q.
show that 3 points are collinear

show that vectors are parallel
Vectors are parallel if one is a scaler multiple of each other. eg A = k x B with k being the multiple. similar to collinear but this is between three points.
sample space

two-way tables

Identify the modal class from a grouped frequency distribution.
find the class interval with the highest frequency.
Estimate and interpret the median, percentiles, quartiles and interquartile range from cumulative frequency diagrams.
A horizontal line is drawn from the calculated median, Q1 or Q3 position on the cumulative frequency (y-axis) to intersect the cumulative frequency curve.
Calculate with frequency density on a histogram
On histograms, the vertical axis is labelled ‘Frequency density’.
frequency density = frequency ÷ class width.
When you know two sides and the included angle calculate area of triangle
Area = ½ * a * b * sin(C)
- the two sides of the triangle are ('a' and 'b').
area of trapezium
1/2 x (upper length + lower length) x height