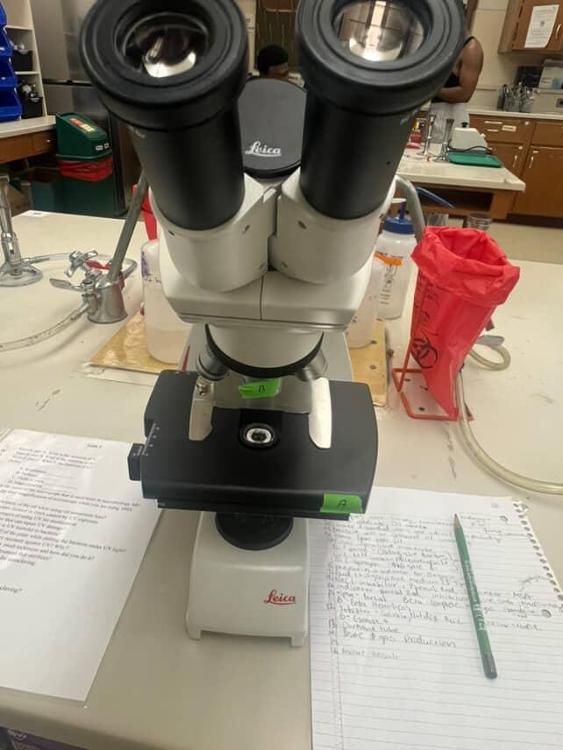

Identify part A and its function
The stage which holds the slide in place with small clamps to be accurately viewed and allows for relocation of the slide under the objectives if desired.

Identify part B and its function
The objective lenses which magnify the plate at 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x.
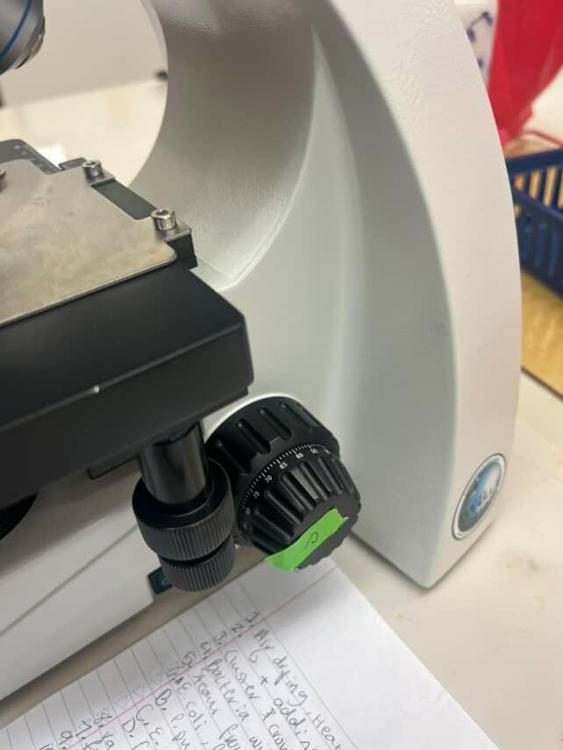

Identify part C and its function
The fine adjustment knob which is used for focusing the higher power objective lenses (10x, 40x, 100x)
Define "resolution"
Ability to distinguish two separate points on a specimen
Define "parfocal"
Refers to the ability of changing lenses without having refocusing or only refocus slightly
Define "field of view"
Refers to the area of the plate you can see when looking through the ocular lenses (the circle we view the specimen through)
Define "magnification" and how to calculate total magnification
The ability to enlarge an image of an object
Total magnification= 10x (Ocular lens magnification) x objective lens magnification
ie. ocular 10x X objective 4x = 40x total magnification
What is the name of the microscope used in the microbiology lab?
Compound light microscope bright-field
What is the total magnification of microscope when you are using 100x objective lens
1000x
10x (ocular) X 100x (objective) = 1000x total mag
What is the purpose of using immersion oil?
It reduced light refraction when viewing through the 100x objective lens
Name the structure formed in DNA caused by UV exposure
Pyrimidine dimers, or more specifically thymine dimers are formed and cause DNA damage
What are two disadvantages of using UV for sterilization?
UV may not kill all pathogens, most effective in direct path of UV light so any sort of obstruction can render the process ineffective, harmful to other bacteria and DNA, can cause thymine dimers or other bodily damage
What is the enzyme that can repair UV damage?
Photolyse
At what wavelength is UV harmful to bacteria?
260 nm (tiny wavelengths)
In the micro lab, why did we cover half of the plate while putting bacteria under the UV light?
So only half of the plate was fully exposed to the UV light. This demonstrates the effectiveness of UV sterilization on bacterial growth at the tested time intervals
In the micro lab, which bacteria was more resistant to the UV light? Why?
Bacillus megaterium was more resistant due to the fact it produces endospores which aid in its survival and protection
Why did we use the 3-way swab technique? Briefly explain the technique.
The 3 way swab technique was used to completely cover the side of the plate swabbed with bacteria. Since we aren't looking at the individual cells and are instead looking at colony growth patterns, we don't have to worry about crowding the plate with bacteria
Technique: Using a sterile cotton swab, the bacteria is streaked across the plate from left to right, top to bottom, and diagonally to ensure an evenly covered sample for the UV test.
What is the name of the lab instrument that sterilizes?
The autoclave
What are the conditions for autoclaving?
15 psi
15 min
121 degrees C
Why do we use indicators when autoclaving?
To ensure we have an accurate reading as to when everything is completely sterilized. This helps prevent sample contamination.
Describe 3 important steps in preparing a smear for staining.
Proper inoculation of the plate depending on the sample used (broth, plate, slant), complete airdrying, and thoroughly heat-fixing
Describe 4 important steps in the preparation of a smear from agar.
Adding a singular drop of water, proper + sterile plate inoculation, complete airdrying, and thoroughly heat-fixing.
What happens if you grab too many bacteria cells for a gram stain?
The plate will be overcrowded when looking through the microscope and you will not be able to accurately see the individual cells morphology
What will happen if you don't heat-fix before beginning the staining process?
During the staining process the bacteria will be washed off the plate
What will happen if you don't completely airdry before heat fixing the plate during a smear prep?
When heat-fixing, the residual moisture will steam and kill/disfigure the bacterial cells

Classify organism in tube A (generalized by reaction to oxygen)
Facultative anaerobe

Classify organism in tube B (generalized by reaction to oxygen)
Microaerophile

Classify organism in tube C (generalized by reaction to oxygen)
microaerophile
What is the name of the media used in the oxygen tolerance test
fluid thioglycolate medium
What does "MSA" stand for? Give the name of the inhibitor and indicator in MSA.
MSA= Mannitol salt agar
Indicator: Phenol Red
Inhibitor: salt 7.5%
What is the name of the indicator used in the 2042 oxygen tolerance test?
Resazurin
What type of bacteria grows in MSA?
Staphylococci
What is the inhibitor and indicator in MacConkey media?
Inhibitor: bile salt
indicator: neutral red
What bacteria does MacConkey promote the growth of?
Gram negative and enteric bacteria
What is hemolysis? Define alpha, beta, and gamma hemolysis.
Hemolysis: ability to break down blood cells
alpha: partial hemolysis
beta: full hemolysis
gamma: no hemolysis
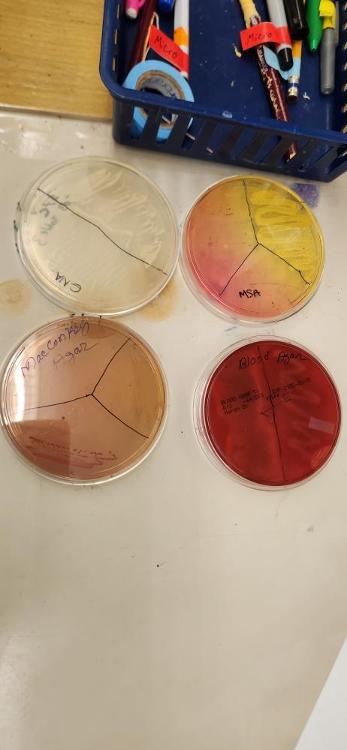
What type of hemolysis is shown on plate E?
Beta hemolysis
What does Columbia "CNA" stand for? What is the main inhibitor in Columbia CNA media?
Columbia CNA= colistin nalidixic acid agar
Inhibitors: Colistin/nalidixic acid
What bacteria grows in Columbia CNA agar?
Gram positive bacteria

Does this tube represent a positive or negative test? What is the name of the inverted tube in the glucose/lactose test tube? What does this tube test for?
This test is positive shown by the bright yellow color (formerly bright red) which means there was carbohydrate fermentation
Durham tube
If the tube appears clear and/or has a bubble in it, the test is positive for gas production
What is the name for the technique used to streak a plate to isolate colonies?
4 quadrant streak method
Define a pure vs a mixed culture.
A pure culture contains only one bacteria while a mixed culture contains multiple bacteria
What type of media would you use to determine if a culture is mixed or pure?
Differential media which allows for multiple different bacteria to grow at once
Which did we use for our lab experiments: pure or mixed cultures?
We used both to see the differentiation in a mixed and pure culture
What happens if you omit flaming the loop before inoculation of the media?
Flaming is a technique used for sterilization so if omitted could lead to contaminated cultures and inaccurate results.
Do we take culture for inoculation for each quadrant in the 4-quadrant streaking method? Why or why not? What is the proper way of streaking the 4 quadrants?
No, it could lead to different DNA cultures rather than a pure, isolated colony.
Instead, you flame the loop in between each quadrant and continue the original line of inoculation through each quadrant.
What position are plates incubated in the incubator?
Upside-down to prevent lids falling off or plates getting mixed up
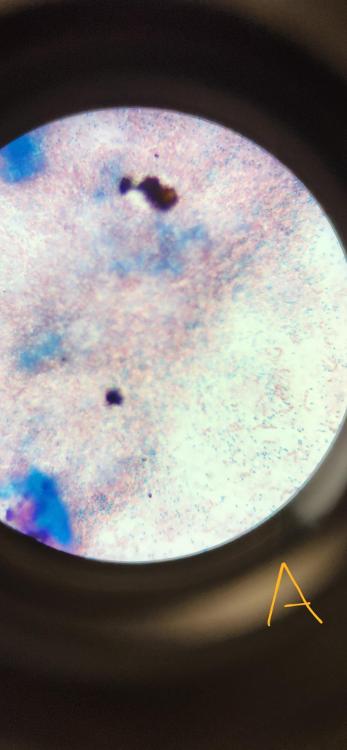
What staining technique was used in the provided picture?
Endospore stain (Schaeffer-Futton method)
What are the dyes and decolorizer used for a gram stain (in order)
malachite green (primary stain)
DI water (decolorizer)
safranin (counterstain)
In the endospore stain done in lab, what were the green-stained specimen and what were the pink-stained specimen?
The green was the malachite green stained endospores
The pink was safranin stained gram negative rods

What bacteria was used in this stain?
Clostridium sporogenes
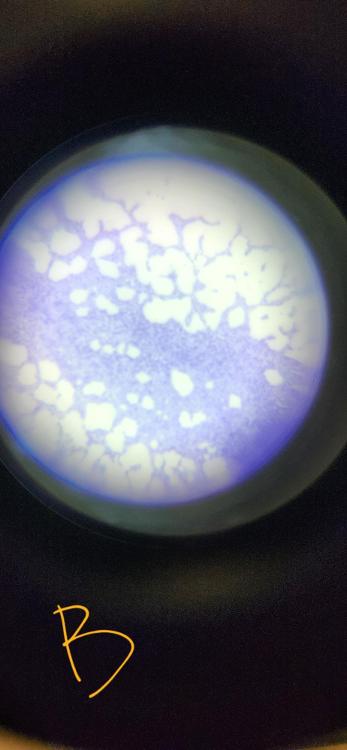
What staining technique was used in this picture?
gram stain

What bacteria was featured in this gram stain?
Bacillus megaterium
What are the dyes and decolorizer for a gram stain?
Crystal violet (primary)
iodine (mordant)
ethyl alcohol (decolorizer)
safranin (counter stain)
What is the purpose of each component of a gram stain?
Primary stain is used to color the bacteria walls
the mordant is used to bind the primary stain to the walls
the decolorizer is used to remove the dye from everything but the dyed bacteria
the counterstain is to differentiate any gram-negative bacteria that is unable to be stained from the primary stain

What is the name of the media present?
Agar plate; solid media

What is the name of the media present?
nutrient broth; liquid media

What is the name of the media present?
Agar slant; solid media
Why do we use agar instead of gelatin?
Gelatin melts at room temperature and can sometimes be eaten away at by the bacteria cultures; agar cannot
Define "osmosis".
The diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane