During repolarization of an action potential...
sodium channels get deactivated
Features of action potentials are all of the following EXCEPT:
answer choices:
The nerve action potential has a short duration (about 1 msec)
Nerve action potentials are elicited in an all-or-nothing fashion
Nerve cells code the intensity of information by the frequency of action potentials.
A change in potential that increases the polarized state of a membrane
A change in potential that increases the polarized state of a membrane
The absolute refractory period...
is a period of time after the initiation of one action potential when it is impossible to initiate a second action potential no matter how much the cell is depolarized.
During depolarization of an action potential...
sodium channels get activated
The membrane potential will never reach its ideal value (the sodium equilibrium potential) because...
contined K+ permeability
A major difference between the changes in the K+ channels and the changes in the Na+ channels is that...
the K+ channels are slower to activate or open
Allows one neuron to relay information to its neighbor. Long chains of these can be used to propagate information through the nervous system.
feedforward excitation
Tetrodotoxin (TTX)...
blocks the voltage-dependent changes in Na+ permeability, but has no effect on the voltage-dependent changes in K+ permeability
During hyperpolarization of actional potential...
both sodium and potassium channels are activated
During resting state of an action potential...
both sodium and potassium channels are deactivated
T/F: The second part of the calcium hypothesis for chemical synaptic transmission involves the consequences of the Ca2+ influx. The opening of the Ca2+ channel allows for calcium to flow down its concentration gradient from the outside to the inside of the synaptic terminal. This influx leads to an increase in the concentration of the Ca2+ in the presynaptic terminal, which by interacting with proteins associated with synaptic vesicles leads to the release of the chemical transmitter substance.
True
Exocytosis involves the following processes in the order of happening:
mobilization, docking, fusion, release
The amplitude of the endplate potential is about 50 mV, but only about 30 mV is needed to reach threshold. The extra 20 mV is called the...
safety factor
Which of the following is needed for neurotransmitter release at the synaptic cleft?
Ca
___ is a distinct separation between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membrane
synaptic cleft
T/F: Presynaptic density is darkly staining material of postsynaptic cell adjacent to the synapse. Receptors, ion channels, and other signaling molecules are likely bound to this material.
False
Neuroglia differ from neurons in several general ways in that they...
retain the ability to divide
Synapses can be identified by the presence of the following components except:
A presynaptic complement of membrane-bound synaptic vesicles exists
Many mitochondria are present
synaptic cleft
Na-K pump
Na+-K+ pump
T/F: When neurons interact with muscle fibers, the region of functional contact is called the neuromuscular junction or motor endplate
True
Each neuron has only one axon and it is usually straighter and smoother than the dendritic profiles. Axons also contain bundles of ........ and ...... and scattered ......
microtubules, neurofilaments, and neurofilaments
(Note: I think she meant to put microfilaments/actin filaments)
T/F: Microglia, in contrast to the other types of glial cells, originate from embryonic mesoderm
True
___ cells have only one cell process and are primarily found in invertebrates
unipolar
The following glial cell wraps a myelin sheath around axons of the central nervous system
oligodendrocyte
T/F: Synapse is the junction that allows signals to pass from a nerve cell to another cell or from one nerve cell to a muscle cell. The synaptic cleft is the gap between the membrane of the pre- and postsynaptic cell. In a chemical synapse the signal is carried by a diffusable neurotransmitter. The cleft between the presynaptic cell and the postsynaptic cells is 20 to 40 nm wide and may appear clear or striated. Recent studies have indicated that the cleft is not an empty space per se, but is filled with carbohydrate-containing material.
True
The cone-shaped region of the cell body where the axon originates is termed the...
axon hillock
T/F: Exocytosis of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft occurs when fusion takes place. This step is Ca2+-stimulated. A vesicle protein called syntaxin binds Ca2+ to initiate fusion
False
Tetanus toxin...
Clostridial neurotoxin with zinc-dependent protease activity; Cleaves synaptic vesicle proteins in the CNS and thereby blocks release of neurotransmitters.
T/F: Because of the tetanus, there will be spatial and temporal summation of the EPSPs produced by the multiple afferent synapses on the common postsynaptic cell. Consequently, the membrane potential of the postsynaptic neuron will become very depolarized.
True
Axosomatic (synapses)
synapses that are made onto the soma or cell body of a neuron
VAMPs are...
synaptic vesicles
Dynein
Transport proteins move retrogradely and slower than kinesin (fast anterograde protein transport)
There are two fundamental differences between the process of synaptic transmission at the sensorimotor synapse in the spinal cord and the process of synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction...
First, the transmitter substance released by the sensory neuron is not ACh but rather glutamate
Second, the amplitude of the synaptic potential in a spinal motor neuron, as a result of an action potential in a 1A afferent fiber, is only about 1 mV
Vinblastine prevent axoplasmic transport through
disruption of the microtubules
A very enduring form of synaptic plasticity is called
long-term potentiation (LTP)
tetrodotoxin (TTX)
Fish toxin that blocks the pore of voltage-dependent Na+ channels
___ receptors produce generator potentials and action potential discharges that follow the time-varying waveform of pressure changes produced by a vibrating stimulus
The rapidly-adapting receptors
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND SENSATION:
muscle spindle
muscle stretch
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND SENSATION:
golgi tendon organ
muscle tension
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND SENSATION:
joint: pacinian
joint movement
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND SENSATION:
joint: golgi organ
joint torque
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND ADAPTATION:
muscle spindle
rapid initial transient and slow sustained
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND ADAPTATION:
muscle: golgi tendon organ
slow
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND ADAPTATION:
joint: pacinian
rapid
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND ADAPTATION:
free nerve ending
depends on information carried
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND THE SIGNAL:
muscle spindle
muscle length and velocity
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND THE SIGNAL:
muscle: golgi tendon organ
muscle contraction
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND THE SIGNAL:
joint: pacinian
direction and velocity
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND THE SIGNAL:
joint: ruffini
pressure and angle
The somatosensory systems process information about, and represent, several modalities of somatic sensation:
pain, temperature, touch, proprioception
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND ITS TYPE:
meissner corpuscle
encapsulated and layered
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND ITS TYPE:
Ruffini corpuscle
encapsulated collagen
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND ITS TYPE:
free nerve ending
unencapsulated
MATCH THE RECEPTOR AND ITS TYPE:
merkel complex
specialized epithelial cell
The encapsulated cutaneous receptors include
meissner corpuscles, pacinian corpuscles, and ruffini corpuscles
MATCH THE SENSATION TO THE RECEPTOR:
meissner corpuscle
touch: flutter and movement
MATCH THE SENSATION TO THE RECEPTOR:
pacinian corpuscle
touch: vibration
MATCH THE SENSATION TO THE RECEPTOR:
ruffini corpuscle
touch: skin stretch
MATCH THE SENSATION TO THE RECEPTOR:
merkel complex
touch: pressure, form
Peripheral somatosensory neurons
The cell bodies of the first-order (1°) somatosensory afferent neurons are located in posterior root or cranial root ganglia
Propioceptive stimuli
are internal forces that are generated by the position or movement of a body part
These fibers are myelinated, have a fast conduction velocity
A-delta fibers
learning to respond to sudden pain and psychosomatic pain is the following type of response and pain
somatic pain, behavioral response
This pathway is responsible for the immediate awareness of a painful sensation and for awareness of the exact location of the painful stimulus.
Neospinothalamic pathway
Neospinothalamic tract decussate in
the anterior white commissure
T/F: many of the visceral nociceptors are silent
True
Skin nociceptors may be divided into four categories based on function, all of the following except...
unimodal nociceptors
Factors that Activate Nociceptors are all of the following except...
acetylcholine (ACh)
An increased painful sensation in response to additional noxious stimuli...
hyperalgesia
Development of inflammatory arthritis can be caused by the liberation of the following peptides...
substance P (SP) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)
Pain caused by inflammation, burned skin, etc., is carried by the C fibers
burning pain or soreness pain
T/F: Visual acuity is the ability to detect and recognize small objects visually depends on the refractory (focusing) power of the eye's lens system and the cytoarchitecture of the retina
True
The process of producing a single image from the two disparate monocular images is called...
binocular fusion
Bitemporal heminopia is caused by a lesion at the...
optic chiasm
What is the main function of Photoreceptors?
capture light and convert it to electrical signals
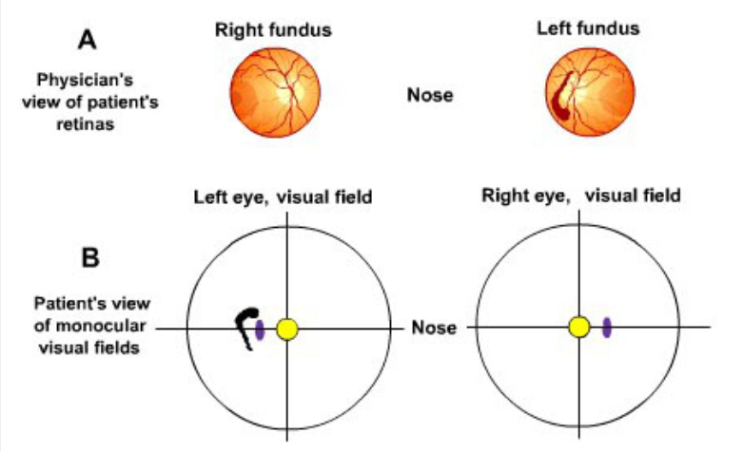
Symptoms: The patient is having his semiannual physical examination. As he is diabetic, the physician examines his retinas and performs a confrontation test of his visual fields. An abnormality is detected in his left fundus (Figure 15.12) but the confrontational field test detects nothing.
Perimetry testing is requested.
Perimetry Test Results: The results indicate the right eye's visual field is normal and that there is a peripheral scotoma (i.e., loss of vision that does not follow the boundaries of the visual field quadrants) in the left eye's temporal hemifield (Figure 15.13).
The patient has all of the following EXCEPT:
answer choices:
retinal damage in the left eye
damage located in the nasal half of the left retina
damage related to the patient's diabetes - diabetic retinopathy
damage related to the patient's glaucoma
damage related to the patient's glaucoma
Vision in the peripheral visual field
is more sensitive to dim light
T/F: light passes the eye and reaches the photoreceptors directly without passing through any other cell
False
Right homonomous hemianopia is cause by a lesion at the
left occipital cortex
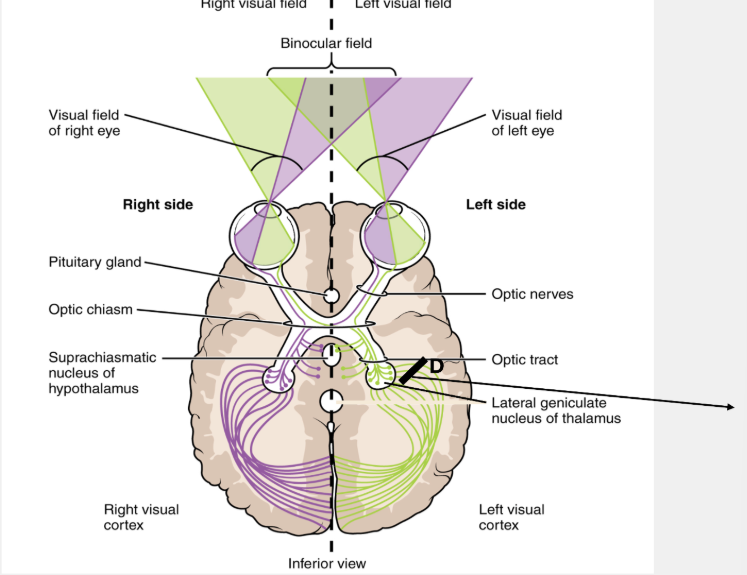
The following lesion in D causes which of the following
left superior quadrantanopia
The axons in the optic tract terminate in the following nuclei within the brain except
the infraachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus
The striatum is composed of the
caudate and putamen
The net effect of the indirect pathway of processing signals in the basal ganglia is...
inhibitory
The loss of ......... neurons in Parkinson’s disease causes the poverty of movement that characterizes this disease, as the balance between direct pathway and indirect pathway is tipped in favor of the ....... pathway, with a subsequent pathological global ............ of motor cortex areas.
dopaminergic, indirect, inhibition
The lenticular nucleus is composed of....
the putamen and the globus pallidus
The primary fissure separates the corpus cerebelli into a ................
posterior lobe and an anterior lobe
The corpus striatum is composed of all of the following except...
substantia nigra
The cerebellum is involved in the following functions except...
sensory learning
The net effect of the direct pathway of processing signals in the basal ganglia is...
excitatory
The following disease is characterized by slowness or absence of movement (bradykinesia or akinesia), rigidity, and a resting tremor (especially in the hands and fingers)
Parkinson’s disease
The substantia nigra is composed of...
the pars compacta and the pars reticulata
Information flows into and through the hippocampus by three principal pathways except...
the indirect pathway
PET scans have shown an increase in blood flow during panic attack to the...
parahippocampal gyri
hippocampal formation typically refers to all of the following except...
cingulate cortex
Major Output Pathways of the Amygdala are all of the following except...
directly to the hypothalamus
The postcommissural fornix projects to which structure?
mamillary bodies
Which structure is NOT part of the Papez circuit?
Ventral nucleus of the thalamus
___ is the integrative center for emotions, emotional behavior, and motivation
amygdala
The limbic system includes all of the following except...
occipital and parietal lobes
Retrograde amnesia refers to
loss of old memory
T/F: The process by which an initially labile memory is transformed into a more enduring form is called consolidation
True
Emotional responses to classical conditioning is controled by
amygdala
Declarative memory examples are...
facts and events
Explicit memory take place in
medial temporal lobe
Nondeclarative memory includes all the following except
facts
Short term memories can involve all of the following processes EXCEPT:
regulation of gene expression
Simple classical conditioning is
implicit memory
Anterograde amnesia refers to
inability to form new memory
Skills and habits are stored in
striatum