Limbic means border. What is this border in between?
neocortex and the subcortical structures (diencephalon)
limbic system includes the
hippocampal formation
amygdala
septal nuclei
cingulate cortex
entorhinal cortex
perirhinal cortex
parahippocampal cortex
hippocampal formation typically refers to the
dentate gyrus, the hippocampus proper and the subicular cortex
hippocampal formation is located in the
temporal lobe of each cerebral cortex
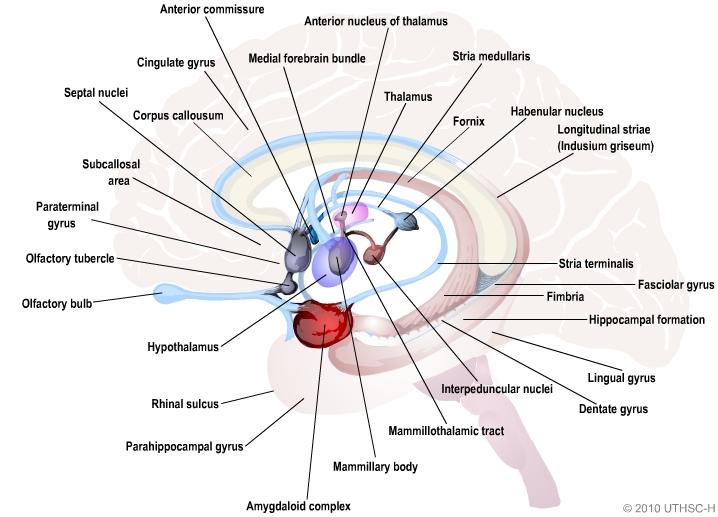
septal nuclei
corpus callousum
cingulate gyrus
anterior commissure
thalamus
fornix
stria
terminalis
hippocampal formation
mammillary
body
mammillothalamic tract
amygdala
Two major pathways into and out of the hippocampus are the
fornix and entorhinal cortex
The precommissural branch of the fornix connects to the
septal, preoptic, ventral striatum, orbital cortex and anterior cingulate cortex
The postcommissural branch of the fornix connects to the
anterior nucleus of the thalamus and the mammillary bodies of the hypothalamus
The mammillary bodies are destroyed in _________ as the result of alcoholism and thiamine deficiency
Korsakoff’s syndrome
Patients with Korsakoff’s syndrome have profound difficulty forming _____ _______ because the mammillothalamic tract also goes to the anterior thalamic nucleus, the hippocampus can affect the thalamus indirectly as well as directly.
new memories
The anterior thalamic nuclei in turn connect to the _______. It projects back to the entorhinal cortex of parahippocampal gyrus, completing a “great” loop called the _______.
cingulate cortex
Papez circuit
The Papez circuit is involved in
learning and memory, emotion, and social behavior
The input paths are just the
reverse of the output paths
The _________ is a major source of inputs to the hippocampus
entorhinal cortex
The ____ cortex, ______ lobe cortex, ______, _____ cortex, and ______ bulb all have inputs to the hippocampus via the entorhinal cortex
cingulate
temporal
amygdala
orbital
olfactory
Information flows into and through the hippocampus by three principal pathways: 1. The ______ pathway from the entorhinal cortex to granule cells of the dentate gyrus
2. The ______ fiber pathway from the granule cell of the dentate gyrus to the pyramidal cells of the CA3 region of the hippocampus
3. The _____ collateral pathway from the
CA3 region of the hippocampus to
the
CA1 region of the hippocampus.
perforant
mossy
Schaffer
Amygdala is the integrative center for
emotions, emotional behavior, and motivation
major pathways communicate
bidirectionally and contain both efferent and afferent fibers
The amygdala receives inputs from all senses as well as ______
visceral inputs
Visceral inputs come from the
hypothalamus, septal area, orbital cortex, and parabrachial nucleus.
Auditory, visual and somatosensory
information comes from the
temporal and anterior cingulate cortices
Major Output Pathways of the Amygdala
1. Ventral amygdalofugal pathway
2. Stria terminalis
3.
Directly to the hippocampus
4. Directly to the entorhinal
cortex
5. Directly to the dorsomedial nucleus of the thalamus
Ventral amygdalofugal pathway
This pathway continues to the
anterior olfactory nucleus
anterior perforated substance
piriform cortex
orbitofrontal cortex
anterior cingulate cortex
ventral striatum
The ventral amygdalofugal pathway is important because it is a link whereby
motivation and drives can influence responses & is a link where responses are learned
Stimulation of the amygdala causes
intense emotion, such as aggression or fear.
Destructive lesions of the amygdala cause
tameness in animals, and a placid calmness in humans characterized as a flatness of affect.
did not become conditioned to colors followed by the loud horn. But when asked how many colors were presented and which were followed by the horn, their recall was correct.
amygdala patients
showed learning and conditioning to the colors followed by the horn, but could not recall which they were
hippocampal patients
no conditioning and had no explicit
memory about which colors
were followed by the horn
lesions in both amygdala & hippocampal