Property classification: Residential (1)
RC-MAU-APO
untilled land not suitable for production of row crops and has a human abode
Examples:
- vacant land where most likely use is residential development
- mobile homes
- apartment building with 3 or less units
Property classification: Commercial (2)
RC-MAU-APO
buying and reselling goods for a profit and providing services to other classes
Examples:
- apartments with more than 3 units
- hotels/resorts
- mobile home parks
- golf course
- stores with apartments above
- quarries and pits not depleted yet
Property classification: Manufacturing (3)
RC-MAU-APO
anything used in the making/assembling/manufacturing of tangible personal property for profit
Examples:
- warehouses or offices in support of manufacturing
- assembling component parts of manufactured product
- personal property owned or used to engage in manufacturing (raw materials, supplies, equipment)
Property classification: Agricultural (4)
RC-MAU-APO
production of crops & keeping of livestock without including any buildings or improvements
Examples:
- Christmas tree farms
- orchards
- production of crops, plants, vines, or trees
- caring of livestock for sale of livestock, sale of livestock products, livestock increase, or value increase
- sod farms
Property classification: Undeveloped (5)
RC-MAU-APO
land that does not produce and is not capable of producing
Examples:
- swamp or wasteland (bog, marsh, lowland brush)
- depleted or abandoned quarries and pits
- rock outcroppings
- borrow pits
- shoreland
Property classification: Agricultural Forest (5m)
RC-MAU-APO
productive forest but needs to be next to 100% AG land, be within AG land from 2004, or be within converted land from 2005 or later that is 50% or more AG
Property classification: Productive Forest (6)
RC-MAU-APO
land producing or is capable (even if no current commercial use) of producing commercial forest products
Examples:
- growing trees for industrial wood
- Obtaining tree products like sap, bark, and/or seeds
Property classification: Other (7)
RC-MAU-APO
land required for improvements on AG land
What property classifications are assessed at full value?
residential, commercial, manufacturing, productive forest, & Other
What property classifications are assessed at 50% of full value
undeveloped & agricultural forest
What property classification is assessed at use-value
Agricultural
Asking price of property owners generally establishes the ______ of value
- upper limit
- lower limit
- market limit
- normal limit
upper limit
when property owners are listing their sale, we can assume they want the full market value which can be seen as the Upper Limit of the property value
- no such thing as a normal limit
- no such thing as a market limit
Offering price by buyers normally establishes the ______ of value
- lower limit
- upper limit
- market limit
- normal limit
lower limit
when buyers are first offering a price for the property it will be lowest price they believe the property owners will think the sale is worth. This will be lower than the asking price (upper limit) and can be seen as the Lower Limit for the property value
- upper limit is for the sellers/property owners
- no such thing as a market limit
- no such thing as a normal limit
An agreement which permits one to buy, sell, or lease a property within a stipulated period of time is known as a (an) ______
- contract
- option
- deed
- mortgage
option
WPAM chapter 9
"With an option contract the property owner gives a prospective purchaser the right to buy a property at a specified price within a given period of time."
Key here is the stipulated period of time
- contract is too general since there are many types
- deed is a written instrument that conveys an interest in real property
- mortgage is a legal document that an owner of a property pledges the property to a creditor as security for the payment of a debt
______ capitalization is a method of converting future net benefits into present value where each future net benefit is discounted at a proper yield rate (present worth factor)
- direct
- income
- yield
- sales
yield
WPAM chapter 9 & 13
Key here is each future net benefit is discounted at a proper yield rate
Think of matching the words YIELD and combining EACH net benefit, not just a year's worth
- direct means to convert a single year’s net operating income into an estimate of value
- income capitalization = direct capitalization
- no such thing as sales capitalization
The best source for verification or documentation of sales data is ______
- what you have heard
- internet or MLS listing information
- direct interview of the buyer or seller
- a property record card
direct interview of the buyer or seller
- first option is an obvious bad answer
- internet and MLS listing information pull their information from public records like the RETR, so it's a secondary source of info
- the PRC isn't the best for verifying SALES data but property/parcel information
Comparable sale properties should be visually inspected to enable the assessor to make an accurate analysis of the sales and reflect the dissimilarities existing between the comparable sales and the subject property by means of the ______
- mortgage equity ratio
- adjustments
- tax rates
- sales equity ratio
adjustments
WPAM chapter 9, Sales Comparison Approach
key here is reflect dissimilarities existing between the comparable sales and the subject property
Straight line capitalization assumes a (an) ______ income stream during the remaining economic life of the improvements
- increasing
- stable/straight
- declining
- recaptured
declining
Appropriate units of comparison for the valuation of vacant land are all of the following except
- front foot
- square foot
- acre
- neighborhood
neighborhood
WPAM Chapter 12, Units of Comparison
You can value parcels based on neighborhoods but it is not a Unit of Comparison
The formula for a developing a gross income multiplier is
- GIM = assessed value/net income
- GIM = sales price/gross income
- GIM = gross income/sales price
- GIM = sales price/net income
GIM = sales price/gross income
WPAM chapter 9, Gross Rent Multiplier
Gross Rent or Gross Income Multiplier (GRM/GIM)
It is asking you to find a formula to figure out how many years of the yearly income fits into the sale price
Appropriate units of comparison for the valuation of apartment houses are
- apartment unit, apartment room, square ft. of building, gross rent multiplier
- apartment unit, apartment room, square ft. of building, utility costs
- apartment unit, apartment room, square ft. of building, land to improvement ratio
- apartment unit, apartment room, square ft. of building, operating income before taxes
apartment unit, apartment room, square ft. of building, gross rent multiplier
WPAM Chapter 12, Units of Comparison
Analyzing the answer options, you'll notice all the answers are the same except the last item in the list so we just need to find which last list item is the best unit of comparison for valuing apartments
- utility costs can vary so much so it's not a good measure
- land to improvement ratio is also called the Allocation Method is a method for valuing land not property so it's not a good measure
- operating income before taxes can vary so much so it's not a good measure
Adjustments in the comparable sales approach are always made to the ______
- sale (comparable property)
- subject property
- square footage
- number of baths
sale (comparable property)
WPAM chapter 12, Adjustment Process
"By modifying the sale prices of comparable properties to reflect the characteristics of the subject, the assessor can estimate the value of the subject property."
The ______ rate is another name for the return ______ the investment
- discount, on
- recapture, on
- effective, on
- capitalization, of
discount, on
WPAN chapter 11, Income Approach
"The capitalization rate is composed of three different
rates:
1. Discount rate (return on investment)
2.
Recapture rate (return of investment)
3. Effective tax rate
(expressed as a percentage of market value)"
The adjustment process involves the application of the ______ of an item (or factor) to the total property
- replacement cost
- present worth of one
- assessed value
- contributory value
contributory value
WPAM chapter 12, Adjustment Process
"The principle of contribution is the underlying principle in the adjustment process. The assessor must determine what a particular feature contributes to the value of the property as a whole, i.e., how much more or less would a purchaser typically pay for a property with or without a certain characteristic."
Elements for which adjustments can be made are
- time, location, physical condition, size, components, and soil productivity
- location, physical condition, size, landscaping, and material type
- time, location, classification, and zoning
- location, physical condition, components, size, and income potential
time, location, physical condition, size, components, and soil productivity
WPAM chapter 12, Adjustment Process
"Characteristics for which adjustments are typically made include time of sale, location, and physical factors."
Key here is knowing TIME is the most important adjustment, if the answer doesn't include Time as one of the options then it is automatically wrong. From there you can see physical factors is only in the first option making it the best answer
The correlating of the value indications of the various sales into a single indicator of value is known as ______
- use value
- equalization
- reconciliation
- equated value
reconciliation
Key here is into a single indicator
this connects most with the word reconciliation
When plus or minus adjustments are expressed in terms of percentages, the adjustment for ______ should be made prior to any other adjustments
- age
- time
- location
- size
time
WPAM chapter 12, Adjustment Process
"In general, sales are first adjusted for time to reflect the sale price as of the appraisal date. All other adjustments are made to the time adjusted sale price."
Capitalization may be described as
- valuing income generated by a business on a property
- conversion of future income stream to present worth
- measuring gross economic income of a property
- none of the above
conversion of future income stream to present worth
An improved property is valued at $50,000. The building-land ratio is 4:1. By allocation, what is the estimated land value?
- $7,500
- $20,000
- $5,000
- $10,000
$10,000
You are given the building to land ratio which says the land is valued at 1/4 of the building.
Land Value = Property Value * Land Ratio
50,000 x 0.25 = $12,500
We can assume because it's an estimated value we can go to the closest answer which is 10,000
What are the four government rights to a property?
Taxation, Escheat, police power, Eminent Domain
Who appoints the real property lister?
County board or administrator
Who is responsible for the discovery of property and omitted?
The assessor
When is the last day the personal property forms can be delivered back to the assessor?
March 1
How far back can the assessor assess omitted property?
2 years
How far back can the assessor go to pick up assessment errors?
1 year
What is the three main function of the assessment process?
Discovery, Listing, valuation
What must be listed if the parcel is greater than one tract?
The number of acres in each tract
Who can order an Assessors plat?
The local governing body
Who may end up paying for the Assessors plat?
The affected land owners
The authority to levy taxes is granted to all taxing districts by:
The State Legislature
The requirement of uniformity of taxation is a mandate from:
The State Constitution
The state legislature is solely responsible for:
Establishing the criteria for exemptions
The local tax rate is determined by dividing:
the Levy by the total assessed value of the district
All real property shall be assessed as of:
The close of business Jan 1 of each year
State law (sec. 70.32(2)(c)1d, Wis. Stats.), defines agricultural
forest as land that is capable of producing commercial
forest
products. How long must the roll be kept for?
20 years (from 2004)
The only evidence that may properly be used by the board of review is:
Evidence given orally under oath at the board of review hearing
As assessment quality improves, the:
Property tax collections remain the same
How many classes of real property are there?
eight
How is non-agricultural real estate to be valued:
Based on market value by sale
Explain the difference between market value and true cash value?
No difference, they are the same
When does the assessor sign the affidavit/roll?
On or before the first Monday in may prior to the BOR
If the affidavit/roll is unsigned?
Still valid not a nullity, burden on municipality
What constitutes a quorum?
A majority constitutes a quorum except that 2 members may hold a hearing of evidence required. If two were at the hearing than another member must review the transcript and then the 3 will decide.
Time and place of BOR meeting:
Shall meet annually at any time during a 30 day period beginning the second Monday in May. At least 15 days before the first session the clerk of the BOR must publish a first class notice and place a notice in at least 3 public places and place a notice on the door of the town hall, village hall or council chambers at city hall of the time and place of the first meeting.
What if the BOR has to adjourn?
If an adjournment be had for more than one day, a written notice shall be posted on the outer door of the place of said meeting, stating to what time said meeting adjourned.
True or False: Metes and bounds descriptions are always tied to a known point
True
True or False: Metes and bounds must be read from the beginning and followed through while the rectangular survey descriptions are read backwards:
True
What is Metes and Bounds?
A means of describing land by starting from a known point and following the outside boundaries of the parcel
True or False: The income approach derives an expression of present worth by converting future benefits into a market value.
True

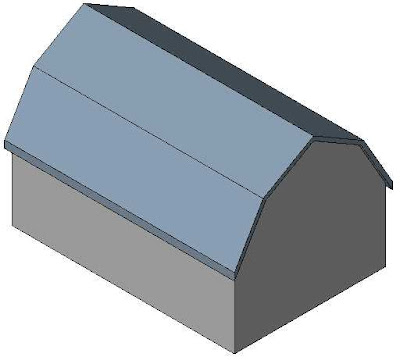
- Mansard
- Hip
- Gambrel
- Gable
Hip
Angled/sloping sides that meet at a hip (edge)
- Mansard
- Hip
- Gambrel
- Gable
Gambrel
2 different angles of slopes (smaller angle & bigger angle) that meet at top hip (edge)

- Mansard
- Hip
- Gambrel
- Gable
Mansard
4 sloped sides with steep angles meeting at a flat top (hip with a flat top)
gives extra room in the house and translate to increase in value
bad paint job or leaky roof
- physical, functional, or economical?
- short or long life?
- curable or uncurable?
physical deterioration, short life, curable
roof framing
- physical, functional, or economical?
- short or long life?
- curable or uncurable?
physical deterioration, long life, curable
inharmonious land use or population changes
- physical, functional, or economical?
- short or long life?
- curable or uncurable?
economical obsolescence, N/A, uncurable
old-fashioned plumbing fixtures
- physical, functional, or economical?
- short or long life?
- curable or uncurable?
functional obsolescence, N/A, curable
bad floor plan/layout
- physical, functional, or economical?
- short or long life?
- curable or uncurable?
functional obsolescence, N/A, incurable
foundation or bearing walls need replacing/are faulty
- physical, functional, or economical?
- short or long life?
- curable or uncurable?
physical deterioration, long-life, incurable
all kitchen appliances are old/worn and will cost more than added value
- physical, functional, or economical?
- short or long life?
- curable or uncurable?
physical deterioration, short life, incurable
what class of depreciation does Condition (CDU) connect with?
- physical deterioration
- functional obsolescence
- economic obsolescence
physical deterioration
what class of depreciation does Desirability (CDU) connect with?
- physical deterioration
- functional obsolescence
- economic obsolescence
economic obsolescence
what class of depreciation does Usefulness (CDU) connect with?
- physical deterioration
- functional obsolescence
- economic obsolescence
functional obsolescence
If a property's depreciation is at 60%, what is the Percent Good?
- 60%
- 100%
- 40%
- 120%
40%
Percent good is the other half of depreciation, 60 and 40 come together to make a whole
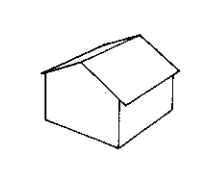
gable
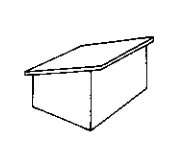
shed/single pitch
what's the difference between live load and dead load?
dead load is the weight of the building and all permanent objects while the live load includes the weight of occupants and anything removable with the building weight
what action does plottage describe?
- splitting apart land into smaller pieces
- plotting out boundaries of a property
- combining 2 lots into 1 to have a greater singular value
combining 2 lots into 1 to have a greater singular value
process of creating/improving land from flooded areas
reclamation
What are the 5 rights a property owner must have to claim Fee Simple Ownership Interest?
(S, L&O, M, G, all or nothing)
- right to sell
- right to lease and occupy
- right to mortgage
- right to give away
- right to do none or all these things
Which government limitation goes with this definition?
power to take property title if owner dies without an heir
Escheat
Which government limitation goes with this definition?
power to take property for public use with owner being compensated
Eminent Domain
Which government limitation goes with this definition?
right to regulate use of property
Police Power
Which government limitation goes with this definition?
power to tax property
Taxation
one-story house that usually has an attached garage and a large picture window facing the street. The shape of the house is either rectangular or an "L" or "U" shape. The houses have low-pitched roofs and extended eaves (edge of roof)
Ranch
a one-story house with a full basement at half grade. The partially excavated basement typically has daylight windows in the lower level. The two levels are split by a foyer at grade level
Bi-level (raised ranch)
living areas staggered on two or more levels, separated by one half grade. There are typically two or more short sets of stairs running up or down and have a split roof design
Split-level
A one story with attic or a one and one-half story house with dormers, extra gables, or shed dormers, generally built after the 1920's. It is characterized by a steep roof slope and dormers which project from the roof and have windows on their fronts
Cape cod
one-story house, often with finished attic area, popular in the early
20th century, and generally built from 1905 to 1930. This style has
one or more low-pitched overhanging gables, and is characterized by
exposed beams, projecting brackets, and use of natural materials.
Porches usually extend across the front and are supported by wide
columns. Windows are generally casement or double
hung
bungalow
small, plain single family house. It is usually one story built with minimum construction standards resulting in narrow boxy exterior appearance with little or no ornamentation & low pitch roof
cottage
constructed of mixed natural materials (wood, stone, and brick) with lowpitched roofs, wide eaves, and exposed brackets. Most homes of this style have porches with thick round or tapered square columns. The style is generally symmetrical with double hung windows and multi-gables or hipped roofs
craftsman
low pitched roofs, generally gabled and enclosed, often with hip or flat roofs. Boxy and low-proportioned with strong horizontal lines and oversized eaves
Prairie
built between 1900 and 1950 that is typically built at a quality grade less than C. It has a simple design that often includes only a single bathroom and has small bedrooms. It often includes an unfinished attic and an unfinished basement
basic single story
multi-story style with large front porches or wraparound decks and have gable roofs that may cover the porch. They are minimally ornamental and have large windows to bring in light. The exterior is faced with horizontal siding and the homes often have a simple rectangular floor plan with side wings
farmhouse
from the 19th century, asymmetrical, two + stories with steep roof
pitches which may include turrets and dormers. Large porches are
embellished with decorative
railings and posts
victorian
rectangular shaped two-story home. Each floor is two rooms deep, and has approximately the same square footage. The roof structure has a medium slope, with limited attic space that is not intended for living area
colonial
modern style, single or multi-story and may be of split level construction. Houses typically incorporate tall, irregularly shaped windows, open planning and angular exterior lines. Roofs may be flat, shed, gable or various combinations thereof
contemporary
single story, high ceilings, and moderate to steep pitched hip or multi-gabled roof. Windows are large and abundant, permitting extensive natural light. Prominent garages with 3-4 stalls are common.
modern single story
Prominent 3-4 stall garages, and a mix of exterior wall coverings are common in this style. Features include tall entrance ways, abundant large windows, and high ceilings
modern multi-story
A large, luxury home built using the highest quality materials of brick or cut stone. These homes commonly have three or more baths, two or more fireplaces, and expansive entries with elaborate open stairways. These largescale homes are typically 4,000 to 12,000 square feet per story, and are often located in prestigious neighborhoods
executive mansion
A form of fee ownership of whole units or separate portions of multi-unit buildings by statute, which provides the mechanics and facilities for formal filing and recording of a divided interest in real property, where the division is vertical as well as horizontal. Fee ownership of units in a multi- unit property and joint ownership of the common areas.
condo
Any two-unit residence not qualifying as a townhouse, built after the mid-20th century
duplex
A building containing multiple self-contained living units
apartment
Recapture rate formula
annual amount recaptured / amount of original investment
how to calculate remaining economic life of property
economic life - effective age
Economic life: 50 years
Effective age: 20 years
50-20 = 30
how to calculate depreciation ratio & apply it
effective age / economic life then multiplied against the Cost New
Economic life: 50 years
Effective age: 20 years
Cost New: 100,000
20 / 50 = 0.40 --> 40%
100,000 x 0.4 = 40,000
The house has depreciated by 40,000 so we would subtract that
What type of expenses should and should not be included when calculating income approach's net income?
Good: management, repairs, utilities, insurance
Bad: mortgage interest or debt service, depreciation, capital expenses
how many hours of CE are needed for recertification?
30
What day does the municipalities assessment need to be complete (other than 1st and 2nd class cities)?
- 1st Monday of April
- 4th Monday of April
- 1st Monday of May
- 2nd Monday of June
1st Monday of April
When should the assessment roll be delivered to the clerk?
- 1st Monday of April
- 4th Monday of April
- 1st Monday of May
- 2nd Monday of June
1st Monday of May
When does the BOR meet?
- 1st Monday of April
- 4th Monday of April
- 1st Monday of May
- 2nd Monday of June
4th Monday of April starts up a 45 day period BUT cannot be sooner than 7 days after open book
When is the MAR report due to DOR?
- 1st Monday of April
- 4th Monday of April
- 1st Monday of May
- 2nd Monday of June
2nd Monday of June
how many acres in 1 square mile?
60
how many miles is one township on each side?
6