Digital images are a recording of __________ received by a sensor.
photons
What is the difference between the possible values given by analogue vs digital instruments?

Analogue: infinite number of possible values
Digital: discrete number of possible values (no in between)
What is a charge-coupled device (CCD)?
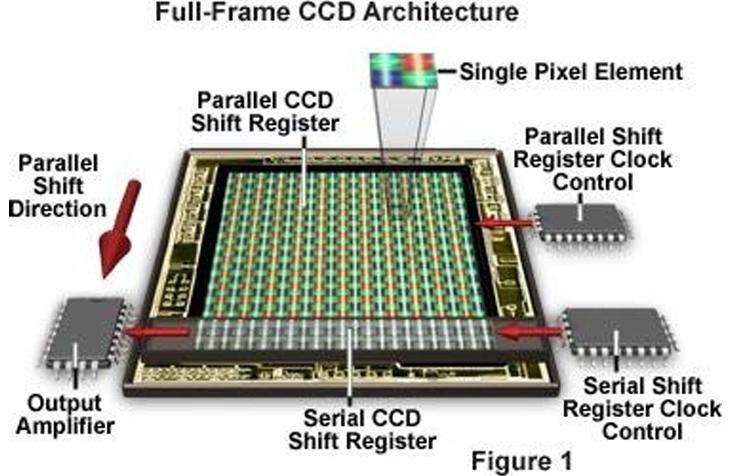
An array of silicon atoms (a grid) whose bonds can be broken by absorbing light (photons) of various wavelengths.
What is an Instantaneous field of view (IFOV)?
A sensor's angular cone of visibility
Define spatial resolution.
The smallest unit of area the sensor can collect
information about
What are Digital Numbers (DN)? What are they also referred to as?
The energy measured in a single pixel according
to a
predetermined scale, Brightness Value (BV)
DN is measure ___________, not reflection.
radiance
A low DN value means ___________ radience.
little
What is Radiometric Resolution?
A sensor’s ability to determine fine differences in energy measurements
AKA
Sensitivity of a sensor to differences in signal strength
What is a Bit?
short for ‘Binary Digit’, Basic unit of information used in computing and digital communications
What values can a bit have? What is the expression for how many possible combinations of bit values there are?
only one of two values, most commonly either 0 or 1
2n (n = number of bits), therefore 2 bits would have 4 (22) values
The __________ of a radiometric resolution corresponds to the number of bits used for coding numbers in a binary format.
range
Most commonly sensors will have _____ bit data but more advanced sensors have _____ bit data
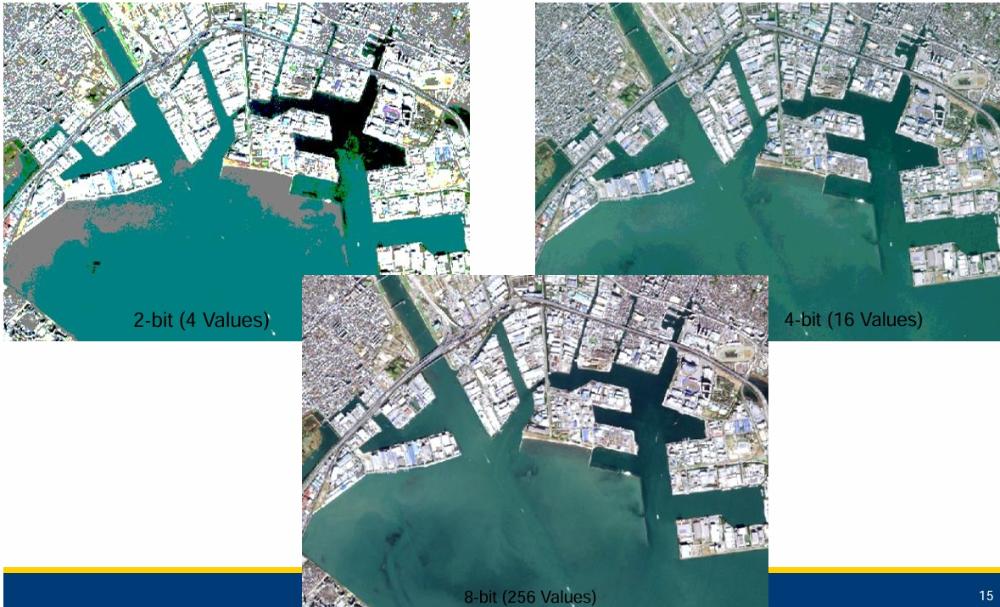
8, 12
The bands of colour used to render digital images are (discrete/continuous).
Discrete
Why don't digital images have colour? What does this mean for the initial display of digital numbers?
Colour is used for interpretation, greyscale presentation
A _____________ sensor measures the visible spectrum as one band. This results in a ___________-and-___________
Panchromatic, black-and-white
A ____________ ____________ is an image formed by displaying the DNs of one band as red, a second band as green, and a third as blue.
colour composite
How is True colour composite different from a colour composite?
True colour matches red, green and blue to DN values that are red, green and blue respectively in real life. It is a type of colour composite.
An image where the distribution of the band
differs from a true
colour composite is called what?
A False colour composite
What is the standard for which bands are represented by RGB in a false colour composite?
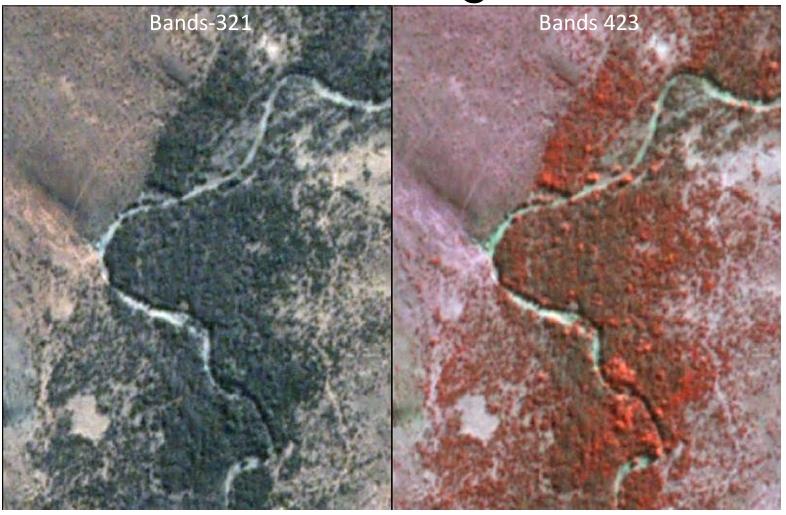

• NIR represented by red
• Red represented by green
•
Green represented by blue
What is the spectral resolution of an sensor?
The number and width of bands measured by a
sensor
A multispectral sensor will have ___-10 ___________ bands while a hyperspectral sensor will have hundreds of ___________ bands.
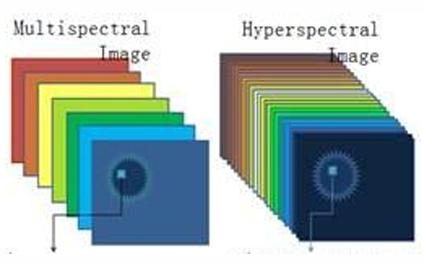
3, wider, narrow