What does Erythrocytes mean?
Red blood cells
What does Leucocytes mean?
White blood cells
What are Thrombocytes?
cell fragments that flow in the blood that clot up a space to stop bleeding
What are Functions of the Heart?
- pump blood(pressure the blood to move)
- separate systematic and pulmonary blood blood circulation to not allow oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to mix
- not allowing regurgitation(inverse blood flow)
- control blood flow, to move the blood to places where its needed the most rather than evenly distributing
What is the structure of blood vessels?
- Tunica intima
- Tunica Media
- Tunica adventitia
What is the Tunica intima made of?
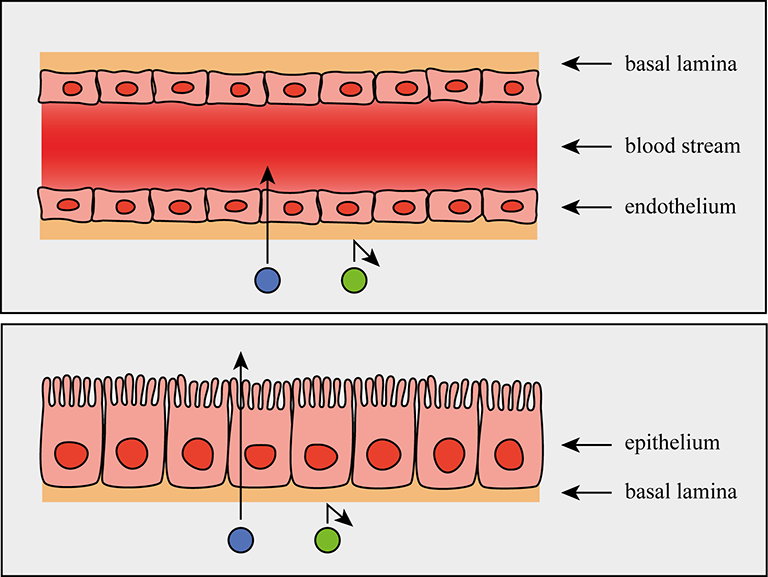
endothelium layer(which is a type of epithelium that covers the innermost layer of blood vessels) + basal lamina
What is the Tunica adventitia made of?
collagen fibers, which are the most abundant type of fibers in the human body
Classify blood vessels.
- conducting blood vessels
- resistant blood vessels
- exchange blood vessels
- distributing blood vessels
- reservoir blood vessels
Explain Conducting blood vessel.
blood vessels that are big and have thick elastic walls to transform large amount of blood
Explain resistance blood vessel.
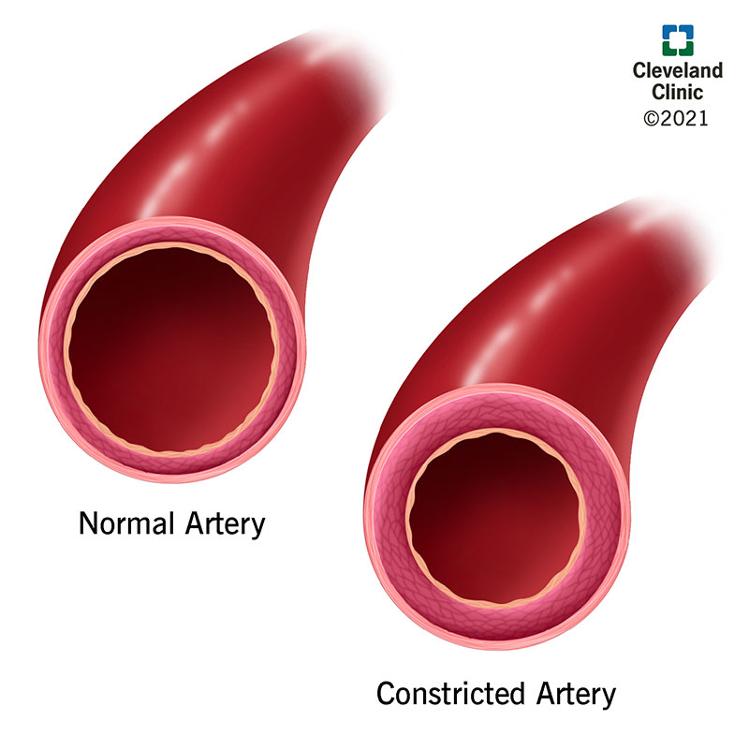
blood vessels that can do:
- vasodilation: widening the blood vessels lumen(opening)
- vasoconstriction: narrowing blood vessels lumen(opening)
to regulate blood pressure
Explain exchange vessel.
capillaries
Explain distributing blood vessel.
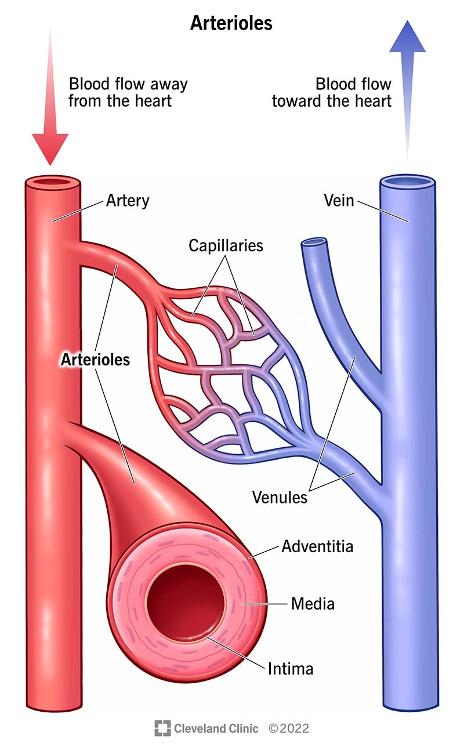
Arterioles and Venules
Explain reservoir blood vessel.
Veins
Which one has smaller lumen Arteries or Veins?
Arteries
What is the difference between elastic and muscular arteries?
- Elastic: have more elastic fibers/tissue in their Tunica Media
- Muscular: have more Smooth muscle tissue in their Tunica Media
What is the size of Arterioles?
lesser than 0.1mm
What are Terminal Arterioles?
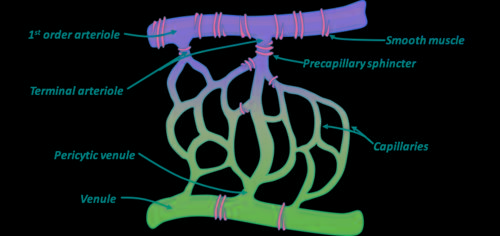
they are like the last branches of Arteries before the beginning of capillaries
What are meta-Arterioles?
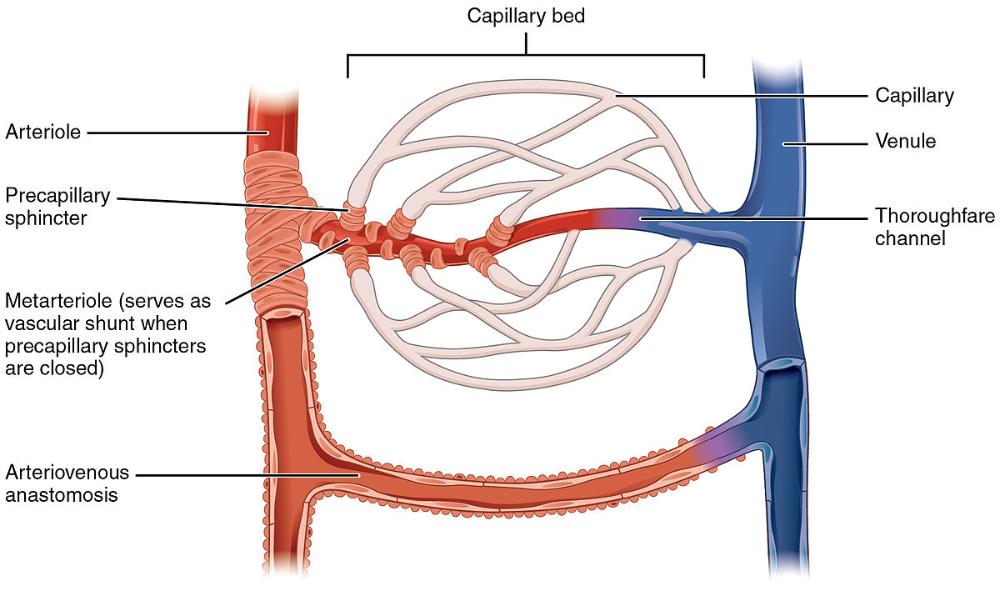
they are the sort of Plan B for transporting blood from arteries to veins if the precapillary sphincters close the capillaries the meta-arterioles are the only way to transport blood from arteries to veins
What are thoroughfare channels?

they are like the meta-arterioles for veins and venules
what is the diameter of capillaries?
5-8 microns or micrometers
classify capillaries.
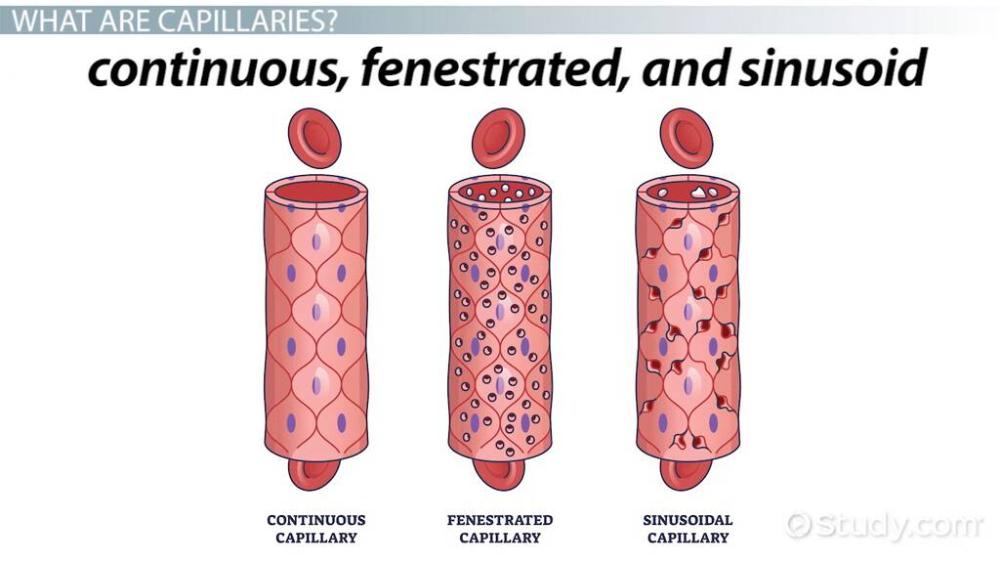
- Continuous capillaries
- Fenestrated capillaries
- Sinusoid capillaries
Where Continuous capillaries are found?
skin, lung, smooth muscles and connective tissue
Where fenestrated capillaries are found?
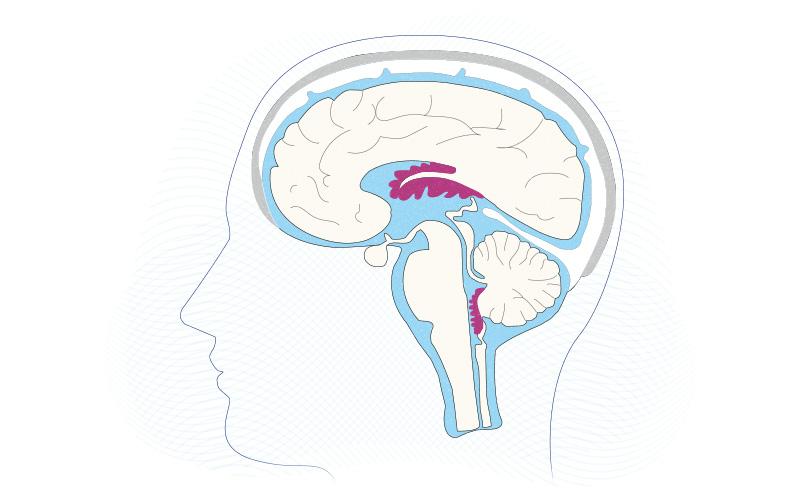
Pancreas, endocrine glands, small intestine, choroid plexus(which is the part of the brain that makes cerebrospinal fluid), ciliary process(folds of the choroid of the eye)
how large are the spaces in the sinusoid capillaries?
30-40 microns
Where Sinusoid capillaries are found?
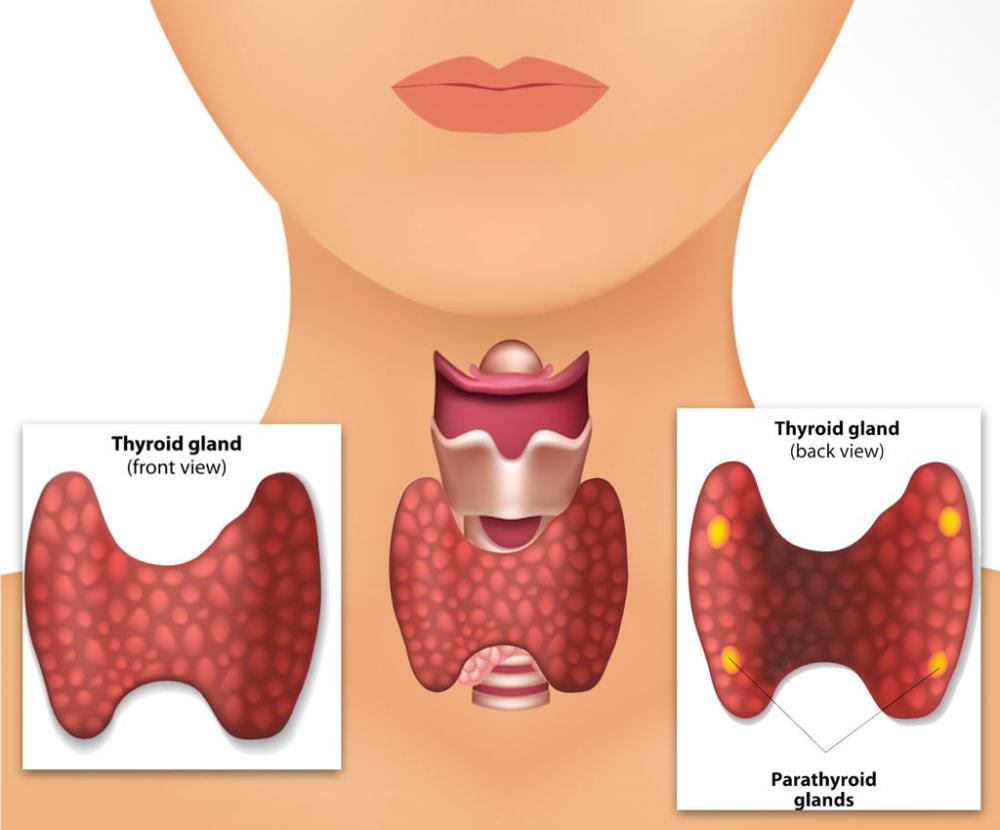
Spleen, liver, bone marrow, adrenal gland and parathyroid gland
What is the size of portal vein's diameter?
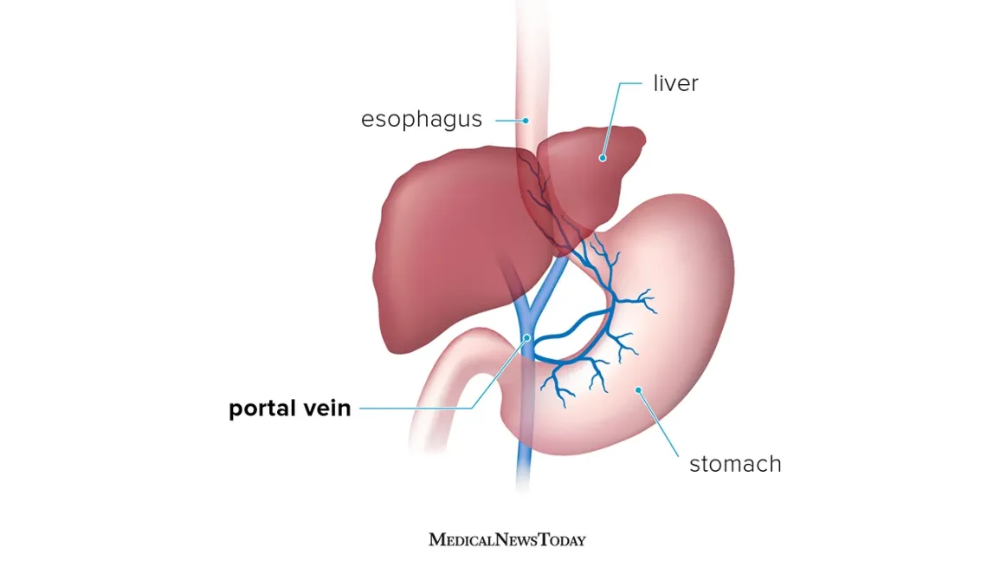
less than 2mm
Where are the Veins without valves located?
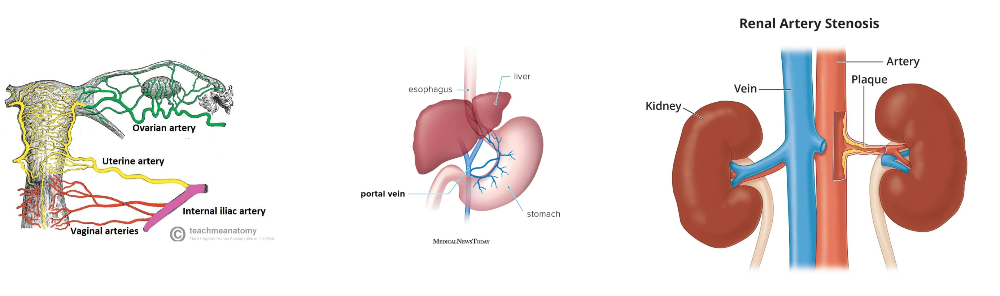
SVC & IVC
Hepatic, Renal
Uterine, Ovarian
Facial
Pulmonary
Umbilical
Portal Veins
Where are the Veins without muscular tissue located?
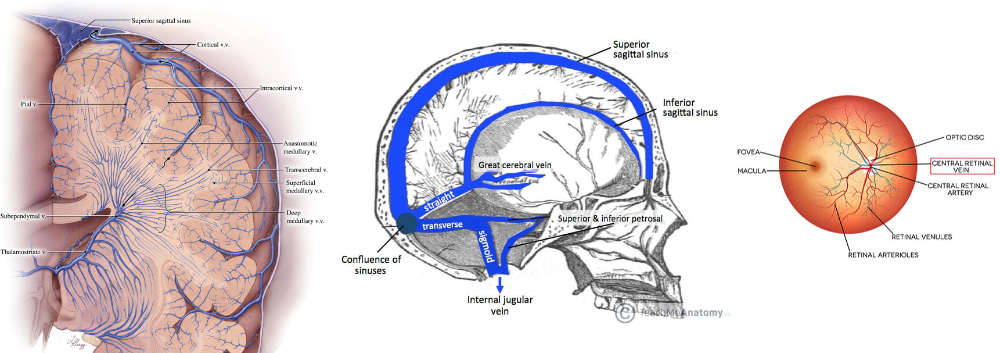
Dural venous sinuses(draining the cranial cavity)
Pial Veins
Retinal
Veins of erectile tissue of sex organs
spongy bones
What are the factors that affect venous return(return of blood to the heart)?
- Muscle contraction
- negative thoracic pressure(contraction of the diaphragm)
- gravity
- valves
- Pulsation of arteries
What is anastomosis?
its connecting two things that each are normally branching to elsewhere
name anastomosis types.
- End to end(convergent)
- Potential
Where can you find end to end(convergent) anastomosis?
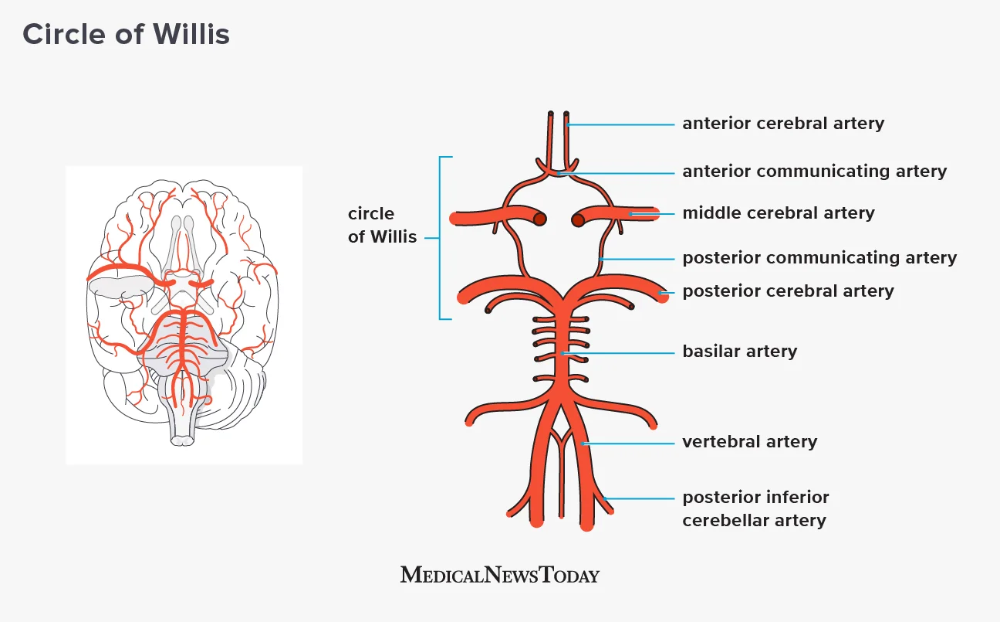
in the circle of Williams which are vessels connecting under the brain
Where can you find Potential anastomosis?
around Joints and coronary
Where can you find arteriovenous anastomosis?
1. Skin of nose
2. Lips
3. External Ear
5. Erectile
tissue of sex
organ
6. Thyroid
7. Tongue
What are end arteries?
arteries that don't anastomose with any other artery so if blood doesn't flow in them the part they supply will be damaged or dead
Where can we find end arteries?
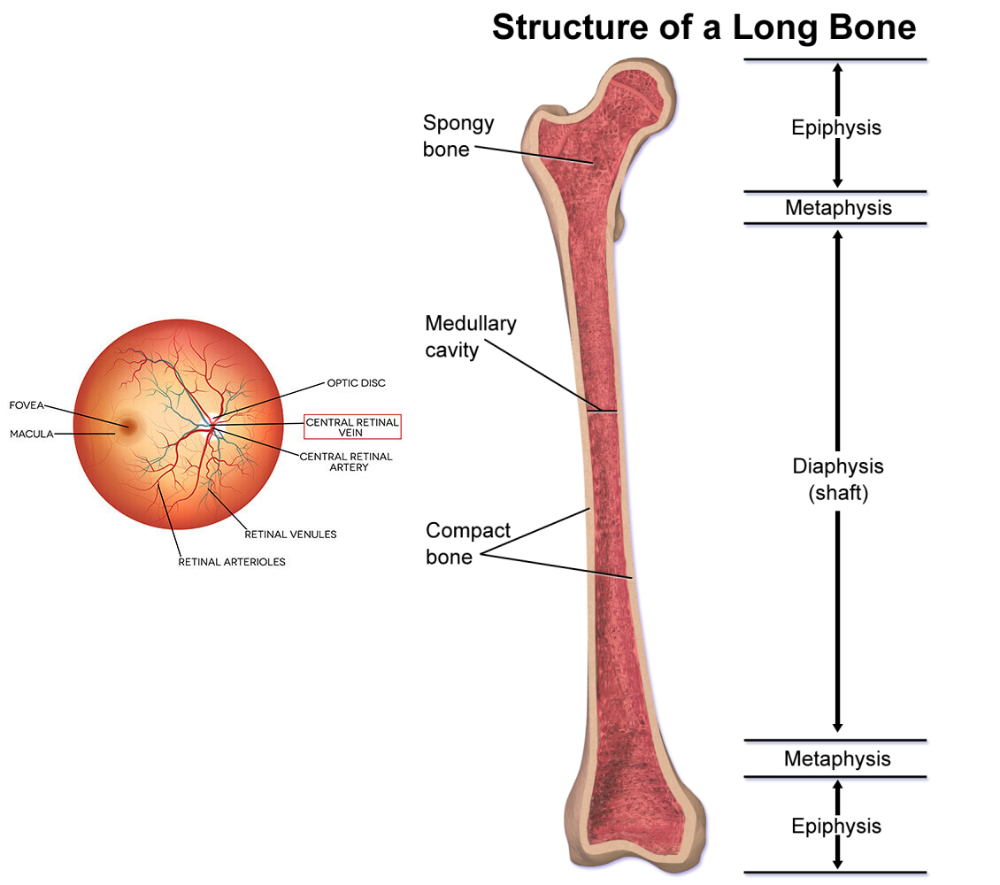
- Central retina artery
- spleen
- liver
- kidney
- metaphysis of long bones
- central part of the cerebral cortex
Name types of circulation?
- coronary
- systematic
- pulmonary
- fetal
In terms of intercostal spaces, where is the base of the heart?
In the 2end intercostal space, between 2end and 3rd rib
In terms of intercostal spaces, where is the apex of the heart?
In the 5th intercostal space, between 5th and 6th rib
What are the branches of the ascending aorta?
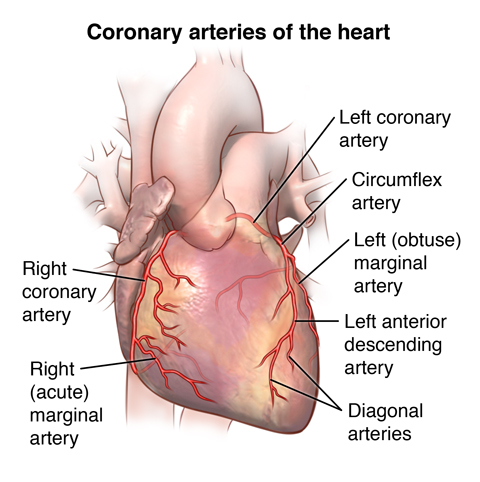
Left and right coronary arteries
What are branches of the Aortic arch?
- Brachiocephalic trunk(that devides to 1-right subclavian and common carotid)
- Left subclavian
- Left common carotid
What are the branches of the common carotid arteries?
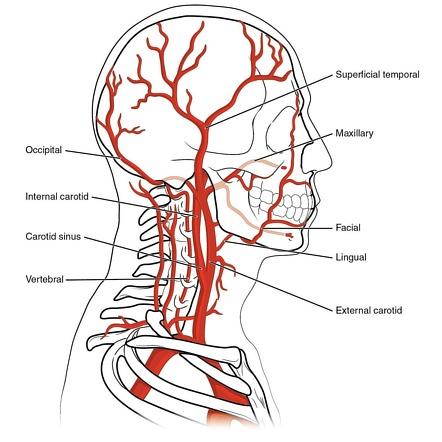
Internal and external common carotid
What do internal common carotid artery supply blood to?
The brain
What do external common carotid artery supply blood to?
Maxillary, face, neck and some regions of the head
Explain how does the Subclavian artery change?
Its called subclavian first-> Axillary(when its at the armpit region)-> brachial artery(after it passes the teres major muscle)-> it divides into radial and unlar a.
What are the branches of the abdominal aorta?
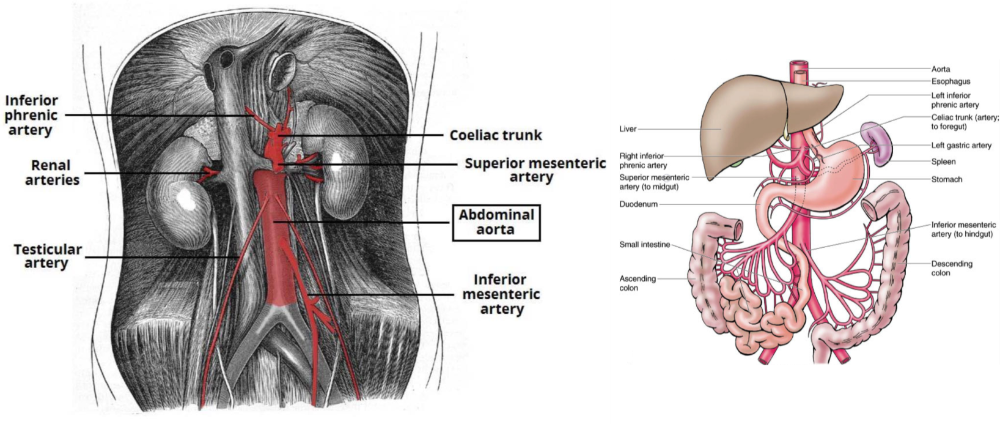
- Renal a.
- Testicular a.
- Common illiac a.
How does the illiac artery change?
It divides into internal and external illiac artery and the external illiac arter->the external illiac artery becomes femoral a.-> the femoral becomes(popliteal a. Which is the fossa behind the knee)-> the popliteal a. Divides to anterior and posterior tibial a.
Where does the internal common illiac a. Provide blood to?
The pelvis and the buttocks
what are the terminal branches of the external carotid artery
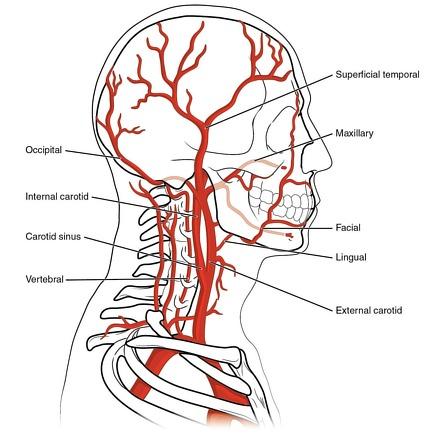
The maxillary and superficial temporal region of the skull
Where will the brachiocephalic artery bifurcate to the right subclavian and right common carotid artery?
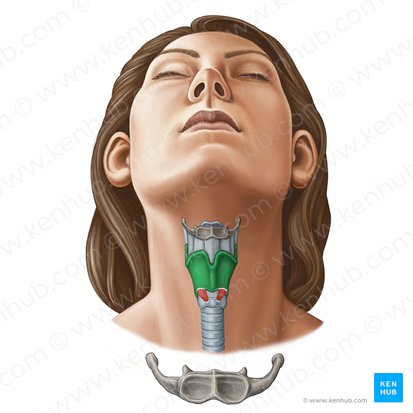
At the thyroid cartillage level or C4(4th cervical vertebrae)