Nitrogen 78%`
Mostly in the form of N2 (unusable to plants without being fixed)
Argon 0.93%
Inert, noble gas
CO2 0.04%
Most important GHG; leads to global warming, removed from atmosphere by photosynthesis
Oxygen 21%
Produced by photosynthesis in plants and is needed for human and animal respiration
Water Vapor 0-4%
Varies by region and conditions; acts as a temporary GHG, but less concerning than CO2, quickly cycles through atmosphere

What is the order of the earth's atmosphere #1
Troposphere: Tropo= change, weather occurs here, 0-16km, most dense due to the pressure of the other layers above it, most of the atmosphere gas molecules are found here, ozone in the troposphere is harmful to humans

What is the order of the earth's atmosphere #2
Stratosphere: "S" for second, 16-60 km, less dense due to pressure from layers above, thickest O2 layer is found here, absorbs UV-B and UV-C rays which can mutate DNA of animals (cancer)

What is the order of the earth's atmosphere #3
Mesosphere: Meso= for middle, 60-80km, even less dense

What is the order of the earth's atmosphere #4
Thermosphere: Them= hottest temp, absorbs harmful X-rays and UV radiation, charges gas molecules glow under intense solar radiation producing northern lights (aurora borealis)

What is the order of the earth's atmosphere #5
Exosphere: Outermost layer where atmosphere merges with space
Temperature
Layers of earth's atmosphere are based on where temperature gradients change with distance from earth surface, as you move away from the earth it gets colder, with each layer above it will change from cold to hot
Troposphere
temperature decreases as the air gets further from the warmth of earth's surface
Stratosphere
temp increases because top layer of stratosphere is warmed by UV rays (like pool surface)
Mesosphere
temp decreases because density decreases, leaving fewer molecules to absorb the sun, the coldest place on earth -150 degrees
Thermosphere
temp increases due to the absorption of highly energetic solar radiation, the hottest place on earth 3,100 degrees
4.4 takeaways
1. the atmosphere is made of a mix of gases in varying percentages
2. layers of the atmosphere thin out as you travel higher
3. temperature oscillates for various reasons including content and radaiton
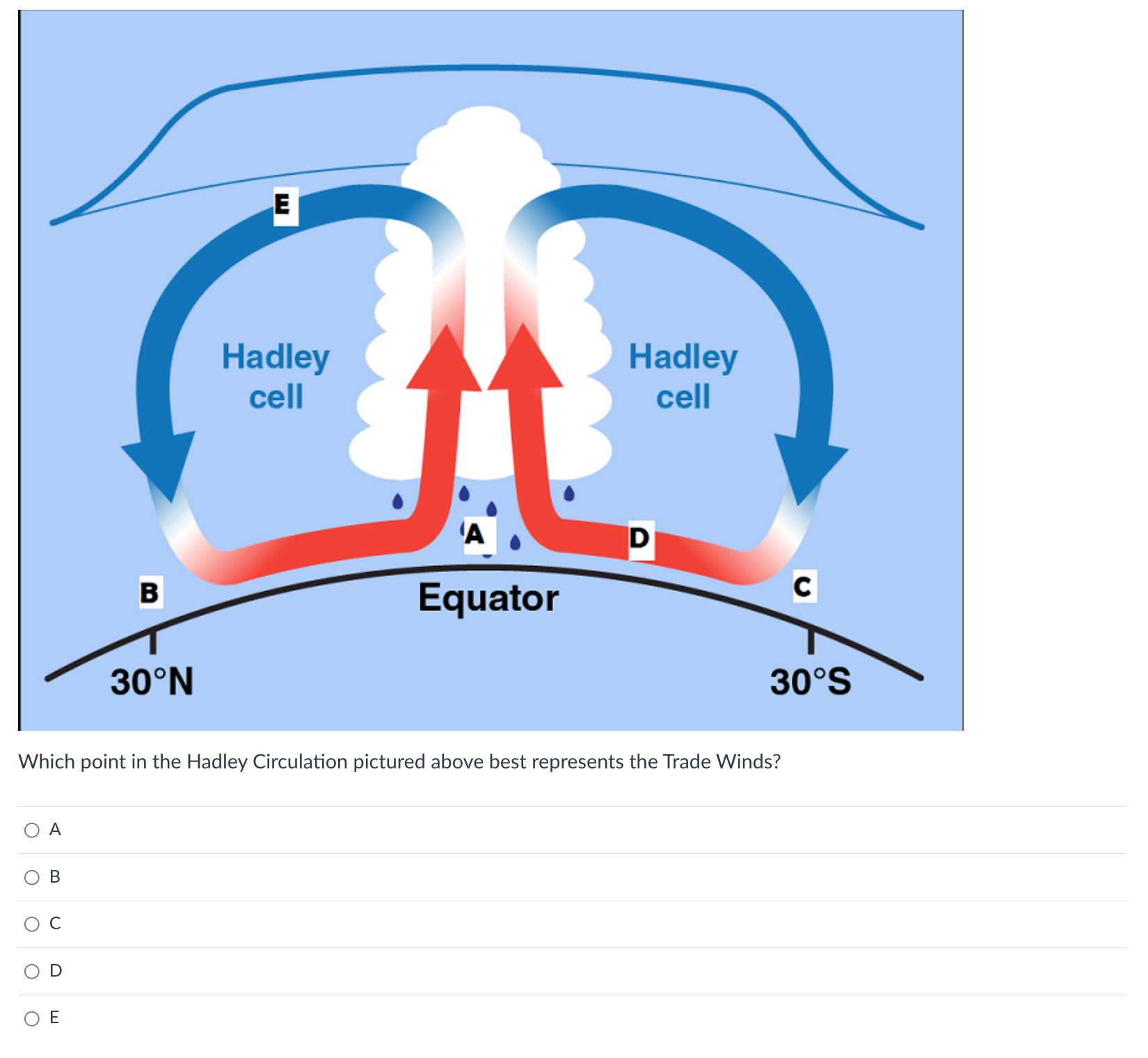
Hadley cell #1
More direct sunlight at the equator warms the air, warm air rises

Hadley cell #2
Warm air rises, cools, and expands, H20 vapor condenses into rain, warm air holds more moisture than cold

Hadley cell #3
Air continues to rise, cool, and expand, rising air expands and cools

Hadley cell #4
Cooling, expanding air spreads out, cool air cant hold as much H2O vapor (condenses and turns into rain)

Hadley cell #5
Cool, dry air sinks back down to earth at 30 degrees North and South, deserts form here due to lack of moisture in air, after cooling and expanding, air sinks
Coriolis effect
deflection of objects traveling through atmosphere due to spin of earth
Coriolis effect air at 30 degrees
moves back to low pressure of equator
Coriolis effect wind between 0-30 degrees
moves from east to west because earth is spinning west to east
Coriolis effect wind between 30-60 degrees
moves west to east because earth spins faster at 30 degrees than at 60 degrees
Global Wind Patterns 0 degrees
Low pressure
Global Wind Patterns 30 degrees
High pressure
Global Wind Patterns 60 degrees
Low pressure
4.5 takeaways
1. winds are driven by certain factors: solar radiation and the Coriolis effect
2. these factors lead to patterns that are predictable
3. wind patterns can lead to patterns in climate and habits at thoes climates