Force
Push or pull on an object
Internal forces
- Act within an object or system whose motion is under investigation
- Forces come in pairs (action and reaction)
Internal forces: tensile force
When pulling forced act on the ends of an internal structure
Internal force: compressive forces
When pushing forces act oj the ends of an internal structure
External forces
Act on an object as a result of its interaction with the environment surrounding it (when two objects touch)
Weight
W = m*g
w (newtons)= m(in kilograms)*g(9.81m/s^2)
Translation:
linear motions in which all parts of a rigid body move parallel to & in the same direction as every other part of the body
Rotation:
- motion in which a (assumed) rigid body moves in a circular path around some pivot point,
- thus the entire body moves in the same angular direction & across the same number of degrees
Kinematics can be_____
active or passive
Degrees of freedom:
the number of independent directions of movements allowed at a joint
max degrees of angular freedom
3 degrees for 2 cardinal planes
Arthrokinematics: the trio
- roll
- slide
- spin
Roll-slide
- As primary movement of bone is to rotate across another bone’s surface
- concurrent but equal + opposite side
spin
- Spinning of one articular surface on another
- NO SLIDE
THE RULE: Convex-on-concave =
opposite
THE RULE: Concave-on-convex
same
Joint articulation fits “the best” where?
- at end range = close packed
- provide more stability
Kinetics
The study of mechanics that describes the effect of forces on the
body
Rectilinear:
- all points on a body/object move in a straight line.
- Direction of motions& orientation of object do not change.
- All points on object move the
same distance.
Curvilinear:
- all points on a body or object move
- orientation does
not
change & all points move the same distance - path the object follows is
curved.
Angular motion
- rotation/rotary motion
- More numerous than linear motion (human movement)
General motion
- Combination of angular motions producing linear motions of multiple body parts
Displacement
- vector quantity
- has direction & magnitude
Speed
- rate of motion
- AVG= d/change in time
Velocity
- rate of motion in a specific direction
- AVG= velocity(or d)/change of time
Baseball fastpitch example
- baseball released @16.8m
- velocity @47.162m/s
- v= d/change of time
- change of t= d/velocity
- 16.8m/47.163(m/s)= 0.356 seconds
hang time when initial vertical velocity (20 m/s) and initial horizontal velocity (15 m/s) is known

L = mv
- L = linear momentum
- m = mass
- v = instantaneous velocity
- L constant => sum of forces = 0
elastic collisions
momentum is conserved (transferred) and no energy is lost
inelastic collisions
momentum is conserved but energy is lost
Impulse
the product of force and the time the force acts
Torque equations
- T= F*r
- F = force
- r = moment arm (perpendicular distance from axis of rotation)
Stability
- dependent upon height of center of gravity, size of base of support, and the weight of an object
Locating Center of gravity
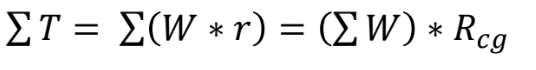
sum of force
centric forces
act through the center of gravity of an object and cause linear translation
Eccentric forces
- (not muscle contractions) do not act through the center of gravity
- they cause both linear and angular motion
Force couples
- create angular motion
- couples are forces that
are equal in size, non-colinear, and act in opposite directions
1st class levers
- HUGE forces
- SMALL distance
2nd class levels
- middle
- output forces are modest, input distance is modest
3rd class:
- WEAK output forces
- HUGE distances
Potential Energy (2 types)
- Gravitational
- Strain (or spring) energy
Power
- strongest contraction force is produced at the slowest speed
- max POWER occurs at 1/3 -1/2 of a muscles max contraction velocity
Energy
the capacity to do work
Tension
the stress that acts perpendicular (or normal) to the analysis plane
Shear
A transverse stress that acts parallel to the plane of analysis
Bending
- More complicated
- creates different stresses at the
analysis
plane
• creates both tensile & compressive forces
Wolff's Law
Bone remodels according to the stresses place upon it
Torsion
Occur when torques act about the long axis of an object
Poisson’s Ratio
- Each material has a property (Poisson’s ratio)
- determines the amounts of
axial strain to transverse strain experienced during loading
Elasticity
The ability to stretch under tensile load but then return to it’s original shape
Elastic modulus
The ratio of stress-to-strain is called elastic modulus of a material
Resilient:
the ability to absorb stress/shock/assualt and return to a previous state
Bone is strong against ____
compression
Bone is weak against ____
shearing force
What determines stretch? (x2)
- muscle spindles
- GTO
Why does speed kills?
- Increase of speed means more energy in the KE equation
- values are multiplied so V^2 produces more KE
Static vs. dynamic stretching
Static < dynamic stretching