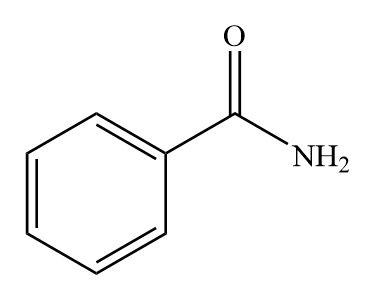
Structure of amide
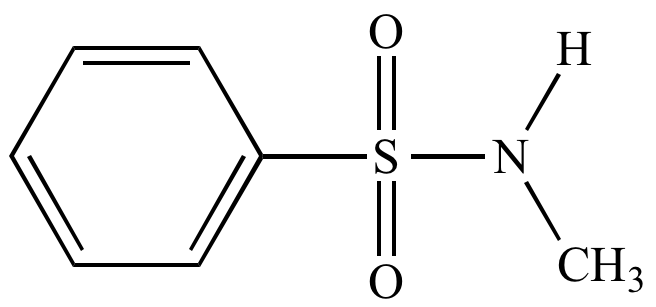
Structure of sulfonamide
Which NSAID has sulfonamide functional group?
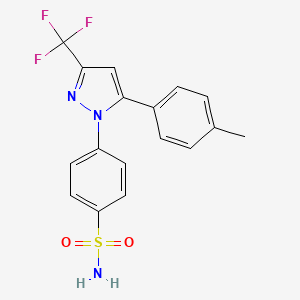
Celecoxib
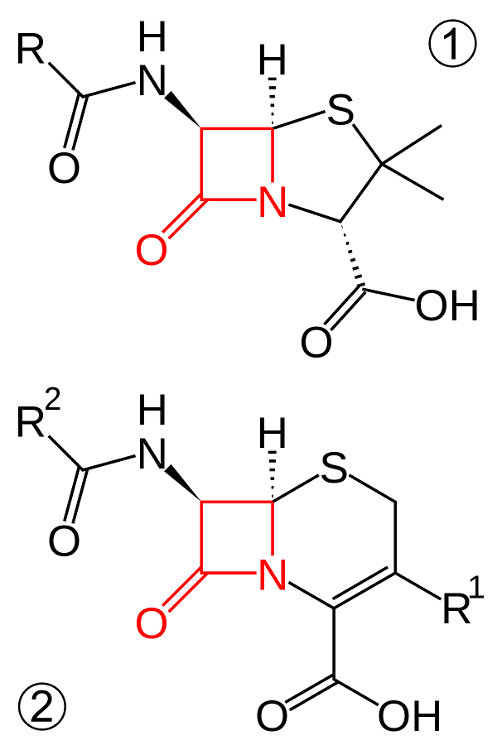
Structure of beta-lactam antibiotics
Define substrate/ligand
A substance that creates a signal or produces an effect by binding to a receptor, enzyme or transporter
Define endogenous
A substance that is produced by the body (such as naturally-produced substrate)
Define exogenous
A substance that is produced outside of the body (such as a drug or other chemical)
Define agonist
A substance that combines with a receptor to initiate a reaction, can be endogenous or exogenous (mimicking endogenous)- activates receptors
Define antagonist
A substance that reduces or blocks a reaction, can be endogenous or exogenous (blocks/inhibits, does not produce a reaction)
Primary neurotransmitter involved in the somatic nervous system
acetylcholine (ACh)
How does the parasympathetic nervous system ("rest and digest") work
By releasing ACh which binds to nicotinic receptors
What are the physiologic responses when the parasympathetic system is activated
SLUDD (salivation, lacrimation, urination, defection, digestion)
How does the sympathetic nervous system ("fight or flight") work
By releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine which acts on adrenergic receptors (alpha-1, beta-1 and beta-2) in the cardiovascular and respiratory system
Activation of the SNS results in
increased BP, HR and bronchodilation and pupil dilation
(decrease salivation, urination, peristalsis)
Where are muscarinic receptors located
stomach and bladder
Where are adrenergic receptors located
Heart (beta-1), smooth muscles including blood vessels (alpha-1), lungs (beta-2)
Competitive inhibition
occurs when an antagonist binds to the same active site of a receptor as the endogenous substrate, preventing it from binding and causing a reaction
Non-competitive inhibition, that antagonist binds to the receptor at a
site other than the active site (allosteric site) which changes the shape of the active site and prevents the endogenous substrate from binding
Define pharmacodynamics
refers to the effect or change that a drug has on the body
Define pharmacokinetics
refers to the effect or change that the body has on a drug
CYP inhibitors
will have a decrease rate of drug metabolism and an increased serum drug level
Common CYP inhibitors
G-PACMAN
grapefruit, protease inhibitors, azole antifungals, cyclosporine, macrolides, amiodarone, non-DHP CCBS
CYP inducers
will have an increased rate of drug metabolism and a decreased serum drug level
Common CYP inducers
PS PORCS
phenytoin, smoking, phenobarbital. oxcarbazepine, rifampin, carbamazepine, st. johns wart
When a drug blocks/inhibits P-gp, a drug that is a P-gp substrate
will have increased absorption and the substrate drug level will increase
Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) involves
obtaining a drug level or other relevant labs to monitor efficacy and safety
What is included in a CBC
WBC, RBC PLTs
(CBC w/ diff, other WBCs are analyzed)
What is included in a BMP
electrolytes, glucose, renal function (SCr, BUN), HCO3, bicarbonate
What is included in a CMP
BMP + albumin, ALT, AST, total bilirubin, total protein
increased WBC
leukocytosis
increased RBC
polycythemia
increased PLTs
thrombocytosis
decreased WBC
leukopenia
decreased RBC (or low Hgb)
anemia
decreased PLTs
thrombocytopenia
When should you calculate corrected calcium
when albumin is low
What drugs can increase Ca+
vitamin D, thiazide diuretics
What drugs can decrease Ca+
long-term heparin, loop diuretics, bisphosphonates, cinacalcet, systemic steroids, calcitonin, topiramate
What drugs can decrease Mg
PPIs, diuretics, amphotericin B, chronic alcohol intake, diarrhea
What drugs can increase K+
ACEi, ARB, aldosterone antagonist, canagliflozin, bactrim, mycophenolate, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, drospirenone-containing contraceptives
What drugs can decrease K+
beta-2 agonist, diuretics, insulin steroids
What drugs can increase Na+
tolvaptan, hypertonic saline
What drugs can decrease Na+
carbamazepine, SSRIs, diuretics
When is BUN increased
renal impairment and dehydration
Define peak level
highest concentration in the blood a drug will reach
Define trough level
lowest concentration in the blood a drug will reach in the blood and is drawn right before the next dose
Obtaining drug levels at steady state is
often preferred (but not always)
USP 795
non-sterile
USP 797
sterile
USP 800
hazardous
What is the orange book (FDA)
list of approved drugs that can be interchanged with generics based on therapeutic equivalence
What is the pink book (CDC)
information on epidemiology and vaccine-preventable diseases
What is the purple book (FDA)
list of biological drug products, including biosimilars
What is the red book
drug pricing information
Long acting drugs provides a
smooth level of drug release over time which reduces high "peaks" and decreased side effects
Chemical incompatibility causes
drug degradation or toxicity due to a hydrolysis, oxidation or decomposition reaction
Drugs with leaching/adsorption/absorption issues with PVC containers
LATTIN (leach absorbs to take in nutrients)
lorazepam, amiodarone, tacrolimus, taxanes, insulin, nitroglycerin
Drugs that are compatible with saline (no dextrose)
A DIAbetic Cant Eat Pie
ampicillin, daptomycin, infliximab, ampicillin/sulbactam, caspofungin, ertapenem, phenytoin
Drugs that are compatible with dextrose (no saline)
Outrageous Bakers Avoid Salt
oxaliplatin, bactrim, amphotericin B, synercid
Central lines are required for
highly concentrated drugs, long-term antibiotics, drugs with a pH, drugs that can damage tissue
Drugs that require filter requirements
my GAL Is PAT who has a MaP
golimumab, amphotericin B, lipids 1.2 micron, isavuconazonium, phenytoin, amiodarone, taxanes, mannitol, parental nutrition
What drugs are "do not refrigerate"
Dear Sweet Pharmacist Freezing Makes Me Edgy
dexmedetomidine, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, phenytoin, furosemide, metronidazole, moxifloxacin, enoxaparin
What drugs do you have to protect from light
Protect Every Necessary Med from Daylight
phytonadione (vitamin K), epoprostenol, nitroprusside, micafungin, doxycycline