definition of plague (for this class)
an epidemic disease causing a high rate of mortality
"plague" always has a negative connotation
distinguish the DISEASE from the MICROBE that causes it
...
AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is caused by
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)
COVID-19 is caused by
SARS-CoV-2
TB (tuberculosis) is caused by
mycobacterium tuberculosis
malaria is caused by
plasmodium
plagues mostly focused on in this course
AIDs, TB, malaria (big three)
micron size
10^-6
HIV - 0.1 micrometers
SARS-CoV-2 - 0.1 micrometers
mycobacterium tuberculosis - 2 micrometers
plasmodium - 1-80 microns (depending on size bc diff stages are diff sizes)
human cells 20x bugger than bacterium
HIV/AIDs
cases:
cases in 2022:
deaths in 2022:
cases: 39 million HIV+
cases in 2022: 1.3 million
deaths in 2022: 630,000
COVID
cases:
deaths as of 2023:
cases: 769 million
deaths as of 2023: almost 7 million
(numbers are for 2.5 years so far), suspect actual # deaths is 2x this (in some countries are 3 to 4x as much))
Mycobacterium/TB
cases: 1/4 of humanity (about 2 billion)
- 10% of those who have it develop symptoms
1.6 million deaths
in 2022
plasmodium/malaria
1/2 population at risk
247 million cases
619,000 deaths
in 2021
adults usually survive. most deaths are children
goals of course
- Understand these diseases from the ground up .
- How these diseases are being fought.
- Appreciate why we haven’t eliminated these diseases.
- Make YOU a (relative) expert.
HIV/AIDs
- HIV = virus, must infect cell to produce more
- is
OBLIGATE PARASITE
- requires host to reproduce
4 key events of HIV cellular infection cycle
- HIV attachment
- immune system disease
- reverse transcription
- drug target, why vaccine has yet to be developed
- integration of provirus into
chromosomes
- why cannot be cured of HIV
- virion maturation
- drug target
HIV cellular
HIV exists in 2 forms:
- virion (virus particle)
- infectious form
- early phase
- anatomy: circle around RNA, reverse transcriptase, integrase, gp120, protease
- obligate parasite like all viruses
- free virus particle, extracellular form
- has 2 protein shells
- GENETIC MATERIAL IS RNA
- has 2 copies of RNA
- provirus
- hidden form
- genetic material incorporated into the human host's genetic material
- late phase
what is the genetic material of HIV?
KNOW THIS
RNA
KNOW THIS
(2 copies)
early phase
provirus
- 1st part cellular infection process
- membrane of virus fuse w/ cell membrane = contents of viral particle are released into the cell (HIV guts spill into cell)
- after RNA released into cell -> converts into DNA (uses reverse transcriptase, already in virus)
- DNA made -> go to nucleus (where genetic material of host cell is)
- DNA integrates into host cell's chromosomes = what makes
HIV difficult to handle
- use integrase enzyme to do this (also in the HIV virus)
- = VIRAL DNA NOW IN PROVIRUS FORM
reverse transcription step
after RNA released into cell -> uses reverse transcriptase to convert RNA into DNA
what makes HIV impossible to cure? how does it do this?
DNA integrates into host cell's chromosomes
uses integrase
when is HIV in provirus form? (LATE PHASE)
once viral DNA integrate with host DNA
what type of virus is HIV?
a retrovirus
what was original central dogma of biology (before 1970s?)
DNA -> RNA -> protein
only worked this way
found out there is more, not jsut this is possible
there can be
RNA -> DNA
later reverse transcriptase was discovered, and now RNA could -> DNA
- never thought possible before
- RNA eventually degraded and = double stranded DNA
Called retroviruses bc is backwards (REVERSE transcription)
DNA -> RNA process
transcription
enzyme: RNA polymerase
RNA -> DNA process
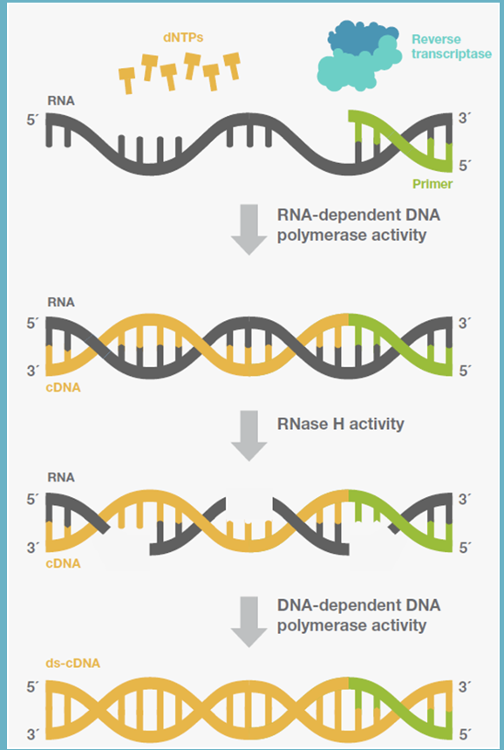
reverse transcription
enzyme: reverse transcriptase
reverse transciption discovery
1970, making dna from rna template (see slide 15)
all retroviruses have
reverse transcriptase
video to watch
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=odRyv7V8LAE
Specifically, knowing these 4 key events of the HIV cellular infection cycle makes it easier to understand …
- HIV attachment ( AIDS is a disease of the immune system )
- ‘Reverse Transcription’ ( drug target and why a vaccine has yet to be developed )
(1:35 – 2:10)
- Integration of the provirus into the chromosome ( Why one can’t be ‘cured’ of HIV )
(2:10 – 2:44)
- Virion maturation ( drug target )